RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Environmental Chemistry Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 14.1.
Define Environmental Chemistry.
Answer:
Environmental chemistry jg the branch of science which deals with the chemical changes in the environment. It includes our surroundings such as air, water, soil, forest etc.
Question 14.2.
Explain tropospheric pollution in loo words?
Answer:
Tropospheric pollution occurs due to the presence of undersirable substances present in air due to human activities. These may be the gaseous and particulate air pollutants. These are given as below:
- Gaseous Air Pollutants : Oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon, hydrogen suiphide, hydrocarbons, ozone and other oxidants.
- Particulate Pollutants : Dust, mist, fumes, and smog etc.

Question 14.3.
Carbon monoxide gas is more dangerous than carbon dioxide gas. Why?
Answer:
It is due to the fact that carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin to form a very stable compound known as carboxyhaemoglobin when its concentration in blood reaches 3-4%, the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood is highly reduced. This results into suffocation, headache, nervousness and sometimes death of the person. Whereas, CO2 does not combine with haemoglobin and hence is tess harmful than CO.
Question 14.4.
Which gases are responsible for greéñhouse effect ? Name them.
Answer:
The main gas responsible for greenhouse effect is carbon dioxide. Other greenhouse gases are methane, nitrous oxide, water vapour, CFCs and ozone.
Question 14.5.
Statues and monuments in India are affected by acid rain. How? .
Answer:
This is mainly due to the large number of industries and power plants in the nearby areas which release oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. These oxides when react with rain water, nitric acid and sulphuric acid are formed which make the rain acidic. When it comes in contact with various statues or monuments, the acid reacts chemically with calcium carbonate.
CaCO3 H2SO4 CaSO4 H2O CO2
Question 14.6.
What is smog ? How is classical smog different from photochemical smog?
Answer:
The term smog is a combination of smoke and fog. It is a type of air pollution that occurs in many cities throughout the world. Classical smog occurs in cool humid climate. It is also called as reducing smog. Whereas, hpot.ochemical smog occurs in warm and dry sunny climate. It has high concentration of oxidising agents and hence, it is also called as oxidising smog.
Question 14.7.
Write down the reactions involved during the formation of photochemical smog.
Answer:
Mechanism of formation of photochemical smog:
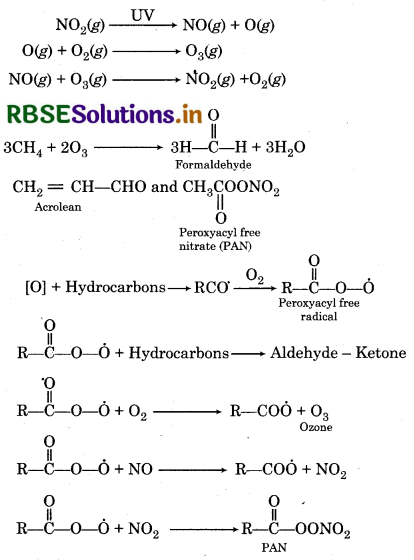
Question 14.8.
What are the harmful effects of photochemical smog and how can they be controlled?
Answer:
Harmful effects of photochemical smog:
- High concentration of photochemical smog causes headache, chest pain and dryness of the throat.
- Ozone and PAN act as powerful eye irritants.
- It leads to cracking of rubber and extensive damage to plant life.
- It causes corrosion of metals, stones, building materials, painted surface etc.
Control Measures:
- Catalytic converters should be used in automobiles which prevent the release of nitrogen dioxide and hydrocarbons to the atmosphere.
- Pinus, Quercus, Pyrus etc. can metabolise nitrogen dioxide thus tleir plantation could help to some extent.

Question 14.9.
What are the reactions involved for ozone layer depletion in the stratosphere?
Answer:
The reaction can be shown as follow:
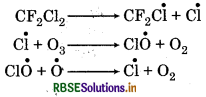
Question 14.10.
What do you mean by ozone hole ? What are Its consequences?
Answer:
hole Depletion of ozone layer creates some sort of holed in the blanket of ozone which surround us, this is known as ozone hole.
Consequences of Ozone hole:
- Aging of skin
- Cataract
- Sunburn
- Skin cancer
- Mutation
- Dizziness
- By killing many of the phytoplanktons, it can damage the fish productivity.
- Rate of evaporation increases through the surface and stomata of leaves which can decrease the moisture content of the soil.
Question 14.11.
What are the major causes of water pollution? Explain.
Answer:
Causes of water pollution:
There are two major cause-s of water pollution:
1. Point Source Pollutants: These are the single source of pollution from which pollutants are discharged. Examples : sewage, lead, arsenic, mercury D.D.T etc.
(i) Pathogns : Pathogens include bacteria and other microorganisms that enter water from domestic sewage and animal excreta.
(ii) Organic wastes from industries: Organic wastes when added to water, as these are biodegradable, bacteria decomposes organic matter and consume dissolved oxygen in water. When the concentration of thssolved oxygen of water is below 6 ppm, the growth of fish getsinhibited. Breakdown of the organic wastes by anaerobic bacteria produces chemicals that have a foul smell and are harmful to human health.
(iii) Industriel Effluents: Some inorganic chemicals as an industrial waste-s dissolve in water like Cd, Hg. Ni etc. These metals are dangerous to humans and other animals. These metals can damage kidneys and central nervous system, liver etc. Petroleum products pollute many sources of water,
2. Non-Point Source Pollutants : When the source of pollution cannot he identified as the sources are diffused, they are termed as non-point or diffused sources. Examples Agricultural discharges Le.. use of fertilizøra, pesticides etc.
Question 14.12.
Have you ever observed any water pollution in your area ? What measures would you suggest to control it?
Answer:
Water pollution occurs due to human activities. This includes industrial wastes, industrial effluents, domestic wastes, municipal wastes as well as agricultural discharges in water bodies which pollute water. These pollutants make water unfit for drinking. To control water pollution, all industrial and chemical discharges should be made free from toxic metals before allowing them to enter a water body. Proper monitoring of water bodies for the concentration of such toxic metals
should be done on regular basis. Compost should he used instead of chemical fertilizers to avoid water pollution.

Question 14.13.
What do you mean by biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)?
Answer:
The amount of oxygen required by bacteria to break down the organic matter present in a certain volume of a sample of water is called biochemical oxygen demand (BOD).
Question 14.14.
Do you observe any soil pollution in your neighbourhood ? What efforts will you make for controlling the soil pollution?
Answer:
Industrial wastes and agricultural wastes such as fertilizers and pesticides are the major sources of soil pollution. Insecticides and toxic met.aLq remain for a long time in the soil and decrease the soil fertility. They can enter the trophic levels through food chain causing metabolic and physiologial disorder in living organisms. To control soil pollution, all industrial wastes should undergo proper treatment. They should be recycled and only then, allowed to be dumped. Compost should be used instead of chemical fertilizers to avoid soil pollution.
Question 14.15.
What are pesticides and herbicides ? Explain giving examples.
Answer:
PestIcides These are the chemical compounds used in agriculture to control the damages caused by insects, rodents, weeds and various crop diseases. Examples: Aldrin, Dialdrin, B.H.C. etc. HerbIcides: These are (he chemicals used to control weeds. Example Triazinea.
Question 14.16.
What do you mean by green chemistry? How will it help In decreasing environmental pollution?
Answer:
Green Chemistry is a way of thinking and is about utilising the existing knowledge and principles of chemistry and other sciences to reduce the adverse impact on environment.
It will help in decreasing environmental pollution as follows:
- Automobile engines have been fitted with catalytic converters which prevent the release of the hydrocarbon vapours and oxides of nitrogen into acrolein and peroxyacetyl nitrate.
- Carbon dioxide has replaced CFCs as blowing agents in the manufacture of polystyrene foam sheets.
Question 14.17.
What would happened if the greenhouse gases were totally missing in the earth’s atmosphere ? Discuss.
Answer:
Greenhouse gases such as CO2, CH4,O and CFCs absorb solar energy radiated back from the earth surface, which are present near the earth’s surface. They heat up the atmosphere near the earth’s surface and keep it warm. As a result of this, there is growth of vegetation which supports the life. In the absence of green house effect, there will be no life of both plants and animals on the surface of the earth.
Question 14.18.
A large number of fishes are suddenly found floating dead on a lake. There is no evidence of toxic dumping but you can find an abundance of phytoplankton. Suggest a reason for the fish kill.
Answer:
A large number of phytoplankton (organic pollutants such as leaves, grass trash etc) present in water are biodegradable. Bacteria decompose them in water. For this process, they consume the dissolved oxygen present in water. Due to which, the level of dissolved oxygen falls below 6 ppm, hence, a large number of fishes are suddenly found floating dead on a lake.

Question 14.19.
How can domestic waste be used as manure?
Answer:
Domestic waste consists of biodegradable wastes which can be converted into manure by using suitable method.
Question 14.20.
For your agricultural field or garden you have developed a compost producing pit. Discuss the process in the light of bad odour, flies and recycling of wastes for a good produce.
Answer:
The compost producing pit should be kept covered so that flies cannot be entered into compost pit and bad odour is minimized. The waste materials which are nonbiodegradable like glass, plastic, polythene etc. must be handed over to the vendors for recycling.
