RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Important Questions Structure of Atom
Multiple Choice Questions:
Structure Of Atom Class 11 Important Questions Question 1.
The modern base of atomic mass is:
(1) O16 = 16.000
(2) C12 = 12.000
(3) O = 16.00
(4) 1H = 1.000
Answer:
(2) C12 = 12.000
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Extra Questions Question 2.
The difficulty in discovery of neutrons was:
(1) Its zero charge or chargeless
(2) Less charge on it
(3) Negligible mass
(4) Neligible e/m ratio
Answer:
(1) Its zero charge or chargeless

Structure Of Atom Class 11 Important Questions With Answers Question 3.
When electron jumps from L to K shell then:
(1) It absorbs energy
(2) It emits energy
(3) Neither absorbs nor emits energy
(4) Some time absorbs and some time emits
Answer:
(2) It emits energy
Atomic Structure Class 11 Important Questions Question 4.
Mass of electron in comparision with lighest nucleus is:
(1) 1/80
(2) 1/800
(3) 1/1800
(4) 1/2800
Answer:
(3) 1/1800
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Important Questions With Answers Question 5.
Rutherford's a-particles scattering experiment shows first time that atom possess:
(1) Electron
(2) Proton
(3) Nucleus
(4) Neutron
Answer:
(3) Nucleus
Important Questions Of Structure Of Atom Class 11 Question 6.
According to Bohr's theory angular momentum of electron in 5th energy level is:

Answer:
\(\text { (4) } \frac{2 \cdot 5 h}{\pi}\)
Structure Of Atom Important Questions Class 11 Question 7.
Which series of hydrogen spectrum will be in visible region:
(1) Pfund
(2) Lyman
(3) Balmer
(4) Brackett
Answer:
(3) Balmer
Class 11 Structure Of Atom Important Questions Question 8.
In 1932 positron was discovered by:
(1) Chedwick
(2) Rutherford
(3) C.D. Anderson
(4) None of these
Answer:
(3) C.D. Anderson

Chemistry Class 11 Chapter 2 Important Questions Question 9.
Value of absorbed and emitted energy is said to be:
(1) kinetic energy
(2) quanta
(3) free energy
(4) none of these
Answer:
(2) quanta
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Short Question Answer Question 10.
If Bohr's first orbit's radius is r1 and third orbits radius is r2 there r1 /r2 will be:
(1) 3
(2) 1/3
(3) 1/9
(4) 9
Answer:
(3) 1/9
Ch 2 Chemistry Class 11 Extra Questions Question 11.
The ratio of 1st, 2nd and 3rd Bohr's orbit of H-atom, He+ ion and Li2+ ion will be:
(1) 4 : 3 : 2
(2) 4 : 2 : 3
(3) 2 : 3 : 4
(4) 2 : 4 : 3
Answer:
(2) 4 : 2 : 3
Important Questions From Structure Of Atom Class 11 Question 12.
Ratio of velocity of electron in first Bohr's orbit of H-atom and He+ ion will be:
(1) 1 : 2
(3) 1 : 3
(2) 2 : 1
(4) 3 : 1
Answer:
(1) 1 : 2
Ch 2 Chemistry Class 11 Important Questions Question 13.
For g-sub shell the correct one is:
(1) n = 5
(2) m = 3
(3) l = 4
(4) l = 5
Answer:
(3) l = 4
Structure Of Atom Important Questions Question 14.
Which species is not diamagnetic ?
(1) Cl-
(2) Be-
(3) Ne 2+
(4) As+
Answer:
(1) Cl-
Questions On Structure Of Atom Class 11 Question 15.
Isoelectronic species is:
(1) F-‚ O2-
(2) F-, O+
(3) F-, O-
(4) F-, O2+
Answer:
(1) F-‚ O2-
Structure Of Atom Extra Questions Class 11 Question 16.
Line spectrum of helium ion is analog to:
(1) H-atom
(2) Lition
(3) He-atom
(4) Li-atom
Answer:
(1) H-atom

Structure Of Atom Class 11 Extra Questions And Answers Question 17.
In any set of degenerate orbits, electrons distributed in such manner that they can get their spin. This statement is related to:
(1) Pauli exclusion principle statement
(2) Aufbau principle
(3) Hund's rule
(4) Slater's rule
Answer:
(3) Hund's rule
Chapter 2 Chemistry Class 11 Important Questions Question 18.
For any electron spin angular mamentum is:
\(\text { (1) } s=\sqrt{s(s+1)} \frac{h}{2 \pi}\)
\(\text { (2) } s=s \frac{h}{2 \pi}\)
\(\text { (3) } s=\frac{3}{2} \times \frac{h}{2 \pi}\)
(4) none of these
Answer:
\(\text { (1) } s=\sqrt{s(s+1)} \frac{h}{2 \pi}\)
Question 19.
Number of nodes in 3p-orbitals is:
(1) 0
(2) 1
(3) 2
(4) 3
Answer:
(2) 1
Class 11 Chemistry Structure Of Atom Important Questions And Answers Question 20.
For elctronic transition wavelength of spectrum line is inversely proportional to :
(1) No. of electrons in transition
(2) Nuclear charge of atom
(3) Difference of energy level in transition
(4) Velocity of electron in transition
Answer:
(3) Difference of energy level in transition
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Important Questions For Structure Of Atom Class 11 Question 1.
What will be mass of 1 mole of electrons?
Answer:
6.23 × 1023 × 9.1 × 10-28 g = 56.693 × 10-5 g.
Structure Of Atom Class 11 Extra Questions Question 2.
Who discovered nucleus?
Answer:
Rutherford.
Questions Based On Structure Of Atom Class 11 Question 3.
On which nature of anode rays depends?
Answer:
Gas in discharge tube.
Important Questions Of Atomic Structure Class 11 Question 4.
Bohr's model is based on which principle?
Answer:
It depends on Planck's quantum theory.
Important Questions Of Chapter 2 Chemistry Class 11 Question 5.
Which types of atomic spectrum are explained by Bohr's atomic model?
Answer:
It explained H-atom, He+, Li2+ etc.

Question 6.
Give the formula to calculate the frequency A of lines in spectrum region?
Answer:
\(\bar{v}=R\left[\frac{1}{n_1^2}-\frac{1}{n_2^2}\right] \mathrm{cm}^{-1}\)
Question 7.
Among Dalton's sugggestions which is still valuable?
Answer:
Atom takes part in chemical reaction.
Question 8.
Why mass of atom M and its ion M+ is similar?
Answer:
Because both contain the equal number of protons and neutrons.
Question 9.
How it is proved that maximum part of atom is empty or hallow?
Answer:
In Rutherford's a-particle scattering experiment, most of the a-particles passed through gold foil without deflection which proves that in atom most of the part is hollow or empty.
Question 10.
"The emitted energy by atom is quantised". Who proposed this first time?
Answer:
It was proposed by Bohr.
Question 11.
What is similarity between isotopes of any element?
Answer:
They have similar atomic number.
Question 12.
Which particles in atom are responsible for atomic weight?
Answer:
Protons and neutrons are responsible for atomic weight.
Question 13.
If the speed for small particle is changed then elment what will be its effect on wavelength. Why?
Answer:
Because wavelength is reciprocal to velocity i.e., it A means an increasing velocity, λ will be decreased and vice-versa.
Question 14.
According to Bohr's model, for each stationary state, the En is given as
\(E_n=\frac{-1312}{n^2} \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\)
What is 'n' in this expression?
Answer:
Here 'n' denotes energy level.

Question 15.
What will be the maximum number of electrons in 4th orbital?
Answer:
Maximum number of electron = 2n2
= 2 × (4)2 = 32
Question 16.
What is neutron? How it is differ from proton?
Answer:
0n1, neutron is netural particle while op1 proton is positive particle.
Question 17.
"The energies of all photons are not equal”. Justify?
Answer:
Energy of photon depends upon wavelength of light
\(E=\frac{h c}{\lambda}\)
Question 18.
What is relation between Cl- and S2- ions?
Answer:
There are isoelectronic.
Question 19.
When energy of electron assumed to be zero?
Answer:
When its distance from nucleus is infinite at this me the attraction force between electron and nucleus is ero and energy becomes zero.
Question 20.
If hydrogan gas is filled in one discharge tube and oxygen gas is filled in another discharge tube. The number of electrons and positive ions in cathode rays and anode rays will be similar or different?
Answer:
The number of electrons will be equal but number positive ions will be different.
Question 21.
When a-particles bombarded to thin gold foil then some a-particle did not pass through foil and go back. What does it prove?
Answer:
It proves that there is small nucleus in atom.
Question 22.
What is electron cloud?
Answer:
The negatively charged electron spread around ucleus in an atom in form of cloud. The density of cloud much in that region where probability of finding of ectron is high.
Question 23.
What is Pauli exclusion rule?
Answer:
No two electrons can have same values for all four quantum numbers.
Question 24.
For azimuthal quantum number (l) = 2, write the value of magnetic quantum number m.
Answer:
For 2, m = -2, -1, 0, +1, + 2

Question 25.
How much orbitals are present in subshell p, d, f?
Answer:
The number of orbitals will be 21 + 1.
Question 26.
Write the four quantum numbers of last electron of 21 Sc.
Answer:
Since last electron of Sc = 3d1.
Thus
n = 3
l = 2
m = 2 s = +- 1/2
Question 27.
What is the rule to fill the electron in atom
Answer:
Electrons are filled by(n + 1) rule.
Question 28.
What the following symbols indicate?
s, n, l, m
Answer:
s → indicate spin of electrons in orbital
n → principal quantum number
l → azimuthal quantum number
m→ magnetic quantum number
Question 29.
Correct the following configuration of atom : 1s2, 2s2, 2p, 2py, 2Pz
Answer:
1s2, 2s2, 2p1x, 2p1y, 2p2
Question 30.
When an electon jumps from high level to the low level (n = 2) then what is the name series obtained in line spectrum?
Answer:
Balmer series.
Question 31.
Which subshell is spherical in shape?
Answer:
s-subshell.
Question 32.
Who' proposed the quantisation of angula momentum of orbital in atom?
Answer:
Bohr.

Question 33.
How many electrons are possible in 4t orbital?
Answer:
No.of maximum electrons = 2n2 = 2(4)2
Question 34.
Why Pauli's rule is considered as exclusio rule?
Answer:
It is considered on exclusion rule becaus according to this in any orbital the possibility of thir electron in any orbital is prohibited.
Question 35.
"Electron with same spin quantum numbe can not accomodate in orbital." This statement based on which principle?
Answer:
Pauli's Exclusion Principle.
Question 36.
"It is possible to determine the momentum and position of an electron with absolute accuracy". this statement based on which principle?
Answer:
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle.
Question 37.
If there is zero uncertainty in momentum of electron there what uncertainty will be in this position?
Answer:
Infinite.
Question 38.
How does the change in velocity of small moving particle affect the wavelength?
Answer:
The wavelength is reciprocal to velocity λ = h/mv It means if velocity is increased then wavelength will decrease.
Question 39.
What is meant by nodal surface?
Answer:
It is the surface where probability of finding of electron is negligible i.e., at this point imm
Question 40.
The velocity of an electron around nucleus can not be calculated with accuracy. Why?
Answer:
According to Heisenberg's principle there is uncertainty in velocity of electron around the nucleus.
Question 41.
Why spin of two electrons in an orbital is opposite?
Answer:
The spin of two electrons in an orbital is of opposite sign because electrons of same spin repel to each others.
Question 42.
What is Stark's effect?
Answer:
The splitting of spectrum lines in electric field is known as Stark's effect.
Question 43.
What is Zeeman's effect?
Answer:
The splitting of spectrum lines in magnetic field is known as Zeeman's effect.
Question 44.
What is meant by quantisation of energy?
Answer:
The energy levels have specific value of energy. Due to specific values of energy, these are quantised.
Question 45.
Write a note on black body radiation?
Answer:
An ideal body which can absorbs or emits radiation of all frequencies. It is known as black body. The radiation emitted from this body in known as black body radiation.
Question 46.
What is wave number?
Answer:
It is the number of wavelengths per unit length. Its unit in m or cm-1.
Question 47.
What is diffraction?
Answer:
It is the bending of waves around obstacle and opening.
Question 48.
Why we should not wear black clothes in summer season?
Answer:
As we know that black body are good absorber of light, it can absorb all radiation. So if we will wear black cloth then we will feel much hot.
Question 49.
Does moving cricket ball shows wave character?
Answer:
According to de Broglie,λ = h/mv Since mass of cricket ball is too high which gives the least value of wavelength that is impossible to measure. So moving th cricket ball does not shows wave character.
Question 50.
Why train is not seen as moving wave?
Answer:
Because it has large mass that's why value of wavelength is negligible. So we can not see the train in wave form.
Question 51.
What is the significance of de-Broglie relationship?
Answer:
It is used to observe the dual nature of microscopic particles i.e., particles posses wave nature. This relation is not suitable for macroscopic or large particles whose A mass is high. These particles have negligible value of wave- length so do not show wave character.
Question 52.
If a moving electron and proton have similar wavelength then which of these will have more velocity?
Answer:
According to, λ = h/mv mass and velocity are in reciprocal relation according to question, electron and proton have same value of h and λ. Particle with lower mass will have high velocity, so electron will be in higher in velocity.
Question 53.
'The line spectrum of any elements is known as its finger print'. Comment on this fact
Answer:
The line spectrum of each atom contain certain wavelength: Hence any element can be identified using its line spectrum. So line spectrum is considered as finger print.
Question 54.
"The energy levels of H-atom are quantised" Comment on this.
Answer:
H-atom energy levels are quantised. Since absorption spectrum of H-atom is line spectrum in which only certain energy value is possible.
Question 55.
Which experiment proves wave and particle nature of matter?
Answer:
The wave nature and particle nature of matter can e proved by de-Broglie principle.

Question 56.
Name those spectral series which represent the following regions of electromagnetic radiation:
(i) Visible region,
(ii) ultravoilet region,
(iii) infrared region.
Answer:
(i) Balmer series,
(ii) Lyman series,
(iii) Pfund series.
Question 57.
What is emission spectra?
Answer:
The spectra of radiation emitted by a substance at has absorbed energy is called emission spectra. This pectra can be obtained only at high temperature.
Question 58.
Write notes on electromagnetic radiations.
Answer:
These are radiations which oscillate in sky in form E electrical and magnetic waves. e.g., infrared, Itraviolet, visible and X-rays.
Question 59.
The possible electronic configuration of copper [Z = 29] should be [Ar] 3d9, 4s2 while its real configuration is [Ar] 3d1o, 4s1, explain it.
Answer:
Since completely filled subshell is more stable.、
Question 60.
Write the electronic configuration following and calculate the number of unpaired electrons.
(i) Mn1+,
(ii) Cr3+
(iii) Fe3+
(iv) Ni2+
(v) CO2+ and
(vi) Cu2+
Answer:
|
Electronis Configuration |
No of unpaired electrons |
|
25Mn4+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d3 |
3 |
|
24Cr3+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d6 |
3 |
|
26Fe3+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d5 |
5 |
|
28Ni2+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d8 |
2 |
|
27CO2+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d7 |
3 |
|
29CU2+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d9 |
1 |
Question 61.
The electronic configuration of carbon atom is 1s2, 2s1, 2p1X, 2p1y,2p1z. What does it mean?
Answer:
It means that carbon atom is in excited state.
Question 62.
If Pauli exclusion principle would not b then what will be the electronic configuation of Li?
Answer:
3Li = 1s3
Question 63.
In which elements, number of electrons o s-orbital will be equal to number of electro of p-orbital?
Answer:
80 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p1 (No. of electron in s and p = 4
12 Mg→ 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2 (No. of electrons in s an p = 6)
Question 64.
Write the electronic configuration of Zn and Sc2+.
Answer:
Zn2+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d1o
Sc2+ →1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6,3d1

Question 65.
Find the order of energy level of 4th sub-she for following atoms?
(1) H-atom
(2) Br-atom
Answer:
|
Properities |
CU |
CU+ |
CU2+ |
CU3+ |
|
Total number of electrons |
29 |
28 |
27 |
26 |
|
Total number of s -electrons |
7 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
|
Total number of p-electrons |
12 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
|
Total number of d-electrons |
10 |
10 |
9 |
8 |
|
Number of unpaired electrons |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
Total spin =+1/2 unpaired electrons |
+1/2 |
0 |
+1/2 |
+1 |
|
Paramagnetic or diamagnetic character |
P |
D |
P |
P |
8. Cu+ ion will be most stable because of fullyfilled d-orbital.
Question 67.
Write down the electronic configuration o
(i) 18 F,
(ii) 18 Ar
(iii) 12S, and find out :
1. Which will possess maximum nuclear charge
2. Minimum number of neutrons.
3. Maximum mass number.
4. Maximum number of unpaired electrons.
Answer:
(i) 18 9F → 1s2, 2s2, 2p5
(ii) 36 18 Ar → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6
(iii) 3216 S → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p1
1. Maximum nuclear charge = Ar
2. Minimum number of neutrons = F
3. Maximum mass number = Ar
Question 66.
Write down the electronic configurations of Cu, Cu2+ and Cu3+ and following.
1. Total number of electrons.
2. Total number of electrons in subshells.
3. Total number of electrons p-subshell.
4. Total nunber of electron in d-subshell.
5. Total number of unpaired electron.
6. Total number of spins.
7. Paramagnetic or diamagnetic character.
8. Most stable ion.
Answer:
1. Electronic configuration
29 Cu → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d10, 4s1
29 Cu+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d10
29 Cu2+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d9
29 Cu3+ → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d3
4. Maximum number of unpaired electrons = 5
Question 68.
Nitrogen atom shows electronic configuration as 1s2, 2s2, 2p1x, 2p1z but not 1s2, 2s2, 2p2x, 2p1y. Why?
Answer:
It is according to Hund's rules. Degenerate orbitals filled first with equal spin electrons, there is not pairing.
Question 69.
Energy of 1s electron is less then 2s electron, why?
Answer:
It is because of 1s electrons are near to nucleus as compared to 2s electrons and 1s electrons experience more attraction force which results less energy.
Question 70.
In which d-oribtal, four lobes are not present?
Answer:
dz2, which contains only two lobes.
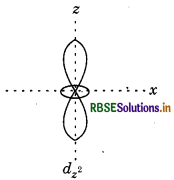
Question 71.
In which d-orbital four lobes are present along the axis?
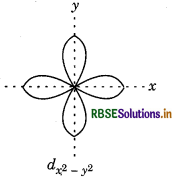
Answer:
dx2-y2 In it four lobes are present along with axis.
Question 72.
Which of the following is meaningfull configuration and which is meaningless configuration 2p5, 2d4, 4s2, 3f7, 4p10?
Answer:
2p5 - meaningless configuration.
2d4 - meaningless configuration.
4s2 - meaningfull configuration.
3f7 - meaningless configuration.
4p10 - meaningless configuration.

Question 73.
A p-subshell in which three orbitals are present as P1x, P1y and p2. If only 1 electron is there then in which orbital it will accomodate?
Answer:
The electron may accomodate in P1x P1y and P2z because these are degenerate orbitals.
Question 74.
How radial nodes are different for 1s and 2s orbitals?
Answer:
In 1s orbital there is no node while in 2s orbital one node is present because number of radial nodes is equal to(n - 1), where n is the principal quantum number.
Question 75.
For any element, mass number is double to its atomic number. If p-orbital contains 4 electrons then find the name of element and write its configuration.
Answer:
The electronic configuration is 1s2, 2s2, 2p1 i.e., its atomic number is 8 and mass number is 16, element is oxygen.
Question 76.
What is difference between symbol m and M?
Answer:
Here 'm' means third quantum number and M is third energy level. M has constant value while 'm' varies from -1 to +1 including zero.
Question 77.
2d and 3f orbitals are not possible, why?
Answer:
Because of for n = 2, the value of l is equal to 0 and 1 i.e., for n = 2, only s and p orbitals possible hence d orbitals not present. Similarly for n = 3, the value of will be 0, 1 and 2. So, in n = 3 orbitals, f orbitals are not possible.
Question 78.
What will be value of all four quantum numbers for 8th electron of oxygen atom?
Answer:
O → 1s2, 2s2, 2p1
So quantum number will be.
n = 2
l = 1
m = + 1 or -1
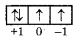
Question 79.
Calculate the value of all four qunatum numbers for 4th electron in 3p6 configuration?
Answer:
For 3p6, p-orbitals may be represented as.
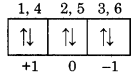
For 4th electron n = 3, l = 1, m = + 1, s = -1/2
Question 80.
If l = 2, then it will represent which subshell? What will be the number of electrons to accomodate in this subshell.
Answer:
For 7 = 2, there will be d-sub-shell and maximum 10 electrons will be accomodate in this.
Question 81.
Find out the value of n,l,m and s for 3d2 electron?
Answer:
For 3d2 electron
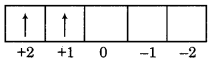
n = 3, l = 2, m = + 1, S = +1/2
Question 82.
Name the quantum number which represent following:
1. Size and energy level of orbitals.
2. Shape and energy level.
3. Configuration of orbitals.
4. Spin of electrons.
Answer:
1. Principal quantum number (n)
2. Azimuthal quantum number (1)
3. Magnetic quantum number (m)
4. Spin quantum number (s)
Question 83.
Describe the orbital for n = 4 and l = 0.
Answer:
For n = 4 and l = 0, it is 4s orbital.
Question 84.
The group of quantum number n = 3, l = 2 m = - 1, s = + 1/2 is permitted or not?
Answer:
Yes, it is permitted group of quantum numbers.

Question 85.
Find out the ground state and excited state configuration from following
(i) 1s2, 2s2, 2p1
(ii) 1s2, 2s2 2p6, 3s2, 3p1
(iii) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p1
(iv) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6,3d10,4s2
(v) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p1‚3d1
Answer:
(i) Ground state
(ii) Ground state
(iii) Ground state
(v) Excited state
(iv) Ground state
Question 86.
Write the name of orbitals when
(i) n = 2, l = 0
(ii) n = 3, l = 2
(iii) n = 5, l = 1
(iv) n = 4, l = 3
Answer:
(i) 2s
(ii) 3d
(iii) 5p
(iv) 4f
Question 87.
Which of the following orbitals are digenerate?
3dxy, 4dxy, 3dz2, 3dyz, 4dyz, 4dz2
Answer:
Degenerote orbitals are the orbitals of the same sub shell of the same main shell.'
Hence these are (3dxy, 3dz2 3dyz) and (4dxy, 4dyz, 4dz2)
Question 88.
If electron and proton possess similar wavelength then which will have more velocity?
Answer:
Velocity of that particle will be more which will have less mass.
Since λ = h/mv therefore electron will have more velocity
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is difference between proton and hydrogen atom?
Answer:
Proton is very small or microscopic fundamental particle of atom containing unit positive charge Hydrogen atom consists of only one electron and one
proton. When electron is expeled from H-atom then unit positively charged proton is obtained.
Question 2.
What do you meant by isoelectronic?
Answer:
A group of positive ions and negative ions of atom which have similar electronic configuration are called iso-electronic. For example
(i) He, Li+, Be++ and B+++ are isoelectronic because all have 2 electrons.
(ii) O2-, F-, Ne, Na+, Mg++ Al+++ because all have 10 electrons are isoelectronic.
Question 3.
Explain the Planck's quantum theory?
Answer:
Max Planck's (1901) propound quantum theory related to rediation. According to this theory:
(i) When a body absorbs or emits radiation in form of light or heat, it can not do it continuously.
(ii) Emission or absorption of energy furnished in certain amount i.e., in form of bundles or packets which are known as quanta.
(iii) The radiated energy is also known as photon if frequency of radiation is u then energy of photon will be
\(\begin{aligned} & E=h v=\frac{h c}{\lambda}\left\{\because v=\frac{c}{\lambda}\right\} \\ & E=h c \bar{v}\left\{\because \bar{v}=\frac{1}{\lambda}\right\} \end{aligned}\)
Question 4.
How photon and quantum are different?
Answer:
Quantum is a bundle of certain energy and its e value is E = hv, quantum can be obtained by any source. While photon is quantum of light energy only.

Question 5.
What are the differences between proton and electron?
Answer:
|
Proton |
Electron |
|
1. Proton is unit positively charged particle of each atom. |
It is unit negativity charged particle of each atom. |
|
2. The charge on proton is + 1.6 × 10-19 C |
The charge on electron is – 1.6 × 10-19 C |
|
3. Mass of proton is 1.6726 × 10-24 g. |
Mass of electron is 9.1095 × 10-28 g. |
|
4. Radius of proton is 10-13 cm |
The radius of electron is 2.8 × 10-13 cm. |
|
5. Proton exists in nucleus of atom. |
Electron exists inorbit around nucleus. |
|
6. Proton is denoted by 1H1 or p. |
It is denoted by -1 e0 or -1 |
Question 6.
What is the composition of nucleus?
Answer:
The central part of atom is known as nucleus. In nucleus the proton and neutron exist. Proton has positive charge while neutron is neutral. Due to positive charge on proton, nucleus is also positively charged. The ex sum of number of proton and neutron is nucleus is called de mass number. The particles present in nucleus like p neutron, proton etc are known as nucleons. The atomic S weight of any element depends upon its mass number or W equal it number of nucleons.
Atomic number = No. of proton = No. of electrons
Mass number - No. of protons + No. of neutrons
Question 7.
When value of energy becomes zero for an electron?
Answer:
When electron is located at infinite distance from nucleus its energy is considered as negligible or zero, or in other words when interaction between electron and nucleus is about zero, then its energy will be zero.
Question 8.
What was the drawbacks of Rutherford model of atom?
Answer:
The drawbacks of Rutherford's atomic model are given below:
1. It could not explain the stablity of atom.
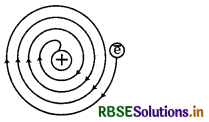
2. It could not explain the arrangement of electron around nucleus.
3. It could not provide the knowledge to calculate the number of protons and electrons present in atom
4. It could not explain the spectrum of hydrogen and other atoms.
Question 9.
Prove that "electron is universal particle”.
Answer:
Electrons are of cathode rays which are obtained y discharge tube. Beside this electron can be obtained om various sources. These sources are as follows:
1. From the fibres of hot metal.
2. From active metals such as Na and K are interacted with UV rays.
3. From radioactive elements in the form of ß-particles. since electron can be obtained from any source its e/m ratio remain constant so it is universal particle.
Question 10.
What is importance of de-Broglie's relationship?
Answer:
de-Broglie gave an equation mvr = nh/2π plain angular momentum of electron. According to e-Broglie electron possesses wave charater. It is only possible then its radius is simple multiple of wavelength.
so 2πr = nλ
r = radius of orbit
λ = wavelength
n = 1, 2, 3, 4
Question 11.
Explain the Schroedinger's wave equation?
Answer:
Schroedinger gave an equation on the basis of pothesis of de-Broglie and Heisenberg's uncertainty inciple. In this equation the behaviour of an electron in be expressed in wave equation. The Schroedinger euation is
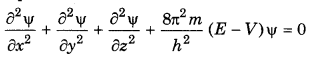
where
m = mass of electron
h = Planck's constant
E = total energy of electron
V = potential energy of electron
φ = wave function
x, y, z = coordinates

Question 12.
Differentiate between orbit and orbital:
Answer:
|
Orbit |
Orbit |
|
1. Idea of orbit was given by Bohr. |
1. It is based on wave mechanics. |
|
2. It is two dimensional route where electron rotates. |
2. It is three dimensional space where probability of finding of electron is maximum. |
|
3. The maximum number of electron in an orbit is 2n2 |
3. In an orbital only 2 electrons can accomodate. |
|
4. All orbits are circular. |
4. Orbitals have different shapes. |
|
5. are non directional. |
5. Except s-orbitals all orbitals are directional. |
Question 13.
How spectrum of hydrogen can be obtained
Answer:
The spectrum of hydrogen can be obtained whe hydrogen gas is filled in discharge tube at very lo pressure and electric current passes through it. The emitted light is analysed with help of spectroscop Following series occur in hydrogen spectrum:
1. Lyman series
2. Balmer series
3. Paschen series
4. Brackett series
5. Pfund series
Question 14.
Write the applications of Pauli's exclusion principle.
Answer:
Following are the applications of this principle:
1. For main energy level the maximum number electrons are given by 2n2.
2. In main energy level, the total number of su energy levels or sub shell is equal to principa quantum number of main energy level.
3. Total number of orbitals in main energy level given by n2.
4. In an orbital only two electrons of opposite spin can acccomodate.
Question 15.
Clarify the dual nature of electrons.
Answer:
It was proved on the basis of a series experiments that electron possesses properties of bot wave as well as particle nature. It is clear from followin facts.
1. Cathode rays (which contain electrons only) rotate a light paddle wheel placed in their path. I proves that electron possesses character particles
2. Like light rays, electron rays also exhibit the phenomenon of diffraction and interferenc which show the wave character of electron.
Question 16.
Write the differences between electro magnetic waves and matter waves.
Answer:
Differences between electromagnetic waves an matter waves
|
Electomagnetic waves |
Matter waves |
|
1. The velocity of all electromagnetic waves is similar to the velocity of light i.e., 3 × 108 m/s |
The velocity of matter waves is less than velocity of light. |
|
2. They have large wavelength which can be calculated using given formula. Λ = C/V |
They have small wavelength which can be calculated using de-Broglie equation λ = h/mv |
|
3. Their energies are quantised. |
They have unquantised energy. |
|
4. Their wavelength is large and covers full spectrum range. |
The wavelength of matter wave is of low range. |
|
5. They move with uniform speed. |
Matter waves move with variety of speed. |
Question 17.
Differentiate between particle and wave.
Answer:
|
Particle |
Wave |
|
1. Particle occupies a well defined position in space i.e., particle is localized in space. |
Wave is spread out in space. Thus wave is delocalised in space. |
|
2. When a particle occupies a particular space, the same space can not be occupied by other simultaneously i.e. particles do not interfere. |
Two or more waves can co-exist in the same region of space and hence interfere. |
|
3. When a numbers of particle are present in given region of space, their total volume is equal to their sum i.e., it is neither less or more. |
When a number of waves are present in given region of space, to interfere the resultant wave can be large or small then the individual wave interference may be destructive. |
|
4. Particles can be count. |
Waves are not countable. |
Question 18.
"Electron can not exist in the nucleus." Comment on this.
Answer:
An electron could exist in the nucleus if uncertainty in its velocity (Av) should be less than speed of light i.e.,
(3 × 108 m/s). Hence we calculate real value of ∆v. If electron could be a part of nucleus than uncertainty in its postion ∆x not exceed than radius of nucleus i.e., 10-15 m. The mass of electron is 9.0 × 10-31 kg.
Then

= 5.79 x 10 ms-1
Since this value is more than velocity of light (3 × 108 m/s). It means electron can not exist in nucleus.
Question 19.
Calculate nodal planes of 3s and 3p orbitals?
Answer:
There are two types of nodal planes for each orbital.
(i) Angular nodal planes = l
(ii) Spherical nodal planes = n - l - 1
Hence total nodal planes = 1 + (n − l − 1) = (n - 1)
For 3s orbital,
Angular nodal surface = 0
Spherical nodal planes = 3 - 0 - 1
Total nodal planes = 0 + 2 = 2
For 3p orbital
Angular nodal planes = 1
Spherical nodal planes = 3 - 1 - 1 = 1
Total nodal planes = 1 + 1 = 2

Question 20.
Write complete electronic configuration for following elements with given atomic number and determine their place in perodic
21, 24, 27.
Answer:
(i) 21 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6,3d1, 4s2
(ii) 24 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d3, 4s1
(iii) 27 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d7, 4s2
Their period is (4) and group is (viii)
Question 21.
Write the symbols for orbitals with the help of given quantum numbers
1. n 3, 1 = 1, m + 1
2. n = 5, 1 = 2, m = 1
Answer:
Value of n, 1, m represent the shell, subshell and orbital respectively,
1. For n = 3, l = 1, indicates p-subshell:
m = 1 or -1, 0 -1 or +1
So, symbol will be 3px or 3py:
(2) For n = 5, l = 2 i.e., d-subshell:
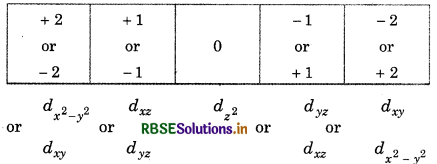
Hence, symbol = 5dyz or 5dxz
Question 22.
In hydrogen atom, what information obtained from (i) radial probable density, R2 and (ii) radial probability function 4πr2R2. With the help of dirgrams show them for 1s orbital of H-atom. How they change with r?
Answer:
(i) Radial probability density (R2) → it gives he probability of finding of electron alongwith radial ine at certain point. For 1s orbital, its relation with r is shown in figure A.
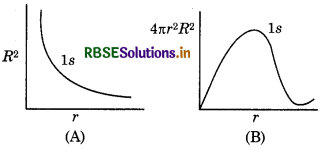
(ii) Radial probability function (4nг2R2) → it gives he probability of finding of electron in a spherical shell between r and r + dr]. The volume of this shell will be The relation between r and 4лr2 dr is given in figure B).
Question 23.
Draw a plot between R2 and 4лr2R2 with respect tor for 2s orbital of hydrogen atom.
Answer:
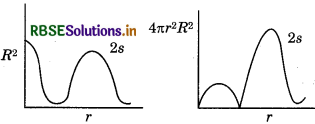
Question 24.
What is azimuthal quantum number and how it is related to principal quantum number?
Answer:
Azimuthal quantum number determines the aumber of subshells in main shell. It given also size, ngular momentum in three dimensional space. It is lenoted by ‘7. It can have positive value starting from 0 o (n - 1) for principal quantum number 'n'.
Total value of '7 is equal to no. of principal quantum number
For example n = 4
∴ from 7 = 0 to 3(0, 1, 2, 3)
l = 0 1 2 3
Subshell = s, p, d, f,
In any subshell the maximum number of electrons will be 2(2l + 1) and number or orbital will be (2l + 1).

Question 25.
With the help of (n + 1) rule, answer the following:
(a) Arrange following orbitals according to their increasing order of energy:
(i) 1s, 2s, 3s, 2p
(ii) 4s, 3s, 3p, 4d
(iii) 5p, 4d, 5d, 4f, 6s
(iv) 5f, 6d, 7s, 7p
(b) Which orbital has maximum energy among the following.
5p, 5d, 5f, 6s, 6p
(c) Which orbital has minimum energy among following
4d, 4f, 5s, 5p
Answer:
(a)
(i) 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s
(ii) 3s < 3p < 4s < 4d
(iii) 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d
(iv)7s < 5ƒ < 6d <7p
(b) The 5s orbital has minimum energy.
(c) The 4f orbtital has maximum energy.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What do you mean by quantum number? Give their types and how they are related to each other, explain with suitable example.
Answer:It is denoted by ‘n’. It determines the main energy level or shell in which electron is present. Value of energy of electron mainly depends on value of ‘n’. The value of ‘n’
varies from 1 to but not zero. The values of ‘n’ are also represented by K L. M, N, O shells.
n = 1,2,3,4, 5...
Shells = K, L, M, N, O,...
The maximum number of electrons in any shell is equal to 2n2 i.e.
Shells = K, L, M, N, O, P
‘n’ values = 1 2 3 4 5 6
Number of electons(2n2)= 2,8, 18, 32, 50, 72
With the help of principal quantum number, the size of atom and distance of electron from nucleus can be determined.
\(r=0.529 \times \frac{n^2}{Z}\)
Beside of this, the energy of electron in atom can also be calculated:
E = - 13.6 x n2eV
As distance of electron from atom increases the value of energy also increases.
K < L < M < N.

Question 2.
Define spectra. Explain various types of spectra
Answer:
Emission spectrum:
When a substance is heated or the energy is provided to it, then atoms and molecules of element absorb energy and reach to a higher energy state and become unstable. For returning to their normal energy state, (more stable) the atoms and molecules emit radiation in various regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The spectrum of radiation emitted by a substance that has absorbed energy is called an 'emisssion spectrum' By following phenomenon, we can emit radiation:
- Emitted radiation from sun or electric bulb
- From electric discharge of gas at low pressure
- By heating a substance at high temperature
Emission spectrum is divided into two parts
1. Continuous spectra
2. Line spectra or atomic spectra
1. Continuous spectra : When sunlight or light from electric bulb is analysed by spectroscope, these spectra obtained on photographic plate containing a series of coloured bands. These seven colours are overlapped to each other. Hence it is called continuous spectrum
2. Line or atomic spectra: When atoms of any element are excited then radiation in emitted when this radiation is analysed by spectroscope. These series line found in discontinuous pattern i.e., dark space between two lines or in other words, we can say that there is black line between two coloured lines. This type of spectrum is known as line or atomic spectrum. For example if platinum wire wetted with KCl solution is burned at bunsen burner, then specific violet coloured flame is obtained, such spectra is known as finger print of atom.
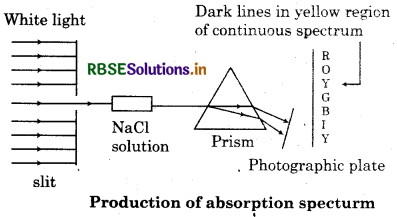
Absorption Spectra:
A spectrum of electromagnetic radiation transmitted through a substance, showing dark lines or bands due to absorption at specific wavelength. An absorption is like the photographic negative of an emission spectrum. A continuous of radiation is passed through a sample which absorb radiation of certain wavelength. The missing wavelength which corresponds to the radiation absorbed by matter leave dark space in the bright continuous spectrum.
Question 3.
Write down the various rules used for filling the electrons in orbitals.
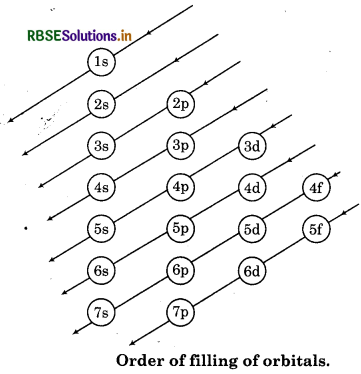
Answer:
The word 'Aufbau' is of German language which means 'building up.' The building up of orbital means the filling of orbitals with electrons. According to this principle" in the ground state of the atoms, thè orbitals are filled in order of their increasing order of energy". In other words electrons first occupy the lowest energy orbital available then enter into high energy level. The increasing order of energy levels for various orbitals is shown in following figure.
Question 4.
Why fully filled and half filled subshells are most stable? Explain
Answer:
1. Symmetrical distribution of electrons : It is well known that symmetry leads to stability. The completely filled or half filled subshells have symmetrical distribution of electrons in them and therefore are more stable. Electrons in the same subshell 3 d have equal energy but different spatial distribution. Consequently, their, shielding of one another, is relatively small and the electrons are more strongly attracted by the nucleus.
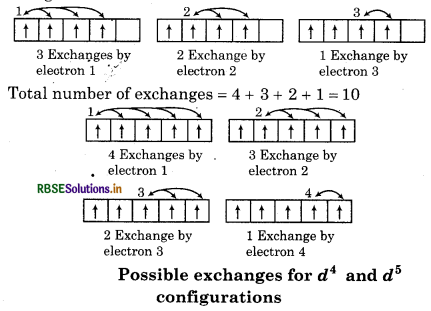
2. Exchange Energy: Whenever two or more electrons with the same spin are present in the degenerate orbital of subshell then stablizing affect arises. "These electrons tends to exchange their position and the energy related due to this exchange is called exchange energy". The number of exchanges that can take, place is maximum when the subshell is either half filled or fully filled. As a result of exchange energy is maximum and so is stability.
Exchange energy is the basis of Hund's rule in such a way electron have parallel spin as far as possible. In other words, the extra stability of half filled and fully filled subshell is due to
(i) relatively small shielding
(ii) smaller Coulombic repulsion energy and
(iii) larger exchange energy.
The number of exchanges that can take place in d4 configuration are as follows:
Total number of exchanges = 3 + 2 + 1 = 6
The number of exchanges that can take place in d5 configuration áre as follows:

Question 5.
Write short notes on the following
(a) Black body radiation
(b) Explanation of photoelectic effect by quantum theory.
Answer:
(a) Black Body Radiation : It is explained by Max Planck in 1900. An ideal black body is that which emits and absorbs radiations of all frequencies. The radiation emitted by such body is called black body radiation.
When an iron rod, is heated then colour changes from dull red to red with increment in temperature intensity of colour increase. After sometime, colour becomes white and blue due to high temperature. But these observations do not satisfy the principle of radiation colour because according to this principle, on increasing thermal energy, intensity of that particular colour i.e., red colour should be increased rather than change in colour. It means that at given temperature, the intensity of emitted radiation increases with decreasing of wave length.
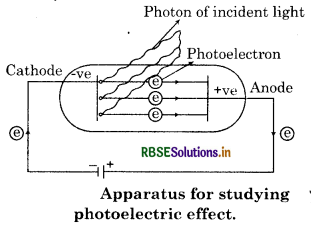
(b) Photoelectric Effect: In 1887 , Hertz observed this effect. When radiation with certain minimum frequency strikes the surface of a metal, the electrons are ejected from the surface of the metal. This phenomenon is called photoelectric effect. For example, when light of certain frequency strikes the surface of some metal like potassium, rubidium, caesium etc, electrons are ejected.
Numerical Questions:
Question 1.
Two elements X and Y possess equal atomic weight and their atomic number are 18 and 19 respectively. If X element has 12 neutrons in its nucleus then calculate number of neutrons in Y element?
Answer:
Since atomic mass of X and Y are similar i.e., they are isobars.
Atomic mass = No. of proton + No. of neutrons
or
Atomic mass - Atomic number + No. of neutrons
For X, Atomic mass = Atomic number + No. of neutron
= 18 + 21 = 39
For Y, Atomic mass = Atomic number + No. of neutrons
39 = 19+ No. of neutrons
No. of neutrons = 39 - 19 = 20
Question 2.
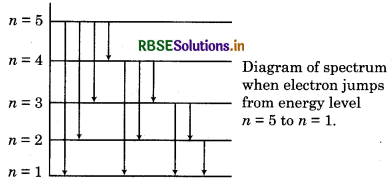
Calculate the total lines in spectrum of H-atom when electron jumps from 5th orbit to 1st orbit?
Answer:
Total lines in spectrum
\(=\frac{n(n-1)}{2}=\frac{5(5-1)}{2}=\frac{5 \times 4}{2}=10 \)
There lines are represented as follow
Question 3.
Calculate the frequency and wavelength of photon in H-atom when transition occurs from n = 4 to n = 2?
Answer:
n = 4, n1 = 2
So, in this transition, one spectrum line obtained in Balmer series.
AE = 2.18 × 10-18
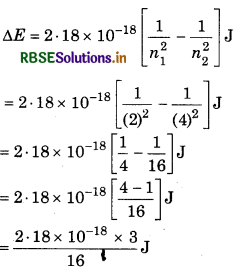
= 0.40875 × 10-18 J
= 4.09 × 10-19 J
∆E = hv
\(v=\frac{\Delta E}{h}=\frac{4 \cdot 09 \times 10^{-19}}{6 \cdot 626 \times 10^{-34}}\)
= 0.617 × 1015
\(\lambda=\frac{c}{v}=\frac{3 \times 10^8}{6.17 \times 10^{14}}\)
= 468 × 10-9 m = 468nm
Question 4.
Calculate the energy associated with first I orbit of Li2+ ion. What will be radius of this orbit?
Answer:
\(E_n=-\frac{2 \cdot 18 \times 10^{18}}{n^2} \times Z^2 \mathrm{~J}\)
For Li2+ n = 1 and Z = 3
\(\begin{aligned} E_n & =-\frac{2 \cdot 18 \times 10^{18}}{(1)^2} \times(3)^2 \\ & =-\frac{2 \cdot 18 \times 10^{18} \times 9}{1} \end{aligned}\)
En = - 19.62 × 1018J
rn = 0.0529 × n2/Z nm = 0.0529 × (1)2/3 nm
= 0.0176 nm

Question 5.
Calculate the frequency of spectrum line when electron jumps from 4th level to first H level in H-atom?
Answer:
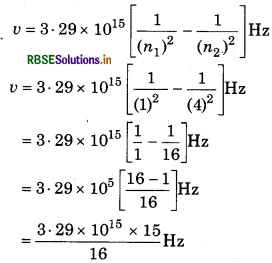
= 3.08 x 1015 Hz
Question 6.
Calculate wavelength of photon associated with lev energy?
Answer:
Energy of photon = 1 eV
E = 1.602 × 10-19 J
Planck's constant h = 6.626 × 10-34 J S
Velocity of light c = 3 × 108 m/s
E = hv
\(\begin{aligned} & E=\frac{h c}{\lambda} \\ & \lambda=\frac{h c}{E}=\frac{6 \cdot 626 \times 10^{-34} \times 3 \times 10^8}{1 \cdot 602 \times 10^{-19}} \end{aligned}\)
λ = 12.41 × 10-7 m
= 12.41 × 103Å
Question 7.
The wavelength of blue coloured light is 480 Calculate its frequency and wave number.
Answer:
Wave length (λ) = 480 nm 480 × 10-9 m
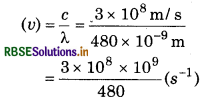
v = 0.00625 × 1017 s-1
V = 6.25 × 1014 Hz
Wave number (v)
\(\frac{1}{\lambda}=\frac{1}{480 \times 10^{-9}}=\frac{10^9}{480}\)
= 0·00208 × 109
= 2.08 × 106m-1
Question 8.
If photon associated with wavelength 700 nm has energy E then what will be wavelength of photon whose energy is 2E?
Answer:
E = \(\frac{h c}{\lambda}\)
here he is constant then,
\(E \alpha \frac{1}{\lambda}\)
E1λ1 = E2 λ2
E x 700 = 2E × λ2
\(\lambda_2=\frac{700}{2}\)
350 nm
Question 9.
In an experiment of photoelectric effect, a metal produces electron with frequency of 5.2 × 1014 s-1 and maximum kinetic energy of 1.3 x 10-19 J. What will be threshold frequency of the metal?
Answer:
As we know, hv = hv° + K.E
hv - hv° = K.E
h (v - v°) = K.E or (v - v°) \(=\frac{K \cdot E}{h}\)
= 5.2 × 1014 \(\frac{1 \cdot 3 \times 10^{-19}}{6 \cdot 626 \times 10^{-34}}\)
= 5.2 × 1014 -1.96 × 1014
= 3.24 × 1014s-1
Question 10.
When a light with wavelength 4000 nm falls on the metal surface whose work function is 2.0 eV, then calculate:
(i) Energy of photon.
(ii) Kinetic energy of photoelectrons.
Answer:
Wavelength of light (2) = 4000Å
= 4000 × 10-10 m = 4 x 10-7 m
Work function (hu) = 2.0 eV
= 2.0 × 1.6 × 10-19 J
= 3.2 × 10-19 j
(i) Energy of photon,
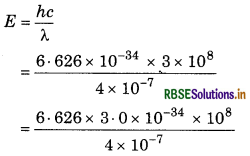
= 4.97 × 10-19 J
(ii) K.E. of photoelectron,
hv - hvo = K.E
\(\frac{h c}{\lambda}-h v_0\) = K.E
4.97 × 10-19 - 3.2 × 10-19 = K.E
1.77 × 10-19 = K.E
K.E = 1.77 × 10-19J
Question 11.
A bulb emits light of wavelength of 4500 Å. If bulb is of 150 watt and in which 8% energy emits in form of light then calculate the number of photons emitted in one second.
Answer:
Energy a photon (E) = \(\frac{h c}{\lambda}\)
Here
h = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
c = 3 x 108 m/s
λ = 4500Å = 4500 × 10−10.
Now,
\(E=\frac{h c}{\lambda}\)
or
\(E=\frac{6 \cdot 626 \times 10^{-34} \times 3 \times 10^8}{4500 \times 10^{-10}}\)
= 4.417 × 10-19 J
Energy emitted by bulb = 150 x \(\frac{8}{100} \mathrm{~J}\)
ETotal = n.E = 150 × \(\frac{8}{100} \mathrm{~J}\)
n × 4.417 × 10-19 = \(\frac{150 \times 8}{100}\)
\(n=\frac{15 \times 8}{10 \times 4 \cdot 417 \times 10^{-19}}\)
So number of photon
n = 27·17 × 1018
Question 12.
The vapour density of oxide of nitrogen is 62. Calculate the total number of electrons in its 108 g.
Answer:
Suppose formula of oxide is N2O x
The molecular mass of N2Ox ⇒ 2 × 14 + 16 x
Molecular mass by vapour density = 2 × vapour density
= 2 × 62
= 124
Thus,
28 + 16x = 124
16x = 124 - 28
16x = 96
\(x=\frac{96}{16}=6\)
Therefore formula of nitrogen oxide
= N2O6 = NO3
Now, number of electrons in 1 mole of N2O6
= 2 × 7+ 6 × 8 = 14 + 48 = 62
No. of electrons in Avogadro's molecules
= 62 × 6.02 × 1023
= 3.73 × 1025

Question 13.
A bulb of 105 watt, emits a coloured light of wavelength of 400 nm. Calculate the number of photons emitted per second?
Answer:
Electric power of bulb = 105 W = 105 J/s
Energy of one photon; E = hv
or
\(\begin{aligned} E & =\frac{h c}{\lambda} \\ & =\frac{6 \cdot 626 \times 10^{-34} \times 3 \times 10^8}{400 \times 10^{-9}} \end{aligned}\)
= 4.969 × 10-19 J
Number of emitted photons =
\(\frac{105 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}}{4 \cdot 96 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{~J}}\)
= 21.13 × 1019 photons/second.
Question 14.
If in H-atom for any transition, it produce wavelength of 100 nm, then what will be wavelength of same transition in He+ atom?
Answer:
For H-atom
\(\frac{1}{\lambda_{\mathrm{H}}}=R_{\mathrm{H}}\left[\frac{1}{\left(n_1^2\right)}-\frac{1}{\left.n_2^2\right)}\right]\) ........ (i)
For He+ atom
\(\frac{1}{\lambda_{\mathrm{He}^{+}}}=R_{\mathrm{H}} \cdot Z^2\left[\frac{1}{\left(n_1^2\right)}-\frac{1}{\left(n_2^2\right)}\right]\) ........ (ii)
In equation (1) and (2)
\(\lambda_{\mathrm{He}^{+}}=\frac{\lambda_{\mathrm{H}}}{Z^2}=\frac{100}{(2)^2}=\frac{100}{4}=25 \mathrm{~nm}\)
Question 15.
One ion of any element contains 1 electron. For this ion, the difference in wavelength of first Balmer series and first Lyman series is 59.3 nm. Predict the name of this ion.
Answer:
According to the relation,
\(\frac{1}{\lambda}=R_{\mathrm{H}}(Z)^2\left[\frac{1}{\left(n_1^2\right)}-\frac{1}{\left(n_2^2\right)}\right]\)
For first line of Balmer series, n1 = 2, n2 = 3
\(\begin{aligned} & \frac{1}{\lambda}=R_{\mathrm{H}}(Z)^2\left[\frac{1}{(2)^2}-\frac{1}{(3)^2}\right] \\ & \lambda=\frac{36}{5 R_{\mathrm{H}}(Z)^2} \end{aligned}\)
For first line of Lyman series, n1 = 1, n = 2
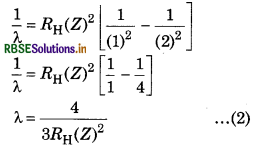
The difference of both wavelength is 59.3 nm
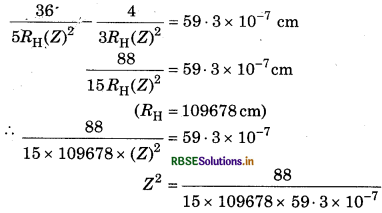
(Z)2 = 9
Z = √9
Z = 3
So this ion will be Li3+.
Question 16.
Calculate the wavelength of electron whose mass is 9.1× 10-31 kg and kinetic energy is 3.0 x 10-25 J.
Answer:
K.E = 1/2 mv2
2 K.E = mv2
or mv2 = 2K.E
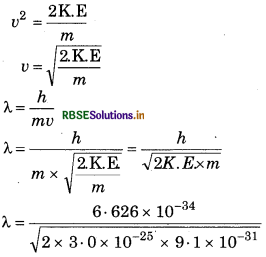
λ = 8967 × 10-1 m
λ = 896 7 nm
Question 17.
Find out the uncertainty in position of an electron whose mass is 9.1× 10-28 g and the value of its uncertainty in velocty is 5.7 × 107 cm/s.
Answer:

Ax = 1·02 × 10-8 cm
Question 18.
Calculate the de-Broglie's wavelength of an electron which has velocity equal to 1% of velocity of light?
Answer:
According to de-Broglie
\(\lambda=\frac{h}{m v}\)
here
m = 9.1 x 10-31 kg
h = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
Velocity of electron (Av)= 1% of velocity of light
\(=\frac{3 \times 10^8 \times 1}{100}\)
= 3 × 108 × 0.01
= 3 × 106 m s-1
\(=\frac{h}{m v}=\frac{6 \cdot 626 \times 10^{-34}}{9 \cdot 1 \times 10^{-31} \times 3 \times 10^8}\)
= 2.43 × 10-10 m
Question 19.
Velocity of an electron is 30 m/s which is up 98.99% pure. What will be uncertainty in its position?
Answer:
Given
h = 6.626 x 10-34 J s
m = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
∆u = 30 ms-1
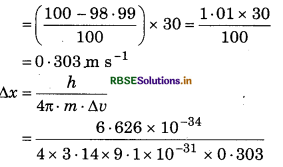
= 0.191 × 10-3
∆x = 1.91 x 104m
Question 20.
An electron mass can be diffracted by crystal. What should be potential of electro mass taken that's why its wavelengt becomes 1. 54 Å?
Answer:
For an electron
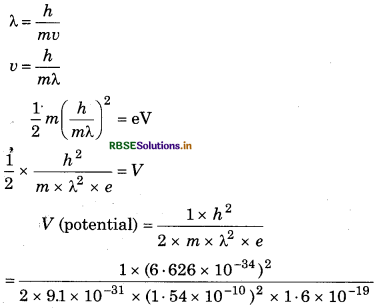
V = 63.6 volt
Question 21.
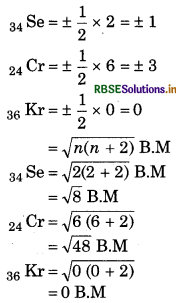
Find out magnetic moment and total spin fo the atoms whose atomic numbers are 34, 1 and 36.
Answer:
Electronic configuration for atoms
34 Se → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d1o, 4s2,
(unpaired electron = 2)
24 Cr → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d5, 4s1
(unpaired electron = 6)
36 Kr → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d1o, 4s2, 4p6
(unpaired electrons = 0)
Total spin = +1/2 x No. of unpaired electron
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
In H-atom the energy of nth Bohr's orbit is:

Answer:
\(\text { (a) } \frac{-13 \cdot 6}{n^2} \mathrm{eV}\)
Question 2.
In spectrum of H-atom absorption of a photon with less energy transition occur n = 6 to n = ... energy level.
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 3
(d) 4
(e) 2
Answer:
(c) 3

Question 3.
The group of which quantum shows less energy?
(a) n = 4, 10, m = 0 s = + 1/2
(b) n = 3, 10, m = 0, s = + 1/2
(c) n = 3, l = 1, m = 1, s = + 1/2
(d) n = 3 l = l, m = 1, s = + 1/2
Answer:
(d) n = 3 l = l, m = 1, s = + 1/2
Question 4.
How many electrons can accomodate in an orbital for which n = 3 and l= 1?
(a) 14
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 10
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 5.
Two electrons are accomodated in an orbtial. They are different in:
(a) Principal quantum number
(b) Magnetic quantum number
(c) Azimuthal quantum number
(d) Spin quantum number
Answer:
(d) Spin quantum number
Question 6.
The value of first excited enrgy state for H-atom will be:
(a) - 13.6 eV
(b) -1.51 eV
(c) -3.40 eV
(d) -0.85 eV
Answer:
(b) -1.51 eV
Question 7.
Orbital angular momentum for d-electron will be:

Answer:
\(\text { (b) } \frac{\sqrt{6 h}}{2 \pi}\)
Question 8.
Gadolinium (Gd) atomic number (64), electonic configuration will be
(a) [Xe] 4f8, 5d9, 6s2
(b) [Xe] 4f8 5d1 6s2
(c) [Xe] 4ƒ3, 5ď6, 6s2
(d) [Xe] 4f6, 5d2, 6s2
Answer:
(b) [Xe] 4f8 5d1 6s2
Question 9.
Which of the following specimen is isoelectronic?
(a) Ne, Na+
(b) Ar, K
(c) Cl, Cl-
(d) Mg2+, Al
Answer:
(a) Ne, Na+
Question 10.
For two electrons the set of quantum number is following :
P = -3, 2,- 2; Q = 3, 0, 0
Which statement is correct?
(a) P has less energy than Q
(b) Both P and Q are similar in energy
(c) P and Q show equal number of electrons
(d) P has more energy than Q
Answer:
(d) P has more energy than Q

Question 11.
Which explain order of filling electrons in an orbital?
(a) Hund's rule
(b) Octet rule
(c) Aufbau's rule
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Aufbau's rule
Question 12.
Be2+ ion is isoelectronic to:
(a) Mg2+
(b) Na+
(c) Li+
(d) H+
Answer:
(c) Li+
Question 13.
Find out the value of energy in Joule for light whose wavelength is 4nm.
(h = 6.63 × 10-34 J sec and c = 3 × 108 m/s)
(a) 4.42× 10-15
(b) 4.42 × 10-18
(c) 6.67 x 1015
(d) 6.67 × 1011
Answer:
(b) 4.42 × 10-18
Question 14.
Correct set of quantum number of valance electron of Rb (Z = 37) is:
(a) 5, 0, 0, + 1/2
(b) 5, 1, 0, + 1/2
(c) 5, 1, 1 + 1/2
(d) 6, 0, 0 + 1/2
Answer:
(a) 5, 0, 0, + 1/2
Question 15.
The maximum number of orbitals for following quantum number will be n = 3, 1 = 1, m = 0:
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer:
(c) 1

Question 16.
Which series does not belong to IR region in hydrogen spectrum series?
(a) Pfund
(b) Brackett
(c) Paschen
(d) Lyman
Answer:
(d) Lyman
Question 17.
The energy of an electron represented as E = 2.078 × 10-18 J What will be wavelength of light to excite an electron from n 1to n 2 in H-atom?
(a) 1.2114 x 10-7 m
(b) 2.816 × 10-7m
(c) 6.500 x 10-7 m
(d) 8.500 x 10-7m
Answer:
(a) 1.2114 x 10-7 m
Question 18.
The electrons maximum number of associated with orbital of quantum number n = 3, 1= 1, m = - 1, is :
(a) 2
(b) 10
(c) 6
(d) 4
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 19.
Electronic configuration of CO in ground state will be:
(a) 1σ2 , 2σ2, 1π2 3σ2
(b) 1σ2 , 2σ2, 3σ2 1π2, 2π2
(c) 1σ2 , 2σ2, 1σ2 , 3σ2 , 2π2
(d) 1σ2 , 1π2 , 2σ2, 3σ2
Answer:
(a) 1σ2 , 2σ2, 1π2 3σ2
Question 20.
Which is not isoelectronic ?
(a) CO
(b) NO+
(c) CN-
(d) O2
Answer:
(d) O2
Question 21.
Which Structure of Atom 115 group does not isoelectronic species ?
(a) NO+, C2- CN ̄, N2
(b) CN ̄, N2, O2, C2-
(c) N2, O2, NO+, CO
(d) C2, O2, CO, NO
Answer:
(a) NO+, C2- CN ̄, N2
Question 22.
The valance shell represent of an element has 8 electrons then for this element suitable statement is:
(a) It will lose electron
(b) The number of electron will increase
(c) Neither electron will be lost nor gained
(d) None of above
Answer:
(c) Neither electron will be lost nor gained
Question 23.
The ratio occupied by first and second orbtial will be:
(a) 1 : 2
(c) 8 : 1
(b) 1 : 16
(d) 16 : 1
Answer:
(d) 16 : 1

Question 24.
Out of following which set of quantum numbers is not possible?
(a) 3, 2, 0, +1/2
(b) 2, 2, 1, + 1/2
(c) 1, 0, 0, +1/2
(d) 3, 2, -2, +1/2
(e) 2, 1, 1, +1/2
Answer:
(b) 2, 2, 1, + 1/2
Question 25.
An element form diatomic molecule with triple bond. What will be its configuration ?
(a) 1s2, 2s2, 2p5
(b) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6
(c) 1s2, 2s2, 2p3
(d) 1s2, 2s2, 2p
Answer:
(c) 1s2, 2s2, 2p3
Question 26.
The value of quantum number of outer most electron of Na (Z – 11) atom will be :
(a) n = 2, l= 1, m = 1, s = - 1/2
(b) n = 3, l = 0, m = 0, s = + 1/2
(c) n = 3, l = 2, m = -2, s = - 1/2
(d) n = 3, l = 2, m = 2, s = + 1/2
Answer:
(b) n = 3, l = 0, m = 0, s = + 1/2
Question 27.
Which rule shows the pairing of electrons in orbital?
(a) Pauli's exclusion principle
(b) Hund's rule
(c) Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
(d) Hess rule
Answer:
(b) Hund's rule
Question 28.
Electrons are arranged in order of increasing energy which are identified by quantum number n and 1:
(a) n = 4, l = 1
(b) n = 4, l = 0
(c) n = 3, l =2
(d) n = 3, l = 1
(a) (3) < (4) < (2) < (1)
(b) (4) < (2) < (3) < (1)
(c) (2) < (4) < (1) < (3)
(d) (1) < (3) < (2) < (4)
Answer:
(b) (4) < (2) < (3) < (1)
Question 29.
Which set of quantum
(a) n = 3, l = 1, m = + 2
(b) n = 3, l = 2, m = - 2
(c) n = 3, l = 1, m = +1
(d) n = 3,l = 1, m = -1
Answer:
(a) n = 3, l = 1, m = + 2

Question 30.
In which orbital the the electron is zero at probability of finding xy surface
(a) Px
(b) Pz
(c) dyz
(d) dx2 - y2
Answer:
(b) Pz
Question 31.
What will be maximum number electron in shell represented by principal quantum number (n)?
(a) n
(b) 2n
(c) n2
(d) 2n2
Answer:
(d) 2n2
Question 32.
The total number of orbitals in 4th energy level will be:
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 16
(d) 32
Answer:
(c) 16
Question 33.
The energies of two radiations E1 and E2 are 2 eV and 0 eV. What will be the relation between their wavelengths i.e. λ1 and λ2:
(a) λ1 = λ2
(b) λ2 =λ2
(c) λ1 = 2λ2
(d) λ = 4λ2
Answer:
(c) λ1 = 2λ2
Question 34.
In spectrum of H-atom the wavelength which transition will be similar to wavelength of transition n = 4 to n = 2 in He spectrum?
(a) n = 4 to n = 3
(b) n = 3 to n = 2
(c) n = 4 to n = 2
(d) n = 3 to n = 1
(e) n = 2 to n = 1
Answer:
(c) n = 4 to n = 2

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure