RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 9 Hydrogen
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 9 Hydrogen Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Important Questions Hydrogen
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Which is used as hydrogen generator?
(a) NaH
(b) HI
(c) S6H3
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) NaH
Question 2.
Hydrogen burns in air with a:
(a) light bluish flame
(b) yellow flame
(c) green flame
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) light bluish flame

Question 3.
Among the following, which cannot act as both oxidising and reducing agent?
(a) H2O2
(b) H2
(c) SO2
(d) HNO3
Answer:
(b) H2
Question 4.
The colour of hydrogen is :
(a) colourless
(b) black
(c) yellow
(d) orange
Answer:
(a) colourless
Question 5.
The adsorption of hydrogen by metals is called :
(a) dehydrogenation
(b) hydrogenation
(c) occlusion
(d) absorption
Answer:
(c) occlusion
Question 6.
The sum of protons, neutrons and electron in heaviest isotope of hydrogen is :
(a) 6
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 4
Question 7.
An element reacts with hydrogen to form a compound A which on treatment with water. liberates hydrogen gas. The element can be:
(a) nitrogen
(b) chlorine
(c) selenium
(d) calcium
Answer:
(d) calcium
Question 8.
Heavy water is :
(a) product of oxygen and isotope of hydrogen.
(b) water of mineral springs
(c) heavier isotope of hydrogen and heavier isotope of oxygen
(d) ordinary water containing dissolved salts of heavy metals
Answer:
(a) product of oxygen and isotope of hydrogen.
Question 9.
When zeolite is treated with hard water, sodium ions are exchanged with:
(a) OH ions
(b) SO2- ions
(c) Ca2+ ions
(d) H+ ions
Answer:
(c) Ca2+ ions
Question 10.
The molarity of pure water at 4°C is :
(a) 1M
(b) 2.5 M
(c) 5M
(d) 55.5 M
Answer:
(d) 55.5 M
Question 11.
Which of the following will determine whether the given colourless liquid is water or not?
(a) Melting
(b) Tasting
(c) Phenolphthalein
(d) Adding a pinch of anhydrous CuSO4
Answer:
(d) Adding a pinch of anhydrous CuSO4
Question 12.
Lead pipes are not used for carrying drinking water because :
(a) They are covered with a coating of lead carbonate
(b) They are corroded by air and moisture
(c) Water containing dissolved air attacks lead forming soluble hydroxides
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Water containing dissolved air attacks lead forming soluble hydroxides

Question 13.
The alum used for purifying water is:
(a) ferric alum.
(b) chrome alum
(c) potash alum
(d) ammonium alum
Answer:
(c) potash alum
Question 14.
When two ice cubes are pressed over each other, they unite to form one cube. Which of the following forces are responsible to hold them together?
(a) hydrogen bond formation
(b) vander Waal's forces
(c) covalent attraction
(d) ionic interaction
Answer:
(a) hydrogen bond formation
Question 15.
Fenton's reagent is:
(a) FeSO4 + H2O2
(b) Zn + HCl
(c) Sn + HCl
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) FeSO4 + H2O2
Question 16.
Hydrogen peroxide is used as:
(a) oxidising agent
(b) reducing agent
(c) both oxidising and reducing agent
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) both oxidising and reducing agent
Question 17.
H2O2 used in rockets has the concentration :
(a) 50%
(b) 70%
(c) 30%
(d) 90%
Answer:
(d) 90%
Question 18.
Polyphosphates are used as water softening agents because they :
(a) form soluble complexes with anionic species.
(b) precipitates anionic species.
(c) form soluble complexes with cationic species.
(d) precipitate cationic species.
Answer:
(c) form soluble complexes with cationic species.
Question 19.
Hydrogen can behave as a metal:
(a) at very high temperature.
(b) at very low pressure.
(c) at very high pressure
(d) at very low temperature
Answer:
(c) at very high pressure
Question 20.
D2O is preferred over H2O as a moderator in nuclear reactors because :
(a) D2O slows down fast neutrons better
(b) D2O has high specific heat
(c) D2O is cheaper
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) D2O slows down fast neutrons better

Question 21.
When the same amount of zinc is treated separately with excess of sulphuric acid and excess of sodium hydroxide, the ratio of volumes of hydrogen evolved is:
(a) 1 : 1
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 9 : 4
Answer:
(a) 1 : 1
Question 22.
When electric current is passed through an ionic hydride in the molten state :
(a) hydrogen is liberated at the anode
(b) hydrogen is liberated at the cathode
(c) no reaction takes place.
(d) hydride ion migrates towards cathode
Answer:
(a) hydrogen is liberated at the anode
Question 23.
The reaction
Ag2O+ H2O2 → 2Ag + H2O + O2 place in
(a) basic medium
(b) bleaching agent
(c) neutral medium
(d) both in acidic and basic medium takes
Answer:
(a) basic medium
Question 24.
Which of the following compounds turns white on treatment with hydrogen peroxide?
(a) HgS
(b) PbS
(c) NiS
(d) CuS
Answer:
(b) PbS
Question 25.
Semi water gas is a mixture of :
(a) CO + H2
(b) CO + N2
(c) CO + H2 + Ng
(d) SbH3
Answer:
(c) CO + H2 + Ng
Question 26.
The strongest base is:
(a) ammonia
(b) phosphine
(c) arsine
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) ammonia
Question 27.
Ordinary hydrogen at room temperature is a mixture of:
(a) 75 % o-Hydrogen + 25% p-Hydrogen
(b) 25% o-Hydrogen + 75% p-Hydrogen
(c) 50 % o-Hydrogen + 50% p-Hydrogen
(d) 1 % o-Hydrogen + 99% p-Hydrogen
Answer:
(d) 1 % o-Hydrogen + 99% p-Hydrogen
Question 28.
The metal which displaces hydrogen from a boiling caustic soda solution is:
(a) As
(b) Zn
(c) Mg
(d) Fe
Answer:
(b) Zn

Question 29.
Example of compound having hydrogen bonding is:
(a) chlorine gas
(b) neon
(c) sodium chloride
(d) water
Answer:
(d) water
Question 30.
Atom which must be present in hydrogen bonding is :
(a) hydrogen
(b) sodium
(c) calcium
(d) sulphur
Answer:
(a) hydrogen
Question 31.
Hydrogen closely resembles halogens because:
(a) strong reducing agent
(b) diatomic gas
(c) colourless gas
(d) reduction potential is 0.0 V
Answer:
(b) diatomic gas
Question 32.
Which of the following is correct about hydrogen?
(a) A reductant
(b) An oxidant
(c) Both oxidant and reductant
(d) Neither oxidant nor reductant
Answer:
(c) Both oxidant and reductant
Question 33.
An atom of deuterium has:
(a) a neutron and a proton
(b) one positron and one neutron
(c) two protons and one neutron
(d) one proton and two neutrons
Answer:
(a) a neutron and a proton
Question 34.
Nuclear isotopes of hydrogen are:
(a) ortho
(b) para
(c) ortho and para
(d) neither ortho nor para
Answer:
(c) ortho and para
Question 35.
Which of the following is lightest element?
(a) hydrogen
(b) helium
(c) neon
(d) argon
Answer:
(a) hydrogen
Question 36.
In India, heavy water is produced in:
(a) Delhi
(b) Mumbai
(c) Bhilai
(d) Nangal
Answer:
(d) Nangal
Question 37.
Which of the following is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen?
(a) 1H1
(b) 1H2
(c) H3
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) H3
Question 38.
Commercially hydrogen is prepared by:
(a) marsh gas
(b) oil gas
(c) producer gas
(d) coal gas
Answer:
(a) marsh gas
Question 39.
What is the percentage of hydrogen in hydrogen peroxide by mass?
(a) 5.88
(b) 6.25
(c) 25
(d) 50
Answer:
(a) 5.88
Question 40.
Which of the following is used to detect the hardness of water?
(a) Oxalic acid
(b) EDTA
(c) sodium citrate
(d) sodium thio sulphate
Answer:
(b) EDTA
Question 41.
What is the oxidation state of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide?
(a) -2
(b) -1
(c) +1
(d) +2
Answer:
(b) -1
Question 42.
In nuclear reactors, heavy water is used as:
(a) as a coolant
(b) as a moderator
(c) both as moderator and coolant
(d) neither moderator nor coolant
Answer:
(b) as a moderator

Question 43.
What is the atomic mass of heavy water?
(a) 10
(b) 18
(c) 20
(d) 22
Answer:
(c) 20
Question 44.
The density of water is maximum at 4°C. The temperature for maximum density of heavy water is:
(a) 8.1°C
(c) 9.3°C
(b) 6.1°C
(d) 11.2°C
Answer:
(d) 11.2°C
Question 45.
Who discovered heavy water?
(a) Louis MacDonald
(b) Urey and Washburn
(c) Taylor, Iring and Frost
(d) Berg and Mangel
Answer:
(b) Urey and Washburn
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Which isotope of hydrogen is used as a tracer in organic reactions?
Answer:
Deuterium is used as a tracer in organic reactions.
Question 2.
What is hydride gap?
Answer:
The region of the periodic table from groups 7 to 9 which does not form hydrides is called hydride gap.
Question 3.
Why oxide ion is called a hard ion?
Answer:
Oxide ion is very small in size and cannot be easily polarized and hence is called a hard ion.
Question 4.
Write the formula of Zeolites.
Answer:
Na2O SiO2 Al2O3 xH2O
Question 5.
What is water gas? How is it prepared?
Answer:
An equimolar mixture of CO and H2 is called water.
C+ H2O → CO + H2

Question 6.
Write the classification of hydrides with
Answer:
1. Ionic or saline hydrides: BeH6
2. Covalent or molecular hydrides : CH
3. Interstitial or metallic hydrides: COH2.
Question 7.
What is the reason of temporary hardness of occurring in them. Thus, heavy hydrogen does not water?
Answer:
It is due to the presence of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium.
Question 8.
Why water has high melting and boiling point as compared to H2S?
Answer:
Due to the presence of hydrogen bonding in water. Concentrated sulphuric acid is not used because it which is absent in H2S.
Question 9.
What is isotopic effect?
Answer:
The difference in properties due to difference in atomic masses is called isotopic effect.
Question 10.
Concentrated sulphuric acid cannot be used for drying H2. Why?
Answer:
Concentrated sulphuric acid absorbs water from moist H2 produces so much heat that H2 catches fire.
Question 11.
Which isotope of hydrogen is radioactive?
Answer:
Tritium.
Question 12.
When H2O2 is added to blood, rapid evolution of a gas occurs. Explain?
Answer:
The enzyme present in blood catalyses the oxidation of H2O2 and hence rapid evolution of O2 takes place.
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2↑
Question 13.
Why is di-hydrogen gas not preferred in balloons?
Answer:
Because di-hydrogen is combustible in nature, it may react with oxygen highly violently.
Question 14.
Can sodium bicarbonate make water hard?Explain.
Answer:
Sodium bicarbonate cannot make water hard because soaps themselves are sodium salts of fatty acids which are soluble in water.
Question 15.
Why can’t sea animals live in distilled water?
Answer:
Distilled water does not contain dissolved O2.Therefore, sea animals cannot live in distilled waterbecause of the absence of dissolved oxygen for breathing.
Question 16.
What is the trade nameof hydrogen peroxide used as an antiseptic?
Answer:
Perhydrol.

Question 17.
Which hydrides are formed by d and f block elements?
Answer:
Interstitial hydrides.
Question 18.
How is heavy water a toxic substance?
Answer:
Heavy water is injurious to human beings, plants and animal since it s1ows down the rates of reactions occurring in them. Thus, heavy hydrogeñ does not support life.
Question 19.
What is hydrolith?
Answer:
Hydrcilith is a common name of CaH2.
Question 20.
Why concentrated sulphuric acid is not used to prepare of di-hydrogen?
Answer:
Concentrated sulphuric acid is not used because it forms SO2 with zinc instead of H2.
Question 21.
Why a solution of hydrogen peroxide cannot be stored for a longer time?
Answer:
Because it decomposes into water and oxygen. In H2O2, oxidation state of oxygen is - 1 which is intermediate between the values for O2 and H2O. Therefore, the aqueous solution of H2O2 readily decomposes.
Question 22.
In which of the isotope of hydrogen neutron is absent?
Answer:
Protium.
Question 23.
Name the hydrogen in which nucleus rotates in one diíection.
Answer:
Ortho hydrogen.
Question 24.
Name the metals which react with NaOH to release hydrogen gas.
Answer:
Al and Be.
Question 25.
A sample of hard water has the hardnèss 6°. What is the meaning of this statement?
Answer:
This means that its hardness is one parts per million.
Question 26.
Write two examples of covalent hydride.
Answer:
B2H6,CH4.
Question 27.
A small amount of phosphoric acid or glycerol or acetanilide is added to H2O2- during its storage. Explain.
Answer:
All the three additives act as negative catalyst for the decomposition of H2O2 and thus decomposition of H2O2 is checked off.
Question 28.
What is the use of hydrogen in the manufacture of Vanaspati Ghee?
Answer:
H2 is used as reducing agent to convert vegetable oil into vegetable ghee.

Question 29.
Name the phenomenon of adsorption of hydrogen on metal surface.
Answer:
Occlusion.
Question 30.
Name a substance which can oxidise H2O2.
Answer:
Acidified KMnO4.
Question 31.
What type of elements form interstitial hydrides?
Answer:
d-block and f-block elements. .
Question 32.
Write two example of metallic hydrides.
Answer:
ZrH and TaR
Question 33.
Write two examples of ionic hydrides.
Answer:
CaH2 and SrH2.
Question 34.
What is the nature of aqueous solution of sodium carbonate?
Answer:
Alkaline.
Question 35.
What is the importance of heavy water with regard to nuclear power generation?
Answer:
It is used as a moderator and helps to control the nuclear reaction.
Question 36.
Why is sodium chloride less soluble in heavy water than in ordinary water?
Answer:
The dielectric constant of heavy water is less than that of normal water, therefore ionic compounds like NaCl are less soluble in it.
Question 37.
Why density of heavy water is more than ordinary water.
Answer:
Because of its molecular mass.
Question 38.
How many electrons are there in one molecule of heavy water?
Answer:
10 electrons.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
How dihydrogen is prepared in laboratory?
Answer:
In laboratory, hydrogen is prepared by following reaction:
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
Granulated zinc is taken in a Woulfe's bottle. Dilute sulphuric acid is poured dropwise through thistle funnel on granulated zinc pieces. The gas evolved is collected over water by downward displacement of water.

Question 2.
Distinguish between permanent and temporary hardness of water.
Answer:
|
Permanent hardness |
Temporary hardness |
|
1. It is due to the presence of soluble chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium. |
It is due to the presence of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium. |
|
2. It cannot be removed by simply boiling and filtering the water. |
It can be removed by simply boiling and filtering the water. |
|
3. It is also called as non-carbonate hardening. |
It is also called as carbonate hardening. |
Question 3.
Hydrogen peroxide is strong oxidizing agent both in acid and alkaline medium. Explain.
Answer:
Hydrogen peroxide can act as oxidizing agent both in acidic and basic medium. The oxidation state of O in H2O2 is -1. Therefore, it gets oxidized to O2 (zero oxidation state) or reduced to H2O (oxidation state, -2).
In acidic medium : H2O2 + 2H’ + 2e → 2H2O
Example : 2FeSO4 + H2SO4 + H2O2 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 2H2O
In basic medium : H2O2 + 2e- → 2OH(aq)
Example : MnSO4 + H2O2 + 2NaOH → MnO2 + Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Question 4.
Why is hydrated barium peroxide is used in preparation of hydrogen peroxide instead of anhydrous barium peroxide?.
Answer:
If anhydrous barium peroxide is used in the preparation of H2O2, barium sulphate formed during the reaction forms an insoluble protective coating on thesurface of solid barium peroxide as:
BaO2(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + H2O2 (aq)
This prevents further action of acid and therefore, stops the reaction. If however, hydrated barium peroxide is used, the water of crystallization does not allow BaSO4 to deposit on the surface of BaO2 and the reaction goes on completion.
Question 5.
What are the advantages of using hydrogen as a fuel?
Answer:
Hydrogen is used as a rocket fuel in space research and in fuel cells for generating electrical energy. It has many advantages over conventional fuels as:
- It does not cause any pollution.
- It releases larger energy per unit mass of fuel in comparison to gasoline and other fuels.
- The only product of combustion is water.
- Internal combustion engine can be easily modified to use hydrogen as a fuel.
Question 6.
Write the uses of H2O2.
Answer:
Uses of hydrogen peroxide are :
- Hair bleach and mild disinfectant
- As an aerating agent for sponge rubber
- As an antiseptic by the name perhydrol
- For pollution control
- As an antichlor.

Question 7.
Hydrogen forms three types of bonds in their compounds. Describe each type of bonding using suitable example.
Answer:
Hydrogen forms following three types of bonding in their compounds:
1. Ionic Bond: This type of bond is formed by hydrogen with metals having low electronegativity values and is electropositive with respect to hydrogen. These are formed by transfer of electrons from metal to hydrogen. Compounds formed by this type of bonding are called as ionic hydrides.
Example : 2K + H2 → 2KH (potassium hydride)
2. Covalent Bond: This type of bond is formed by hydrogen and element having high electronegativity. It is formed by sharing of electrons between hydrogen and other element. Compounds formed by covalent bonds are known as covalent or molecular hydrides. Example: H2 + F2 → 2HF
3. Metallic Bond: This type of bond is formed by hydrogen and elements belonging to d and f-block elements. The bond formed is metallic in nature. Compounds formed by metallic bond are known as metallic or interstitial hydrides. Example: YH2, TiH2 etc.
Lead paintings get blackened due to formation of lead sulphide by the action of H2S present in air. On treatment with H2O2, lead sulphide (black) is converted to lead sulphate (white) and thus colour of lead paintings is restored.
Question 8.
Why do lakes freeze from top towards sulphates of calcium and magnesium. It cannot be bottom?
Answer:
The density of ice is less than that of liquid water. Therefore, ice floats on surface. Thus, the ice layer at lower temperature floats over water below it. Due to this the freezing of water into ice occurs continuously from top towards bottom.
Question 9.
How the colour of lead paintings is restored by hydrogen peroxide?
Answer:
Hydrogen peroxide oxidizes lead sulphide to lead sulphate
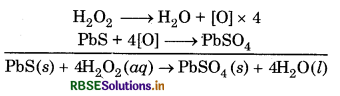
Lead paintings get blackened due to formation of lead suiphide by the action of H2S present in air. On treatment with H2O2 lead sulphide (black) is convertedto lead sulphate (white) and thus colour of lead paintings is restored.
Question 10.
When the first element of the periodic table is treated with di-oxygen, it gives a compound whose solid state floats on its liquid state. This compound has an ability to act as an acid and a base. What products will be formed when this compound undergoes auto ionization?
Answer:
The first element of periodic table is hydrogen and its molecular form is H2. It reacts with oxygen to form water whose solid state is ice which is lighter than water and floats on it. Water is amphoteric in nature i.e., it acts as an acid in the presence of strong base and as a base in the presence of strong acid.
As an acid :
2H2O(l) + NH3(aq) → NH4+(aq) + OH (aq)
As a base :
2H2O(l) + H2S(aq) → H3O+ + HS- Due to amphoteric nature, water undergoes self ionization as:
H2O + H2O → H2O+ + OH-
Question 11.
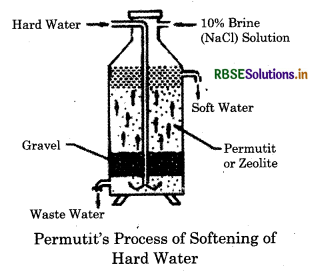
What is the reason of permanent hardness of water? Describe permutit method for removal of permanent hardness of water.
Answer:
It is due to the presence of soluble chlorides and suiphates of calcium and magnesium. It cannot be removed by simply boiling and filtering the water. It is also called as non-carbonate hardening. Permutit method for water softening
1. Water is softened by exchanging Ca2+ and Mg2+ ion with the help of zeolite. That's why it is also called zeolite or permutit process.
2. Zeolite is taken into the tank. Then hard raw water is entered into the inlet pipe. When water comes in contact with zeolite, water is softened.
3. Zeolite is not used for every time while softening water. 10% NaCl is used through the zeolites and the zeolites are regenerated again.

Question 12.
Give equation for the following reactions:
1. Reduction of acidified permanganate ion by hydrogen peroxide.
2. Barium peroxide is treated with cold dilute sulphuric acid.
3. Peroxidisulphuric acid is hydrolyzed.
Answer:
1. 2MnO4(aq) + 6 H+(aq) + 5H2O2(aq) → 2Mn2+(aq) + 8 H2O (aq) + 5O2(g)
2. BaO2 8H2O + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + H2O2 + 8H2O
3. H2S2O8 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4 + H2O2
Question 13.
What mass of hydrogen peroxide will be present in 2 L of a 5 molar solution? Calculate the mass of oxygen which will be liberated by the decomposition of 200 mL of this solution.
Answer:
Molar mass of H2O2 = 34 g/mol
1 L of 5M solution of H2O2 will contain = 34 × 5g
2 L of 5M solution of H2O2 will contain = 2 × 34× 5 =340 g
200 mL of 5M solution will contain
340/2000 × 200 = 34 g
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
68 g on decomposition will give O2 = 32 g
34 g will give = 32/68 × 34 = 16 g
Question 14.
What are the problems of using hydrogen as a fuel?
Answer:
1. Hydrogen is highly combustible and is difficult to handle safely. Because of its combustible nature, it burns with explosion.
2. It is an expensive fuel because cost of production is high.
3. It is not easy to store or transport hydrogen safely and compactly from one place to another. A cylinder of hydrogen weighs about 30 times as much as a tank of petrol containing same amount of energy. Moreover, it is converted to liquid state by cooling to 20 K. This would require expensive insulated tanks.
Question 15.
Complete the following reactions :
(1) RCH2 = CH2 + CO + H2 .........
(2) CH4 (g) + H2O(g) → CO2 (g) + 3H2(g)
(3) 2FeSO4 + H2SO4 + H2O2 →
Answer:
1. RCH2 = CH2 + CO → RCH2CH2CO
2. CH4 (g) + H2O(g) → CO2 (g) + 3H2(g)
3. 2FeSO4 + H2SO4 + H2O2 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 2H2O
Question 16.
Why is hard water softened before its use in boilers?
Answer:
Hard water cannot be used in boilers because on heating it gives precipitates of CaCO3 and MgCO3 alongwith CaSO4 which forms scales in boilers. To avoid the scales formation, hard water is softened before its use in boiler.
Question 17.
Which isotope of hydrogen is used as a trace in organic reactions?
Answer:
Hydrogen has three isotopes, viz, H, D and T. Due to difference in masses, the rate constants of three isotopes with the same substance are different. In other words, both D and T show isotopic effect. But since T is not only radioactive but is also least abundant hydrogen isotope. Therefore D is used as a trace to study the mechanism of organic reactions.
Question 18.
Statues coated with white lead on long exposure to atmosphere turns black and the original colour can be restored on treatment with H2O2. Why?
Answer:
On long exposure to atmosphere, white lead is converted into black PbS due to the action of hydrogen sulphide present in the atmosphere. As a result, statues turn black
Pb+ H2S → PbS + H2
On treatment of these blackened statues with H2O2, the black PbS get oxidized to white and the colour is restored.
PbS + 4H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O

Question 19.
Show with suitable example hydrogen acts as reducing agent as well as oxidizing agent?
Answer:
In the reaction of hydrogen with metals to form metal hydrides, it acts as an oxidizing agent.
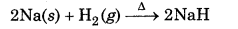
Here Na has been oxidized to Na while H2 is reduced to hydride ion. In the reaction of heated cupric oxide with dihydrogen to form H2O and copper metal, dihydrogen acts as a reducing agent
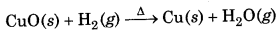
Here, CuO is reduced to Cu while dihydrogen is oxidized to water.
Question 20.
Water cannot be used to extinguish petrol fires. Why?
Answer:
Water is used to extinguish most fires because it lowers the temperature of burning material. However, in case of petrol fires, petrol being lighter than water floats on over water and fire spreads instead of being extinguished.
Question 21.
An aqueous solution of an inorganic compound (X) shows the following reaction:
(a) It decolurises an acidified potassium permanganate solution accompanied with evolution of oxygen gas.
(b) It liberates iodine from acidified potassium itself (e.g., NH3) it acts as an acid.
(c) It removes black stains from old oil paintings.
Answer:
Since X removes black stains from old oil paintings, it is hydrogen peroxide.
(a) 5H2O2 + 2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 5O2
(b) H2O2 + 2K1 + H2SO4 → I2 + K2SO4 + 2H2O,
(c) 4H2O2 + PbS → PbSO4 + 4H2O
Question 22.
There are three isotopes of hydrogen and three naturally occurring isotopes of oxygen (16 O, 17 O, 18 O). How many kinds of water are possible? Write their formula.
Answer:
H-16 O-H, H-170-H, H-18O-H.
H-160-D, H-170-D, H-180-D.
H-16O-T, H-170T, H-18OT.
D-160-D, D-170-D, D-180-D.
T-16O-D, T-17OD, T-18 O-D.
Т- 16ОТ, Т- 17 ОТ, Т. 18 ОТ.
Question 23.
Ferric chloride is reduced when zinc and hydrochloric acid are added to its solution and not by passing H2 gas through its solution. Explain.
Answer:
Ordinary H2 is less reactive and therefore, it does not reduce acidified ferric chloride solution. However, when zinc is added to acidified ferric chloride solution, nascent hydrogen is produced which has enormous energy. It is more reactive than ordinary H2 and reducesthe solution.
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 (Nascent hydrogen)
FeCl3 + H2 → No reaction
2FeCl3 + H2 → 2FeCl2 + 2HCl
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Can we use concentrated sulphuric acid and pure zinc in the preparation of dihydrogen? Write the chemical reactions to show the amphoteric nature of water. Why is hydrogen peroxide stored in wax-lined plastic coloured bottles?
Answer:
Conc. H2SO4 cannot be used because it acts as an oxidizing agent also and gets reduced to SO2.
Zn + 2H2SO4 (conc.) → ZnSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
Pure Zn is not used because it is non-porous and reaction will be slow. The impurities in Zn help in constitute of electrochemical couple and speed up reaction. Water is amphoteric in nature and it behaves both as an acid as well as base. With acids stronger than itself (e.g., H2S) it behaves as a base and with bases stronger than
(i) As a base :
H2O(l) + H2S(aq) → H3O+(aq) + HS-(aq)
(ii) As an acid:
H2O(l) + NH3 (aq) → OH(aq) + NH(aq)
The decomposition of H2O2 occurs readily in the presence of rough surface (acting as catalyst). It is also decomposed by exposure of light. Therefore, wax-lined smooth surface and coloured bottles retard the decomposition of H2O2.

Question 2.
Account for the following:
(i) Dihydrogen gas is not preferred in balloons.
(ii) Conc. H2SO4 cannot be used for drying H2.
(iii) How is dihydrogen prepared from water by using a reducing agent?
(iv) Give the industrial use of dihydrogen which depends upon heat liberated when it burns.
Answer:
(i) Dihydrogen is the lightest gas but due to its highly combustible nature it is not preferred in balloons.
(ii) Conc. H2SO4 on absorbing H2O forms moist H2 produces so much heat that hydrogen catches fires.
(iii) Dihydrogen is prepared from water by the action of alkali metals like Na and K which is a strong reducing agent.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
(iv) For welding purposes,
H2 (g) + 1/2O2(E) → H2O(g) + Heat
Question 3.
Differentiate between ionic and covalent hydrides.
Answer:
|
Ionic hydrides |
Covalent hydrides |
|
These are formed by combination of hydrogen with metal whose electronegativity is low and are electropositive with respect to hydrogen as group 1 and group 2 |
These hydrides are formed by the combination of elements of comparatively higher electronegativity as of p- block elements. |
|
These are white or light grey non-volatile and non-conducting crystalline solids. |
These hydrides are soft and have low electrical conductivity. |
|
They have high heat of formation and always stoichiometric. |
They have low melting and boiling point generally volatile in nature. |
|
These hydrides are formed by transfer of electrons from metals to hydrogen atom and thus contain hydride ion |
These consist of discrete covalent molecules which are held together by weak Vander Waal's forces of attraction |
|
Ionic hydrides decompose to evolve dhydrogen which ignites spontaneously. They are used as solid fuels and are good reducing agent. |
Due to intermolecular H bonding, these hydrides exist as associated molecules. |
Question 4.
Explain the structure of water with diagram.
Answer:
A molecule of water consists of two hydrogen atoms joined to an oxygen atom by covalent bonds. The oxygen atom has six electrons (1s2 2s2 2p4) in its outermost shell. The 's' and 'p' orbital of the valence shell are sp hybridized to form four sp3 hybrid orbital oriented tetrahedrally around the oxygen atom. Two of the hybrids orbitals are singly occupied, while the lone-pairs of electrons occupy the other two. Each singly occupied sp3 orbital overlaps with the half-filled 1s orbital of 'H' atom.
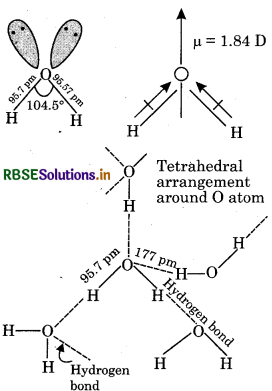
Thus, oxygen is bonded to the two hydrogen atoms by two O-H covalent bonds, and there are two lone-pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom. Due to the presence of two lone-pairs of electrons on the O atom, the H-0-H bond angle is 104.5°, which is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle of 109°28′. Therefore, the structure of water molecule is an angular or bent structure. Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen; its high electronegativity causes the oxygen atom to pull the shared pairs of electrons more towards itself. As a result, the O-H bond acquires polarity. The actual dipole moment of water molecule is 1.84 Debye, (denoted as D) is the unit of dipole moments.
Question 5.
Hydrogen is used as fuel. Comment.
Answer:
In order to meet the growing demands of energy and limited resources, alternate sources of energy are used. Hydrogen can also be used as a fuel in various fields. Hydrogen is used as a rocket fuel in space research and in fuel cells for generating electrical energy. It has many advantages over conventional fuels as:
- It does not cause any pollution.
- It releases larger energy per unit mass of fuel in
comparison to gasoline and other fuels.
- The only product of combustion is water.
- Internal combustion engine can be easily modified to use hydrogen as a fuel.
However, there are some of the problems of using hydrogen as fuel. These are due to following reasons:
- Hydrogen is highly combustible and is difficult to handle safely. Because of its combustible nature, it burns with explosion.
- It is an expensive fuel because cost of production is high.
- It is not easy to store or transport hydrogen safely and compactly from one place to another. A cylinder of hydrogen weighs about 30 times as much as a tank of petrol containing same amount of energy. Moreover, it is converted to liquid state by cooling to 20 K. This would require expensive insulated tanks.
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the following statement is not correct about ortho and para hydrogen?
(a) Their boiling point are different form.
(b) Ortho form is more stable than para form.
(c) Their nuclear spins are different.
(d) Ortho form changes to para hydrogen proportionate to temperature.
Answer:
(b) Ortho form is more stable than para form.

Question 2.
Which of the following statement is incorrect related to water?
(a) Water can acts both as an acid and a base
(b) Its condensed form has extensive inter hydrogen bonding.
(c) Ice made of heavy water generally sinks in water.
(d) In photosynthesis, water is oxidised to oxygen.
Answer:
(b) Its condensed form has extensive inter hydrogen bonding.
Question 3.
Which of the following is not oxidised by hydrogen peroxide?
(a) O3
(b) KI/HCl
(c) PbS
(d) Na2SO3
Answer:
(a) O3
Question 4.
Choose any one statement regarding hydrogen peroxide:
(a) It is only oxidant.
(b) It is decomposed by light.
(c) It is stored in dark in plastic or wax coated bottles.
(d) It is kept away from dust.
Answer:
(a) It is only oxidant.
Question 5.
Which of the following is used to soften hard water by Clark’s method?
(a) CaCO3
(b) Ca(OH)2
(c) CaSO4
(d) HCl
Answer:
(b) Ca(OH)2
Question 6.
Hydrogen peroxide acts as which of the following when it reacts with KIO4 and NH2OH?
(a) As a reductant as an oxidant
(b) As a reductant as a reductant
(c) As an oxidant as an oxidant
(d) As an oxidant as a reductant
Answer:
(a) As a reductant as an oxidant

Question 7.
In which of the following difference between neutron and proton is positive ?
(a) Hydrogen atom
(b) Deuterium
(c) Tritium
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Tritium
Question 8.
In which of the following, most active hydrogen atom is present?
(a) CH3-CH3
(b) CH3-CH2-CH3
(c) CH3-CH(CH3)-CH3
(d) CH3-C(CH3)2 -CH3
Answer:
(c) CH3-CH(CH3)-CH3
Question 9.
The bond length of 0-0 in O2 and H2O2 is 1.21 A and 1.4 A respectively. The average bond length of 0-0 in ozone is :
(a) 1.28 A
(b) 1.18 A
(c) 1.44 A
(d) 1.52 A
Answer:
(a) 1.28 A
Question 10.
By which of the following purest hydrogen (99.9%) can be prepared?
(a) Reaction of steam on methane
(b) By mixture of natural hydrocarbons of high molecular weight
(c) By hydrolysis of water
(d) By reaction of water with salts like hydrides
Answer:
(d) By reaction of water with salts like hydrides
Question 11.
Syngas mixture is:
(a) CO2 + H2
(b) CO + H2
(c) CO + CO2
(d) CO + N2
Answer:
(b) CO + H2
Question 12.
The strength (in g/L) of H2O2 in 11.2 volume solution of H2O2 is:
(a) 17
(b) 51
(c) 34
(d) 85
(e) 68
Answer:
(c) 34

Question 13.
When a zeolite which is hydrated aluminium silicate, is treated with hard water, then sodium ions are exchanged by:
(a) with H+ ions
(b) Ca2+ ions
(c) SO2- ions
(d) Mg2+ ions
(e) OH- ions
Answer:
(b) Ca2+ ions
Question 14.
Which of the following is responsible for permanent hardness of water?
(a) Bicarbonates of sodium and potassium
(b) Chlorides and sulphates of sodium and potassium
(c) Chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium
(d) Bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium
(e) Phosphates of sodium and potassium
Answer:
(c) Chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium
Question 15.
It is used for laboratory preparation of H2O2:
(a) H2SO4
(c) Na2O2 + H2SO4
(b) NHHSO4
(d) All the these .
Answer:
(c) Na2O2 + H2SO4
Question 16.
Which of the following property is same in ortho and para hydrogen?
(a) Heat conductivity
(b) Magnetic properties
(c) Chemical properties
(d) Heat capacity
Answer:
(c) Chemical properties
Question 17.
Which of the following method is used for removal for permanent hardness of water?
(a) By mixing soda lime
(b) By mixing sodium bicarbonate
(c) By mixing washing soda
(d) By mixing sodium chloride
Answer:
(c) By mixing washing soda
Question 18.
Some statements about heavy water are given below :
1. Heavy water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors.
2. Heavy water is more associated than ordinary water.
3. Heavy water is more efficient solvent than ordinary water.
Which of the above statements are true?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1,2 and 3
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3
Answer:
(a) 1 and 2

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter