RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 8 Redox Reactions Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Important Questions Redox Reactions
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
In the course of a chemical reaction an oxidant:
(a) loses electrons
(b) gains electrons
(c) both loses and gains electrons.
(d) electron change takes palace.
Answer:
(b) gains electrons
Question 2.
H&S reacts with halogens, the halogens:
(a) form sulphur halides
(b) are oxidised
(c) are reduced
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(c) are reduced
Question 3.
Following reaction describes rusting of iron
4Fe + 3O2 → 4Fe3 + 6O2-
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) This is an example of redox reaction.
(b) Metallic iron is reduced to Fe3+
(c) Fe3+ is an oxidising agent.
(d) Metallic iron is a reducing agent.
Answer:
(b) Metallic iron is reduced to Fe3+

Question 4.
In the following reaction which element is reduced?
Cr2O7 + 14H+ + 6I- → 2Cr3+ + 3H2O + 3I2
(a) Cr
(b) H
(c) O
(d) I
Answer:
(a) Cr
Question 5.
Which of the following is most powerful oxidising agent?
(a) F2
(b) CI2
(c) Br2
(d) I2
Answer:
(a) F2
Question 6.
Which of the following is a good reducing agent?
(a) NaOCI
(b) HI
(c) FeCl3
(d) KBr
Answer:
(b) HI
Question 7.
The oxidation number of Ba in barium peroxide is :
(a) +2
(b) +6
(c) 1
(d) +4
Answer:
(a) +2
Question 8.
Chlorine has oxidation number of +1 in :
(a) HCl
(b) CHIO4
(c) ICl
(d) Cl2O
Answer:
(d) Cl2O
Question 9.
Starch paper is used to test for the presence of:
(a) iodine
(b) oxidising agent
(c) iodide ion
(d) reducing agent
Answer:
(a) iodine
Question 10.
Which of the following will act as anode when connected to standard hydrogen electrode?
(a) Al3+ / Al Eo = - 1.66
b) Hg2+ / Hg E = + 0.88
(c) Cu2+ / Cu E = + 0.34
(d) 2F / F2 E° = + 2.87
Answer:
(a) Al3+ / Al Eo = - 1.66
Question 11.
Which of the following act as both oxidising and reducing agent?
(a) Cl-
(b) ClO-4
(c) ClO-
(d) MnO4
Answer:
(c) ClO-
Question 12.
Small quantities of solution of compound TX, TY and TZ are put into separate test tubes containing X, Y and Z solution. TX does not react with any of these. TY react with both X and Z. TZ reacts with X. The decreasing order of ease of oxidation of the anions X,Y,Z is;
(a) Y, Z, X-
(b) Z, X, Y-
(c) X, Y, Z-
(d) X-, Z-, Y-
Answer:
(a) Y, Z, X-
Question 13.
The oxidation number of two nitrogen atoms from left to right in NH4NO3 respectively:
(a) + 1, − 1
(b) -3, +5
(c) +3, +5
(d) -1, +1
Answer:
(b) -3, +5

Question 14.
When phosphorous reacts with caustic soda, the products are PH3 and NaH2PO2. The reaction is an example of:
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) disproportionation
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) disproportionation
Question 15.
The standard reduction potential values of three metallic cations X, Y, Z are 0.52, -3.03 and -1,18 V. The order of reducing power of corresponding metals is:
(a) Y > Z > X
(b) X > Y > Z
(c) Z > Y > X
(d) Z > X > Y
Answer:
(a) Y > Z > X
Question 16.
For decolourization of 1 mole of KMnO4, the moles of H2O2 required is :
(a) 1/2
(b) 3/2
(c) 5/2
(d) 7/2
Answer:
(c) 5/2
Question 17.
Which of these will not be oxidised by ozone?
(a) Kl
(b) FeSO4
(c) KMnO4
(d) KMnO4
Answer:
(c) KMnO4
Question 18.
In the redox reaction,
XKMnO4 + NH3 → yKNO3 + MnO2 + KOH + H2O
(a) X = 4, y = 6
(b) X = 3 , y = 8
(c) X = 8, y = 6
(d) X = 8, y = 3
Answer:
(d) X = 8, y = 3
Question 19.
If the half cell reaction are given as
i. Fe2+ (aq) + 2e → Fe(s); E° = -0.44 V
ii. 2H+(aq) + 1/2 O2 (g) + 2e → H2O(l) E° = + 1.23 V
The E° for the reaction is:
(a) + 1.67 V
(b) - 1.67 V
(c) + 0.79 V
(d) - 0.79 V
Answer:
(a) + 1.67 V
Question 20.
For an electrochemical cell which is not correct?
(a) Anode is negatively charged.
(b) Cathode is positively charged.
(c) Oxidation occurs at cathode.
(d) Electrons flow from anode to cathode in external circuit.
Answer:
(c) Oxidation occurs at cathode.
Question 21.
How many moles of K2Cr2O7 can be reduced by 1 mole of Sn2+ ?
(a) 1/3
(b) 1/6
(c) 2/3
(d) 1
Answer:
(a) 1/3
Question 22.
Which of the following does not occur, when a rod of Zn metal is dipped in the solution of CuSO4 ?
(a) blue colour of the copper sulphate fades gradually.
(b) mass of Zn-metal rod decreases.
(c) colour of the surface of Zn rod become saffron-red.
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) colour of the surface of Zn rod become saffron-red.
Question 23.
In the reaction, 2Na + S → Na2S substance acts as oxidizing agent?
(a) Na
(b) S
(c) Na2S
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) S
Question 24.
Which of following elements does not possess positive oxidation number in any of its compound?
(a) O
(b) F
(c) Cl
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) F
Question 25.
Which of the following oxidation number possesses by oxygen in its compounds?
(a) - 1
(b) + 3
(c) - 4
(d) + 5
Answer:
(d) + 5

Question 26.
What will be the value of x and y respectively AlFx Oy-6?
(a) 1, 4
(b) 3, 2
(c) 2,.2
(d) 4, 3
Answer:
(a) 1, 4
Question 27.
In which of the following reaction, H2O2 acts as oxidizing agent?
(a) HOCI + H2O2 → H3O + Cl- + O2
(b) I2 + H2O2 + 2OH- → 2I- + 2H2O + O2
(c) PbS + 4H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O
(d) In given all three.
Answer:
(c) PbS + 4H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O
Question 28.
In an electrochemical cell for which of the following alternative shows E° cell = E° cell?
(a) k = 1
(b) cell reaction is in equilibrium, then
(c) concentration of both the half cells become equal, then
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
Question 29.
What is the unit of constant 0.059 in Nernst equation?
(a) Coulomb
(b) Volt
(c) Faraday
(d) No unit
Answer:
(b) Volt
Question 30.
Which of the following is a correct ascending order, when oxidation number of sulphur of sulphurus acid, thiosulphuric acid, oleum, dithianic acid is arranged in ascending order?
(a) H2SO3 < H2S2O3 < H2S2O7 < H2S2O6
(b) H2SO3 < H2S2O3 < H2S2O6 < H2S2O7
(c) H2S2O3 < H2SO3 < H2S2O7 < H2S2O6
(d) H2S2O3 < H2SO3 < H2S2O6 < H2S2O7
Answer:
(d) H2S2O3 < H2SO3 < H2S2O6 < H2S2O7
Question 31.
In which of the following compound, oxidation number of all C atoms are same?
(a) ethane
(b) cyclohexane
(c) benzene
(d) given all three compounds
Answer:
(d) given all three compounds
Question 32.
Arrange the following metals in increasing order of their reducing capacity?
(a) K< Mg < Fe < Zn
(b) K< Mg < Zn < Fe
(c) Fe< Zn < Mg < K
(d) Zn < Fe< Mg < K
Answer:
(c) Fe< Zn < Mg < K
Question 33.
Which of the halogen acid is best reducing agent?
(a) HCl
(b) HBr
(c) HI
(d) HF
Answer:
(c) HI
Question 34.
Which of the following is best reducing agent in electrochemical series?
(a) Li
(b) Na
(c) Cs
(d) Ra
Answer:
(a) Li
Question 35.
Which of the following metal will replace hydrogen from acids ?
(a) Fe
(b) Zn
(c) Mg
(d) Cu
Answer:
(c) Mg
Question 36.
What are the oxidation numbers of F and O in F2O?
(a) - 1,-2
(b) -1, +2
(c) - 2, +2
(d) +2, -1
Answer:
(b) -1, +2
Question 37.
What is the oxidation number of nitrogen in N3H H2N2O2, HNO3 or hydrazoic acid, hyponitrous acid, nitrus acid respectively?
(a) 1, +1, +3, + 5
(b) 1/3, +1, + 3, + 5
(c) +1, +1, +3, +5
(d) + 13, + 2, + 2, + 5
Answer:
(b) 1/3, +1, + 3, + 5

Question 38.
The oxidiation number of sulphur in H2SO3, H2SO4, H2O5 or sulphuric acid, Caros acid (permono sulphuric acid) is respectivity :
(a) +4, +6, +7
(b) +3,+4,+6
(c) +4, +6, +6
(d) +5,+6, +6
Answer:
(c) +4, +6, +6
Question 39.
Arrange the following elements in the order of increasing reactivity?
(a) Ca < Na < Li
(b) Ni< Na < Ca
(c) Au< Mg < Zn
(d) Su < Ag< Au
Answer:
(b) Ni< Na < Ca
Question 40.
The oxidation number of nitrogen in NaNO2 is:
(a) + 3
(b) + 5
(c) - 3
(d) - 5
Answer:
(a) + 3
Question 41.
A substance (atom, ion or molecule) which can readily accept electrons, from other substances is called
(a) oxidising agent
(b) reducing agent
(c) none of them
(d) both a and b
Answer:
(a) oxidising agent
Question 42.
How many electrons are involved in oxidation by KMnO4 in basic medium?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 5
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 5
Question 43.
2Na(s) + Cl2 → NaCl (s) the oxidising agent is:
(a) Sodium
(b) Chlorine
(c) Sodium chloride
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Chlorine
Question 44.
CuSO4 (aq) + Zn (s) → Cu(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) is:
(a) Metal displacement reaction
(b) Disproportionation reaction
(c) Combination reaction
(d) Non-metal displacement
Answer:
(a) Metal displacement reaction
Question 45.
The valency of S in Sg is:
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Answer:
(a) 0
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electrons.
Answer:
Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons.
Question 2.
What is oxidation state of nickel in Ni (CO)4?
Answer:
Zero. Oxidation state of metal in metal carbonyls is zero.
Question 3.
What is a redox couple?
Answer:
A redox couple consists of oxidized and reduced form of same substance taking part in oxidation or reduction half reactions.
Question 4.
Define EMF of the cell.
Answer:
EMF of the cell is defined as the difference in the electrode potentials of the two half cells when the cell is not flowing current through the circuit.
Question 5.
Define oxidation number.
Answer:
Oxidation number is defined as the charge which an atom of the element has in its ion or appears to have when present in the combined state with other atoms

Question 6.
Which element is strongest oxidizing agent and strongest reducing agent?
Answer:
Fluorine is strongest oxidizing agent and lithium is strongest reducing agent.
Question 7.
Define displacement reaction giving an example.
Answer:
Reaction in which one ion in a compound is replaced by an ion of other compound.
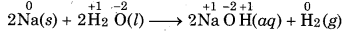
Question 8.
Give an example of compound each in which oxidation state of H is (a) +1 and (b)-1.
Answer:
HCl (O.N=+1)
LiH (O.N.= -1)
Question 9.
Define electrode potential.
Answer:
Electrode Potential: The tendency of an electrode to loose or gain electrons is called electrode potential.
Question 10.
What is the electrode potential of standard hydrogen electrode?
Answer:
It has zero electrode potential.
Question 11.
Why fluorine does not show disproportionation reaction?
Answer:
Fluorine is most electronegative and strongest oxidizing agent and therefore, it does not show positive Oxidation states.
Question 12.
Which method can be used to find out the strength of oxidant or reductant in a solution?
Answer:
The method is to connect redox couple of that species to normal hydrogen electrode and measure its electrode potential.
Question 13.
At what concentration of Cu2+ will its electrode potential becomes equal to its standard electrode potential?
Answer:
At1 M concentration.
Question 14.
Nitric acid is an oxidizing agent and reacts with PbO but not with PbO2. Explain why?
Answer:
PbO is basic oxide and react with nitric acid and simple acid base reaction takes place. But in PbO2 lead is in +4 oxidation state and cannot be further oxidized. Therefore, it does not react with nitric acid.
Question 15.
Fluorine react with ice and results in change:
H2O(s) + F2(g) → HF(g) + HOF(g).
Justify this reaction as a redox reaction.
Answer:
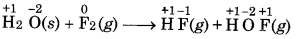
Here, the O.N. of F decreases from 0 in F, to -1 in HF and increases from 0 to +1 in HOF. Therefore, F2 is both An oxidized and reduced. Therefore, it is a redox reaction ele and more specifically it is a disproportionation reaction.
Question 16.
A solution of silver nitrate was stirred with iron rod. Will it cause any change in the concentration of silver and nitrate ions?
Answer:
Since E° of Fe2+/Fe is lower than that of Ag/Ag electrode, therefore Ag gets reduced and Fe gets oxidized. As a result, concentration of Ag+ will decrease while that of NO3- ion will remain constant.
Question 17.
Can we use KCl as electrolyte in salt bridge of cell, Cu(s) | Cu2+ (aq) || Ag+ (aq) | Ag (s)?
Answer:
KCl cannot be used as electrolyte in the salt bridge will because Cl- will combine with Ag+ ions to form white sul precipitate of AgCl.
Question 18.
What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NF3?
Answer:
+3
Question 19.
Why zinc displaces copper from solution of its salt but copper does not replace zinc?
Answer:
Because reduction potential of zinc is lower than that of copper, it can remove copper from its solution but reverse never happens.

Question 20.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their electrode potential Mg, K, Ba, Ca.
Answer:
K, Ba, Ca, Mg.
Question 21.
Why is it not possible to measure single electrode potential ?
Answer:
Because the half cell containing single electrode cannot exist independently, as charge cannot flow on its vn in a single electrode.
Question 22.
Name the factor on which emf of a cell depends.
Answer:
Emf of a cell depends on nature of reactants, ncentration of solution in two half cells and mperature.
Question 23.
Reduction potentials of 4 metals P, Q, R and S are -1.66 V, +0.34 V, +0.80 V and -0.76 V. What is the order of their reducing power and reactivity?
Answer:
P > S > Q > R
Question 24.
What is the use of platinum foil in the hydrogen electrode?
Answer:
It is used for the in flow and out flow of electrons.
Question 25.
Why is it necessary to use a salt bridge in a Galvanic cell?
Answer:
To complete the inner circuit and to maintain ctrical neutrality of the electrolytic solutions of the If cells.
Question 26.
Which reference electrode is used to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes?
Answer:
SHE, whose electrode potential is taken as zero.
Question 27.
What is the EMF of the cell when the cell reaction attains equilibrium?
Answer:
Zero.
Question 28.
Can we store copper sulphate in iron vessel? Why?
Answer:
No, because iron is more reactive than copper. It I displace copper from its solution and forms ferrous phate.
Question 29.
Write Nernst Equation for single electrode.
Answer:
Consider an electrode reaction:
Mn+ + ne- → M
Nerest Equation is:
E = E° + 2.303RT/nF log 10 [Mn+]
Define electrochemical cell.
Question 30.
Define Electrochemical cell.
Answer:
Electrochemical cell is a device in which the redox etion is carried indirectly and the decrease in free rgy appears as electrical energy.
Question 31.
What is the source of electrical energy in a Galvanic cell?
Answer:
In a Galvanic cell due to redox reaction released rgy gets converted into the electrical energy.
Question 32.
What is a redox couple?
Answer:
A redox couple consists of oxidised and reduce form of the same substance taking part in the oxidatio or reduction half reaction.

Question 33.
Define oxidation in terms of electroni concept.
Answer:
Oxidation involves loss of one or more electrons b a species during a reaction.
Question 34.
What is meant by reducing agent? Name the best reducing agent.
Answer:
A species which loses electrons as a result oxidation is a reducing agent. Li (Lithium).
Question 35.
What is salt bridge?
Answer:
It is a U-shaped tube filled with agar-aga containing inert electrolyte like KCl or KNO3 whic does not react with solutions.
Question 36.
Define oxidation and reduction in terms oxidation number.
Answer:
Oxidation involves increase in O.N while reductio involves decrease in O.N.
Question 37.
What is oxidation number of Fe in [Fe(CO)5]
Answer:
x + 5 (0) = 0, x = 0
Question 38.
In the reaction.
M4O2 + 4HCI → M4Cl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O which species is oxidised?
Answer:
HCl gets oxidised.
Question 39.
What is redox reaction? Give one example.
Answer:
The reaction in which oxidation and reducti takes place simultaneously is called redox reaction.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Question 40.
What is electronation?
Answer:
The process in which an atom, ion or molecu accepts one or more than one electron is call electronation.
Question 41.
What is the main difference between valency and oxidation number?
Answer:
Oxidation number can be fractional but valen can not be fractional.
Question 42.
SnO + H2 → Sn + H2O
Is this a reaction possible?
Answer:
Yes, the reaction is possible.
Question 43.
Whose oxidation state will be positive in compound made up of two metals?
Answer:
The metal with highest electronegativity.
Question 44.
Which metals can not reduce water vapour?
Answer:
The metals whose standard electrode potential is n less than zero i.e., the metals which lies below hydrogen in activity series.
Question 45.
In the following reaction which one is oxidising agent and which one is reducing agent?
2KI + Cl2 → 2KCl + I2
Answer:
Here Cl2 is oxidant and KI is reductant.
Question 46.
Explain with reason whether the following reaction is possible or not?
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
Answer:
In the reaction, Fe is above the hydrogen in reactivity series. It is capable of giving electrons. Therefore, it displaces H2 from H2SO4. Hence the reaction is possible.

Question 47.
Zinc react with dilute hydrochloric acid whereas copper do not? Explain with reason.
Answer:
The electrode potential of zinc is higher than hydrogen. Thus, it replaces hydrogen from acid whereas copper is below the hydrogen in activity series. Therefore, it cannot displace hydrogen from acid.
Question 48.
When Iron nails are dipped in copper sulphate solution, copper is deposited on them. Explain with the electrochemical series.
Answer:
Fe is more reactive than copper as it lies above Cu in electrochemical series. Iron displaces copper from its solution. The displaced copper is then deposited on the iron nails.
Question 49.
Which metals do not replace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid?
Answer:
The metals which are below the hydrogen in electrochemical series do not replace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid.
Question 50.
Arrange the following elements in the order of increasing reactivity:
Al, Ag, Fe, Ca, Cu
Answer:
Ag < Cu < Fe < Al < Ca
Question 51.
Arrange the following elements in the order of decreasing reducing capacity:
Fe, Na, Cu, Zn
Answer:
Na > Zn > Fe > Cu
Question 52.
Arrange the following elements in the order of decreasing oxidising capacity:
I2, Cl2, Br2, F2
Answer:
I2 < Br2 < Cl2 < F2
Question 53.
Arrange the following halogen acids in the An order of increasing reducing capacity:
HCI, HI, HF, HBr
Answer:
HF < HCl < HBr <HI
Question 54.
What is the reason that sodium react with water at normal temperature but magnesium in 1 react only at high temperature?
Answer:
Magnesium have a protective layer of its oxide on e.g. the surface. Due to this, reaction of magnesium becomes slow at normal temperature.
Question 55.
What will happen if silver wire is dipped in copper sulphate solution?
Answer:
No reaction occurs.
Question 56.
What will be the sum of oxidation number of all the atoms in KMnO4 ?
Answer:
Zero.
Question 57.
What will be the minimum oxidation number of N, S and Cl?
Answer:
Minimum oxidation number = Group number - 8
N = 5 - 8 = - 3
S = 6 - 8 = 2
Cl = 7 - 8 = 1
Question 58.
Why does fluorine always show oxidation in number of -1?
Answer:
Because fluorine is the most electronegative element, it has negative oxidation state. Minimum oxidation state = 7 - 8 = 1
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Calculate the oxidation number of the following.
(i) S in Na2S2O3,
(ii) Fe in Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3,
(iii) Cl in CaOCl2
Answer:
(i) O.N. of S in Na2S2O3,
2(+1) + 2x + 3(-2) = 0
2 - 6 = 2x
x = +2
(ii) O.N. of Fe in Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3,
4x + 3x + 6(-1)] = 0
4x + 3x - 18 = 0
x = 18/7
(iii) O.N. of Cl in CaOCl2
(+2) + (-2) + 2x = 0
x = 0

Question 2.
Define oxidant and reductant with examples. Hend
Answer:
Oxidising agent or oxidant is a substance which ps in oxidation but it-self gets reduced. It is a ostance which accepts one or more electrons.
e.g: Zn2+ + Cu → Zn + Cu2+ (Zn2+ is an oxidizing agent) ducing agent or reductant is a substance which helps reduction but it-self gets oxidized. It is a substance ich donates one or more electrons. e.g: Zn2+ + Cu → Zn + Cu2+ (Cu is reducing agent)
Question 3.
MnO2-4 undergoes disproportionation reaction in acidic medium but MnO4- does not. Give reason.
Answer:
In MnO4, Mn is in the highest oxidation state of +7 I hence it cannot undergo disproportionation. In trast in MnO2, the O.N. of Mn is +6. Therefore, it can increase its O.N. to +7 or decrease its O.N to some er value. Thus, it undergoes disproportionation in lic medium as;
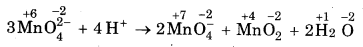
Question 4
Define decomposition and combination reactions with examples.
Decomposition Reaction: Chemical reactions which a compound breakup into two or more simple stances.
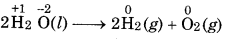
Combination Reaction: In this reaction, two or more stances combine to form a single substance.
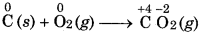
Question 5.
What is redox reactions? Give examples.
Answer:
The reaction in which oxidation and reduction s place simultaneously is called redox reaction. ox (reduction-oxidation) reactions include all nical reaction in which atoms have their oxidation e changed. These are complementary reactions. mples of redox reactions :
(i) MnO2 + 4 HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O
(ii) 2 Na + Cl2 → 2Na + Cl-
Question 6.
Nitric acid acts only as an oxidizing agent while nitrous acid can act both as an oxidizing as well as reducing agent. Why?
Answer:
(i) HNO3
Oxidation number of N = +5
imum oxidation state of N = +5
mum oxidation state of N = -3
since oxidation number of N in HNO3 is maximum. efore, it can only decrease by accepting electrons. ce it can work only as oxidizing agent.
(ii) HNO2
Oxidation number of N = + 3
Maximum oxidation state of N = +5
Minimum oxidation state of N = -3
Thus, oxidation number of N can either be increased decreased by accepting or loosing electrons. Hence it ca work both as oxidizing as well as reducing agent.
Question 7.
An iron rod is immersed in a solutio containing 1.0 M NiSO4 and 1.0 M ZnSO4 Predict giving reasons which of the followin reaction is likely to proceed?
(i) Fe reduces Zn 2+ ions.
(ii) Iron reduces Ni 2+ ions.
Given E0 Zn2+/Zn = 0.76 V
E0 Fe2+/Fe = 0.44 V
E0 Ni2+/Ni = 0.25 V
Answer:
(i) Since E° of Zn is more negative than F therefore Zn will be oxidized to Zn2+ ions and Fe2+ be reduced to Fe. In other words, Fe will not reduce Zn
(ii) Since Eo of Fe is more negative than that of therefore, Fe will be oxidized to Fe2+ ions while Ni 2+ be reduced to Ni. Thus, Fe reduces Ni 2+ ions.

Question 8.
Arrange the following metals in increasi order of reactivity. Which one will be t strongest and weakest reducing agent? Mg, Na, Ag, Cu, Fe, Zn
Answer:
According to electrochemical series, the order above elements will be,
Ag < Cu < Fe < Zn < Mg < Na
This order is in accordance to the E° values of t elements. Na has highest negative values of reducti potential. Hence, it is the strongest reducing agent. Ag has positive value of electrode potential and le among the given series. Therefore, it is the weak reducing agent.
Question 9.
Predict whether the following reaction feasible or not?
Cu2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) → Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq)
Answer:
From the electrochemical series, E° values of and Ag are,
Cu = + 0.34 V
Ag = + 0.80 V
Since the reduction potential of Ag is more than tha Cu, this means that silver has greater tendency to reduced in comparison to copper. Thus, the reduction of Ag occurs more readily than Cu. This can be represented as:
Ag+ (aq) + e → Ag(s)
Since reduction potential of copper is less than silver, it n can be easily oxidized as compared to silver as shown below:
Cu(s) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2e-
Therefore, silver will be reduced and copper will be g oxidized and above reaction is not feasible.
Question 10.
1.80 g of impure sample of oxalate was dissolved in water and solution is made to 250 mL. On titration 20 mL of this solution required 30 mL of M/50 KMnO4 solution. Calculate the percentage purity of the sample.
Answer:
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
2MnO4 + 5C2O2 + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 10CO2 + 8H2O
Applying molarity equation,
(M1V1/n1)KMnO1 = (M1⁄2V1⁄2/n2)C2O2-4
1/50 × 30/2 = M2 × 20/5
M2 = 30 × 5/50 × 20 × 2 = 0.075 M
Molecular mass of C2O2-4 = 88
he Mass of C2O2-4 = 0.075 × 88 = 6.6 g
In 250 mL = 6.6/1000 × 250 = 1.65 g
% purity = 1.65/1.80 x 100 = 91.7%

Question 11.
Write the differences between valency and Oxidation State.
Answer:
|
Valency |
Oxidation State |
|
It is the combining capacity of an element. |
It is the charge which an atom has or appears to have when present in combined state. |
|
It is a whole number only. |
It can be positive or negative. |
|
It cannot be zero. |
It can be zero. |
|
It cannot have fractional values. |
It can be in fraction also. |
|
The valency may be variable but variation is limited. |
The variation in oxidation state is too large. |
Question 12.
Balance the following equation by oxidation An number method :
P(s) + OH- → PH3 (g) + H2PO2(aq)
Answer:
Step 1: The skeletal equation with oxidation number is written as
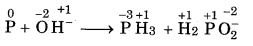
O.N. increases by 1 per atom
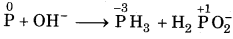
O.N. decrease by 3 per atom
Step 2: To balance increase and decrease, multiply The H2PO2 by 3.
P + OH- → PH3 + 3 H2PO2
Step 3: To balance all atoms (other than H and O) multiply P by 4.
4P + OH- → PH3 + 3 H2PO2
Step 4: To balance O atoms add OH ions to L.H.S.
4P + OH- + 5OH- → PH3 + 3 H2PO2 + 3OH-
Step 5: To balance H atoms add H2O molecules on LHS and equal number of OH- ions on other side.
4P + 6OH- + 3H2O → PH3 + 3 H2PO2 + 3OH-
Question 13.
Explain the function of salt bridge.
Answer:
The functions of salt bridge are:
(i) It connects the solutions in the two half cells and completes the cell circuit.
(ii) It keeps the solutions in two half cells electrically neutral: during the working of an electrochemical cell, metal at anode loses electrons and changed to positive ion. These positive ions go to solution. 16 As a result there is accumulation of positive Ans charge around the anode. On the other hand, at elect cathode metal ion accepts electrons. After cher sometime, there is accumulation of negative Wor charge around cathode. This accumulation of Read charge results in prevention of flow of electrons and finally cell stops working. This accumulation can be prevented by salt bridge. When there is accumulation of positive charge on anode, sufficient amount of negative ions of electrolyte of salt bridge migrate to anode and positive ions towards Follo cathode. Thus, maintain the neutrality of the cell.
Question 14.
What is Standard Hydrogen Electrode? How it works?
Answer:
It consists of platinum wire sealed in a glass tube has platinum foil attached to it. The foil is coated ch finely divided platinum and acts as platinum ctrode. It is dipped into an acid solution containing H+. s in 1M concentrated HCl. Pure hydrogen gas is obled into the solution at constant temperature of 298 The surface of the foil acts as a site for the reaction. It standard hydrogen electrode works as anode:
H2(g) → 2H+ + 2e-
standard hydrogen electrode works as cathode:
2H++ 2e- → H2 (g)
The electrode potential of an electrode can be ermined by connecting its half cell with a standard Irogen electrode.
Question 15.
What is electrochemical series? What are its applications?
Answer:
The arrangement of elements in order of reasing reduction potential values is called trochemical series. It is also known as activity series. plications of electrochemical series:
- Relative strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents: An element with lower reduction potential acts as stronger reducing agents and an element having higher reduction potential acts as stronger oxidizing agent.
- Comparison of reactivity of metals: A metal occupying lower position in series can replace the metal lying above it.
- Calculation of EMF of the cell: EMF of cell can be calculated as:
\(\mathbf{E}_{\text {cell }}^0=\mathbf{E}_{\mathrm{R}}^0-\mathbf{E}_{\mathrm{L}}^0\)
Question 16.
How does an electrochemical cell works?
Answer:
An electrochemical cell is a device to convert crical energy produced in a redox reaction into nical energy.
Working of electrochemical cell:
Reactions taking place in an electrochemical cell:
At anode: oxidation takes place.
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
At cathode: reduction takes place.
CU2+ + 2e- → Cu
following changes take place:
- There is flow of electric current through the external circuit.
- The zinc rod loses its mass and copper plate gains mass.
- The concentration of ZnSO4 solution increases and th of CuSO4 decreases. The solutions in the two beakers remain electrical neutral.
Question 17.
Explain the following:
(i) It is not possible to determine the absolute value of single electrode.
(ii) In an electrochemical cell, an electrode wi as t lower electrode potential acts reducing agent.
(iii) Iron undergoes oxidation more readily tha
Answer:
(i) The potential difference between two electrod can be determined by connecting them to voltmeter. Therefore, it is not possible determine the potential of a single electro because a single electrode constitutes a half o and a half cell reaction cannot take pla independently. An electrode in a half cell cannot lose or ga electrons by itself. For transfer of electrons, half cell has to be connected to some other h cell. Thus, we cannot determine the absol value of potential of single electrode. In ot] words relative values can be determined connecting half cell with some standard electr as the reference electrode.
(ii) An electrode with lower electrode potential more tendency to get oxidized. In other words has more tendency to release electrons and he acts as a reducing agent.
(iii) The electrode potential of iron is lower than t of copper and hence Fe has greater tendency get converted to Fe2+ ions than copper. Th iron undergoes oxidation more readily copper.

Question 18.
Chlorine is used to purify drinking wat Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess chlorine is removed by treating with sulp! dioxide. Present a balanced equation for t reaction taking place in water.
Answer:
The skeletal equation for the reaction is:
Cl2 (aq) + SO2 (aq) + H2O (l) → Cl-(aq) + SO2-(aq)
Reduction half cell: Cl2 (aq) → Cl- (aq)
Balance Cl atoms: Cl2 (aq) → 2Cl- (aq)
Balance O.N. by adding electrons :
Cl2 (aq) + 2e- → 2Cl-(aq)
Oxidation half cell: SO+42 (aq) → SO2-4 (aq) + 2e- + 4H+
Balance O.N. by adding electrons :
SO2 (aq) → SO2-(aq) + 2e-
Balance charge by adding H+ ions :
SO2 (aq) → SO2-(aq) + 2e- + 4H+(aq)
Balance O atom by adding H2O:
SO2 (aq) + 2H2O → SO2-4 (aq) + 2e- + 4H+(aq)
Adding both the equations we get:
Cl2 (aq) + SO2(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2Cl-(aq) + SO2-(aq) + 4H+
This represents balanced equation.
Question 19.
Justify the reaction as redox reaction:
H2O(s) + F2(g) → HF (g) + HOF (g)
Answer:
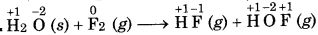
In the above reaction, F, is reduced to HF and oxidized to one HOF. Therefore, it is a redox reaction. HOF is unstable half and decomposes to form O2 and HF.
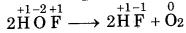
In this reaction, F of HOF is reduced while O is oxidized. Therefore, it is a redox disproportionation reaction.
Question 20.
Classify the following reaction
(a) N2 (g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g)
(b) 2 Pb(NO3)2 (s) → 2PbO (s) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
(c) NaH (s) + H2O (l) → NaOH (aq) + H2 (g)
Answer:
(a) 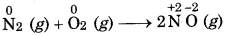
The compound nitric oxide is formed.
Therefore, it is a combination redox reaction.
(b) 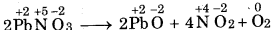
In this reaction lead nitrate decomposed to give lead oxide, Therefore it is decomposition reaction.
(c) 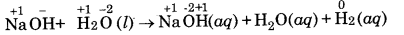
In this reaction, hydrogen of water is displaced by hydride ion to form di-hydrogen gas. Therefore, it is a displacement reaction.
Question 21.
(a) Arrange the following in order of increasing O.N. of iodine: I2, HI, HIO2, KIO3, ICI.
(b) Identify the oxidant and reductant in the following redox reaction:
2K2MnO4 + Cl2 → 2KCI + 2KMnO4
Answer:
(a) The increasing order is
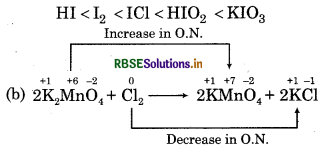
Chlorine is an oxidant and KMnO4 is reductant.
Question 22.
Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing agent for each of the following reactions.
(a) 2AgBr (s) + C6H6O2 (aq) → 2Ag (s) + 2HBr (aq) + C6H4O2 (aq)
(b) HCHO (l) + 2[Ag(NH3)2]+(aq) + 3OH-(aq) → Ag(s) + HCOO-(aq) + 4NH3
(c) N2H4(l) 2H2O2 (l) → N2(g) + 4H2O (l)
Answer:
(a) Ag+ is reduced, C6H6O2 is oxidised. Ag+ is oxidising agent whèrease C6H6O2 is reducing agent.
(b) HCHO is oxidised, Ag+ is reduced. Ag+ is oxidising Le agent whereas HCHO is reducing agent.
(c) N2H4 is getting oxidised thus it is reducing agent. H2O2 is getting reduced thus it acts as an oxidising agent.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Calculate the oxidation state of the underlined atoms.
(a) H2S2O7
(b) NaHSO4
(c) CH3COOH
(d) Cu(NH3)4 SO4
(e) NH+4
Answer:
(a) O.N. of S in H2S2O7
Let the oxidation number of S be x. We know that,
Oxidation number of H = +1
Oxidation number of O=-2
Then, we have,
2(+1) + 2(x) + 7(-2) = 0
2 + 2x - 14 = 0
2x = 12
X = +6
Hence, the oxidation number of S is +6.
(b) O.N. of S in NaHSO4
Let the oxidation number of S be x.
We know that,
Oxidation number of Na = +1
Oxidation number of H = +1
Oxidation number of O= -2
Then, we have.
(+1) + 1(+1) + (x) + 4(-2) = 0
1 + 1 + x = 8
x = +6
hence, the oxidation number of S is + 6.
(c) O.N. of C in CH3COOH, Oxidation number of
hydrogen = + 1
Let the oxidation number of carbon be x.
Then we have.
1(x) + 3(+1) + 1(x) + 2(−2) + 1(+1) = 0
4 + 2x - 4 = 0
x = 0
Hence, the oxidation number of carbon is 0.
(d) O.N. of N in Cu in Cu(NH3)4 SO4
Let the oxidation number of Cu is x.
+ (4 × O.N. of NH3) + O.N. of S + 4 × (O.N. of O)) = 0
x + 0 + 6 + (-8) = 0
x - 2 = 0
x = +2
(e) O.N. of N in NH+4
Let the oxidation number of N is x.
x + (4 × O.N. of H) − + 1
x + {4 × (+1)} = +1
x + 4 = +1
x = - 3
Thus, oxidation number of N in NH+4 is -3.

Question 2.
Calculate the oxidation number of the underlined atom and suggest the structure.
Answer:
(a) O.N. of s in H2S4O6: In this molecule, let idation number of S be x.
Oxidation number of H = +1
Oxidation number of O = -2
then, 2(+1) + 4(x) + 6(-2) = 0
2 + 4x - 12 = 0
4x = 10
x = 2.5
However, the oxidation number cannot be fractional.
So S atoms must be present in different oxidation states.
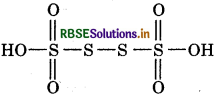
The oxidation number of two of the four S atoms in
H2S4O6 is +5 and that of other two S atoms is 0.
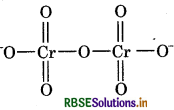
(b) O.N. of Cr in Cr2O2
As we know,
Oxidation number of oxygen = -2
Let the oxidation number of Cr be x.
Then we have,
2(x) + 7(-2) = -2
x = 6
The oxidation number of Cr is +6 so, there is no fallacy about oxidation number of Cr. The structure of Cr2O2 is shown as follows:
(c) O.N. of Cr in CrO5
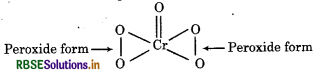
In peroxide, oxidation state of oxygen is -1 whereas in oxides, the oxidation state of oxygen is -2. Therefore,
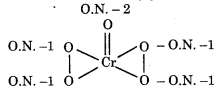
Therefore oxidation number of Cr is +6.
Question 3.
Balance the following equation by Oxidatio Number Method.
Cu + NO-3 → NO2 + CU2+
Answer:
Step 1: Write the skeletal equation of all t reactants and products of the reaction.
Cu + NO-3 → NO2 + Cu2+
Step 2: Indicate the oxidation number of each element above its symbol.
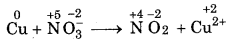
Step 3: Identify the elements which undergo change oxidation number.
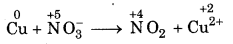
Oxidation number of copper has increased from 0 to +2 and nitrogen has decreased from+ 5 to + 4.
Step 4: Calculate the increase or decrease in oxidation number per atom. If more than one atom of the same element is involved, find out the total number of increase or decrease in oxidation number.
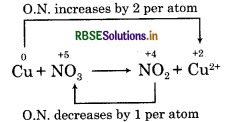
Step 5: Equate the increase in oxidation number with decrease in oxidation number on reactant side by multiplying the formula of oxidising and reducing agent. Multiply NO3- by 2 and Cu by 1.
CU + 2NO3- → NO2 + CU2+
Step 6: Balance all other atoms except H and O.
CU + 2NO3- → 2NO2 + CU2+
Step 7: Finally balance H and O by adding H2O molecule using hit and trial method.
- f reaction is taking place in acidic medium, add H+ ions to the side deficit in hydrogen atoms.
- If reaction is taking place in basic medium, add H2O molecules to the side deficient in hydrogen atoms and simultaneously add equal number of OH- ions on the other side of the equation.
Cu + 2NO-3 + 4H+ → 2NO2 + Cu2+ + 2H2O
Question 4.
Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
Cr2O72-(aq) + Fe2+ (aq) → Cr3+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq)
Answer:
Step 1: Write the skeletal equation and indicate the oxidation number of all the elements which appear in skeletal equation above their respective symbols.
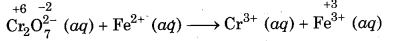
Step 2: Find out the species which are oxidised and nt which are reduced.
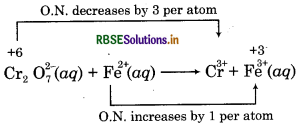
Cr2O2-7 gets reduced and Fe2+ gets oxidised.
Step 3: Split the skeletal equation in two half reactions
i.e. oxidation half reaction and reduction half reaction.
Oxidation half equation: Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+ (aq)
Reduction half equation: Cr2O2 (aq) → Cr3+ (aq)
Step 4 Balance the two. half reaction separately by following steps:
(i) In each half cell, first balance the atoms of the elements which have undergone a change in oxidation number.
Oxidation half equation: Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq)
Reduction half equation: Cr2O2-7 (aq) → 2Cr3+ (aq)
(ii) Add electrons to whatever side is necessary to make up the difference in oxidation number in each half reaction.
Oxidation half equation: Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + e-
Reduction half equation: Cr2O2-7 (aq) + 6e- → 2Cr3+ (aq)
(iii) Balance charge by adding H+ ions if the reaction occurs in acidic medium and by adding OH- if the reaction occurs in basic medium.
Oxidation half equation:"
Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + e-(balanced)
Reduction half equation:
Cr2O2-7 (aq) + 14H+ (aq) + 6e- → 2Cr3+ (aq)
(iv) Balance oxygen atoms by adding required number of H2O molecules to the side deficient in O atoms.
Cr2O2-7 + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Oxidation half equation:
Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+(aq) + e-(balanced)
Reduction half equation:
Cr2O2-7 (aq) + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ (aq) + 7H2O
(v) In acidic medium, H atoms are balanced by H+ ions to the side deficient in H atoms. In basic medium, H atoms are balanced by adding H2O molecules equal in number to the deficiency of H atoms and equal numbers of OH ions are included in opposite side of the equation.
Oxidation half equation:
Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+(aq) + e-(balanced)
Reduction half equation:
Cr2O2-7(aq) + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(balanced)
Step 5: The two half reactions are then multiplied by suitable integers so that the total number of electrons gained in one half reaction is equal to number of electrons lost in other half reaction. The two half cells are then added up.
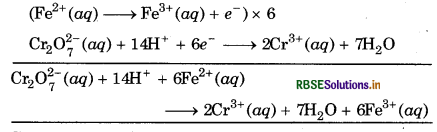
Step 6: To verify whether the equation thus obtained is balanced or not, the total charge on either side of equation must be equal.
Total charge on L.H.S.
= (-2) + 6 × (+2) + 14 × (+1) = + 24
Total charge on R.H.S. = 2 × (+3) + 6 × (+3) = +24

Question 5.
Explain competitive electron reactions by suitable example.
Answer:
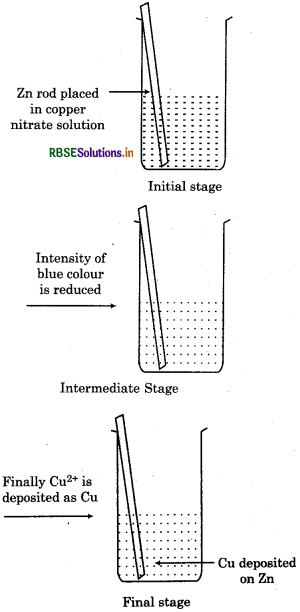
1. When a rod of metallic zinc is dipped in a solution of copper nitrate solution, following changes
occur:
Zinc rod start dissolving gradually.
- Reddish brown copper metal starts depositing on the zinc rod.
- Blue colour of copper nitrate solution starts fading and ultimately becomes colourless.
- Reaction is exothermic and solution becomes hot.
- The solution becomes electrically neutral. Reaction between copper and zinc can be represented as :
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s)
This reaction can be explained as :
Zinc loses electrons and forms Zn2+ ion i.e., zinc gets ionised.
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e ̄
Cu2+ ion gains two electrons i.e., it gets reduced.
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Overall reaction can be represented as
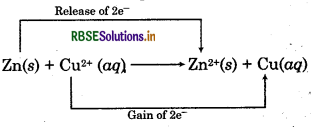
2. When a rod of copper is placed in zinc sulphate solution, no reaction occurs.
3. When a rod of copper is placed in silver nitrate solution, following changes occur:
Silver metal gets deposited over Cu rod.
Solution acquire blue colour.
The reaction can be represented as :
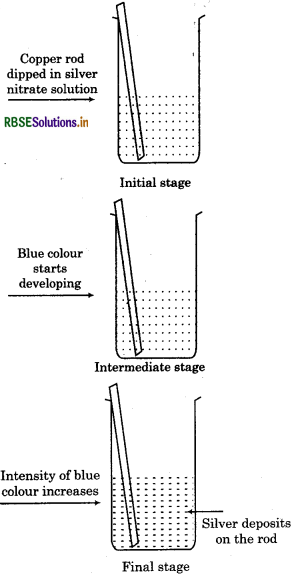
In the reaction between copper and silver,
• Cu loses electrons and forms Cu2+ i.e., it gets. oxidised.
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e
Ag2+ ion gains electrons and forms Ag i.e., it gets reduced.
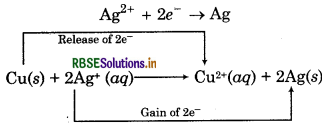
The electron releasing tendency of the three metals is in the order:
Zn > Cu > Ag
Question 6.
(a) Out of aluminium and silver vessel, which one is more suitable to store 1 M HCl solution and why?
(b) Element A will reduce the cation of element B but will not reduce the cation of element. Will element C reduces the cation of element B? Explain.
(c) While H2O2 can act as oxidising as well as reducing agent in their reactions, O3 and HNO3 acts as oxidants only.
Answer:
(a) Since reduction potential of silver is more than that of hydrogen, silver vessel will be suitable to store 1M HCl. On the other hand reduction potential of aluminium is less than that of hydrogen so that hydrogen will be liberated if stored in aluminium vessel.
(b) Since A will reduce B+, B has higher reduction potential than A and therefore, B lies above A in the electrochemical series. Now, A will not reduce C+, C has lower reduction potential than A and therefore lies below A in electrochemical series. Therefore, C must be below B in series and hence C will reduce B+.
(c) In H2O2 oxidation number of 0-1 and can vary from 0 to -2 (+2 is possible in OF2). The oxidation number can decrease or increase, because of this H2O2 can act both oxidising and reducing agent.
Question 7.
(a) Why the colour of KI solution containing starch turns blue when it is shaken with cold Cl2 water?
(b) What would happen if there is no salt bridge in the electrochemical cell?
(c) Both Cr2O4(aq) and MnO4(aq) can be used to titrate Fe2+(aq). If in a given titration, 24.50 cm3 of 0.1 M Cr2O were used, then what volume of 0.1 M MnO4 solution would have been used for the same titration?
Answer:
(a) Since Cl2 is stronger oxidizing agent than I2, therefore, when Cl2 is passed through KI solution, Cl2 gets reduced to colourless Cl- ions while I ions get oxidized to violet colour iodine.
Cl2(aq) + 2I-(aq) → 2Cl-(aq) + I2(s)
The I2 thus produced forms a blue coloured inclusion complex with starch and hence the solution turns blue.
(b) If there is no salt bridge in electrochemical cell, the positive ion formed by loss of electrons will accumulate around anode and negative ions left after reduction will accumulate around cathode. Thus, solution will develop charges and current stops flowing. Further, since the inner circuit is not complete, therefore, the current stops.
(c) The chemical equation for the redox reaction is:
Cr2O72- + 6Fe2+ + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 6Fe3+ + 7H2O
MnO-4 + 5Fe2+ + 8H+ → Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O
Since V2 cm3 of M2 Fe2+ is titrated against 24.50 cm3 of 0.1 M Cr2O2-7 And V1 cm3 of 0.1 M MnO-4 solutions,
then,
24.5 × 0.1/1 (Cr2O2-7) = M2V2 /6 (Fe2+ )
V1 × 0.1/1 (MnO4- ) = M2V1⁄2 /6 (Fe2+)
Equating two equations,
V1 = 24.5 × 6/5 = 29.4 cm3
Question 8.
(a) E° (Cu2+/Cu) and Eo (Ag+/Ag) is + 0.337 V and +0.799 V respectively. Make a cell whose EMF is +ve. If the concentration of Cu2+ 0.01M and E cell at 25°C is concentration of Ag+
(b) Calculate the potential of the cell at 298 K: Cd/Cd2+ (0.1M)|| H+(0.2M)/Pt, H (0.5 atm) 2 Given Eo for Cd2+/Cd = 0.403 V, R = 8.314 J-1 mol F = 96500 C mol-1
Answer:
(a) Cu is more reactive than silver, so that the cell is as Cu/Cu2+ (0.01M)||Ag+(C)/Ag or cell reaction
Cu + 2Ag + → Cu2+ + 2Ag
E∞H = F
(b) The cell reaction is Cd + 2H+ (0.2m) → Cd2+ (0.1M) + H (0.5 atm)
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
Reducing agent in cell Pb (s) Pb2+ (1 M) ||Ag+ \(1 M) |Ag (s) :
(a) Pb
(b) Pb2
(c) Ag
(d) Ag+
Answer:
(a) Pb

Question 2.
Hot concentrated sulphuric acid is a medium oxidising agent. Which of the following reaction do not show its oxidation nature?
(a) CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HF
(b) Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
(c) 3S+ 2H2SO4 → 3SO2 + 2H2O
(d) C + 2H2SO4 → CO2 + 2SO2 + 2H2O
Answer:
(a) CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HF
Question 3.
What is the oxidation number of Co in K[Co(CO)4]?
(a) + 1
(b) + 3
(c) -1
(d) - 3
Answer:
(c) -1
Question 4.
V → v2 + 2e-
V2+ + 2e- → V3+ + 2e-
In the above reactions, oxidation number of vandium is 2, 3 respectively. Then, what will be the oxidation state of Vanadium in the following reaction?
v3+ + H2O → VO2+ + 2H+ + e
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(d) 4
Question 5.
What is the highest oxidation state shown by group 17 elements ?
(a) + 1
(b) + 3
(c) + 5
(d) + 7
Answer:
(d) + 7
Question 6.
In basic medium, on reducing two elecrons by HO2, we get :
(a) OH-
(b) H2O
(c) O2
(d) O2-
Answer:
(a) OH-
Question 7.
In which of the following processes oxidation of iron does not take place?
(a) de-colouration of blue solution of copper sulphate by iron
(b) formation of Fe from Fe(CO)5
(c) release of hydrogen by the action of steam on iron
(d) rusting of iron seat
Answer:
(b) formation of Fe from Fe(CO)5
Question 8.
Which of the following disproportion gives MnO2 (1 mol) in neutral medium?
(a) 2/3 mole of MnO̟4- and 1/3 mole of MnO2
(b) 1/3 mole of MnO4- and 2/3 mole of MnO2
(c) 1/3 mole of Mn2O7 and 1/3 mole of MnO2
(d) 2/3 mole of Mn2O7 and 1/3 mole of MnO2
Answer:
(a) 2/3 mole of MnO̟4- and 1/3 mole of MnO2
Question 9.
(i) H2O2 + O3 → H2O + 2O2
(ii) H2O2 + Ag2O2Ag + H2O + O2
What is the function of hydrogen peroxide in above reactions?
(a) Reductant (i) and (ii)
(b) Oxidant in (i) and (ii)
(c) Oxidant in (i) and reductant in (ii)
(d) Reductant in (i) and oxidant in (ii)
Answer:
(c) Oxidant in (i) and reductant in (ii)
Question 10.
In which of the following reactions, H2O2 acts as reducing agent?
(a) H2O2 + 2H + 2e → 2H2O
(b) H2O2 - 2e → O2 + 2H+
(c) H2O2 + 2e- → 2OH-
(d) H2O2 + 2OH+ - 2e- → O2 + 2H2O
Answer:
(d) H2O2 + 2OH+ - 2e- → O2 + 2H2O
Question 11.
Which of the following reaction is balanced and gives actual results?
(a) Li2O + 2KCl → 2LiCl + K2O
(b) [COCl(NH3)5]+ + 5H+ → CO2+
(d) CuSO4 + 4KCN → K2 [Cu(CN) 4] + K2SO4
Answer:
(b) [COCl(NH3)5]+ + 5H+ → CO2+
Question 12.
If 0.1 mole of MnO2 is completely reduced, then how much electricity is required?
(a) 9650 C
(b) 96.50 C
(c) 965000 C
(d) 2x 96500 C
Answer:
(a) 9650 C

Question 13.
Consider the following reaction
I- + ClO3 + H2SO4 → Cl- + HSO4- +12
Which of the following is true if above reaction is balanced?
(a) The coefficient of HSO4- is 6.
(b) Iodine is oxidised
(c) Sulphur is reduced
(d) Water is a product
Answer:
(a) The coefficient of HSO4- is 6.
Question 14.
Which of the following is not correct about the reaction; Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+?
(a) Fe3+ is reduced
(b) The oxidation state of Fe is changed
(c) Fe3+ can be called as oxidant
(d) Fe3+ and Fe2+ can be called as basic radical.
Answer:
(d) Fe3+ and Fe2+ can be called as basic radical.
Question 15.
Which of the following is reductant in the reaction; Pb(s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Pb2+ + Cu(s) ?
(a) Pb2+ (aq)
(b) Cu2+
(c) Pb (s)
(d) Cu(s)
Answer:
(a) Pb2+ (aq)
Question 16.
In the given redox reaction:
MnO4 + C2O2-4 + H+ → Mn2+ + CO2 + H2O
What is the correct number of coefficients for reactants in the balanced chemical equation?
(a) 2 5 16
(b) 16 5 2
(c) 5 16 2
(d) 2 16 5
Answer:
(a) 2 5 16
Question 17.
In the following reaction,
3Br2 + 6CO2-3 + 3H2O → 5Br- + BrO-3 + 6HCO3-
(a) oxidation of bromine and carbondate take place
(b) reduction of bromine and oxidatin of water take place
(c) neither oxidation nor reduction of bromine take place
(d) Both oxidation and reduction of bromine take place
Answer:
(d) Both oxidation and reduction of bromine take place
Question 18.
H2S, may provide the colloidal sulphur by possible?
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
(c) Neutralisation
(d) Hydrolysis
Answer:
(a) Oxidation
Question 19.
H5IO6 is a:
(a) strong reductant
(b) strong base
(c) strong oxidising agent
(d) weak base
Answer:
(c) strong oxidising agent
Question 20.
Which of the following series of compounds is in decreasing order of oxidation number of nitrogen?
(a) HNO3, NO, NH4 Cl, N2
(b) HNO3, NO, N2, NH4 Cl
(c) HNO3, NH Cl, NO, N2
(d) NO, HNO3, NH4 Cl, N2
Answer:
(b) HNO3, NO, N2, NH4 Cl
Question 21.
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, then the change of oxidation state of chlorine is?
(a) zero to + 1 and zero to 5
(b) zero to -1 and zero to + 5
(c) zero to 1 and zero to+ 3
(d) zero to + 1 and zero to - 3
Answer:
(b) zero to -1 and zero to + 5
Question 22.
In which of the following compounds, the oxidation state of nitrogen is maximum?
(a) N2H4
(b) NH3
(c) N3H
(d) NH2OH
Answer:
(c) N3H

Question 23.
When mixture of potassium chlorate and sulphuric acid is heated, then oxidation state of which of the following element changes to maximum extent?
(a) S
(b) H
(c) Cl
(d) C
Answer:
(c) Cl
Question 24.
Phosphine and an other phosphorous compound is formed by reaction of aqueous NaOH and white phosphorous. What is the reaction type and oxidation state phosphorous containing compound?
(a) Redox reaction, - 3 and + 5
(b) Redox reaction + 3 and + 5
(c) Disproportionation Reaction - 3 and + 5
(d) Disproportionation Reaction - 3 and + 3
Answer:
(c) Disproportionation Reaction - 3 and + 5
Question 25.
Which of the following reaction shows reducing nature of SO2?
(a) 2H2S + SO2 → 3S + 2H2O
(b) I2 + SO2 + H2O → SO2 + 2I- + 4H+
(c) 3Fe + SO2 → 3FeO + FeS
(d) 4Na + 3SO2 → Na2SO3 + Na2S2O3
Answer:
(a) 2H2S + SO2 → 3S + 2H2O
Question 26.
In organic reactions, which behaviour is shown by lithium metal in liquid ammonia?
(a) as an oxidant
(b) as a reductant
(c) as a colourant
(d) as a dehydrating agent
Answer:
(b) as a reductant
Question 27.
In the reaction, H2S + H2O2 → S + 2H2O:
(a) H2S is an acid and H2O2 is a base
(b) H2S is a base and H2O2 is an acid
(c) H2S is an oxidant and H2O2 is a reductant agent
(d) H2S is a reducing agent and H2O2 is oxidising
Answer:
(d) H2S is a reducing agent and H2O2 is oxidising
Question 28.
What is the oxidation state of Pin cyclotrimeta phosphoric acid?
(a) + 3
(b) + 5
(c) + 2
(d) - 2
Answer:
(b) + 5

Question 29.
What is the oxidation of Fe3O4?
(a) 3/2
(b) 4/5
(c) 5/4
(d) 8/3
Answer:
(d) 8/3
Question 30.
Oxidation state of metal in hematite and magnetite ores:
(a) II, III in hematite, III in magnetite
(b) II, III in hematite, II in magnetite
(c) II in hematite, II, III in magnetite
(d) III, in hematite, II, III in magnetite
Answer:
(d) III, in hematite, II, III in magnetite

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter