RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Important Questions Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
In which compound, both covalent and ionic bonds are found?
(1) Calcium carbide
(2) Dehydrated aluminium chloride
(3) Calcium hydroxide
(4) Aluminium hydroxide
Answer:
(1) Calcium carbide
Question 2.
Order of boiling points of H2O, H2S and H2Se is
(1) H2Se > H2S > H2O
(2) H2O > H2S > H2Se
(3) H2S > H2O > H2Se
(4) H2O > H2Se > H2S
Answer:
(4) H2O > H2Se > H2S

Question 3.
Which compound does not obey octet rule?
(1) Carbon tetrachloride
(2) Phosphorus pentachloride
(3) Calcium oxide
(4) Barium nitrate
Answer:
(2) Phosphorus pentachloride
Question 4.
Which molecule has odd number of electrons?
(1) B2H6
(2) O2
(3) CO
(4) NO
Answer:
(4) NO
Question 5.
Which molecule is paramagnetic?
(1) N2
(2) O2
(3) F2
(4) D2
Answer:
(2) O2
Question 6.
Which molecule is isoelectronic to nitrogen molecule?
(1) NO
(2) CO
(3) H2O
(4) HCl
Answer:
(3) H2O
Question 7.
In NO3- ion, what is the number of bond pair and lone pair of electron at N atom?
(1) 3, 1
(2) 4, 0
(3) 2, 2
(4) 3, 3
Answer:
(2) 4, 0

Question 8.
Which molecule has zero dipole moment?
(1) CIF
(2) PCl3
(3) SiCl4
(4) CHCl3
Answer:
(3) SiCl4
Question 9.
Which molecule has one electron pair?
(1) CO
(2) NO
(3) O2
(4) CN
Answer:
(2) NO
Question 10.
In which molecule, octet rule is not applied?
(1) CO2
(2) H2O
(3) O2
(4) CO
Answer:
(2) H2O
Question 11.
Which compound has maximum dipole moment?
(1) CH3Cl
(2) CCl4
(3) CHCl3
(4) CH2Cl2
Answer:
(1) CH3Cl
Question 12.
Molten NaCl can conduct electricity because lin it has :
(1) free electron
(2) free ion
(3) free molecule
(4) atoms of sodium and chloride
Answer:
(2) free ion
Question 13.
Which group has same structure and same number of electrons?
(1) NO3-, CO2-
(2) CO2-3, SO3
(3) SO3, NO3-
(4) CIO3-, CO2-3
Answer:
(1) NO3-, CO2-
Question 14.
Which bond has maximum bond energy?
(1) ionic bond
(2) covalent bond
(3) metallic bond
(4) hydrogen bond
Answer:
(1) ionic bond

Question 15.
Reason for polarity in covalent bond is:
(1) electron affinity
(2) ionization potential
(3) electronegativity
(4) atomic size
Answer:
(3) electronegativity
Question 16.
Number of σ and π bonds in
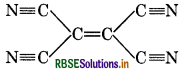
(1) 9 σ and 9π
(2) 9 σ and 5л
(3) 7 σ and 7л
(4) 11σ and 9л
Answer:
(1) 9 σ and 9π
Question 17.
Which molecule has bent geometry?
(1) CO2
(2) O3
(3) N2O
(4) None of these
Answer:
(2) O3
Question 18.
Boiling point of NH3 is more than PH3 because :
(1) molecular weight of NH3 is high
(2) NH3 has ionic bond whereas PH, has covalent Ar bond
(3) NH3 forms hydrogen bond
(4) None of the above
Answer:
(4) None of the above
Question 19.
In NO2-, the bond order of nitrogen-oxygen is :
(1) 1
(2) 1.33
(3) 1.5.
(4) 2
Answer:
(3) 1.5.
Question 20.
Which type of hybridization occurs in SF4 ?
(1) sp
(2) sp2
(3) sp3 d
(4) dsp2
Answer:
(3) sp3 d
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Why BeH2 is linear and not H2S?
Answer:
In BeH2, there is no lone pair on Be atom so it is ear while in H2S, there is lone pair on S-atom. So it is linear.
Question 2.
Why dipole moment of CH2F is more than CH2Cl?
Answer:
Due to more electronegativity of F than that of Cl, -F bond has more dipole moment as compared to -Cl bond.

Question 3.
H atom forms H2 molecule while He molecule does not exist?
Answer:
The bond order of H2 molecule is 1 so it exists but e bond order of He, molecule is zero, so, it does not ist.
Question 4.
Arrange the MgCl2, AlCl3, BeCl2 and CCl in increasing order of ionic character?
Answer:
CCl4 < AlCl3 < BeCl2 <MgCl2.
Question 5.
What will be the nature of bond formed by combination of H and Cl and O and O?
Answer:
Since all these are non metals so bond will be valent in nature :
(i) H - Cl
(ii) O = 0.
Question 6.
What is dry ice? Which type of solid is this?
Answer:
CO2 (s) is known as dry ice. It is a molecular solid.
Question 7.
Arrange the NO2+, NO2- and NO3- in increasing order of bond length of N - O.
Answer:
NO2+ < NO-2 < NO3-.
Question 8.
Among NaCl and CuCl, which is more water soluble?
Answer:
NaCl is more soluble in water because it is ionic in ture while CuCl is covalent in nature.
Question 9.
Out of KCl, C2H5OH and C6H5COOH, which has more boiling point?
Answer:
Since KCl is ionic in nature so it has more boiling int.
Question 10.
What will be the structure of BrF?
Answer:
There are seven valence electrons on Br in BrF5 molecule, in which five electrons form bond with F-atom d one electron pair remains as lone pair. So, structure BrF5 becomes square pyramidal.

Question 11.
Find the bond order of following:
(i) H2 molecule
(ii) O2 molecule
(iii) N2 molecule
(iv) Cl2 molecule
(v) CO molecule.
Answer:
(i) H2 molecule has single bond (H - H), so bo order will be 1.
(ii) O2 molecule has double bond (0 = 0), so bond ord will be 2.
(iii) N2 molecule has triple bond (N = N), so bond ord will be 3.
(iv) Cl2 molecule has single bond (Cl - Cl) so bond ord will be 1.
(v) CO molecule is represented by imm, so its bo order will be 3.
Question 12.
Give the Lewis structure of following:
Answer:
(1) Na2S (Sodium sulphide)
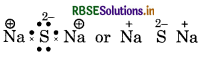
(2) AIF (Aluminium fluoride)
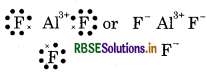
(3) NH4 Cl (Ammonium chloride)
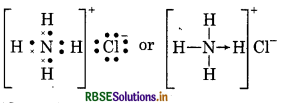
(4) O3 (Ozone)
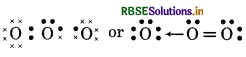
(5) H2O̟2 (Hydrogen peroxide)
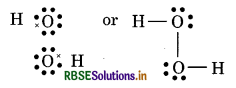
(6) CO (Carbon monoxide)
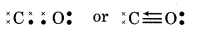
(7) N2O (Nitrogen (I) oxide)
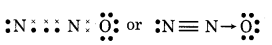
(8) SOCl2 (Thionyl chloride)
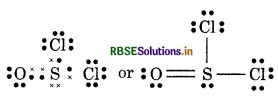
(9) SO2 Cl2 (Sulphuryl chloride)
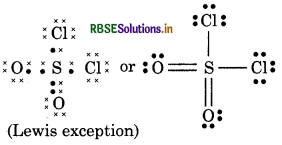
(10) H2CO3 (Carbonic acid)
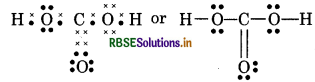
(11) H3 PO2 (Hypophosphorus acid)
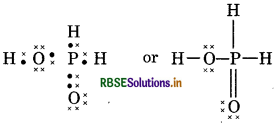
(12) H4 P2O7 (Pyrophosphoric acid)
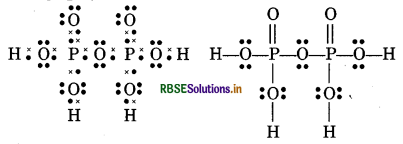
(13) CO2-3(Carbonate ion)
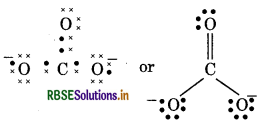
(14) NO2+ (Nitronium ion)
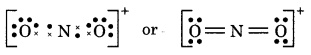
(15) NO2- (Nitrite ion)
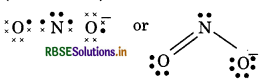
(16) NO3- (Nitrate ion)
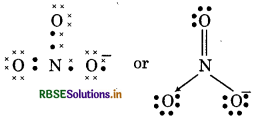
(17) SO2-4 (Sulphate ion)
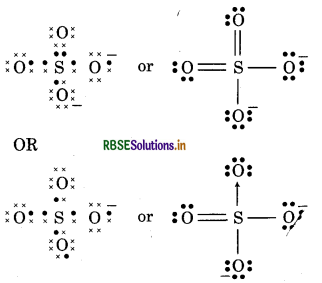
Question 13.
Why NaCl is hard as compared to Na-metal?
Answer:
In NaCl, there is strong ionic bond between Na+ and Cl ions while in Na metal there is weak metallic bond between Na-atoms. Hence, NaCl is harder than Na-metal.

Question 14.
From the given compounds, select those which do not obey octet rule :
SO2, SF2, SF4, SF, OF2, BCl3, , PCl5, IF,
Answer:
SO2, SF4, SF6, BCl3, PCl5, IF, do not follow the octet rule.
Question 15.
What is the order of bond length in C-C bond?
Answer:
C C < C = C < C-C
1.20 Å 1.33 Å 1.54 Å
Question 16.
What is Debye?
Answer:
It is unit of dipole moment. It is denoted by D
1D = 10-10 esu × 10−8 cm = cm = 10-18 esu.cm
Question 17.
SO2 molecule contains dipole moment. Is it linear, Give reason?
Answer:
It is not linear molecule because if it would linear then dipole moment should be zero, but it has dipole moment. Thus, molecule is not linear, it is bent.
Question 18.
Calculate the formal charge on each atom in PCl5 and CH?
Answer:
Formal Charge in PCl5
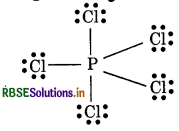
Formal charge of P-atom = 5 - 0 - 1/2 × 10
= 5 - 5 = 0
Formal charge at each Cl atom = 7 - 6 - 1/2 × 10
= 7 - 6 - 1 = 0.
Formal chage in CH3+
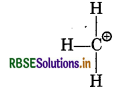
Formal charge at C = 4 - 0 - 1/2 × 6
= 4 - 3 = 1
Formal charge at each H atom = 1 - 0 - 1/2 × 2
= 1 - 1 = 0
Question 19.
Calculate the formal charge of each atom in CH3 and CCl2 radicals.
Answer:
1. For CH3 free radical
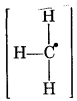
Formal charge at C atom = 4 - 1 - 1/2 × 6
= 4 - 1 - 3 = 0
Formal charge at each H atom = 1 - 0 - 1/2 × 2
= 1 - 1 = 0
1. For dichlrocarbon radical:
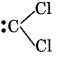
Formal charge at Carbon atom = 4 - 2 - 1/2 × 4
= 4 - 2 - 2 = 0
Formal charge at each Cl atom = 7 - 6 - 1/2 × 2
= 7 - 6 - 1 = 0
Question 20.
N2 gas is generally used as inert gas, why?
Answer:
There is triple bond in N2 gas because of this its bond dissociation energy is high. Since, it is highly stable gas, so it is used as inert gas.
Question 21.
Name such covalent compounds which are conductor of electricity.
Answer:
Graphite is conductor of electricity due to free л electrons.
Question 22.
In PCl5, three P-Cl bonds have more dissociation energy while two others have less, why?
Answer:
The geometry of PCl5 is trigonal bipyramidal in which the bonds are equatorial and two are axial Axial bonds are longer then equatorial bonds because o this they have less bond energy.

Question 23.
Find the hybridisation and geometry in
(i) CIF3 and
(ii) SF4
Answer:
(i) CIF3 = 7+ 3× 7
\(=\frac{28}{8}=\left[3+\frac{4}{2}=5\right]\)
= 5 (sp3d hybridisation)
Geometry = T-shaped.
(ii)
SF1 = 6 + 4 × 7
\(=\frac{34}{8}=\left[4+\frac{2}{2}=1\right]\)
5 (sp3 d hybridisation).
Question 24.
Calculate the total sigma (σ) and pi (π) bond in (i) C6H6, (ii) C(CN)4, (iii) CH3COOH
Answer:
(i) Benzene
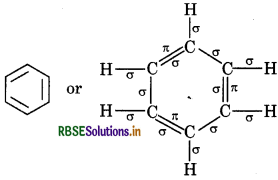
Total σ bonds = 12
Total л bonds = 3
(ii) Carbon Tetra-cyanide
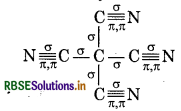
Total o bonds = 8
Total л bonds = 8
(iii) Acetic Acid
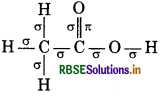
Total σ bonds = 7
Total л bonds = 1
Question 25.
Arrange the O2, O+2, O-2, O2-2 in decreasing order of bond stability, bond energy and bond length.
Answer:
The bond order of O2 = 2.0
O22- = 1.0
O2- = 1.5
O+2 = 2.5
(i) Order of stability : O+2 > O2 > O2- > O22-
Since bond order o stability.
(ii) Order of bond energy : O+2 > O2 > O-2 > O22-
Şince bond order a bond energy.
(iii) Bond length : O2-2 > O-2 > O2 > O+2
Bond length α
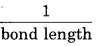
Question 26.
Find the hybridization in following compounds?
Answer:
(i) F2O : 7 × 2 + 6 = 20
= 20/8 = [2 + 4/2 = 4]
= 4 (SP3 hybridisation)
(ii) CO2 : = 4 + 6 × 2
= 16/8 = 2 (SP hybridisation)
(iii) SO2-4: = 6 + 4 × 6 + 2
= 32/8 = 4 (SP3 hybridisation)
(iv) SnCl4 : = 4 + 4 × 7 = 32/8 = 4
= 4 (SP3 hybridisation)
(v) HgCl2: = 2 + 7 × 2 = 16/8 = 2
= 2 (sp hybridisation)
(vi) CH3+: = 4 + 3 -1 = 6/2 = 3
= 3 (SP2 hybridisation)
(vii) ClO4-: = 7 + 4 × 6 + 1
= 32/8 = 4 (SP3 hybridisation)
Question 27.
What will be effect on bond order of C2 in ionisation process? C2 → C2 + e-
Answer:
The bond order decreases when C2 becomes C+2 because bond order of C2 is 2.0 while bond order of C+2 is 1.5.
Question 28.
From the following pair of compounds select increasing order of them as their properties given against them:
(1) NF, NH3 (dipole moment)
(2) CO2, SiO2 (bond angle)
(3) NaCl, LiCl (ionic character)
(4) MgO, CaO (hardness)
(5) HF, HCl (boiling point).
Answer:
(1) NH3 > NF (Dipole moment)
(2) CO2 > SiO2 (Bond angle)
(3) NaCl > LiCl (Ionic character)
(4) MgO > CaO (Hardness)
(5) HF > HCl (Boiling Point)

Question 29.
Match the following compounds with their bond angles :
Compounds
BeCl2, H2O, BCl3, AlCl3, NH3, CCl4 SF6
Bond angle
180°, 109°28', 104.5°, 107°, 120°, 90°
Answer:
BeCl2 : 180°
H2O: 104.5°
Bl3: 120°
AlCl3 : 120°
NH3 : 107°
CCl4 : 109°28
SF6 : 90°
Question 30.
Why I2 sublimates on heating?
Answer:
Iodine is a high covalent non polar molecule. So, its boiling point and melting point are very less. So I2, sublimates on heating.
Question 31.
Out of 1-butene or 1-butyne, which one has high dipole moment and why?
Answer:
1-butyne will possess high dipole moment because it is more polar. It has sp hybrid carbon which is more electronegative.
Question 32.
Arrange the HF, HCl and HBr in decreasing order of their electrocovalent character. The electronegativity of these are as follows:
H = 2.1, F = 4.0, Cl = 3.0, Br = 2.8.
Answer:
(i) Fòr H-F Bond
Difference in electronegativity (XF −XH)
= 4.0 - 2.1 = 1.9
% ionic character = [16(1.9) + 3.5(1.9)2] = 43%
(ii) For HCl Bond
Difference in electronegativity (xCl −XH)
= 3.0 - 2.1 = 0.9
% ionic character = [16(0.9) + 3.5(0.9)2]
= 17.2%
(iii) For HBr Bond
Difference in electronegativity (XBr −XH)
= 2.8 - 2.1 -0.7
%ionic character = [(16× 0.7) + 3.5 × (0.7)2]
= 12.9%
So, decreasing order = HF > HCl > HBr.
Question 33.
Why Br-Br bond is weaker than Cl-Cl bond?
Answer:
Cl-Cl bond forms due to overlapping between 3p - 3p orbitals while Br-Br bond forms due to overlapping between 4p-4p orbitals. 4p-orbitals are far from nucleus and can not form strong bond. Due to this reason, Cl-Cl bond is more strong.
Question 34.
Why (SiHg); N is less basic than that of (CH3)3 N?
Answer:
(SiH3)3 N, has less electron pair on N because of bonding electron on N and there is рπ - dπ bonding in d orbital of Si atom.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Define hydrogen bond. Is it weaker or stronger than van der Waal's force?
Answer:
Hydrogen bond is attraction force which binds one H-atom of a molecule with more electronegative atom like F, O, N. It is denoted by dotted line. Hydrogen bond is stronger than van der Waal's force because it represents strong dipolar interaction.
Question 2.
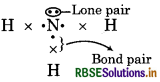
What do you mean by bond pair and lone pair of electrons? Give example of each.
Answer:
Bond Pair : The shared electron pair which found in centre of atoms of elements is called bond pair.
Lone Pair : It is the pair of electron which is not used in bond formation.
For example: NH3
Question 3.
On the basis of molecular orbital theory explain why Be2 molecule does not exist?
Answer:
The atomic number of Be is 4, so 8 electrons will occupy in its molecular orbital. The molecular orbital configuration of Be2 molecule is KK O2s2, σ* 2s2
Bond order = 1/2(2 − 2) = 0
Since bond order of Be, is zero, so this molecule does not exist.

Question 4.
Although CO2 and H2O both are triatomic molecules. But geometry of H2O is V-shape and CO2 is linear. Explain it on the basis of dipole moment.
Answer:
Both CO2 and H2O are triatomic molecules. The geometry of CO2 is linear while H2O has V-shape geometry.
In CO, molecule, two C = O bonds are polar in nature but dipole moment is zero because these two are opposite to each other. So, CO2 possesses linear geometry.
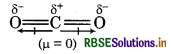
In H2O molecule, there are two O-H bonds, these are also polar in nature and show dipole moment because these are not linear. So, geometry is V-shaped.
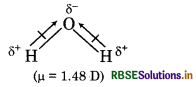
Question 5.
What do you mean by maximum covalency and variable covalency?
Answer:
Maximum Covalency: The number of unpaired electrons present in outer most shell of elements is equal to the maximum number of bonds formed. Only few obey this rule because atoms get excited and hence increase the number of unpaired electrons.
For example: In PCl5, covalency of phosphorous is 5, in SF6 covalency of sulphur is 6 and in CH4, carbon can form 4 bonds.
Variable Covalency: Some elements exhibit more than one covalency, it is known as variable covalency. The main reason for showing variable covalency is availability of d-orbitals in element. For example: Phosphorus has +3 and +5 variable covalency.
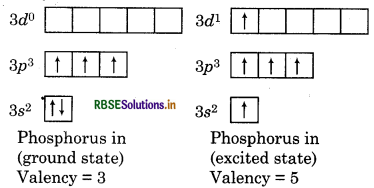
Question 6.
What is meant by polarisation of bonds?
Answer:
The ions with same charge repel each other while ions with opposite charge attract each other; because of this, the size of ion gets distorted rather than spherical. Hence, the distortion in size of atom due to mutual attraction or repulsion is called polarisation of bonds.
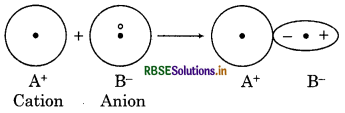
Question 7.
Describe the factors affecting polarization?
Answer:
- Small cation:
- Large anion:
- Large charges:
- Electronic configuration of the cation:
- Percentage of ionic character and charge distribution
- Bond character based on electronegativity differences
- London dispersion forces
- Anomalous behaviour of the 2nd row elements: Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F
- Reactivity of metals and metalloids
- Covalent character
- Catenation
- Multiple Bonds
- Oxidizing ability of oxygen and fluorine
Question 8.
Differentiate between the ionic and the covalent compounds?
Answer:
|
Ionic compounds |
Covalent compounds |
|
1. Ionic compounds are generally solid. |
1. Covalent compounds may be solid, liquid and gas. |
|
2. These are formed by ions. |
2. These are formed by molecules. |
|
3. Ionic bonds are non directional. |
3. Covalent bonds are directional. |
|
4. Ionic compounds do not show isomerism. |
4. They can show isomerism. |
|
5. Ionic compounds are solid and brittle. |
5. These are soft and molten. |
|
6. They have high boiling and melting points. |
6. They have low boiling and melting points. |
|
7. These are soluble in polar solvent. |
7. These are soluble in non polar solvent. |
|
8. Their reactions are very fast. |
8. Their reactions are very slow. |
Question 9.
SiCl4 is hydrolysed while CCl4 does not. Explain?
Answer:
SiCl4 is hydrolysed because in Si atom there is vacant d-orbitals and also Si has maximum covalency of 6. Due to this, Si forms two extra bonds with two molecules of water and distance between H2O molecule and SiCl4 decreases so it form HCl molecule easily. In case of CCl4, there is no d-orbital in C-atom and C-atom cannot form extra bond with H2O and hence is insoluble in water.
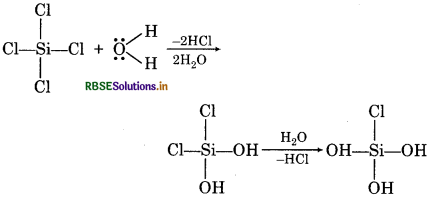
Question 10.
Graphite is conductor of electricity, why? While it is covalent compound.
Answer:
Graphite has layered structure. In graphite, each A carbon atom is attached to three carbon atoms by covalent bond in layer. Each carbon has one free electron which is mobile. Due to the presence of free electrons, graphite is conductor of electricity.

Question 11.
Explain the following bonds, formed between two atoms:
(1) Two atoms having similar electronegativity.
(2) Two atoms having minimum difference in their electronegativity.
(3) Two atoms having maximum difference in their electronegativity.
Answer:
(1) When two atoms have similar electronegativity, n then bond formed between them is 100% covalent.
(2) When their is minimum difference in electronegativity of two atoms then bond formed between them will be polar covalent and has some ionic character.
(3) When difference in electronegativity is maximum, then bond formed between two atoms will be electrovalent with some covalent character.
Question 12.
The bond angle of NH3 is more than PH3. Why?
Answer:
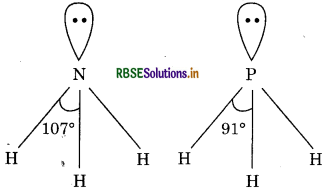
NH3 and PH, both are hydrides of elements of group 15. The electronegativity of nitrogen is more than phosphorus; consequently, shared electron pair in N-H bond is more towards nitrogen whereas in P-H bond this shared pair of electron is less towards phosphorus. Due to more electronegativity of nitrogen, electron density around nitrogen atom increases and repulsion increases. Hence, in NH3, H - N - H bond angle is also 107° while in H-P-H, it is 91°.
Question 13.
The dipole moment of KCl is 3. 336 × 107 which indicates that it is highly polar u molecule. The interatomic distance between K and Cl is 2.6 × 10-10 m. Calculate dipole moment if each nucleus possesses 1 unit opposite charge? Also determine the ionic percentage in KCl.
Answer:
u = q x d = 2.6 x 10-10 m x 1.602 x 10-19 C
= 4.1652 x 10-29

Question 14.
Why dipole moment of HF (1.98 D) is more than dipole moment of HCl (1.03 D)?
Answer:
HF is more polar than HCl because F is more lectronegative than the Cl. As we know that more ifference in electronegativity leads to more polarity i. e., more will be dipole moment.
Question 15.
Dipole moment of LiH is 1. 964 × 10-29 Cm and interatomic distance of Li and H is 1.596 Å. Calculate % age ionic character in LiH.
Answer:
Theoretical dipole moment
= q × d
= 1.602 × 10-19 C× 1.596 × 10-10
= 2.557 × 10-29 Cm

Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
Compound (s) in which two lone pairs are present at central atom :
(a) BrF5
(b) CIF3
(c) XeF
(d) SF4
Answer:
(b) CIF3
Question 2.
According to molecular orbital theory:
(a) C2 is diamagnetic in nature.
(b) O22+ has bond length more than O2.
(c) N+2 and N-2 have same bond order.
(d) Energy of He+2 is equivalent to two He-atoms.
Answer:
(a) C2 is diamagnetic in nature.

Question 3.
Which one of the following is isostructural to CO2 molecule ?
(a) HgCl2
(b) C2H2
(c) SnCl2
(d) NO2
Answer:
(a) HgCl2
Question 4.
Which order will be correct from the following?
(a) lp-lp > lp-bp > bp-bp
(b) lp-lp > bp-bp > lp-bp
(c) bp-bp > lp-bp > lp-lp
(d) lp-bp > bp-bp > lp-lp
Answer:
(a) lp-lp > lp-bp > bp-bp
Question 5.
Which compound has intramolecular hydrogen bond?
(a) cellulose
(b) conc. acetic acid
(c) H2O2
(d) HCN
Answer:
(a) cellulose
Question 6.
Which order is followed by boiling point to HF, HCI, HBr and HI?
(a) HF > HCl > HBr > HI
(b) HF > HI> HBr > HCI
(c) HI> HBr > HCl > HF
(d) HCl > HF > HBr > HI
Answer:
(b) HF > HI> HBr > HCI
Question 7.
Which has strongest H-bond?
(a) O-H ...... S
(b) S-H ...... O
(c) F-H ...... S
(d) F-H ...... O
Answer:
(c) F-H ...... S

Question 8.
Which statement is incorrect for CH3, NH3, and H2O molecules?
(a) In CH4, H - C - H bond angle, in H2O H - O - H bond angle and in NH3 H - N - H bond angle is more than 90°.
(b) Bond angle of H-CH in CH4 is more than bon angle of H - O - H of H2O.
(c) Bond angle of H-O-H in H2O is less than bond angle of H - N - H of NH3.
(d) Bond angle of H-C-H in CH is more than bond angle of H - N - H of NH3.
Answer:
(b) Bond angle of H-CH in CH4 is more than bon angle of H - O - H of H2O.
Question 9.
Which molecule/ion has bond order 3.0 ?
(a) O2 and NO+
(b) N2 and NO+
(c) N2 and NO
(d) N2 and NO+
Answer:
(b) N2 and NO+
Question 10.
What is the correct order of bond length of O - O bond in O2, H2O2 and O3?
(a) O2 > O3 > H2O2
(b) H2O2 > O3 > O2
(c) O3 > O2 > H2O2
(d) O3 > H2O2 > O2
Answer:
(b) H2O2 > O3 > O2
Question 11.
Which of the following pairs is isoelectronic and isostructural ?
(a) SO2-3, NO-3
(b) CIO3- SO2-3
(c) CO2-3 NO-3
(d) ClO3- CO2-3
Answer:
(d) ClO3- CO2-3
Question 12.
What is hybridisation of atomic orbital of nitrogen in NO+2, NO-3 and NH+4 ?
(a) sp2, sp and sp3
(b) sp, sp3 and sp2
(c) sp2, sp3 and sp
(d) sp, sp2 and sp3
Answer:
(d) sp, sp2 and sp3

Question 13.
The correct geometry and hybridization for XeF is:
(a) square planar, sp3 d2
(b) octahedral, sp3 d3
(c) trigonal bipyramidal, sp3 d
(d) planar trigonal, sp3 d3
Answer:
(a) square planar, sp3 d2
Question 14.
Structure of BrF3 is:
(a) trigonal bipyramidal
(b) completely T-shaped
(c) bent-T-shaped
(d) triangular planar
Answer:
(c) bent-T-shaped
Question 15.
What is the hybridisation and shape of BrF5 ?
(a) sp3d, trigonal bipyramidal
(b) sp3 d2, trigonal bipyramidal
(c) dsp2, square planar
(d) sp3 d2, square pyramidal
Answer:
(d) sp3 d2, square pyramidal
Question 16.
Which one is the linear species from SO2, BeCl2, O3, H2O and HgCl2 ?
(a) SO2 and Og
(b) SO2 and H2O
(c) BeCl2 and HgCl2
(d) Og and H2O
Answer:
(c) BeCl2 and HgCl2
Question 17.
Species in which N atom is sp-hybridised :
(a) NO-2
(b) NO-3
(c) NO2
(d) NO+2
Answer:
(d) NO+2
Question 18.
Which statement is incorrect?
(a) I3+ has curved geometry
(b) PH5 and BiCl5 do not exist
(c) SO2 has pл-dл bond
(d) SeF4 and CH4 have same shape
Answer:
(d) SeF4 and CH4 have same shape
Question 19.
The bonds formed between two carbon atoms in calcium carbide are :
(a) lσ, lл
(b) 1σ, 2л
(c) 2σ, 1л
(d) 2σ, 2π
Answer:
(b) 1σ, 2л
Question 20.
In case of (i) HClO (ii) HClO2 (iii) HClO3 and (iv) HClO4, the correct statement is :
(a) The total number of ClO bonds in (i) and (iii) is two
(b) The number of lone pairs at Cl in (ii) and (iii) is three
(c) Cl is sp3 hybridized in (iv)
(d) Strongest acid is (i) from (i) to (iv)
Answer:
(b) The number of lone pairs at Cl in (ii) and (iii) is three
Question 21.
Which one shows weak intermolecular force?
(a) He
(b) HCl
(c) NH3
(d) H2O
Answer:
(a) He
Question 22.
Which one is correct order of bond order?
(a) O+2 > O2 > O-2 > O22-
(b) O22- > O2- > O2 > O+2
(c) O2 > O2+ > O-2 > O2+
(d) O-2 > O22- > O+2 > O2
Answer:
(c) O2 > O2+ > O-2 > O2+

Question 23.
Decreasing order of stability for O2, O-2, O+2 and O2-2 is:
(a) O+2 > O2 > O-2 > O22-
(b) O22- > O2- > O2 > O+2
(c) O2 > O2+ > O-2 > O2+
(d) O-2 > O22- > O+2 > O2
Answer:
(a) O+2 > O2 > O-2 > O22-
Question 24.
The number of lone pair at central atom of H2O, SbCl3, PCl3 and XeF2 is respectively
(a) 2, 1, 1, 3
(c) 3, 1, 1, 2
(b) 2, 2, 1, 3
(d) 2, 1, 2, 3
Answer:
(a) 2, 1, 1, 3
Question 25.
Which species has equal number of σ and л bonds?
(a) XeO4
(b) (CN)2
(c) CH2 (CN)2
(d) HCO3
Answer:
(a) XeO4
Question 26.
Which of the following molecule has maximum dipole moment?
(a) NH3
(b) NF3
(c) CO2
(d) CH4
Answer:
(a) NH3
Question 27.
Which one of following species has trigonal planar shape ?
(a) NO2,
(c) Ng
(b) CO2
(d) NHg
Answer:
(d) NHg
Question 28.
Which of the following property is not shown by NO?
(a) It is diamagnetic in gaseous state.
(b) It is a neutral oxide.
(c) When it combines with oxygen then it forms Nitrogen trioxide.
(d) Its bond order is 2.5.
Answer:
(a) It is diamagnetic in gaseous state.

Question 29.
Which molecule behaves as diamagnetic?
(a) C2
(b) N2
(c) O2
(d) S2
Answer:
(a) C2
Question 30.
The increasing order of stability for Li2, Li-2 and Li+2 is.
(a) Li2 < Li+2 < Li-2
(b) Li2- < Li2 < Li+2
(c) Li2 < Li-2 < Li+2
(d) Li-2 < Li2 < Li+2
Answer:
(d) Li-2 < Li2 < Li+2
Question 31.
In which of the following ionisation process, the bond order increases and magnetic behaviour changes?
(a) C2 → C2+
(b) NO → NO+
(c) O2 → O+2
(d) N2 → N2+
Answer:
(b) NO → NO+
Question 32.
Which one is paramagnetic from the following?
(a) O-2
(b) NO
(c) both (c) and (b)
(d) CN
Answer:
(c) both (c) and (b)
Question 33.
Increasing order of bond angle in given triatomic species is :
(a) NO+2 < NO2 < NO2
(b) NO+2 < NO-2 < NO2
(c) NO-2 < NO+2 < NO2
(d) NO-2 < NO2 < NO+2
Answer:
(d) NO-2 < NO2 < NO+2
Question 34.
The increasing order of ionic character for BCl3, AlCl3 and GaCl3 is
(a) BCl3 < AlCl3 < GaCl3
(b) GaCl2 < AlCl3 < BCl2
(c) AlCl3 < GaCl2 < BCl2
(d) AlCl3 < BCl3 < GaCl2
Answer:
(c) AlCl3 < GaCl2 < BCl2
Question 35.
In following pairs, both species are not isostructural :
(a) CO2- and NO3
(b) PCI and SiCl4
(c) PF and BrF5
(d) AlF and SF6
Answer:
(c) PF and BrF5
Question 36.
Which one of the following pairs is isostructural ?
(a) [BCl, and BrCl3]
(b) [NH3 and NO-3]
(c) [NF and BF3]
(d) [BF and NH]
Answer:
(d) [BF and NH]
Question 37.
Shape of IF7 molecule will be:
(a) octahedral
(b) pentagonal bipyramidal
(c) trigonal bipyramidal
(d) tetrahedral
Answer:
(b) pentagonal bipyramidal
Question 38.
In given bonds which covalent bond length is minimum?
(a) C - O
(b) C - C
(c) C = N
(d) O - H
(e) C = C
Answer:
(d) O - H
Question 39.
Which compound shows highest covalent character?
(a) FeCl2
(b) SnCl2
(c) AlCl3
(d) MgCl2
Answer:
(c) AlCl3
Question 40.
The bond present in N2O4 is.
(a) only ionic
(b) only covalent
(c) covalent and coordinate
(d) ionic and coordinate
Answer:
(c) covalent and coordinate

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter