RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 Important Questions Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Who proposed first periodic classification of elements?
(1) Dobereiner
(2) JAR Newland
(3) Di. Mendeleev
(4) Lothar Meyer
Answer:
(3) Di. Mendeleev
Question 2.
Representative element of group II are:
(1) Be, Mg
(2) Mg, Ca
(3) Be,Al
(4) Be.B
Answer:
(3) Be,Al
Question 3.
Which element (Z = 21) is placed In period and group of
(1) period-3 group Il
(2) period -4. group U
(3) period - 4. group HI
(4) period 111. group III
Answer:
(3) period - 4. group HI

Question 4.
Long fdrm of periodic table depends on which character of element.
(1) Valency
(2) Atomic mass
(3) Atomic size
(4) Electronic configuration
Answer:
(4) Electronic configuration
Question 5.
Which pair is placed In same group of periodic table?
(1) Na,Ca
(2) Na, Cs
(3) Ca, Cl
(4) Hg. Sb
Answer:
(2) Na, Cs
Question 6.
Mendeleev was:
(1) French chemist
(2) German chemist
(3) Dutch chemist
(4) Russian chemist
Answer:
(4) Russian chemist
Question 7.
Which element has most electronegatlve clement in periodic table?
(1) nitrcgen
(2) oxygen
(3) chlorine
(4) fluorine
Answer:
(2) oxygen
Question 8.
Atomic number of 3d-transition element is:
(1) 20- 30
(2) 21 - 30
(3) 21 - 31
(4) 21 - 29
Answer:
(4) 21 - 29
Question 9.
Astatine (At) s:
(1) Alkali metal ‘
(2) Alkaline earti metal
(3) Halogen
(4) Rare earth metal
Answer:
(3) Halogen
Question 10.
Which element has highest jo Izatlon energy?
(1) H
(2) H
(3) Hg
(4) A
Answer:
(2) H

Question 11.
Which the mettaloid:
(1) Zn
(2) Ge
(3) Sn
(4) All o these
Answer:
(2) Ge
Question 12.
Which one has highest electron gain enthalpy?
(1) H
(2) O
(3) F
(4) Cl
Answer:
(4) Cl
Question 13.
The increasing order of electronegativities of C, N, P and Si is:
(1) C, N, Si, P
(2) N. Si. C, P
(3) Si, P, C.N
(4) P,Si,N,C
Answer:
(3) Si, P, C.N
Question 14.
Which one has highest radius?
(1) Na+
(2) O2-
(3) F-
(4) Mg2+
Answer:
(2) O2-
Question 15.
Which one has zero second electron affinity EA2?
(1) Cl
(2) O
(3) S
(4) N
Answer:
(1) Cl
Question 16.
Which one has minimum ionic radius?
(1) K+
(2) Ca2+
(3) Ti3+
(4) Tl4+
Answer:
(4) Tl4+
Question 17.
Which elements has maximum ionisation energy?
(1) [Ne] 3s2, 3p1
(2) [Ne] 3S2, 3p2
(3) [Nel 3S2 , 3p3
(4) [Ar] 3d10, 4S2, 4p2
Answer:
(3) [Nel 3S2 , 3p3
Question 18.
Which one has minimum value of ionisation energy?
(1) Halogens
(2) Inert gases
(3) Alkaline earth metals
(4) Alkali metals
Answer:
(4) Alkali metals

Question 19.
Electron affinity depends on.
(1) Atomic size
(2) Nuclear charge
(3) Atomic number
(4) both 1 and 2
Answer:
(4) both 1 and 2
Question 20.
Pauling scale is useful to measure electronegativity be cause of:
(1) Polarity of molecule
(2) Position in EMF series
(3) Number of subshell
(4) Dipole moment
Answer:
(1) Polarity of molecule
Very Short Anwer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Name any two typical elements?
Answer:
Na and Mg.
Question 2.
How many periods and groups are present in long form of periodic table?
Answer:
There are 7 periods and 18 groups.
Question 3.
An element of p-block, has 4 elecrons in outer most orbital. What is the name of element and what is its group?
Answer:
Group -14(IV - A), Silicon (14 Si).
Question 4.
In periodic table in which group and period, phosphorus is placed.
Answer:
It is placed in group-15 and period III.
Question 5.
What is the place of noble gases in periodic table?
Answer:
Noble gases are placed in zero group (18th group).

Question 6.
What is the place of halogen in periodic table?
Answer:
These are placed in group 17 (VIIA).
Question 7.
What are representative elements?
Answer:
Elements of s.hlock are collectively known as representative elements.
Question 8.
What do you mean by periodicity of properties of elements?
Answer:
It is tendency to reoccur the properties of elements at regunlr interval.
Question 9.
Rare earth Metals possess similar properties. Give reason?
Answer:
Because in these elements, electronic configuratkn of outermost shell is same.
Question 10.
Which is the last element of each period?
Answer:
Noble gas is last element of each period.
Question 11.
What do you mean by coinage metals?
Answer:
Copper, silver, and gold are coinage metal because these are used to make coins.
Question 12.
Why f-block elements are called as Inner transition elements? .
Answer:
Because in f-block elements the last electron enter the (n - 2)1 subshell.
Question 13.
What are alkaline earth metals?
Answer:
The elements whose oxide exhibit basic character are known as alkaline earth metals. Examples Ca, Sr, Ba. Mg etc.

Question 14.
Write the name of radioactive elements of group-17 and group-18.
Answer:
- Astatine (At) - Group.17
- Radon (Rn) - Group 18
Question 15.
What will be IUPAC name and symbol of element whose atomic number is 1s2?
Answer:
Its name will be Unbibium and symbol is Ubb.
Question 16.
Arrange the following elements In their reasing metallic character.
Br. Al, Mg, K
Answer:
The order will be Br < Al < Mg < K.
Question 17.
Write the name of those species which are isoelectronic to following?
(i) Na+
(ii) Cl-
(iii) K+
(iv) Rb
Answer:
(i) Ne
(ü) Ar
(iii) Ca2+
(iv) Sr+
Question 18.
Which element was discovered by Ramsey
Answer:
Krypton (Kr) and Xenon (Xe).
Question 19.
Why third period of periodic table contain 8 elements not 18 elements?
Answer:
Because third period starts with 31 electron and completed at 3p6 electron.
Question 20.
Which element possesses maximum density in periodic table?
Answer:
Osmium (Os).
Question 21.
Determine the position of an element in periodic table whose atomic number is 32?
Answer:
32 - 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2 ,3p6, 4s2, 3d10, 4p2
Block = p
Period = IV
Group = 10 + 2 + 2 = 14

Question 22.
Determine the valency and group of element whose atomic number is 119; also write its electronic configuration of outermost shell and what will be formula of its oxide?
Answer:
Group = 1
Valency = 1
Electronic configuration of outermost shell = 8s1
Formula of oxide = M2O
Question 23.
Halogens are most electronegative. Why?
Answer:
On moving left to right in period effective nuclear charge increases thus tendeney to attract electron pair increases and hence halogens are most electronegative.
Question 24.
Oxides of metals are basic in nature. Why?
Answer:
Because oxides of metals form base when react with water.
Question 25.
Oxides of non-metal are acidic in nature. Why?
Answer:
Because they form acid when react with water.
Question 26.
Why halogens are strong oxidising agent?
Answer:
Because halogens have tendency to accept electron.
Question 27.
Why alkali metals have low ionization enthalpy?
Answer:
They have large atomic size in which attraction force between nucleus and valence electron is minimum.

Question 28.
An element bas third electron gain enthalpy (EA3) zero. If it belongs to third period, then what will be its name?
Answer:
Sulphur (S).
Question 29.
Sodium is strong electropositive element. Why?
Answer:
The ionization enthalpy of sodium is Jess. Since it release an electjron and form cation so it is strong electro positive in nature.
Na → Na+ + e-
Question 30.
What is the relationship between bond length and radius given by Sumaker and Stevenson?
Answer:
Sumaker and Stevenson relationship between bond length and radius is
dA - B = rA + rB = 0.009
Where rA and rB are covalent radius of element A and
= xA - xB (differencé in electronegativities)
Question 31.
What is effective nuclear charge?
Answer:
Nuclear charge experienced by outermost electron in presence of inner electrons is known as effective nuclear charge.
Question 32.
What is the difference between effective nuclear charge in two nearest elements of a general period?
Answer:
Difference between effective nuclear charge of two nearest elements in a period is 0.65.
Question 33.
Which member of period havé smallest atomic size due to maximum effective nuclear charge?
Answer:
In a period, size of halogens is smallest because they have maximum effective nuclear charge.
Question 34.
In periodic table for trangition elements there is continuous decrease in atomic size from Sc to Mn. Why?
Answer:
Because from Sc to Mn, the nuclear attraction force increases which is more than shielding effect. So due to this there is decrease in size.
Question 35.
In periodic table, the transition elements as Mn, Fe, Co and Ni have almost same atomic size. Why?
Answer:
Because in these elements the attractive nuclear force and shielding effect is equivalent that is why Mn, Fe, Coarid Nihave same size.

Question 36.
In alkali metals which one has highest and which one has lowest ionization enthalpy?
Answer:
In alkali metals Li has highest ionization enthalpy and Cs has lowest ionization enthalpy.
Question 37.
Alkali metals are strong reducing agent and most electropositive. Why?
Answer:
Because they hate strong tendency to release electrons and have ¡nimum value of ionization enthalpy. So these are ¡sore electropositive in nature along with strong reducinagent.
Question 38.
Second electron Åain enthalpy (EA2) of halogens is zero. Why?
Answer:
The electronic configuration of halogens is ns2. np5 Hence they accept only one electron and attain stable 1 configuration ns2, np6. In this configuration it is not possible to add second electron. Therefore second electron gain enthalpy (EA2) of halogen is zero.
Question 39.
The atomic size of noble gases is more than halogens. Why?
Answer:
The size of noble gases is more than halogens because vander Wanis radius are larger than covalent radius.
Question 40.
Elements of group 1 are known as alkali metals. Why?
Answer:
Because, their oxides form base when react with water.
Question 41.
Which oxide Is highly basic in nature: Na2O, As2O3, BaO and Al2O3?
Answer:
Basic nature decreases from left to right iii period. Hence Na2O is highly basic.
Question 42.
Out of following the size of members of which group is not similar.
(1) MO and W
(2) Cd and Hg
(3) Ag and Au
(4) Zn and Cd
(5) Cu and Ag ?
Answer:
The sizes of (4) Zn and Cd and (5) Cu andAg are not similar.
Question 43.
The value of first ionization enthalpies of Al and Ga are almost same. Why?
Answer:
Because both Al and Ga have almost same size so their first ionisation enthalpies are almost same.
Question 44.
Why electron gain enthalpy of alkaline earth metals is about zero?
Answer:
they have fully filled orbital ns2. So the electron accepting capacity is least and electron gain enthalpy is almost zero.

Question 45.
The value of electron gain enthalpies of N and P are less than C and Si respectively. Why?
Answer:
Because in N and P. there is half filled orbitaIs (ns2 np3) which are more stable therefore the value of electron gain enthalpies are less than C and Si.
N < C, P < Si
Question 46.
WrIte the correct order of electron gain enthalpy of elements of third period.
Answer:
Mg < Na < P < Al < Si < Cl:
Question 47.
Write the correct order of electron gain enthalpy of elements of second period.
Answer:
Be < Li < N < B < C < O
Question 48.
Why Mg show (+2) oxidation state not +1?
Answer:
Because in Mg, the difference between first and second ionization potential is less than 11 eV.
Question 49.
Arrange the increasing order of strength of acidity of HF, HCl, HBr and HI.
Answer:
HF < HCI < HBr <HI
Question 50.
Arrange the increasing order of thermal stability of HClO. HClO2, HClO3 and HClO4.
Answer:
HCIO < HClO2 < HClO3 < HCIO4
Question 51.
WrIte the Increasing order of reactivity of F2, Cl2, Br2 and F2
Answer:
F2 < Br2 < Cl2 < F2.
Question 52.
Out . of following, which pair has comparatively more negative electron gain enthalpy?
(1) Br, Cl
(ii) F, Cl
(iii) O, S
(iv) O, O-
Answer:
(1) Cl
(ii) Cl
(iii) S
(iv) O
Question 53.
Arrange the following in increasing order ionization energy?
M(g) → M+(g)+ e, ∆ H = ∆E1
M+(g) → M2+(g) + e, ∆ H = ∆E2
M2+(g) → M3+(g) e , ∆ H = ∆E3
Answer:
lE1 < lE2 < lE3.
Question 54.
The electron gain enthalpy of S is more than O why?
Answer:
Since size of O is smaller than S due to this electron density of O is more than S. Because of more electron density on O. the coming electron experiences more repulsion and value of electron gain enthalpy decreases and electitn gain enthalpy of sulphur becomes more.

Question 55.
The size of Cl- ion Is Large than Cl atom. Why?
Answer:
Cl- ion is obtained when Cl atom accept one electron and in Cl- ion effective nuclear charge decreases. Due to this valence shell expands towards out side that is why size increases.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
In periodic table, the number of Lanthanoids and Actinoids is 14 - 14 Why?
Answer:
Both lanthanoids and actinoids are elements of f-block i.e.. in both the last electron enters in f-subshell in which maximum 14 electrons can accomodated. Therefore in lanthanides and actinides only 14 -14 elements are present.
Question 2.
In periodic table, why Ar (Atomic wt - 399) is placed before K (atomic wt -39.1)?
Answer:
In modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number of Ar is 18 while atomic number of K is 19. Therefore. Ar placed before K in periodic table. Ar is an inert gas which belongs to zero group while K is alkali metal and belongs to group -I (IA).
Question 3.
Sodium is strong metal while chlorine is strong non-metal, why?
Answer:
Sodium (ns1 ) has minimum ionisation enthalpy so due to this it has tendency to release electron and is a strong metal while electronic configuration of chlorine is ns2 np5. It has high electron gain entlialpy and tendency to accept electron. Therefore it is strong non-metal.
Question 4.
In periodic table after a regular interval the properties of elements recur. This is known as periodicity. Explain ita reason?
Answer:
In modern periodic table the elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic number, hence electronic configurations of element are repeated after regular interval which is cause of periothcity.
Question 5.
Prove that in periodic table the properties of elements recur In regular Intervals of 2,8.18, or 32.
Answer:
As we know, in modern periodic table elements are arranged in their increasing atomic number. Since in periodic table after regular interval of atomic number 2,8.18 or 32 electronic configurations are repeated, because of this the properties of elements also rader.
Question 6.
On moving down In a group oxidizing character decreases. Why?
Answer:
As we move down to the group the ionization potential decreases. Hence, electron releasing tendency increases which result decreases in oxidizing character.

Question 7.
Detennlne the group and period for the following elements whose atomic numbers are:
(1) 25 (2) 30 (3) 35 (4) 19 and (5) 12
Answer:
(1) 25 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d5, 4s2
Block - d
Period - IV
Group - 7
(2) 30 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d1, 4s2
Block - d
Period - IV
Group - 12
(3) 35 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3p6, 3d10, 4s2, 4p5
Block - p
Period - IV
Group - 17
(4) 19 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s1
Block - s
Period - IV
Group - 1
(5) 12 → 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2
Block - s
Period - Ill
Group - 2
Question 8.
Out of following write the names and atomic number of each:
1. The sixth noble gas.
2. The third alkali metal.
3. The fourth transition element.
4. The fourth halogen.
Answer:
1. Rn - atomic number - 86
2. K-atomic number - 19
3. Cr-atomic number - 24
4. I-atomic number - 53
Question 9.
Applying triads rule, with the help of following data calculate the approximate density of Cs. K = 0.868 mol-1 Rb = 1.532 g mol-1 Cs = ?
Answer:
According to triads law
\(\frac{d_{C s}+d_K}{2}=d_{R b}\)
dcs = 2dRb - dk = 2 x 1.532 - 0.868 = 2.196 g mol-1
Question 10.
Boilihg points of Kr and Rn are - 152°C and - 62°C respectively then what will be approximate boiling point of Xe?
Answer:
According to triads law.
Boiling point of Xe
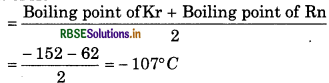
Question 11.
Arrange the following properties in order of:
1. Melting points of alkali metals.
2. Boiling points of halogens.
3. Melting points of halides of sodium.
4. Solubility of fluorides of alkali metals.
Answer:
1. Meltingpointsofalkalimetals:U > Na > K > Rb > Cs
2. Boiling points of halogens: I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
3 Melting points of sodium halides : NaF > NaCl > NaBr > NaI
4. Solubiity of fluorides: CsF > RbF > KF > NaF > UF

Question 12.
If following are electronic configurations of elements then predict the block and group of each element.
(i) 3s2,3p5
(ii) 3d10, 4s2
(iii) 3s2, 3p6, 4s1
(iv) 6s2, 4f3
Answer:
(i) p- block, group - 7
(ii) d - block, group - 12
(iii) 8 - block, group - 1
(iv) f - block, group -3
Question 13.
Write down the symbols and IUPAC names of elements with following atomic number
(1) 104
(2) 108
(3) 110
(4) 115
(5) 120
Answer:
|
Atomic number |
Symbol |
IUPAC name |
|
104 |
Unq |
Unnilquandium |
|
108 |
Unq |
Unnilocation |
|
110 |
Unq |
Unnilium |
|
115 |
Unq |
Unnunpentium |
|
120 |
Unq |
Unbinilium |
Question 14.
How Mendeleev’s periodic table was useful in discovery of new elements?
Answer:
Mendeleev left some gaps for future elements in his original periodic table and gave some information about the properties of these elements. This periodic table was very useful in the discovery of new elements and their properties resembles to the elements existed in periodic table, example: scandium (Sc), Gallium (Ga), Germanium (Ge), were invented later on.
Question 15.
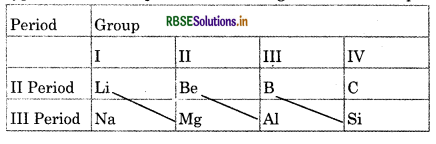
What do you means by diagonal relationship?
Answer:
The properties of 2nd period elements are similar to those elements of 3rd period which are diagonally opposite. The reason behind diagonal relationship is similar size of diagonally related atom. e.g., Li and Mg, Be and Al For example
Lithium in second period resembles to the properties of magnesium in third period, similarly Be and Al, B and Si are similar in properties. Thus, such type of relationship is known as diagonal relationship.
Question 16.
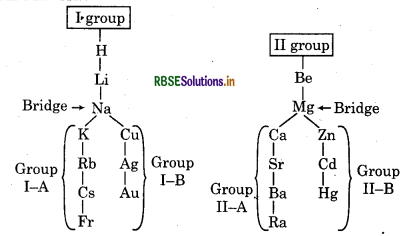
Write note on bridge elements.
Answer:
In 3rd period elements of group I to VII are considered as bridge elements. These elements act as bridge for elements of both subgroups and their properties resembles to the elements of subgroups in which they are present.
Question 17.
What are normal elements?
Answer:
The elements whose properties resemble to bridge elements called normal elements. Bridge elements are also normal elements. All the elements of subgroup A are-normal elements.
Question 18.
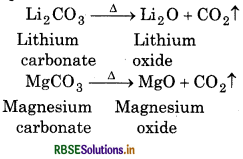
With’ which element lithium shows diagonal relationship. Write the name and symbol of that element. Describe two properties showing diagonal relationship.
Answer:
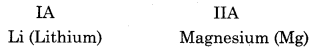
Similar properties due to diagonal relationship:
(i) They have almost similar atomic size.
(ii) They have almost similar eectronegativity.
(iii) Carbonates of both elements are thermally decomposed.
Question 19.
The valency of representative elements is equal to the number of valence electrons or can be obtained by substracting this number from 8. Explain it.
Answer:
The representative elements belong to s-and p-block. Their atom have tendency to attain the electronic configuration of noble gas. To attain noble gas configuration representative elements either lose valence electron or accept valence electron. So, valency is equal to number of valence electron or can be obtained by substracting valence electron from 8.

Question 20.
Write notes on the following:
1. Screening effect
2. Penetration effect
3. Metallic character
Answer:
1. Screening effect: It can be defined as a reduction in the effective nuclear charge on the electron cloud due to a difference in the attraction force on the electrons in the atom, It is also referred to as the screening effect.
2. Penetration effect: It describes the closeness of electrons in an orbital to the nucleus. Electrons which experience greater penetration experience less shielding and therefore experience a larger effective nuclear charge Zeff but shield other electrons more effectively.
3. Metallic character: Tendency to lose electron in chemical reactions as indicated by low ionization energies. Lower the ionisation enthalpy greater its metallic character.
Question 21.
The order of ionic radii of Na, Mg2 and is Na > Mg2 why?
Answer:
If ion have similar number of electrons then atomic size depends on number of protons. As the number of proton increases the effective nuclear charge will be
increased and atomic size will be decreased.
Ions - Na+ > Mg2+ > Al3+
No. of electrons - 10 10 10
No. of protons - 11 12 13
Question 22.
Which ionization energy of any element increases suddenly and why?
Answer:
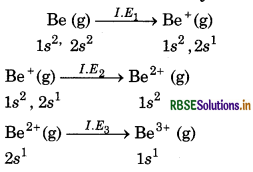
It is clear from above example that electron exist from second orbital when Be+ and Be2+ formed from Be, but when Be3+ formed from Be the electron exist from 1st orbital. As the electron is removed from filled orbit. Hence third ionisation ethalpy increase suddenly.
Question 23.
What is the difference between electronegativity and electro n gain enthalpy?
Answer:
|
Electronegativity |
Electron affinity or Electron gain enthalpy |
|
It is the tendency to attract shared pair of electron. |
It is energy released when isolated gaseous atom accepts electron. |
|
It is the property of bonded atom. |
It is the property of isolated atom. |
|
It does not has any unit. |
Its unit is kJ mol-1 or eV/atom. |
|
It attracts electron relative to atom. |
It attracts unsymmetrical electron of atom. |
Question 24.
The increasing order of reactivity for first group element is Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs where as for group 17 It is as F > Cl > Br > J. Explain it .
Answer:
The reactivity in first group elements occur due to the tendency of electron releasing which is measured by ionization enthalpy. The ionization enthalpy decreases
when we move down to the group thus reactivity of metals increases.
Reactivity of metals = \(\frac{1}{\text { Ionization enthalpy }}\)
So order will be Li< Na < Rb < Cs.
The reactivity of halogens depends on the tendency of formation, of anions on moving down in the group as value’ of electron gain enthalpy decreases so the reactivity of halogens decreases. The reactivity of non-metals electron gain enthalpy. So order will be F > Cl > Br > I.

Question 25.
Match the following elements with their properties
|
Elements |
Properties |
|
Cl |
Related to zero group. |
|
Br |
Contains 6 electrons in its valence shell. |
|
Rn |
Having minimum ionization enthalpy. |
|
O |
Element which forms compounds in large number. |
|
Xe |
Element which is liquid at room temperature. |
|
C |
Element with smaller size. |
|
Cs |
Element with higher electron gain enthalpy. |
Answer:
|
Elements |
Properties |
|
Cl |
Element with highest electron gain enthalpy. |
|
Br |
Element which is liquid at room temperature. |
|
Rn |
Element with smaller size. |
|
O |
Contains 6 electrons in its valence shell. |
|
Xe |
Related to zero group. |
|
C |
Element which form compounds in large number. |
|
Cs |
Element with minimum ionization enthalpy. |
Question 26.
What is the physical basis of arrangement in periodic table?
Answer:
The basis of arrangement in periodic table is to group the elements of similar physical and chemical properties. This idea is useful in study their character. Since this properties depend upon electronic configurations of valence shell, so the electronic configuration of valence shell in same group is similar. On moving down the group electronic configuration repeated after regular interval.
Question 27.
Why the physical and chemical properties are similar of elements placed in same group?
Answer:
The physical and chemical properties of elements are same of the elements present in same group because the electronic configuration of valence shell of there elements are same. Although their atomic size are different which increase on moving down the group. Therefore, in group elements have similar chemical properties but there is small change in their physical properties.
Question 28.
Explain the periodicty of atomic radius in a particular group or period.
Answer:
In a group, atomic radius increases on moving down the group because on moving down in group, number of shells increases and due to this the shielding effect increases. In a period, on moving from left to right atomic radius decreases because electrons fill in same shell and no new shell formed. As a result nuclear attractive force increases and atomic size decreases.
Question 29.
Consider the following species N3-, O2-, F-, Na+, Mg2+, and Al3+, find out
(i) What are similarities in them?
(ii) Arrange them in increasing order of ionic radius?
Answer:
(i) These all are isoelectronic and each has 10 electrons.
(ii) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < F- < O2- < N3-
Question 30.
The energy of electron in ground state of H-atom is - 2.1 x 10-18 J. Calculate the ionization enthalpy in terms of J mol-1
Answer:
Ioniztion enthalpy expressed for 1 mol atoms.
Hence
E(Gs) = (-2.18 x 10-18) x 6.02 x 1023
= -1.312 x 106
Ionization enthalpy = E - E(G.S)
= 0 - (-1.312 x 106 J)
= 1.312 x 106J
Question 31.
The order of actual ionization enthalpy of elements of second period is given as
Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne
Explain
(i) I.E. of Be is more than B.
(ii) I.E. of O is less than N and F.
Answer:
(i) In Be (1s2, 2s2) electrons are present in 2s orbital while in B (1s2, 2s2, 2p1 ) electrons are present in 2p orbital. 2s electrons experience more attraction force of nucleus as compared to 2p electrons therefore more energy is required to remove 2selectrons. So I.E. of Be is more than B.
(ii) Electronic configuration N is 1s2, 2s2, 2p1x, 2p1y, 2p1z in which 2p orbitais are half filled. While in O (1s2, 2s2 2px2, 2py1 , 2pz1) 2p orbital
neither half filled nor fully filled. Since half filled configuration is more stable so it is not easy to remove electron. That is why I.E. is more than O. In case of fluorine F due to small size and more nuclear charge (+ 9) its first ionizaior enthalpy is more than O. Hence ionization enthalpy of O is less than N and F.

Question 32.
Elements whose outer electronic configuration is given as below. Predict the position in periodic table:
(I) ns2 np6 for where n = 3
(ii) (n - 1)d2 ns2, where n = 4
(iii)(n - 2)f-1 (n - 1)d° 2 where n = 6
Answer:
(i) Element is present in third period and group is 16(10 + 2 + 4 = 16).
(ii) Element is present in fourth period and group is 4(2 + 2 = 4).
(iii) Element is present in sixth period and group is 3.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is modern periodic law? Describe long form of periodic table and give its advantages.
Answer:
Advantages:
- In this periodic table elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic number.
- In periodic table, there is non sub-group.
- In modern periodic table, metals and non-metals are placed separately. Metals are placed on left hand side while non-metals and metalloids are placed on right hand side.
- All isotopes are placed in a certain place because isotopes have similar atomic number.
- In this periodic table the positions of lanthanides and actinides are more clear. These are placed in bottom of periodic table
- In Mendeleev’s periodic table elements which were not following the order of increasing atomic weights are now arranged automatically in order of increasing atomic numbers.
- It is easy to understand the electronic configuration of elements.
- Division of elements in s,p,d and f-block could helpful to understand their properties.
Disadvantages:
- Position of hydrogen is not clear. It is similar to Mendeleev’s periodic table.
- No proper place is given to lanthanides and actinides in periodic table.
- Some similar elements are placed at different positions. For example Ba and Pb, Cu and Hg
Question 2.
On the basis of electronic configuration, how elements are classified? Explain.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of elements is performed on the basis of main energy level, Hund’s rule, Paulis exclusion principle and Aufbau’s rule etc,
- First period (n = 1): It starts filling of electron from is orbital. Since in s-subshell, there is one orbital so it contains only two elements i. e., hydrogen is’ and Helium is 2.
- Second period (n = 2): It starts from Li and contains two subshells as s and p. So there are four orbitais present in this period hence it has total 8 elements. First element is lithium whose electronic configuration is 1s2, 2s second is beryllium with electronic configuration 1s2,
- Third period (n = 3): It starts with Na in which electron goes upto 3s orbital. After filling electrons in 3s and 3p orbital completely. The number of elements in third period is 8 i.e., from Na to Ar.
- Fourth period (n = 4): It starts from K and electron starts to enter in 4s orbital. In this period the important thing is that 3d orbital fill first then 4p orbitais which is energetically favourable. 3d orbital forms first transition series which starts from scandium (Sc - 21) with electronic configuration 3d14s2. The fourth period ends at krypton. So there are total 18 elements in this period.
- Fifth period (n = 5): It starts from rubidium (Rb). It is similar to 4th period and it includes 4d-transition series, which starts from Yttrium (Z = 39) this period ends on Xenon. There are 18 elements in this period.
- Sixth period (n = 6) : It contains total 32 elements. In this period outer most electron enters in 6s,4f M and 6p orbitals respectively. Filling of electrons starts from 4f orbitais of (CeriumZ = 58) and ends to Lutetium (Z = 71). 4f series is also known as inner transition series or lanthanoid series.
- Seventh period (n = 7): It is similar to period 6. Electron fills in 7s, 5f, 6d and 7p orbitais. The Man Made radioactive elements belong in this period. In this electron enters in 5f series. This series is also known as 5f inner transition series or actinoid series.
Question 3.
Discuse the Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. What are its defect, also give its applications.
Answer:
In 1871, with the help of basic periodic law Mendeleev arranged the known 63 elements in a table according to the order of their increasing atomic weight. This table.
consist of two main parts.
(a) Periods - Horizontal lines
(b) Groups - Vertical linee
These are explained as follow:
(a) Periods : In Mendeleev’s periodic table there are seven horizontaL lines. These are known as periods:
- In the first period, only two elements as hydrogen (H) and Helium (He) are present. It is also known as shortest period.
- In second and third periods, there are eight elements in each penad and are refered as short period.
- In fourth and fifth periods, each contains eighteen elements and called as long period. The fourth period contains elements from Potassium (K) to Krypton (Kr) whereas fifth peri9d contains from Rubidium (Rb) to Xenon(Xe).
- The sixth period contains 32 elements and called as longest period. In this period out of 32 elements, 14 elements arc known as rare earth metals i.e. ,lanthanides. This period starts from Caesium (Cs) to Radon (Rn).
- The seventh period is the last period of the table. It contains total 32 clelments and out of them 14 elements belong to actinide series.
Defect Applications:
1. Position of hydrogen: Hydrogen is placed at group 1. however it resembles with elements of group I as well as VIlA (Ha’ogens). Thus, its position is not defined.
2. Position of rare-earth and transuranic elements: There is no suitable, place for some new elements lanthanides (rare earth metal), and actinides (transuranium elements) in periodic table.
3. Position of inert gases : After discovery of inert gases, these couldn’t arranged in periodic table because of that these gases were placed in new group of table i.e., in zero group.
4. Positions of isotopes : Isotopes have different atomic masses, but they are placed at same places.
5. Heavier Elements placed before Lighter Elements : In Mendeleev’s periodic table, some elements of heavier atomic weights are placed prior to elements of lighter atomic weights viz the increasing order of atomic weights were not obeyed. Mendeleev violates his law of periodic table that physical properties of element are periodic function of atomic weights.

Question 4.
Write short notes on
(i) Doberenier’s Triad
(ii) Newlands law of octave
(iii) Lother Meyer’s curve of atomic volume
Answer:
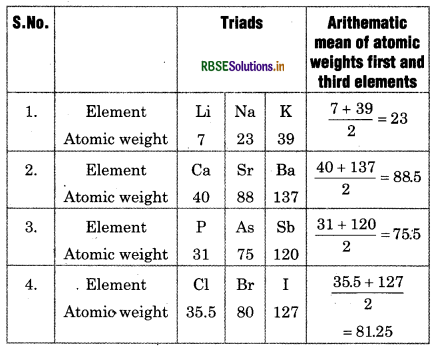
(i) Doberenier’s Triad:
In 1829, a German scientist, Johann Dobereiner found the consistency in atomic mass of similar elements. He classified the elements in group of three which possess same properties. He named this group as ‘Triads’ According to Dobereiner, the elements in, triad had similar properties and the atomic weight of middle element is very close to arithematic mean of other two elements.
(ii) Newlands law of octave:
In 1865, an English chemist John Newland profounded a new law of octaves. According to him, when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of every eighth element is similar to first one as eight note resembles the first in octaves of music. Because of that Newland called it law of octaves.
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
Musical note |
Saa |
Re |
Gaa |
Maa |
Paa |
Dhaa |
Nee |
Saa |
|
Element |
Li |
Be |
B |
C |
N |
O |
F |
|
|
Atomic weight |
7 |
9 |
11 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
19 |
|
|
Element |
Na |
Mg |
Al |
Si |
P |
S |
Cl |
|
|
Atomic weight |
23 |
24 |
27 |
28 |
31 |
32 |
35.5 |
|
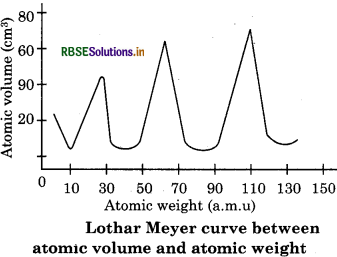
(iii) Lother Meyer’s curve of atomic volume:
In 1869, German Chemist Lothar Meyer proposed that when elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses5 similarities appear in their physical and chemical properties at regular intervals. He plotted a curve between atomic weight and atomic volume then found that element having similar properties occupied almost similar position found that elements. He observed that “the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic function of their atomic weights”.
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
An element x belongs to fourth period and group 15, then which one is correct?
(a) Its s-orbital is completely filled and d-orbital is partially filled
(b) Its s and porbtial are completely filled and 'd' is partiatiy filled
(c) Its s, porbitals are completely filled and 'd' is half filled
(d) s, d orbitals are completely filled pis half filled
Answer:
(d) s, d orbitals are completely filled pis half filled
Question 2.
Which one has highest first ionization enrgy (IE)?
(a) Na
(b) K
(c) Se
(d) Rb
Answer:
(c) Se
Question 3.
If H-atom has ionization enthalpy - 136 eV then what will be ionization potential for He+ ?
(a) 27.2 eV
(b) 54.4 eV
(c) 6.8 eV
(d) 13.0 eV
Answer:
(b) 54.4 eV

Question 4.
Which statement is correct?
(a) Second ionization energy of Mg is more than Na
(b) First ionization energy of Al is more than Mg
(c) First ionization energy of Na is less than Mg
(d) Third ionization energy of Al is less than Mg
Answer:
(a) Second ionization energy of Mg is more than Na
Question 5.
An electron species whose ionisation enthalpy is 54.4 eV is :
(a) Be2+
(b) Be3+
(c) He+
(d) H
Answer:
(c) He+
Question 6.
Which order is incorrect?
(a) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na < F (increasing atomic size)
(b) B < C < NO (increasing electron gain enthalpy)
(c) I < Br < Cl < F (increasing electron gain enthalpy)
(d) Li < Na < K < Rb (increasing metallic radius)
Answer:
(b) B < C < NO (increasing electron gain enthalpy)
Question 7.
Order of ionic radii of N3-, O2- and F- are respectively:
(a) 1.36,1.40 and 1.71
(b) 1.36, 1.71 and 1.40
(c) 1.71, 1.40 and 1.36
(d) 1.71, 1.36 and 1.40
Answer:
(c) 1.71, 1.40 and 1.36
Question 8.
Species Ar, K+ and Ca2+ are isoelectronic What will be order of radius ?
(a) Ca2+ < Ar < K+
(b) Ca2+ < K < Ar
(c) K+ < Ar < Ca2+
(d) Ar < K+ < Ca2+
Answer:
(b) Ca2+ < K < Ar
Question 9.
Among Be, B Mg and Al, which has highest second ionization energy?
(a) B
(b) Be
(c) Mg
(d) Al
Answer:
(a) B
Question 10.
Which one is arranged correctly for ionic radii ?
(a) F- < O > Na+
(b) Al3+ > Mg2+ > N3-
(c) H > He+ > H
(d) Na+ > F- > O2-
Answer:
(c) H > He+ > H
Question 11.
Which one has smallest atomic size?
(a) Na+
(b) Mg2+
(c) Cl
(d) F-
Answer:
(b) Mg2+
Question 12.
Arrange the Ca, B, S, Se and Ar in increasing order of first ionization enthalpy.
(a) Ca < S < B < Se < Ar
(b) S < Se < Ca < Ba < Ar
(c) Ba < Ca < Se < S < Ar
(d) Ca < Ba < S < Se < Ar
Answer:
(c) Ba < Ca < Se < S < Ar

Question 13.
The first ionization energy of Na is 5.1 eV. What will be electron gain enthalpy for Na* ?
(a) - 255 eV
(b) - 51 eV
(c) - 10.2 eV
(d) - 255 eV
Answer:
(b) - 51 eV
Question 14.
Which does not affect periodicity of elements?
(a) Bonding
(b) Electronegativity
(c) Ionisation energy
(d) n/p ratio
Answer:
(d) n/p ratio
Question 15.
Properties of elements are periodic function of present in nucleus:
(a) Proton
(b) Electron
(c) Neutron
(d) Meson
Answer:
(a) Proton
Question 16.
Elements with atomic number 9, 17, 35, 53, 85, are :
(a) Noble gases
(b) Halogens
(c) Heavy metals
(d) Light metals
Answer:
(b) Halogens
Question 17.
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2 belongs to which metal ?
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Fe
(d) Al
Answer:
(b) Mg
Question 18.
Which one is correct order of increasing order of ionic radius ?
(a) Li < Mg2+ < K+ < Al 3+
(b) Al3+ < Li < Mg2+ < K+
(c) Al3+ < Mg2+ < K+ < Li
(d) K+ < Al+3 < Mg+2 < Li+
Answer:
(c) Al3+ < Mg2+ < K+ < Li
Question 19.
Which order is correct for size?
(a) Ca2+ < K+ < Ar < S2- < Cl
(b) Ca2+ < K+ < Ar < Cl- < S2-
(c) Ar < Ca2+ < K+ < Cl- < S2-
(d) Ca2+ < Ar < K < Cl < S2-
Answer:
(b) Ca2+ < K+ < Ar < Cl- < S2-
Question 20.
Increasing order of radius for Br", F, O2- and S2 ions will be:
(a) Br < F < O2- < S2-
(b) S2 < O2 < F < Br
(c) F- < O2- < S2- < Br
(d) F < Br- < O2- < S2-
Answer:
(c) F- < O2- < S2- < Br

Question 21.
For given isoelectronic species, the order of increasing ionic radii will be:
(a) Cl-, Ca2+, K+, S2-
(b) S2-, Cl-, Ca2+, K+
(c) Ca2+, K+, Cl, S2-
(d) K+, S2, Ca2+, Cl-
Answer:
(c) Ca2+, K+, Cl, S2-
Question 22.
The correct order of C, N, O, F is ionization enthalpies for
(a) F < N < C < O
(b) C < NO < F
(c) C < O < N < F
(d) F < O < N < C
Answer:
(c) C < O < N < F
Question 23.
Which one is not correct?
(a) NH3 < PH3 < AsH (Acidic nature)
(b) Li+ < Na+ < K+ < Cs+ (Ionic radius)
(c) Al2O3 < (MgO < Na2O < K2O (Basicity)
(d) Li < Be < B < C (First ionization energy)
Answer:
(d) Li < Be < B < C (First ionization energy)
Question 24.
The decreasing order of first ionization energy IE1 for He, Mg, Na is He > Mg > Na. What, will be increasing order of second ionisation energy I.E for these element
(a) Na < Mg < He
(b) Mg < Na < He
(c) Mg < He < Na
(d) Na < He < Mg
Answer:
(b) Mg < Na < He
Question 25.
Which element has highest electron gain enthalpy ?
(a) Na
(b) S
(c) Mg
(d) Al
Answer:
(b) S
Question 26.
Which element has + ve electron gain enthalpy ?
(a) H
(b) Na
(c) O
(d) F
(e) Ne
Answer:
(e) Ne
Question 27.
Stable oxidation state shown by Tl is:
(a) 0
(b) +1
(c) + 2
(d) + 3
Answer:
(b) +1
Question 28.
Which one is not periodic property?
(a) Polarity
(b) Molecular volume
(c) Covalent radius
(d) Molecular mass
Answer:
(d) Molecular mass

Question 29.
Electonic configuration are given for X, Y, Z and T elements. If we short from inner orbital, which shows maximum metallic character:
(a) X = 2, 8, 4
(b) Y = 2, 8, 8
(c) Z = 2, 8, 8, 1
(d) T = 2, 8, 8, 7
Answer:
(c) Z = 2, 8, 8, 1
Question 30.
Which one is larger in size?
(a) S2-
(b) Se2-
(c) O2-
(d) Te2
Answer:
(d) Te2
Question 31.
Correct order of increasing electronegativity of I-Be, II-O, III-N and IV-Mg will be
(a) II > III > I > IV
(b) III > IV > II > I
(e) I > II > III > IV
(d) I > II > IV > III
Answer:
(a) II > III > I > IV
Question 32.
Which order is correct for increasing basic nature of oxides ?
(a) Al2O3 < MgO < Na2O < K2O
(b) MgO < K2O < Al2O3 < Na2O
(c) Na2O < K2O < MgO < Al2O3
(d) K2O < Na2O < Al2O3 < MgO
Answer:
(a) Al2O3 < MgO < Na2O < K2O
Question 33.
Which pair shows diagonal relationship?
(a) B & Si
(b) B & Al
(c) B & Ga
(d) B & C
Answer:
(c) B & Ga
Question 34.
Which pair has highest ionic radius and hydration enthalpy ?
(a) Na & Li
(b) Li & Rb
(c) K & Na
(d) Cs & Ni
Answer:
(b) Li & Rb
Question 35.
Increasing order of ionic radius of Ca, Mg, P and Cl elements is :
(a) Mg < Ca < Cl < P
(d) Ca < Mg < P < Cl
(c) P < Cl < Ca < Mg
(b) Cl < P < Mg < Ca
Answer:
(d) Ca < Mg < P < Cl
Question 36.
Which one has high ratio of cation and anion?
(a) CsI
(b) CsF
(c) LiF
(d) NaF
Answer:
(b) CsF

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter