RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Important Questions Environmental
Chemistry
Multiple Choice Type Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the following is natural source of air pollution?
(1) Motor Vehicle
(2) Fire on forest
(3) Mining
(4) War house
Answer:
(2) Fire on forest

Question 2.
Which of the following in not green house gas
(1) Carbon dioxide
(2) Methane
(3) Phosgene
(4) Nitrous Oxide
Answer:
(3) Phosgene
Question 3.
Which of the following is the effect of ozone layer?
(1) Skin cancer
(2) Increment in rate of photosynthesis
(3) Melting of polar ice
(4) Change in genetical character
Answer:
(4) Change in genetical character
Question 4.
Amount of oxygen in natural air is:
(1) Less than CO2 but more than N2.
(2) Less than CH4 but more than H2.
(3) Less than H2O vapour but more than Ar.
(4) Less than N2 but more than He and Ar.
Answer:
(4) Less than N2 but more than He and Ar.
Question 5.
What is the purest source of water?
(1) Water of pond
(2) Water of water fall
(3) Water of river
(4) Mountain ice
Answer:
(4) Mountain ice
Question 6.
Which of following affected by industrial waste?
(1) Land, air, water source
(2) Land and water source
(3) Water source and air
(4) Air and land
Answer:
(1) Land, air, water source
Question 7.
Which part of atmosphere possesses climatic change?
(1) Troposphere
(2) Strataphere
(3) Ionosphere
(4) Mesosphere
Answer:
(1) Troposphere

Question 8.
How many times human takes breath in 24 hours?
(1) about 2200 times
(2) about 22000 times
(3) about 12000 times
(4) about 280000 times
Answer:
(2) about 22000 times
Question 9.
Oxygen carrying capactiy of haemoglobin is decreased by following gas?
(1) SO2
(2) NO2
(3) CO
(4) None of above
Answer:
(3) CO
Question 10.
What is main component of photochemical smog?
(1) NO
(2) N2
(3) O2
(4) None of above
Answer:
(1) NO
Question 11.
Inflammation in eye caused by:
(1) HCN
(2) COCN2
(3) NH3
(4) H2S
Answer:
(4) H2S
Question 12.
What is the cause of ozone layer depletion?
(1) Use of CFCs
(2) Use of Chloroform
(3) Use of halogen
(4) All of above
Answer:
(4) All of above
Question 13.
Which of the following gas combines with haemoglobin rapidly?
(1) CO
(2) CO2
(3) NO
(4) NO2
Answer:
(1) CO

Question 14.
Ozone layer protects earth from which rays?
(1) UV rays
(2) IR rays
(3) Cosmic rays
(4) Caser rays
Answer:
(1) UV rays
Question 15.
Air Pollution can be decreased by:
(1) Spraying water
(2) Use of vehichle according to URO norms
(3) Plantation of green tree
(4) All of the above
Answer:
(4) All of the above
Question 16.
What is the main sink of marbel industry?
(1) Acid rain
(2) Earthquake
(3) Metal pollution
(4) Cyclone
Answer:
(3) Metal pollution
Question 17.
Which of following hydrocarbon pollute most?
(1) CH4
(2) C2H6
(3) CgHg
(4) C4H10
Answer:
(1) CH4
Question 18.
Who the nobel prize winner in 2005 in field of environment?
(1) Vej Chauwin
(2) R.H. Groues
(3) R.P. Shork
(4) All of above
Answer:
(4) All of above
Question 19.
Most cold field of atmosphere is?
(1) Stratosphere
(2) Troposphere
(3) Mesosphere
(4) Ionosphere
Answer:
(2) Troposphere
Question 20.
Which diseases caused by ozone layer depletion?
(1) Skin Cancer
(2) Bone Cancer
(3) Brain Cancer
(4) Asthma
Answer:
(1) Skin Cancer
Question 21.
What is the size ofparticles formed by H2SO4?
(1) 50 to 100 nm
(2) 100 to 200 nm
(3) 500 to 100 nm
(4) 1000 to 10000 nm
Answer:
(4) 1000 to 10000 nm
Question 22.
Amount of CO is controlled by following method:
(1) Plantation of Green Plant
(2) Spraying of Water
(3) Plantation of Eukalyptus
(4) Development of algae
Answer:
(3) Plantation of Eukalyptus
Question 23.
Which particle cause poisonous effect?
(1) Smoke
(2) Ash
(3) Fog
(4) Smog
Answer:
(2) Ash
Question 24.
What is the cause of ozone layer depletion in Antarctica?
(1) Chlorine Nitrate
(2) SO2
(3) CO2
(4) O3
Answer:
(1) Chlorine Nitrate
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is meant by word atmosphere?
Answer:
Atmosphere’ word is consist of two word atom and sphere. Hence its meaning is envelope of gases.
Question 2.
What is the two main types of atmosphere?
Answer:
There are two types of atomosphere.
- Physical atmosphere
- Biotic atmosphere
Question 3.
Which gases is found in natural air?
Answer:
In natural air nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%) carbon dioxide (0.03%) and other inert gases is found.

Question 4.
Categorise the material that is cause of water pollution.
Answer:
There are four type of material that caused water pollution.
- Industrial waste
- Sewage
- Dead body of organism
- Mining and transportation
Question 5.
Define pollution.
Answer:
Accumulation of extra undesirable substance that will cause unwanted change in natural atmosphere is called pollution.
Question 6.
What happens if CO2 finished from atmosphere?
Answer:
If CO2 is finished from atmosphere then photosynthesis process becomes stops and oxygen will not produced.
Question 7.
Which pollution is caused by fossil fuel?
Answer:
Air Pollution.
Question 8.
Which energy is formed by green plant from light energy?
Answer:
Chemical energy which is stored in the form of food.
Question 9.
Write various parts of earth atmosphere.
Answer:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Ionosphere
Question 10.
Name the diseases that is caused by air pollution.
Answer:
Due to air pollution, people can suffer from inflamation in respiratory tract and lungs, chest congestion, some throat, tuberculosis, asthma and other diseases.
Question 11.
Due to colouring of cloth in Rajasthan, ground water also becomes coloured. Where water becomes coloured in Rajasthan ?
Answer:
In Pali and Badodara.
Question 12.
What is sewage water?
Answer:
Domestic water which contain domestic waste product is known as sewage water.
Question 13.
Define B.O.D.
Answer:
Amount of dissolved oxygen required by microorganism for complete oxidation of organic and inorganic compound, is known as B.O.D. of water.
Question 14.
Which fuel is used in motor vehicle in place of petrol and diesel?
Answer:
In motor vehicle CNG (Compressed natural gas) is used in place of petrol and diesel.

Question 16.
Name two pollutants of air which contain sulphur.
Answer:
H2S, SO3.
Question 17.
What is the point source of water pollution?
Answer:
Those source which flows out their aquatic pollutant directly to water known as point source.
Question 18.
Name the material which can be recycled?
Answer:
- Plastic
- Metal
- Polythene.
Question 19.
What happens if earth atmosphere do not contain green house gases ? Explain.
Answer:
If earth atmosphere do not contain green house gases like CO2 then temperature of earth is reduced. Plant is not able to photosynthesis (due to absence of CO2). Due to absence of plant, humans also do not exist.
Question 20.
Write three characterstics of drinking water.
Answer:
- Drinking water should be transparent, colourless, and odourless.
- Drinking water should contain adequate amount of dissolved oxygen.
- Drinking water should be free from harmful chemicals and bacteria.
Question 21.
Which chemical causes ozone layer depletion?
Answer:
Mainly airconditioners, Fire extinguishers, solvents etc. are the source and chemical like chlorofluoro carbons, halogen, chloroform, NO mainly causes ozone layer depletion.
Question 22.
Smoke produced from combustion of fuel like petrol are dangerous? Give reason.
Answer:
Smoke produced from combustion of fuel like petrol contains lead particle which causes paralysis asthma, osteoporosis, disease of mind etc. Hence smoke of fuel is dangerous.
Question 23.
What is the harmful effect of ozone layer depletion?
Answer:
Due to ozone layer depletion sunlight rays reaches at earth which cause harm to eye and immunity. More over it causes skin cancer.
Question 24.
What is chlorosis?
Answer:
Due to presence of SO2 in air the process of production of chlorophyll decreases. It is known as chlorosis.
Question 25.
What is London smog?
Answer:
London smog is produced due to accumulation of H2SO4 over suspended particles of atmosphere.
Question 26.
What is the source of ozone in photochemical smog?
Answer:
During photochemical decomposition O atom combines with O2 to form O3.
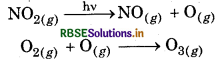
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
How does soil pollution affect human life?
Answer:
Effect of Soil Pollution on Human Life : Soil pollution affects not only the quality of soil but also affect animal life, plant life. Due to soil pollution crop accept harmful substances from soil. These harmful substances reaches to human causes many diseases. Example : Chlorinated hydrocarbon (DDT) do not dissociate- in water and reaches the plant by the absorption of water and minerals. These pollutants reach at human body through food chain and causes many diseases. Due to soil pollution fertility of soil decreases which causes decrease of the production of crops.
Question 2.
Explain the reaction that causes ozone layer depletion.
Answer:
Chlorofluoro-carbons (CFCs) are responsible for ozone layer depletion which are formed by human activities. Chlorofluoro-carbons are used in refrigerators, air conditioners.
During ozone layer depletion following reactions takes place:
(1) CF2Cl2 → Cl + CF2Cl
(2) O3 + Cl → ClO + O2
(3) ClO + O → Cl + O2
The above reactions show that chlorine free radical produced from chlorofluoro-carbon can destroy many molecules of ozone. Nitric oxide, which is produced from supersonic jet plane also destory ozone layer.
NO + O3 → NO2 + O2

Question 3.
What is acid rain? Give two harmful effect of acid rain.
Answer:
Oxide of nitrogen and sulphur present in air combines with rain water form nitric acid and sulphuric acid. These acid comes at earth along with rain. This rain is called acid rain.
Harmful effects of acid rain:
- It makes soil acidic. Hence fertility of soil decreases.
- It causes detereoration of old historical monuments buldings and statues.
Question 4.
What is the difference between smog and photo-chemical smog ?
Answer:
|
Normal Smog |
photochemical smog |
|
1. Normal smog i8 formed by condensation of SO2 vapour, over carbon particle in cold atmosphere. |
This smog is formed by1 chemical reaction of hydrocarbon and photochemical degradation of nitrogen oxide. |
|
2. This smog is found in the form of smoke or gauze. |
Here smoke or gauze is formed. |
|
3. This smog is formed during winter when there is low temperature at morning. |
This smog is formed in sunlight hence clean weather is favourable for this smog. |
|
4. This is known as London smog. |
This is known as Los angles smog. |
Question 5.
Explain two ways by which non biodegradable materials affect environment.
Answer:
Non biodegradable materials affect environment by following ways:
- Non biodegradable substances pollute the environment for a long time. This affects the recycling of materials.
- Many pesticides and insecticides reach to the bodies of living beings (human) through food chain cause harm to living bodies.
Question 6.
How domestic waste used as fertilizer?
Answer:
Domestic waste contains both biodegradable and non-biodegradable components. If we separate both components of waste. Non biodegradable separates like plastic, glass, metal can be recycled while biodegradable wastes are buried in open ground. Biodegradable waste contains organic matter which form compost.
Question 7.
Explain the various methods to control soil pollution.
Answer:
To control soil pollution the following methods are used:
- There should be ban on throwing harmful chemicals to soil without treatment.
- Water which contain industrial effluents should not be thrown at fields.
- Minimum use of pesticides in agriculture should be promoted.
- Organic and biotic fertilizer (manure) should be used in agriculture.
- There should be ban on cutting of trees and uncontrolled catlle grazing.
- Plantation should be promoted to control soil erosion.
- Waste should not thrown on land but it is used for electricity production.
Question 8.
You have made pits for compost at agricultural land, explain this process in term of foul smell, flies and recycling of waste.
Answer:
If waste is not converted to compost then it goes to drain. It is eaten by some cattle. Method of manufacturing of compost produce foul smell. To reduce foul smell and flies it should be covered with soil where waste is converted into compost then it should be removed from the soil.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is smog? How it can classified? Give the various harmful effects of smog.
Answer:
Smog: The word smog is derived from smoke and fog. Thus is the most common example of air pollution that occurs in many places which has low temperature.
There is two types of smog:
1. Reducing Smog: It is a mixture of smoke, fog and sulphur dioxide. Chemically it is a reducing mixture and so it is also called as reducing smog. Classical smog
occurs in cool humid climate. The effect of reducing smog is more after sunrise than before sunrise. The reason behind this is that SO2 is oxidized to SO3 in the presence of sunlight. SO3 reacts with water and forms aerosol of sulphuric acid which combines with Carbon particles of smoke and form smog.
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
2. OxIdizing Smog or Photochomical Smog: Photochemical smog occurs in warm, dry and sunny climate. Chemically, it is xidizing in nature. Photochemical smog has high concentration of oxidizing agents and is, therefore, called as oxidizing smog.

Question 2.
Write a short note on the following:
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Green house effect
(d) Ozone hole
Answer:
(a) Troposphere: It is lowest layer of atmosphere. It spreads 10 km above sea level which contain oxygen, nitrogen and other gases. The change in climate found in troposphere.
(b) Stratosphere: It is the second layer after troposphere. It spreads from 10 to 50 km above sea level. In stratosphere temperature increases. Entire water vapour and about 80 percent weight of air are found in this layer. Ozone layer is also found in stratosphere. Ozone layer absorbs ultra violet rays of sun. Due to presence of pollutants degradation of ozone layer also found in stratosphere.
(c) Green House Effect: Gases like CO2 and CH4 produced by combustion of fossil fuel, trap heat radiation. Hence the temperature of earth increases. It is known as green house effect. Due to this climate changes and level of sea increases due to increase in temperature glaciers melts which causes flood.
(d) Ozone Hole: The process of decrease in thickness of ozone layer by the reaction of hydrocarbon, freons or gaseous plastic wastes, known as ozone hole formation. Due to ozone hole formation ozone layer can not stop harmful ultra violet rays coming from sun. Hence temperature of earth continuously increases.
Question 3.
How acid rain affect statues and monument?
Answer:
Due to acid rain, acid deposited at earth surface due to acidic nature oxide of nitrogen and sulphur flows with particles of atmosphere suspended in liquid form in water or in form of ice. Oxide of nitrogen and sulphur react with water make main contribution in acid rain, because polluted air contain particles which induce oxidation.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(aq)
4NO2(g) + O2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 4HNO3(aq)
This acidic rain destroy the statues and monuments follow. It react with marble (CaCO3).
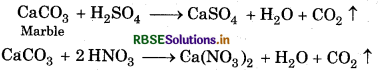
Question 4.
Write short note on following:
(A) Biochemical oxygen demand (B.O.D.)
(B) Chemical oxygen demand (C.O.D.)
Answer:
(A) Biochemical oxygen demand (B.O.D.):
There is adequate amount of organic and inorganic compounds in polluted water. Organic compound is oxidised by the oxygen present in air. Hence amount of dissolved oxygen which is required for the oxidation of organic and inorganic compounds is known as biochemical oxygen demand.
(B) Chemical oxygen demand: To calculate chemical oxygen demand use react water with known amount of oxidant. This oxidant oxidise organic and inorganic compound. We calculate remaining K2Cr2O7 by using Mohr’s s1t. We calculate the amount of oxygen used for oxidation. This value is known as chemical oxygen demand (COD).
Question 5.
Briefly explain chemical reaction of sulphur and its oxides present in atmosphere.
Answer:
Reaction of sulphur and its oxides are as follows:
(1) SO2 is harmful pollutant oxide. SO2 converts to SO3 in presence of sunlight.
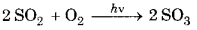
(2) SO3 reacts with H2O to form sulphuric acid.
SO3 + H2O → HSO4
(3) Sulphuric acid reacts with NH3 to form ammounium sulphate.
HSO4 + NH3 → (NH4)2SO4
Due to H2SO4 acid rain is formed. While SO2 mixed with smoke particle and (NH4)2SO4 form smog with water fog.
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the following are not constituents of photochemwal smog?
(1) Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN)
(2) Chiorofuoro carbon (CFCs)
(3) Ozone (O3)
(4) Acrolins
Answer:
(2) Chiorofuoro carbon (CFCs)
Question 2.
Bhopal gas tragedy is caused by which gas in 1984?
(1) Sodium monoxide
(2) Sodium thiocyanate
(3) Potassium isocyanate
(4) Methyl isothiocynate
Answer:
(4) Methyl isothiocynate

Question 3.
DDT is:
(1) a green house gas
(2) a ferlilizer
(3) a biodegradable pollutant
(4) a non biodegradable pollutant
Answer:
(4) a non biodegradable pollutant
Question 4.
Which one of the following statements Is not true about photorhemical smog?
(1) In phot.ochemical smog there is not role of carbon monoxide,
(2) Photochemical smog is reducing in nature
(3) Photochemical reaction related to solar energy is cause of photochemical smog
(4) Photochemical smog is not the cause of inflammation m eyes and throat
Answer:
(2) Photochemical smog is reducing in nature
Question 5.
Main pollutant which cause degradation of ozone layer is:
(1) SO2
(2) NO and chiorofluorocarbon
(3) CO2
(4) CO
Answer:
(2) NO and chiorofluorocarbon
Question 6.
Excess nitrate in drinking water cause:
(1) Methemoglobinemia
(2) Damage of kidney
(3) Damage of liver
(4) Ceucoderma
Answer:
(3) Damage of liver
Question 7.
Which of following is not true statement?
(1) Sulphur. nitrogen and carbon dioxides are air pollutans.
(2) pH of drinking water is 5.5.5.9
(3) 1f DO la below 6 ppm than growth of fishes is more
(4) ROD of pure water must be less than 5 ppm
Answer:
(3) 1f DO la below 6 ppm than growth of fishes is more
Question 8.
Compounds present in thermosphere are
(1) O+2, O+ NO+
(2) O3
(3) N2, O2, CO2, H2O
(4) O3, O+2, O2
Answer:
(1) O+2, O+ NO+
Question 9.
Carbon monoxide is harmful to human because:
(1) It forms carbolic acid
(2) It forms excess CO2
(3) It is carcinogenic
(4) It combines rapidly with haemoglobin compared to oxygen
Answer:
(3) It is carcinogenic
Question 10.
Which of following is not true?
(1) Green house effect is responsible for heating of earth surface
(2) Ozone layer stops infrared rays of sun from coming to earth.
(3) Acid rain mainly caused by nitrogen and sulphur oxide
(4) Chlorofluorocarbons are responsible for ozone layer depletion
Answer:
(2) Ozone layer stops infrared rays of sun from coming to earth.
Question 11.
Eutrophication ¡s caused by:
(1) Increment in concentration of pesticide in water
(2) Increment in concentration of fluonde ions
(3) Decrement in disolved oxygen due to phosphate pollutants
(4) Attack of dioxyacetyl nitrate on small leaves of plants
(5) Increment of radioactivity in water
Answer:
(1) Increment in concentration of pesticide in water
Question 12.
Which of the following ¡s not a method for reducing global warming?
(1) limited use of fossil fuel so that less production of green house gases
(2) Increment in area of forest so that more CO2 used in photosynthesis.
(3) Promoting the use of air conditioner and refrigerators.
(4) Reduciag use of nitrogenous fertilizers in agriculture so that N2O is produced.
(5) Developing the option for chlornfluoro-carhons
Answer:
(3) Promoting the use of air conditioner and refrigerators.

Question 13.
Which of the following is most poisonous?
(1) CO
(2) CO2
(3) C
(4) SQ
Answer:
(4) SQ
Question 14.
Which of the statement is false?
(1) CO is main atmospheric pollutant
(2) All pollutants are not waste
(3) Water pollution is caused by Na and Mg
(4) Lichen is affected by SO2
Answer:
(1) CO is main atmospheric pollutant
Question 15.
Which nf the following is secondary pollutant?
(1) SO2
(2) CO
(3) O
(4) NO2
Answer:
(3) O
Question 16.
The substance in motor vehicle exhaust causes mental disease Is:
(1) NO2
(2) SO2
(3) Pb
(4) Hg
Answer:
(3) Pb
Question 17.
Which of the following is not air pollutant?
(1) CO
(2) CO2
(3) SO2
(4) Hydrocarbon
Answer:
(1) CO
Question 18.
Green house effect is caused by?
(1) Ozone layer in atmosphere,
(2) Infra red rays of earth.
(3) Moisture of atmosphere.
(4) Layer of CO2 atmosphere.
Answer:
(4) Layer of CO2 atmosphere.
Question 19.
Which of the following is the cause of photochentical smog
(1) O3, PAN and CO
(2) HC, NO and PAN
(3) O2. PAN and NO2
(4) O3, PAN, NO3
(5) O PAN and NO2
Answer:
(5) O PAN and NO2
Question 20.
Which pollution is caused by Pb?
(1) Soil pollution
(2) Air pollution
(3) Radioactive pollution
(4) All of above
Answer:
(1) Soil pollution
Question 21.
What is related with photochemical smog?
(1) Soil
(2) Water
(3) Both(1)and(2)
(4) Air
Answer:
(3) Both(1)and(2)
Question 22.
Which country is responsible for most green house gases?
(1) Russia
(2) Germany
(3) Brazil
(4) USA
Answer:
(2) Germany
Question 23.
Photochemical smog alway. contains:
(1) O
(2) CH4
(3) CO
(4) AH of above
Answer:
(1) O
Question 24.
Primary production decreases by which process?
(1) destruction of tissues of leaves
(2) falling of immature leaves
(3) decrement of crop production
(4) all of the above
Answer:
(4) all of the above
Question 25.
What is most harmful effect of radioactive pollution?
(1) Genetic change
(2) Hepatitis
(3) Polio
(4) T,B.
Answer:
(2) Hepatitis
Question 26.
WhIch of following is biodegradable pollutant?
(1) DDT
(2) sheets of aluminium
(3) domestic wastes
(4) salts of Mercury
Answer:
(1) DDT
Question 27.
MeanIng of (BOl) Is:
(1) Biological organism death
(2) Biochemical organic matter decay
(3) Biotic oxygen demand
(4) Biochemical oxygen demand
Answer:
(4) Biochemical oxygen demand
Question 28.
In 2002 AD concentration of CFCs increases by:
(1) 368 ppm
(2) 1750 ppm
(3) 261 ppt
(4) 326 ppb
Answer:
(3) 261 ppt

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter