RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Important Questions Hydrocarbons
Multiple Choice Type Questions:
Question 1.
Reagent used in Sabatier Senderen reduction is.
(a) H2/Ni
(b) Zn-Cu/C2H5OH
(c) HI/P
(d) LiAlH4
Answer:
(d) LiAlH4

Question 2.
Which carbide is used in the formation of methane?
(a) CaC2
(b) Mg2C3
(c) Al4C3
(d) B4C
Answer:
(c) Al4C3
Question 3.
On increasing number of carbon atoms in carbon chain the boiling point of alkane:
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) unaffected
(d) may increase or decrease
Answer:
(a) increases
Question 4.
Which of the following on hydrolysis give methane?
(a) Al4C3
(b) CaC2
(c) nC3H7MgBr
(d) Dry ice
Answer:
(a) Al4C3
Question 5.
Methane and ethane are formed in differen steps from:
(a) C2H4
(b) CH3I
(c) CH3OH
(d) C2H5OH
Answer:
(b) CH3I
Question 6.
The best method for the formation methane:
(a) Liquification of natural gas
(b) Wurtz reaction
(c) Reduction of CH2Cl2
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Wurtz reaction

Question 7.
The bond angle in CCl4 is:
(a) 90°
(b) 109°
(c) 120°
(d) 180°
Answer:
(b) 109°
Question 8.
How many secondary carbon atoms are present in isopentane?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(a) 1
Question 9.
Which of the following compound does not dissolve on heating with conc. H2SO4?
(a) Ethene
(b) Benzene
(c) Hexane
(d) Aniline
Answer:
(c) Hexane
Question 10.
The reactivity order of different hydrogen atoms attached with different carbon atoms of alkane is:
(a) 3° 2° 1°
(b) 1°> 2° > 3°
(c) 3° 1° 2°
(d) 2° 1° 3°
Answer:
(a) 3° 2° 1°
Question 11.
Formation of alkane by the reaction of alkyl halide with zinc is known as :
(a) Frankland reaction
(b) Cannizzaro reaction
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) Kolbe reaction
Answer:
(a) Frankland reaction

Question 12.
When methyl bromide is heated with zinc in a closed vessel then we get:
(a) methane
(b) ethane
(c) ethene
(d) methanol
Answer:
(b) ethane
Question 13.
In C2H6 the bond angle H-C-H is :
(a) 90°
(b) 109.5°
(c) 120°
(d) 180°
Answer:
(b) 109.5°
Question 14.
Which of the following on reaction with Grignard reagent form hydrocarbon?
(a) CH3CH2OH
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3COCH3
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) CH3CH2OH
Question 15.
Which of the following compound mainly show displacement reaction?
(a) alkane
(b) alkene
(c) alkyne
(d) all
Answer:
(a) alkane
Question 16.
Which of the following show cracking?
(a) Alkane
(b) Petroleum
(c) Ether
(d) Benzene
Answer:
(a) Alkane

Question 17.
The compound, whose aqueous solution on electrolysis give ethane, is:
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Acetamide
(c) Potassium acetate
(d) Ethyl acetate
Answer:
(c) Potassium acetate
Question 18.
An example of halogenation of alkane is:
(a) electrophilic substitution
(b) nucleophilic substitution
(c) free radical substitution
(d) oxidation
Answer:
(c) free radical substitution
Question 19.
The name of given reaction is
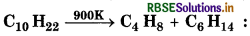
(a) Alkylation
(b) Cracking
(c) Dehydrogenation
(d) Distillation
Answer:
(b) Cracking
Question 20.
The organic product formed from methyl magnesium bromide and ethyl alcohol is:
(a) Methane
(b) Ethane
(c) Propane
(d) Butane
Answer:
(a) Methane
Question 21.
The product formed where 1-butene reacts with HBr is presence of methyl magnesium bromide is:
(a) 1-bromo butane
(b) 2-bromo butane
(c) 1,2-dibromo butane
(d) n-butane
Answer:
(a) 1-bromo butane
Question 22.
The reaction in which alkene forms alcohol on reaction with water is known as:
(a) hydrogenation
(b) hydration
(c) hydrolysis
(d) condensation
Answer:
(b) hydration

Question 23.
Which of the following isomerism is not shown by alkene?
(a) Chain isomerism
(b) Geometrical isomerism
(c) Metamerism
(d) Position isomerism
Answer:
(c) Metamerism
Question 24.
The general formula of alkene is:
(a) CnH2n + 1
(b) CnH2n
(c) CnH2n + 2
(d) CnH2n
Answer:
(c) CnH2n + 2
Question 25.
Which type of hybridisation is present in 1-2 carbon of propylene?
(a) sp
(b) sp2
(c) sp3
(d) None
Answer:
(d) None
Question 26.
The C-C-C bond angle in CH3-CH=CH2 is:
(a) 90°
(b) 109.5°
(c) 120°
(d) 180°
Answer:
(c) 120°
Question 27.
Which of the following alkene show geometrical isomerism?
(a) 1-butene
(b) 2-butene
(c) 2-methyl propene
(d) Propene
Answer:
(b) 2-butene
Question 28.
The compound formed on dehydrohalo-genation of ethylene dibromide is:
(a) Ethene
(b) Ethyne
(c) Butyne
(d) Propyne
Answer:
(b) Ethyne

Question 29.
Ethylene is the member of series:
(a) alkyne
(b) olefins
(c) paraffin
(d) amine
Answer:
(b) olefins
Question 30.
Whose dehydrase form ethylene?
(a) CH3OH
(b) C2H5OH
(c) propyl alcohol
(d) ethyl acetate
Answer:
(b) C2H5OH
Question 31.
When ethyl alcohol is heated with conc. H2SO4 then we get:
(a) CH3COOC2H5
(b) C2H6
(c) C2H4
(d) C2H2
Answer:
(b) C2H6
Question 32.
Which decolourise aqueous KMnO4 solution?
(a) C3H8
(b) C2H4
(c) CH4
(d) CCl4
Answer:
(b) C2H4
Question 33.
The reaction of ethylene with hydrogen bromide is an example of:
(a) Addition reaction
(b) Condensation reaction
(c) Substitution reaction
(d) Polymerisation reaction
Answer:
(a) Addition reaction

Question 34.
The compound which easily decolourise potassium permanganate solution is:
(a) CH3CH3
(b) C10H18
(c) (CH3)4
(d) CH3CH
Answer:
(d) CH3CH
Question 35.
CH3CH = CHCHO can be oxidised CHCH3 into CH3CH=CH-CH by the action of:
(a) Alkaline KMnO4
(b) Ammonical silver nitrate
(c) Selenium dioxide
(d) Osmium tetraoxide
Answer:
(b) Ammonical silver nitrate
Question 36.
The angle H-C-H in ethene is:
(a) 90°
(b) 60°
(c) 180°
(d) 120°
Answer:
(d) 120°
Question 37.
In ethylene C-C bond has:
(a) Тwо л-bоnds
(b) One sigma and one л-bond
(c) Two sigma bonds
(d) One sigma and two л bonds
Answer:
(b) One sigma and one л-bond

Question 38.
How many structural isomers are possible in C4Hg?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
Question 39.
How many isomers 2-butene have?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 40.
The C-H bond energy in ethane, ethylene and acelylene series is :
(a) Similar in all the three compounds
(b) Maximum in ethane
(c) Maximum in ethylene
(d) Maximum in acelylene
Answer:
(d) Maximum in acelylene
Question 41.
A gas do not give any precipitate when passed through ammonical AgNO3 solution, but can decolourise alkaline solution. The gas is KMnO4
(a) C2H6
(b) C2H4
(c) C2H2
(d) C3H8
Answer:
(b) C2H4

Question 42.
Nitration of benzene is :
(a) Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(b) Electrophilic substitution reaction
(c) Nucleophilic addition
(d) Electrophilic addition
Answer:
(b) Electrophilic substitution reaction
Question 43.
Number of σ and π-electrons in benzene are:
(a) 24-σ and 6 - л electrons
(b) 12-σ and 6-π electrons
(c) 12-σ and 3- л еlectrons
(d) 24-σ and 3 - π electrons
Answer:
(c) 12-σ and 3- л еlectrons
Question 44.
Which of the following strongest meta directing group?
(a) -NO2
(b) -SO3H
(c) -CHO
(d) -COOH
Answer:
(a) -NO2
Question 45.
Number of double bonds in BHC is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 0
Answer:
(d) 0

Question 46.
The work of dry aluminium chloride Friedel Craft reaction is:
(a) To absorb water
(b) To absorb HCl
(c) To create electrophilic
(d) To create nucleophilic
Answer:
(c) To create electrophilic
Question 47.
The mixture of sodium benzoate sodalime on heating give:
(a) Benzene
(c) Sodium benzoate
(b) Methane
(d) Calcium benzoate
Answer:
(a) Benzene
Question 48.
In the reaction,
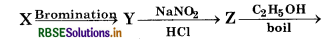
Tribromobenzene, here 'X' is:
(a) Benzoic Acid
(b) Salicylic acid
(c) Phenol
(d) Aniline
Answer:
(d) Aniline
Question 49.
Phenol on distillation with Zn-Power gives :
(a) C6H6
(b) C6H5-C6H5
(c) C6H12
(d) C6H5-0-C6H5
Answer:
(a) C6H6
Question 50.
The most reactive compound for electrophilic nitration is:
(a) Benzene
(b) Nitrobenzene
(c) Benzoic Acid
(d) Toluene
Answer:
(d) Toluene
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
All the bonds in methane are same. Why?
Answer:
Because the carbon atom in methane is sp hybridised and all the C-H bonds are formed b overlapping between sp3-s orbitals.

Question 2.
Yet the electronegativity of F is higher tha Cl, but the dipole moment of CH3Cl is highe than CH3F. Why?
Answer:
Because the bond length of C-Cl bond is highe than C-F bond.
Question 3.
Neopentane give only one type of mon substituted isomer. Why?
Answer:
Because all the hydrogen atom (H) present i neopentane are similar i.e., 1° type.
Question 4.
Write the formula of n-pentane, isobutane and neopentane.
Answer:
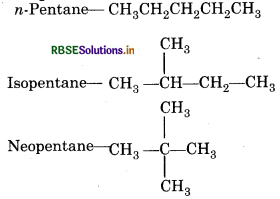
Question 5.
Represent 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogen atoms in 2-methyl butane.
Answer:
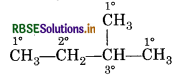
Question 6.
What is decarboxylation?
Answer:
Removal of CO2 from a compound is known as decarboxylation.
Question 7.
Write the name of gaseous products formed at anode on electrolysis of aqueous solution of sodium acetate.
Answer:
On electrolysis of aqueous solution of sodium acetate we get C2H6 and CO2 gas at anode.
Question 8.
Which have higher boiling point among n-pentane and iso-pentane and why?
Answer:
n-pentane has higher boiling point because it - has higher surface area.
Question 9.
Why any alkane is reformed?
Answer:
To increase the octane number of any alkane, it ) is reformed. Reformation is done at very high temperature and high pressure (28-50 atm).

Question 10.
How many secondary carbon atoms are present in 2, 2-dimethyl butane?
Answer:
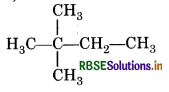
Question 11.
The reactivity of alkane is lower than alkene and alkyne. Why?
Answer:
In alkanes the C-C and C-H bonds are non-polar in nature because of this reason the n attacking species can not attack on it. While in case of r double and triple bond л-electrons present on it, can attract the attacking species E easily. Hence the reactivity of alkane is lower than alkenes and alkynes.
Question 12.
Write the name of reagent which is used in decarboxylation reaction of -COOH group.
Answer:
Soda lime (NaOH + CaO)
Question 13.
Ethene can be dried by concentrated H2SO4 but amine cannot, why?
Answer:
Because ethene is absorbed by conc. H2SO4 and A ethylene hydrogen sulphate is formed.
Question 14.
Write the name of products formed by the cracking of n-butane.
Answer:
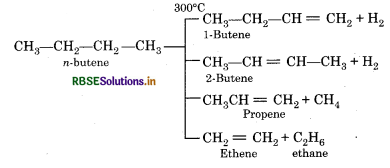
Question 15.
When secondary butyl bromide is treated with alcoholic KOH then different types of alkenes are formed. Write the name of these alkenes and which one is major.
Answer:
When secondary butyl bromide is heated with Ar alcoholic KOH then the mixture of 1-butene and be 2-butene is formed in which 2-butene is major.
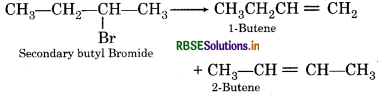

Question 16.
Write how much s-character is present in = C-H (sp-s) bond of alkynes?
Answer:
50% s-character.
Question 17.
How many unhybridised p-orbitals are present on each carbon atom of triple bond.
Answer:
Two unhybridised p-orbitals i.e., p, and p2.
Question 18.
How many bonds are formed by lateral or sidewise overlapping of the two unhybridised p-orbitals of carbon atoms having triple bond?
Answer:
Two-л bоnds are formed.
Question 19.
What type of three dimentional position of both the bonds present in triple bond have?
Answer:
Both the p-orbitals present on each carbon form 90° with respect to each other and with respect to sp-hybridised orbitals.
Question 20.
All the four lobes of both T-bonds exist in which form about the internuclear axis?
Answer:
Electron cloud between two carbon atoms is Ar cylindrically symmetrical about the internuclear axis.
Question 21.
Which compound is formed when CHI is reacted with silver?
Answer:
Acetylene.
Question 22.
What compound is formed when acetylene is passed through ammonium silver nitrate solution?
Answer:
Silver acetylide is formed.
Question 23.
Which bipolymerisation compound is formed of acetylene?
Answer:
Vinyl acetylene.
Question 24.
Which compound is formed by tripolymerisation of propyne ?
Answer:
Mesitylene.
Question 25.
What is the name of artificial rubber?
Answer:
Neoprene rubber.
Question 26.
Which compound is formed by carboxylationof acetylene?
Answer:
Acrylic Acid
Question 27.
Which compound is formed when the oxidation of C2H2 is done with chromic acid?
Answer:
Acetic acid

Question 28.
Yet the bond energy of C-H bond in acetylene is higher than C-H bond of alkane and alkene, but acetylene is acidic, why?
Answer:
The polarity of C-H bond of acetylene is higher cause this bond is formed by overlapping of sp ybridised orbitals and s-orbitals, and sp-hybridised bitals are more electronegative than sp3- and sp ybridised orbitals.
Question 29.
Ortho and para directing group increases the activity of nucleus of benzene. Why?
Answer:
These groups are electron releasing hence their esence increases the electron density on the nzene nucleus, which increases its activity.
Question 30.
Who first time used the word aromatic?
Answer:
Kekule.
Question 31.
A compound burns with smoky flame. What is its nature?
Answer:
Aromatic.
Question 32.
What is the bond length of C-C bond in benzene?
Answer:
1.39 Å
Question 33.
What are aromatic non-benzenoid compounds?
Answer:
Those aromatic compounds which do not have nzene nucleus are called non-benzenoid aromatic molecules.
Question 34.
Write two examples in which aromatic compounds do not have benzene nucleus.
Answer:
Question 35.
Write two examples of aliphatic compounds which burns with smoky flame?
Answer:
CHCl3, CCl4.

Question 36.
Write one example of aromatic compound which do not burn with smoky flame.
Answer:
Benzyl alcohol.
Question 37.
What is arene?
Answer:
Aromatic hydrocarbon.
Question 38.
What are heterocyclic aromatic compounds?
Answer:
Those aromatic compounds whose ring have any hetero atom. For example pyridine.
Question 39.
Which type of reactions are given by aromatic compounds?
Answer:
Generally electrophilic substitution reactions.
Question 40.
Who discovered Benzene?
Answer:
Michael Faraday.
Question 41.
What is B.H.C.?
Answer:
Benzene hexa chloride (B.H.C.) is an insecticide
Question 42.
Why alkenes show geometrical isomerism?
Answer:
Alkenes have π-bond. In π-bond rotation around π-bond is not possible i.e., rotation around bond i restricted. Hence they show show geometrica isomerism.
Question 43.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons. Why?
Answer:
All the alkanes have strong C-C sigma bond and C-H bond is also strong and less polar in nature While alkenes are more reactive due to the presence of л bond in C-C bond.
Question 44.
A hydrocarbon (A) having two carbon atons can decolourise 1 percent alkaline potassium permanganate solution but it does not reac with ammonical silver nitrate solution. Write the name and structural formula o compound (A).
Answer:
Hydrocarbon (A) decolourise alkaline KMnO hence it is unsaturated. As it does not react with ammonical AgNO3 hence it is ethelene not acetylene as it has only two carbon atom, hence (A) is
CH2 = CH2
Question 45.
Arrange the following alkene in decreasing order of their stability.
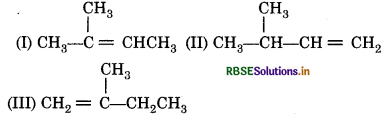
Answer:
Stability order I > III > II

Question 46.
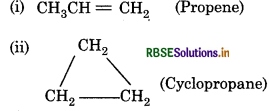
The formula of hydrocarbon is C3H6. Write its structure if
(i) It decolourises the Baeyer's reagent.
(ii) It can not decolourise Baeyer's reagent.
Answer:
Question 47.
Write the formula of mustard gas.
Answer:
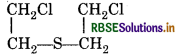
Questionn 48.
CH2=CH is more basic than HC = C- Why?
Answer:
Because its conjugate acid CH2 = CH2 is less acidic than CH = CH.
Question 49.
Write the name of first three members of acetylene series.
Answer:
C2H2, C3H4, C4H6.
Question 50.
What is -C- C-Bond is known?
Answer:
Acetylene bond.
Question 51.
An hydrocarbon (A) having two carbon atoms and decolourises the Baeyer's reagent. When it is passed through Cu2Cl2/NH4OH then it gives precipitate. What is its nature?
Ans:
It is acetylene and have triple bond [CH=CH].
Question 52.
Arrange ethane, ethene and ethyne in increasing order of their acidic behaviour.
Answer:
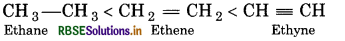
Question 53.
What are the main component of Colour gas?
Answer:
n-butane and isobutane.
Question 54.
Write one reaction which proves that acidic nature of acetylene.
Answer:
It gives acetylide with sodium.
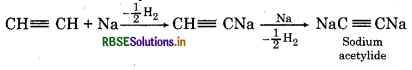
Question 55.
Draw all the possible isomers of C2H2Cl2. Which one is non polar in it ?
Answer:
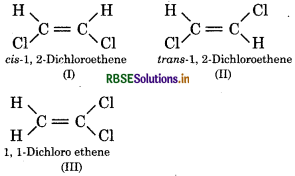
Isomer (II) is non polar in nature.

Question 56.
Staggered and eclipsed conformers of ethane cannot be separated at normal temperature. Why?
Answer:
There is very less difference in the energies of both the conformers hence they cannot be separated at normal temperature.
Question 57.
Concentrate H2SO4 is used to dry ethane not to ethene, why?
Answer:
Because ethane does not react with conc. H2SO4. But ethene forms ethyl hydrogen sulphate with conc. H2SO4·
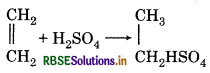
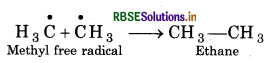
Question 58.
How ethane is formed during chlorination of methane?
Answer:
When the chlorination of methane is done then free radicals are formed. These free radicals react with each other and form ethane. This is termination step.
Question 59.
Why nitro benzene do not give Friedel craft reaction?
Answer:
In nitro benzene-NO2 group is attached with carbon ring and deactivate the benzene ring in such a way that the alkylation by CH+3 and acylation by CH3CO+ group is not possible.
Question 60.
How many sigma and pi bonds are present in one molecule of benzene.
Answer:
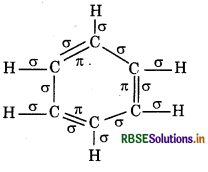
Total o bonds = 12, л bonds = 3
Question 61.
2-Butene has two geometrical isomers while 1-butene do not. Why?
Answer:
In 2-butene both the carbon atom attached with double bond have different groups. While in 1-butene one carbon atom is satisfied by two hydrogen atom. Hence 1-butene cannot show geometrical isomer while 2-butene have
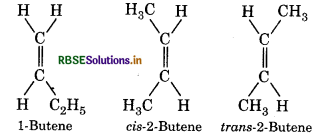
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
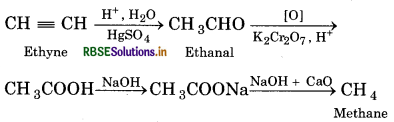
Convert the following:
(i) Methane from ethyne
(ii) Ethyne from ethene
(iii) Ethyne from ethene
(iv) 2-Butyne from ethyne
Answer:
(1) Methane from ethyne:
(2) Ethyne from ethene:
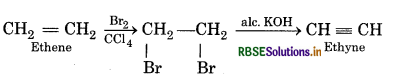
(3) Ethyne from ethane:
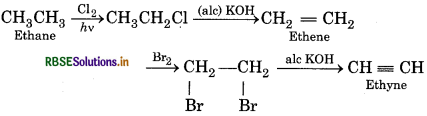
(4) 2-Butyne from ethyne:
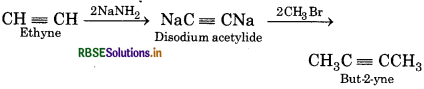
Question 2.
Differentiate between aromatic and aliphatic compounds.
Answer:
|
Aromatic Compounds |
Aliphatic Compounds |
|
1. These are closed chain compounds. |
1. These are open chain compounds. |
|
2. They have higher percentage of carbon. |
2. They have low percentage of carbon. |
|
3. They burn with smoky flame. |
3. They do not bum with smoky flame. |
|
4. These give replacement reactions easily. |
4. These do not give replacement reactions. |
|
5. Their hydroxy compounds are acidic in nature. |
5. Their hydroxy compound are neutral. |
|
6. Their halogen derivatives are less reactive. |
6. Their halogen derivatives are highly reactive. |

Question 3.
Identify 1°, 2° and 3° carbon atoms in given alkane:
CH2 - CH2 - C(CH3)2 - CH2 - CH(CH3)2
Write the number of total hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
Answer:
If carbon atom is attached with one hydrogen -oms then this carbon atom is known as 1o carbon atom.
If carbon atom is attached with two hydrogen atom then this carbon atom is known as 2° carbon atom. If carbon atom is attached with three hydrogen ato then it is known as 3° carbon atom.
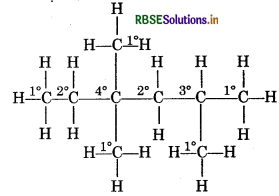
Number of 1° Hydrogen atom = 5
Number of 2° hydrogen atom = 4
Number of 3° hydrogen atom = 1
Question 4.
What happens when (Write only chemica reaction):
(i) Propane reacts with SO2 and Cl2 presence of sunlight?
(ii) Ethyl iodide reacts with red phosphoru and HI?
(iii) Methyl bromide reacts with sodium presence of dry ether?
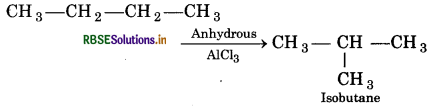
(iv) n-Butane is heated in presence anhydrous AlCl3?
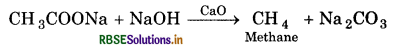
(v) Sodium acetate is heated with mixture NaOH and CaO?
Answer:
(i) Propane sulphuryl chloride is formed.
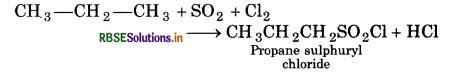
(ii) Ethane is formed

(iii) Ethane is formed
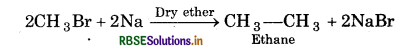
(iv) Isobutane is formed
(v) Methane is formed.
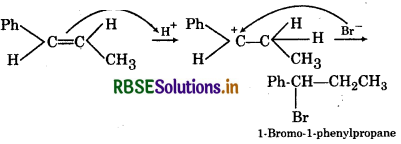
Question 5.
Predict the product of the following reaction:
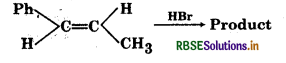
Answer:
Electrophillic addition occurs through the more stable carbocation intermediate:
Question 6.
Write down one-one example of each reaction only reaction.
(i) Decarboxylation
(ii) Clemmensen reduction
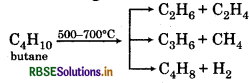
(iii) Catalytic reformation
(iv) Thermal Cracking
(v) Wurtz reaction
Answer:
(i) Decarboxylation:

(ii) Clemmensen reduction:

(iii) Catalytic reformation:
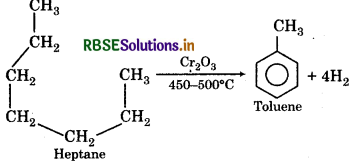
(iv) Thermal Cracking:
(v) Wurtz Reaction:
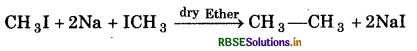
Question 7.
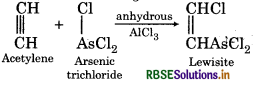
How will you get.
(1) Mustard gas
(2) Lewisite?
Answer:
(1) Mustard gas:
When ethylene reacts with sulphur monochloride then mustard gas is formed.
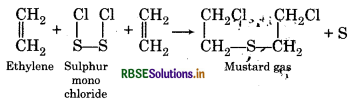
(2) Lewisite: When reacts with arsenictri chloride in presence of anhydrous AlCl3 then Lewisite is formed.
Question 8.
Check the aromaticity of following structures
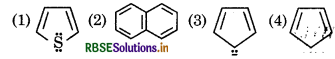
Answer:
According to Huckel's rule those compounds are aromatic in which (4n + 2)л electrons participate in delocalisation. (These electrons can be lone pair also)
(here n = 0, 1, 2 any whole number).
(1) 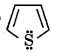
here number of delocalised л electrons are 4 + 2 = 6
According to Huckel issule (4 × 1 + 2) = 6 hence it is aromatic.
(2) 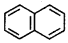
here number of delocalised e 5 × 2 = 10π
According to Huckel's rule (4 × 2 + 2) = 10π hence it is aromatic.
(3) 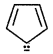
number of e participating in delocalisation is: = 4+2=6
According to Huckel's rule (4 ×1+ 2) = 6 so it is also aromatic.
(4) 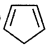
number of e participating in delocalisation = 4
According to Huckel's (4 ×1+ 2) = 6 Hence it is not aromatic.

Question 9.
What are cancer creating and poisonous compounds. Explain with example?
Answer:
Benzene and polynucleur hydrocarbons in which more than two benzene rigngs are joined, known as cancer creating and poisonous organic compounds.
Example:
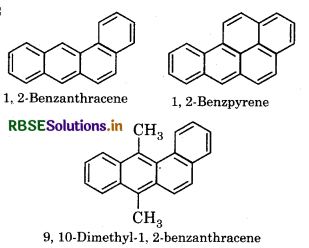
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
The sodium product obtained when methoxide reacts, with 2-chloro-2-methyl pentane in methanol, is:
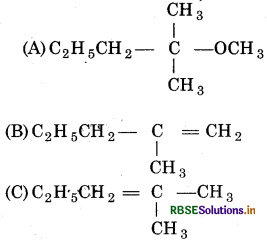
(a) (A) and (C)
(b) Only (C)
(c) (A) and (B)
(d) All of above
Answer:
(c) (A) and (B)
Question 2.
The reagent used in Wolff Kishner reduction is:
(a) NH2-NH2 and KOH in ethylene glycol
(b) Zn-Hg/Conc. HCl
(c) Con. HNO3
(d) Potassium dichromate and dil H2SO4
Answer:
(b) Zn-Hg/Conc. HCl
Question 3.
Which of the following give good yield of primary nitro alkane with the help of oxidised aldoxime?
(a) Trifluoro peroxy acetic acid
(b) Acidified potassium permanganate
(c) Conc. HNO
(d) Potassium dichromate & dil. H2SO4·
Answer:
(a) Trifluoro peroxy acetic acid

Question 4.
The hydrocarbon, in which five carbon atoms with one methyl group is attached in a chain, can form derivative.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 5.
The petrol with octane number 80 have:
(a) 20% n-heptane + 80% iso-octane
(b) 80% n-heptane + 20% cyclo-octane
(c) 20% n-heptane + 80% n-octane
(d) 80% n-heptane + 20% n-octane
Answer:
(d) 80% n-heptane + 20% n-octane
Question 6.
Which of the following compound give methane on reaction with water?
(a) Al4C3
(b) CaC2
(c) VC
(d) Sic
(e) B4C
Answer:
(a) Al4C3
Question 7.
An example of halogenation of alkane is:
(a) Electrophilic substitution
(b) Nucleophilic substitution
(c) Free radical substitution
(d) Oxidation
Answer:
(c) Free radical substitution
Question 8.
Which branched chain isomer of hydrocarbon having molecular weight 724 will give only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide?
(a) Tertiary butyl chloride
(b) Neopentane
(c) Isohexane
(d) Neohexane
Answer:
(b) Neopentane

Question 9.
Which of the following have largest C-H bond length?
(a) C2H2
(b) C2H4
(c) C2H6
(d) C2H2 Br2
Answer:
(d) C2H2 Br2
Question 10.
Which has minimum boiling point?
(a) 1-butene
(b) 1-butyne
(c) n-butane
(d) isobutane
Answer:
(a) 1-butene
Question 11.
Which of the following has maximum boiling point?
(a) n-butane
(b) iso-octane
(c) n-octane
(d) 2, 2, 3, 3-tetra methyl butane
Answer:
(b) iso-octane
Question 12.
n-hexadecane have octane number:
(a) 90
(b) 100
(c) 110
(d) 0
Answer:
(c) 110
Question 13.
Which have minimum boiling point?
(a) 2-methyl butane
(b) 2-methyl propane
(c) 2,2-dimethyl propane
(d) n-pentane
(e) n-butane
Answer:
(a) 2-methyl butane
Question 14.
The correct order of boiling point of 2, 2-dimethyl propane, 2-methyl butane and n-pentane is:
(a) n-pentane > 2, 2-diethyl propane > 2-methyl butane
(b) n-pentane > 2-methyl butane > 2, 2-dimethyl prpopane
(c) 2,2-dimethyl propane > 2-methyl butane > n-pentane
(d) 2-methyl butane > 2, 2-dimethyl propane > n-pentane
Answer:
(b) n-pentane > 2-methyl butane > 2, 2-dimethyl prpopane
Question 15.
An alkane gives only one monochloro alkane when reacts with Cl2 in presence of UV light. The alkane is:
(a) Propane
(b) Pentane
(c) Isopentane
(d) Neopentane
Answer:
(c) Isopentane
Question 16.
An alkene gives only one type of dicarbonyl compound on ozonolysis. The structure of alkene is:
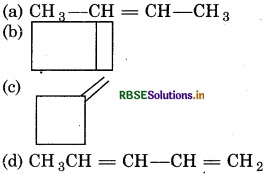
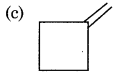
Answer:
Question 17.
The product obtained on ozonolysis, and then reduction by Zn and H2O, of 2, 3-dimethyl-1-Butene will be.
(a) Methanoic acid and 2-methyl-2-butanol
(b) Methanal and 3-methyl-2-butanol
(c) Methanol and 2,2-dimethyl 3-butanone
(d) Methanoic acid and 2-methyl-3-butanone
Answer:
(a) Methanoic acid and 2-methyl-2-butanol
Question 18.
The molecular of Willkinson's catalyst used during hydrogenation of alkene is :
(a) CO(CO)8
(b) [(Pb3P)3 RhCl]
(c) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
(d) K[Ag(CN)2]
Answer:
(b) [(Pb3P)3 RhCl]

Question 19.
The formula of that compound which reacts easily with gaseous bromine is:
(a) C2H4
(b) C3H6
(c) C2H2
(d) C4H10
Answer:
(d) C4H10
Question 20.
The correct order of enthalpy of hydrogenation of following compound is :
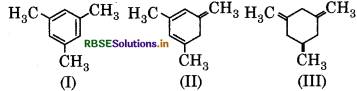
(a) III > II > I
(b) II > III > I
(c) II > I > III
(d) I > II > III.
Answer:
(c) II > I > III
Question 21.
The main product of following reaction is
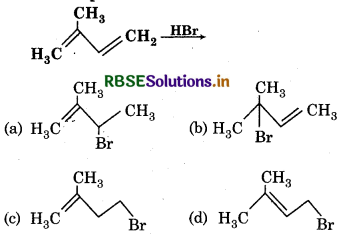
Answer:
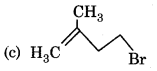
Question 22.
The product 'C' is in the following reaction is
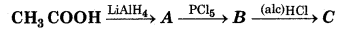
(a) Acetaldehyde
(b) Acetylene
(c) Ethylene
(d) Acetyl Chloride
Answer:
(d) Acetyl Chloride
Question 23.
The 'Z' is
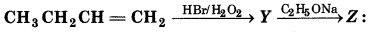
(a) CH3(CH2)4 - O - CH3
(b) CH3CH2 - CH(CH3) - OCH2CH3
(c) CH3 (CH2)3 - O - CH2CH3
(d) (CHn)2 CH2 - O - CH2CH3
Answer:
(b) CH3CH2 - CH(CH3) - OCH2CH3
Question 24.
Which of the following do not use as gaseous fuel?
(a) Gasoline
(b) Acetylene
(c) Carbon monoxide
(d) Ethane
Answer:
(a) Gasoline

Question 25.
Which of the following do not show Anti Markownikoff's rule of HBr?
(a) Propene
(b) But-1-ene
(c) But-2-ene
(d) Pent-2-ene
Answer:
(b) But-1-ene
Question 26.
One mole alkene on ozonolysis forms one mole proponone and one mole formaldehyde. The alkene is:
(a) 2-methyl propene
(b) 2,2-dimethyl-1-butene
(c) Propene
(d) 2-butene
(e) 1-butene
Answer:
(c) Propene
Question 27.
Which is the most stable alkene?
(a) R2C = CR2
(b) RCH = CHR
(c) RCH = CR2
(d) CH2 = CH2
Answer:
(d) CH2 = CH2
Question 28.
Alkene R-CH CH2 and B2H6 reacts rapidly with, each other. The product obtained on oxidation of its product by alkaline H2O2 will be:
(a) RCH2CHO
(b) H-CH2-CH2-OH
(c) RCOCH3
(d) R-CH-CH-CH3
Answer:
(a) RCH2CHO

Question 29.
The product obtained when hex-1-ene reacts with HBr in presence of benzoyl peroxide is:
(a) 2-bromohexane
(b) 2, 3-dibromohexane
(c) 1, 2-dibromo hexane
(d) 2, 4-diboromohexane
(e) 1-bromohexane
Answer:
(d) 2, 4-diboromohexane
Question 30.
The alkene which on ozonolysis form acetone is:
(a) CH2 = CH2
(b) CH3CH = CH2
(c) (CH3)2C = C(CH3)2
(d) CH3-CH = CH-CH3
Answer:
(a) CH2 = CH2
Question 31.
The main product is the reaction is,
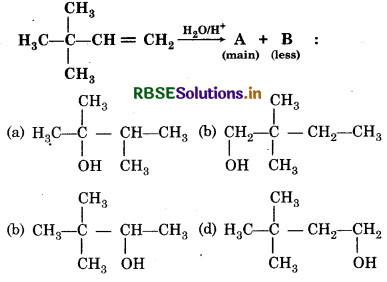
Answer:
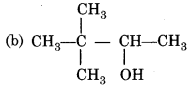
Question 32.
The reaction is:
CH2 CH - CH3 + HBr → CH3 CHBr - CH:
(a) Electrophilic addtion
(b) Nucleophilic addition
(c) Electrophilic substitution
(d) Free radical addition reaction
Answer:
(d) Free radical addition reaction
Question 33.
Which of the following pair do not show cyclic compound of C4H6?
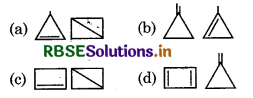
Answer:

Question 34.
In reaction, 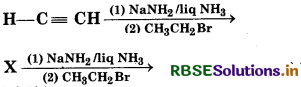
Y, X and Y are:
(a) X = 1-butyne, Y = 3-hexyne
(b) X = 2-butyne Y = 3-hexyne
(c) X = 2-butyne Y = 2-hexyne
(d) X = 1-butyne Y = 2-hexyne
Answer:
(a) X = 1-butyne, Y = 3-hexyne
Question 35.
In Pyrrole
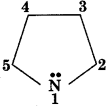
the electron density is maximum at:
(a) 2 & 5
(b) 2 & 3
(c) 3 & 4
(d) 2 & 4
Answer:
(a) 2 & 5
Question 36.
In the following reaction,
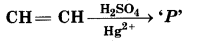
The product 'P' will not give:
(a) Tollen's Reagent Test
(b) Predy's Reagent Test
(c) Victor Mayer's Test
(d) Iodoform Test
Answer:
(c) Victor Mayer's Test
Question 37.
Which has acidic hydrogen?
(a) Ethyne
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethane
(d) Benzene
Answer:
(a) Ethyne
Question 38.
Acetylene give?
(a) White ppt with AgNO3 and red ppt with Cu2Cl2
(b) White ppt with Cu2Cl2 & red ppt with AgNO3
(c) White ppt with both reagents
(d) Red ppt with both reagents
Answer:
(a) White ppt with AgNO3 and red ppt with Cu2Cl2

Question 39.
Which is not related to Friedel Craft's reaction?
(a) Sulphonation
(b) Nitration
(c) Acylation
(d) Reduction
Answer:
(d) Reduction
Question 40.
Which of the one following is benzenoid aromatic compound?
(a) Furan
(b) Thiophene
(c) Pyridine
(d) Aniline
Answer:
(d) Aniline
Question 41.
The product 'P' is:
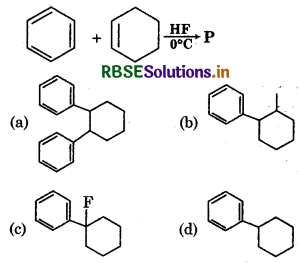
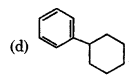
Answer:
Question 42.
The total number of aromatic compounds formed from the following reaction is:
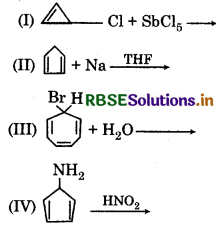
(a) Zero
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(c) Three
Question 43.
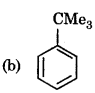
Benzene on reaction with Me3COCl in presence of AICl3 gives:
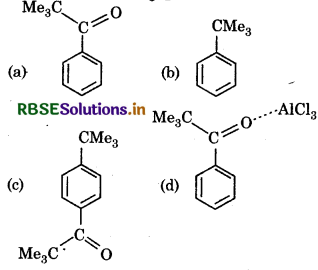
Answer:
Question 44.
 free radical is aromatic because it have:
free radical is aromatic because it have:
(a) 6π-orbital and 7 unpaired e-
(b) 6π-orbital and 6 unpaired e-
(c) 7p-orbital and 6 unpaired e-
(d) 7p-orbital and 7 unpaired e-
Answer:
(b) 6π-orbital and 6 unpaired e-

Question 45.
Which of the following molecule is unstable at room temperature?
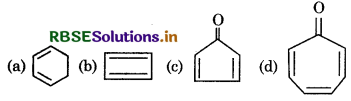
Answer:

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter