RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Important Questions Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the hybridization has highest percentage of s-character?
(a) sp
(b) sp2
(c) sp3
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these

Question 2.
Two volatile liquids A and B differ in their boiling points by 15K. The process which can be used to separate them is:
(a) fractional distillation
(b) steam distillation
(c) distillation under reduced pressure
(d) simple distillation
Answer:
(a) fractional distillation
Question 3.
The best method for the separation of naphthalene and benzoic acid from their mixture is:
(a) Sublimation
(b) Chromatography
(c) Crystallization
(d) Distillation
Answer:
(c) Crystallization
Question 4.
The IUPAC name of C6H5COCl is:
(a) Chlorobenzyl ketone
(b) Benzene chloroketone
(c) Benzene carbonyl chloride
(d) Chlorophenyl ketone
Answer:
(c) Benzene carbonyl chloride
Question 5.
Which of the following carbocation is most stable?
(a) (CH3)2CH+
(b) CH3C+
(c) CH2 = CHCH2
(d) CH3CH2
Answer:
(b) CH3C+
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a cyclic compound?
(a) Anthracene
(b) Pyrrole
(c) Phenol
(d) Neopentane
Answer:
(a) Anthracene
Question 7.
An organic compound having molecular mass 60 is found to contain C = 20%, H = 6.67% while rest is oxygen. On heating it gives NH along with a solid residue. The solid residue gives violet colour with an alkaline copper 1 sulphate solution. The compound is:
(a) CH3NCO
(b) CH3CONH2
(c) (NH2)2CO
(d) CH3 CH2CONH2
Answer:
(d) CH3 CH2CONH2
Question 8.
Which of the following species is not 1 electrophilic in nature?
(a) Cl+
(b) BH3
(c) H3O+
(d) NO2
Answer:
(b) BH3
Question 9.
Which of the following compound gives blood red colouration when its Lassaigne's extract is treated with alkali and ferric chloride?
(a) Thiourea
(b) Diphenyl sulphide
(c) Phenyl hydrazine
(d) Benzamide
Answer:
(a) Thiourea

Question 10.
The boiling point of glycerol is 563 K but it decomposes below 563 K. It is purified by:
(a) Steam distillation
(b) Sublimation
(c) Vaccum distillation
(d) Fractional distillation
Answer:
(d) Fractional distillation
Question 11.
Which of the following compound will not give Lassaigne's test for nitrogen?
(a) NH2NH2
(b) C6H5NHNH2
(c) PhN = NPh
(d) NH2CONH2
Answer:
(c) PhN = NPh
Question 12.
Which of the following is called a carbylamines?
(a) RCN
(b) RCONH2
(c) RCH = NH
(d) RNC
Answer:
(c) RCH = NH
Question 13.
Which of the following method is suitable for the purification of aniline?
(a) Simple distillation
(b) Fractional distillation
(c) Fractional crystallization
(d) Steam distillation
Answer:
(a) Simple distillation
Question 14.
Which of the following is correct regarding-I effect of the substituents?
(a) −NR2 < -OR < -F
(b) -NR2 > -OR > -F
(c) -NR2 > OR < -F
(d) -NR2 < -OR > --F
Answer:
(b) -NR2 > -OR > -F
Question 15.
Which colour is obtained in analysis of sulphur by sodium nitroprusside in an organic compound?
(a) Red
(b) Blue
(c) Violet
(d) Yellow
Answer:
(d) Yellow

Question 16.
The formula of Prussian blue is:
(a) Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3
(b) Fe4 [Fe(CN)3]3
(c) K4[Fe(CN)6]3
(d) K4 [Fe(CN)3]3
Answer:
(c) K4[Fe(CN)6]3
Question 17.
The method employed for estimation of carbon and hydrogen is:
(a) Duma's method
(b) Leibig's method
(c) Carius method
(d) Kjeldahl method
Answer:
(d) Kjeldahl method
Question 18.
The scientist who prepared organic compound first time in laboratory is:
(a) Kekule
(b) Wohler
(c) Lavoisier
(d) Leibig
Answer:
(a) Kekule
Question 19.
Which organic compound was prepared in laboratory for the first time?
(a) Urea
(b) Ethanol
(c) Methane
(d) Acetic acid
Answer:
(b) Ethanol
Question 20.
Who classified organic compounds for the first time?
(a) Nicolas Limeri
(b) Berzelius
(c) Wohler
(d) faraday
Answer:
(d) faraday
Question 21.
The element present in organic compounds is:
(a) oxygen
(b) carbon
(c) nitrogen
(d) hydrogen
Answer:
(a) oxygen
Question 22.
Which of the following is present in vinegar?
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Ethanol
(c) Methane
(d) Methanal
Answer:
(c) Methane

Question 23.
Which of the following compound has the functional group - OH?
(a) 1, 2-ethandiol
(b) 2-butanone
(c) Nitrobenzene
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
(a) 1, 2-ethandiol
Question 24.
The example of dehydration of alcohol is:
(a) displacement reaction
(b) addition reaction
(c) elimination reaction
(d) condensation
Answer:
(a) displacement reaction
Question 25.
Carbocation is:
(a) sp-hybridised
(b) sp3-hybridised
(c) sp-hybridised
(d) sp3-d hybridised
Answer:
(a) sp-hybridised
Question 26.
Which of the following is strongest nucleophile?
(a) -OCOCH3
(b) -OCH3
(c) Cl
(d) -CH3
Answer:
(b) -OCH3
Question 27.
Electrophilic reagent is:
(a) carbonium
(b) chloride ion
(c) alcohol
(d) ferric chloride
Answer:
(d) ferric chloride

Question 28.
Conversion of a ketone to cyanohydrin is a example of:
(a) Electrophilic addition reaction
(b) Nucleophilic addition
(c) Nucleophilic substitution
(d) Electrophilic substitution
Answer:
(c) Nucleophilic substitution
Question 29.
The order of stability of carbanion is:
(a) Methyl > ethyl > isopropyl > tertiary butyl
(b) Tertiary butyl > isopropyl > ethyl > methyl
(c) ethyl > methyl > isopropyl > tertiary butyl
(d) isopropyl > ethyl > methyl > tertiary butyl
Answer:
(a) Methyl > ethyl > isopropyl > tertiary butyl
Question 30.
Most stable carbonium ion is:
(a) methyl carbonium
(b) primary carbonium ion
(c) secondary carbonium ion
(d) tertiary carbonium ion
Answer:
(a) methyl carbonium
Question 31.
Homolytic fission of covalent bond gives:
(a) carbonium ion
(b) carboanion
(c) free radical
(d) a cation and an anion
Answer:
(d) a cation and an anion
Question 32.
Electrophilic reagents are:
(a) electron pair donor
(b) Lewis acid
(c) Odd electron pair
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) Odd electron pair
Question 33.
Electrophilic reagent is:
(a) BF3
(b) NH3
(c) H2O
(d) R-OH
Answer:
(a) BF3
Question 34.
Nucleophilic reagent is:
(a) RзN
(b) SO3
(c) BF2
(d) NO2
Answer:
(c) BF2
Question 35.
Which of the following is not a property of free radicals?
(a) presence of unpaired electron pair
(b) electrical neutrality
(c) formed by homolytic fission
(d) paramagnetic nature
Answer:
(d) paramagnetic nature

Question 36.
Compounds in which electrophilic addition reactions takes place are:
(a) Alkene
(b) Ketone
(c) benzene
(d) Alkane
Answer:
(b) Ketone
Question 37.
The reaction between ethyl bromide and aqueous KOH is:
(a) Substitution
(b) Addition
(c) Elimination
(d) Rearrangement
Answer:
(a) Substitution
Question 38.
A homologous series has:
(a) same molecular formula
(b) same structural formula
(c) same physical properties
(d) same general formula
Answer:
(c) same physical properties
Question 39.
Due to rearrangement many compounds changes into:
(a) higher homologue
(b) lower homologue
(c) isomer
(d) Not defined
Answer:
(b) lower homologue
Question 40.
Which of the following species is active in nitrating mixture?
(a) NO2
(b) NO+
(c) NO2
(d) NO+3
Answer:
(a) NO2
Question 41.
Which of the following is weakest lewis base?
(a) H+
(b) OH-
(c) Cl-
(d) HCO3
Answer:
(d) HCO3
Question 42.
The order of same carbon in benzene is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 1 and 2
(d) alternate 1 and 2
Answer:
(c) 1 and 2
Question 43.
Ammonia molecule is:
(a) electrophile
(b) lewis acid
(c) lewis base
(d) homolytic reagent
Answer:
(b) lewis acid
Question 44.
Which of the following is an intermediate in A acid catalysed dehydration of alcohol?
(a) Free radical
(b) Carbanion
(c) Carbonium ion
(d) Alkoxide ion
Answer:
(c) Carbonium ion

Question 45.
Which of the following is active in A sulphonation of benzene?
(a) HSO3-
(b) SO+2
(c) SO3
(d) HSO4-
Answer:
(a) HSO3-
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is self linking property of carbon known as? Define it.
Answer:
Catenation. It is the property of forming bonds inc with atoms of the same element.
Question 2.
Write the IUPAC name of Freon.
Answer:
Dichlorodifluoromethane.
Question 3.
What is dry ice? Give its one use.
Answer :
Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice. The most common use for dry ice is in food industry where it's used to preserve perishable items and to carbonate liquids.
Question 4.
What species are formed when a covalent bond gets fissioned?
Answer:
Free radicals, carbocations, carbanions.

Question 5.
Write structural formulae of 1-Bromoheptane.
Answer:
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-Br
Question 6.
How will you purify essential oils?
Answer:
Essential oils are volatile and are insoluble in beach water. Therefore, they are purified by steam distillation. HCl use.
Question 7.
Name two compounds which do not contain halogen but give positive Beilstein test.
Answer:
Urea and Thiourea give positive Beilstein test due to formation of volatile cupric cyanide.
Question 8.
What type of compounds is purified by sublimation?
Answer:
Substances whose vapour pressure become equal the atmospheric pressure much below their melting points.
Question 9.
How will you separate iodine from sodium chloride?
Answer:
Either by sublimation or by extraction with CCl4 followed by evaporation.
Question 10.
Define the term 'elution' as applied to column chromatography.
Answer:
It is the process of extraction of different mpounds adsorbed on the column by means of a itable solvent called eluent.
Question 11.
If a liquid compound decomposes at its boiling point, which method (s) can you choose for its purification? It is known that the compound is stable at low pressure, steam volatile and insoluble in water.
Answer:
A liquid which decomposes at its boiling point but steam volatile, insoluble in water and stable at low essure can be purified by steam distillation.

Question 12.
Explain how is the electronegativity of carbon atoms related to their state of hybridization in an organic compound?
Answer:
Since s-electrons are more strongly attracted by the cleus than p-electrons, therefore, electronegativity releases as the s-character of the hybridized orbital releases i.e., in the order:
sp1 > sp2 > sp3.
Question 13.
Why is freshly prepared saturated solution of ferrous sulphate used in the Lassaigne's test for nitrogen?
Answer:
On keeping aq. FeSO4 solution, it undergoes dative-hydrolysis to form basic ferric sulphate,
4FeSO4 + 2H2O + O2 → 4Fe(OH)SO4
The pale yellow colour of Fe3+ ions interferces with the green colour usually obtained in Lassaigne's test.
Question 14.
Without using column chromatography, how will you separate a mixture of camphor and benzoic acid?
Answer:
A chemical method using NaHCO3 solution is dwhen benzoic acid dissolves leaving camphor ion. The filtrate is cooled and then acidified with dil to get benzoic acid.
Question 15.
How will you separate a mixture o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol?
Answer:
Steam distillation o-nitrophenol being stean volatile distills over along with water while p-nitrophenol being non-volatile remains in the flask.
Question 16.
Explain the reason for the fusion of a organic compound with metallic sodium of testing nitrogen, sulphur and halogens.
Answer:
The organic compound is fused with sodium meta to convert these elements which are present in th covalent form to ionic form.
Question 17.
When do we use a flutted filter paper or how water funnel for filtration?
Answer:
To avoid crystallization during filtration, flutte filter paper is used when the volume of the solution to b filtered is small and hot water funnel when the volume large.
Question 18.
On which carbon atom, inductive effect ends?
Answer:
At fourth carbon atom.

Question 19.
Which method is used for estimation halogens?
Answer:
Carius method.
Question 20.
What happens when ammonium cyanate heated?
Answer:
Urea is formed.
Question 21.
Give examples of molecules having zero dipole moment.
Answer:
H2, O2, Cl2, Br2, I2 etc.
Question 22.
What is the electronic structure of outermo shell of central carbon atom in carbonic ion
Answer:
It contain six electrons.
Question 23.
A mixture contains two components A and The solubilities of A and B in water near boiling point are 30 g per 100 mL and 10 g p 100 mL respectively. How will you separate and B from the mixture?
Answer:
It can be separated by fractional crystallizatio When the saturated solution of the mixture is allowed cool, the less soluble component (i.e., B) crystallizes first leaving the more soluble component (A) in t mixture.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What are electrophiles and nucleophile Explain with examples.
Answer:
The positively charged or neutral species which are deficient of electrons and can accept a pair n electrons are called electrophiles. For example: H3O+, Cl+, BF3 etc.
The species having an atom with unshared or lone pair of electrons and seeking positive sites are called nucleophiles. Example: H2O, NH3, OH-, Cl-, Br-, CN etc.
Question 2.
Why is it necessary to use acetic acid and not sulphuric acid for acidification of sodium extract for testing sulphur by lead acetate test?
Answer:
For testing sulphur, sodium extract is acidified e with acetic acid because lead acetate is soluble and does is not interfere with the test. If sulphuric acid were used, lead acetate will react with it forming white precipitate ct of lead sulphate.
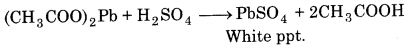
Question 3.
Suggest a method for separation of the following mixtures:
(a) A mixture of liquid A (B.p. 365 K) and liquid B (B.p. 355 K)
(b) A mixture of liquid C (B.p. 348 K) and liquid D (B.p. 478 K)
Answer:
(a) Fractional distillation because the boiling points of the two liquids differs by only 10°.
(b) Simple distillation because the boiling point of two st liquids differ a lot.

Question 4.
0.15 g of an organic compound gave 0.12 g of AgBr by Carius method. Find the percentage of bromine in the compound.
Answer:
Weight of AgBr formed = 0.12 g
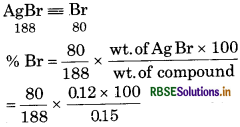
= 34.04%
Question 5.
What is a homologous series? Explain with example.
Answer:
A series of similarly constituted compounds in es? which the members passess the same functional group and have similar chemical characteristics.
- Members of the series can be represented by a general formula.
- Successive members differ from each other by -CH2.
- Physical properties change regularly with increasing number of carbon atoms.
Example: Ethanol, propanol, butanol belongs to same SO homologous series of alcohols.
Question 6.
Arrange the following carbocation decreasing order of stability with reason. Secondary, primary, tertiary.
Answer:
Tertiary > secondary > primary An alkyl group has +I effect. When an alkyl group is attached to a positively charged carbon atom of a carbocation, it tends to release electrons towards that carbon. In doing so, it reduces the positive charge on the carbon. In other words, positive charge gets dispersed and the alkyl group becomes somewhat positively charged. This dispersal of the positive charge stabilizes the carbocation. Thus, more the number of alkyl groups, more is the dispersal of charge and more will be the stability.
Question 7.
Explain why (CH3)3 C+ is more stable than so CH3 CH+2 and CH+3 is the least stable cation?
Answer:
(CH3)3C+ has nine a-hydrogens and hence has nine hyperconjugation structures while CH3CH2+ has only three a-hydrogens and has hence has only three hyperconjugation structures. As a result, (CH3)3C+ is more stable than CH3CH2+. In contrast in CH, the vacant p-orbital is perpendicular filt to the plane in which C-H bond lie and hence cannot overlap with it. Thus, CH3+ is not stabilized by hyperconjugation and is the least stable of the three cations.
Question 8.
Some times a red colour is not produced in the Lassaigne's test even if both nitrogen and sulphur are present in the organic compound. Explain.
Answer:
In principle, if the organic compound contains both N and S, sodium thiocyanate should be formed in Lassaigne's test and this should give blood red colouration with FeCl3
Na + C + N + S → NaCNS
3NaCNS + FeCl3 → Fe(SCN)3 (blood red colour) + 3NaCl
However, if blood red colouration is not obtained, it does ot necessarily mean that S is absent. This is because in esence of excess of sodium metal, sodium thiocyanate itially formed, decomposes to form sodium cyanide and dium sulphide.

Question 9.
Which of the following represents correct IUPAC name for the compound concerned?
(a) 2,2-Dimethylpentane or 2-Dimethyl pentane
(b) 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane
or
4-Chloro-2-methylpentane
Answer:
(a) 2,2-Dimethylpentane because for two alkyl oups on same carbon, the locant is repeated twice.
(b) 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane due to alphabetical order substituents.
Question 10.
Describe the method which can be used to separate two compounds with different solubilities in a solvent S.
Answer:
Two compounds with different solubilities in a vent S can be separated by fractional crystallization. nen a hot saturated solution of these two compounds is owed to cool, the less soluble compound crystallizes t first while the more soluble compound remains in e solution. The crystals are separated from the mother uor and the mother liquor is again concentrated and e hot solution again allowed to cool when the crystals second compound are obtained. These are again ered and dried.
Question 11.
Suggest a method to purify:
(a) Camphor containing traces of common salt.
(b) Kerosene oil containing water.
(c) A liquid which decomposes at its boiling point.
Answer:
(a) Sublimation, Camphor sublimes while common remains as residue in the china dish.
(b) Since the two liquids are immiscible, the technique of vent extraction with a separating funnel is used. The ture is thoroughly shaken and separating funnel is wed to stand. Kerosene being lighter than water ms the upper layer while water forms the lower layer. e lower water layer is run off when kerosene oil is ained. It is dried over anhydrous CaCl2 or MgSO4 - then distilled to give pure kerosene oil. Distillation under reduced pressure.
Question 12.
Give three points of difference between inductive effect and resonance.
Answer:
|
Inductive effect |
Resonance |
|
1. This effect involves -electrons. |
The resonance involves π-electrons or lone pair of electrons. |
|
2. This effect moves upto three carbon atoms and becomes negligible from the fourth carbon atom onwards. |
This effect moves all along the length of the conjugated system. |
|
3. This effect causes slightly displaced electrons. |
This results in complete transfer of electrons. |
Question 13.
Explain fractional distillation.
Answer:
- Fractional distillation is a manufacturi process that separates the differe components (i.e. fractions) in a chemic mixture according to their different boili points.
- The liquid is raised to boiling and vapours pa through a tubular column where temperatu is gradually lowered along its length.
- Components (fractions) with a higher boili point condense on the column and return to solution.
- Fractions with a lower boiling point pa through the column and are collected.
- Gasoline, kerosene and naphtha are fractio separated from crude oil using fraction distillation.
- A fractional distillation process is done in cylinder which has different compartmen having different temperature points.
Question 14.
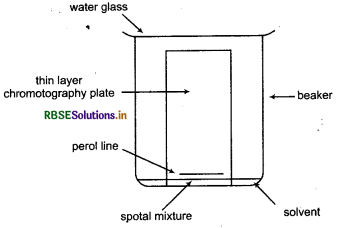
Which technique is used to separate plant pigments? Describe it.
Answer:
Plant pigments can be separated by thin lay chromatography. Separations in TLC invol distributing a mixture of two or more substanc between a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The stationary phase is a thin layer of adsorbent (usual silica gel or alumina) coated on a plate. The mobile phase is a developing liquid which travels up the stationary phase, carrying the samples with it. Components of the samples will separate according to how strongly they adsorb on the stationary phase versus how readily they dissolve in the mobile phase.

Question 15.
Which of the following compounds will not exist as resonance hybrid? Give reason for your answer.
(i) CH3OH
(ii) R-CONH2
(iii) CH2CH = CHCH2NH2
Answer:
(i) CH3OH because it does not contain л-electrons and hence can not be regarded as a resonance hybrid.
(ii) Due to the presence of л-electrons in C = O bond and л electrons on N, amide can be represented as a resonance hybrid of the following resonating structures.
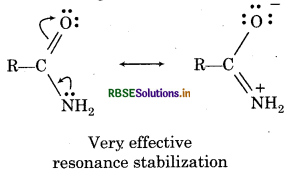
(iii) Since the lone pair of electrons on the N atom is not conjugated with the л electrons of the double bond, therefore, resonance is not possible.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Write short notes on:
(a) Electromeric effect
(b) Inductive effect
Answer:
(a) Electromeric effect: The phenomenon of movement of electrons from one atom to another in ly multiple bonded atoms at the demand of attacking se reagent is called electromeric effect. It is denoted as E-effect and represented by a curved arrow (showing the shifting of electron pair). It is of two types.
(i) Positive electromeric effect: When the transfer of electrons takes place towards the attacking reagent, the effect is called +E effect. Example: The addition of acids to alkenes.
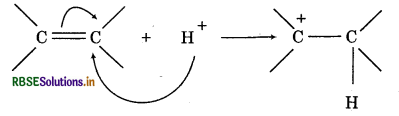
Since,-CH3 group is electron donating, the electrons are transferred in the direction shown.The attacking reagent is attached to that atom on which electrons have been transferred.
(ii) Negative electromeric effect: When the transfer of electrons takes place away from the attacking reagent, the effect is called -E effect. Example: The addition of cyanide ion to carbonyl compounds.
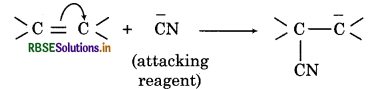
(b) Inductive effect: The polarization of a o-bond due to electron withdrawing or electron donating effect of adjacent groups or atoms is called inductive effect. Some of the properties of inductive effect are:
- It arises due to electronegativity difference between two atoms forming a sigma bond.
- It is transmitted through the sigma bonds and shift of electron density is shown by an arrow that points from positive to negative end of the polar bond.
- The magnitude of inductive effect decreases while moving away from the groups causing it.
- It is a permanent effect.

Question 2.
Give a brief description of the principles involved in the following process:
(i) Chromatography
(ii) Sublimation
(iii) Steam distillation
Answer:
Chromatography:
Chromatography is a technique used for separating or identifying the components in a mixture.
All chromatographic methods require one static part called "the stationary phase" and one moving part "the mobile phase".
In this technique the mixture of substances is applied on to a stationary phase, which may be a solid or a liquid. A pure solvent, a mixture of solvents or a gas is allowed move slowly over the stationary phase. The components of the mixture get gradually separated from one another.
Sublimation :
- Sublimation is the process of vaporizing a solid substance and condensing the vapours to again form the solid directly, without passing through an intermediate liquid state.
- The sublimed body is recovered unchanged chemically, but its physical properties are often more or less altered.
- Camphor, naphthalene, anthracene, benzoic acid, iodine etc. are purified by this process.
Steam distillation :
- The technique is applied to separate substances which are steam volatile and are immiscible with water.
- Steam distillation is a separation process used to purify or isolate temperature sensitive materials, like natural aromatic compounds.
- Steam or water is added to the distillation apparatus, lowering the boiling points of the compounds. The goal is to heat and separate the components at temperatures below their decomposition point.
- Aniline is separated by this technique from aniline - water mixture.
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the following is intermediate?
(a) H3CR
(b) H2C
(c) H2C®:
(d) HC=C®:
Answer:
(c) H2C®:
Question 2.
Hybridisation in carbon atom present in ethane, ethene and ethyne is :
(a) sp3-sp2, sp2-sp2, sp2-sp
(b) sp-sp, sp3-sp2, sp3-sp
(c) sp3-sp3, sp2-sp2, sp-sp.
(d) sp2 -sp3, sp2 -sp, sp2-sp3
Answer:
(c) sp3-sp3, sp2-sp2, sp-sp.
Question 3.
In which orbital an electron pair in the given anion CH, C = CR is present?
(a) 2p
(b) sp
(c) sp2
(d) sp
Answer:
(d) sp

Question 4.
Which of the following radical is most stable?
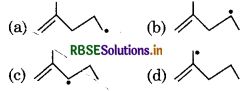
Answer:
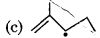
Question 5.
Which intermediate is formed when propene reacts with HOCI (Cl2 + H2O)?
(a) CH3-CH® - CH2 - Cl
(b) CH3-CH(OH)- CH2
(c) CH3- CHCl - CH
(d) CH3-CH® - CH2 - OH
Answer:
(a) CH3-CH® - CH2 - Cl
Question 6.
Which of the following statement is true for following reactions?
(1) CH3CH2CH2 Br + KOH → CH3CH = CH2
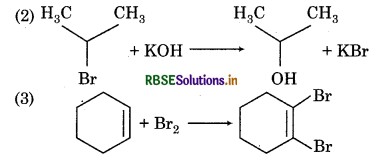
(a) (1) and (2) are elimination reactions whereas (3) is addition reaction.
(b) (1) is elimination reaction, (2) is displacement reaction and (3) is an addition reaction.
(c) (1) is elimination reaction, (2) and (3) are displacement reaction.
(d) (1) is displacement reaction (2) and (3) are addition reactions.
Answer:
(b) (1) is elimination reaction, (2) is displacement reaction and (3) is an addition reaction.
Question 7.
Prefix for compound is
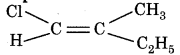
(a) E
(b) Z'
(c) Trans
(d) Anti
Answer:
(a) E
Question 8.
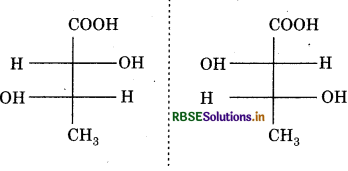
The above pair is called:
(a) Erythro isomers
(b) Threo isomers
(c) Structural isomers
(d) Geometrical isomers
Answer:
(b) Threo isomers

Question 9.
Absolute configuration of given compound is :
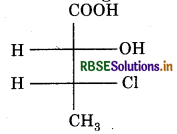
(a) (2s, 3R)
(b) (2s, 3s)
(c) (2R, 3R)
(d) (2R, 3s)
Answer:
(a) (2s, 3R)
Question 10.
Which of the following biphenyl is active?
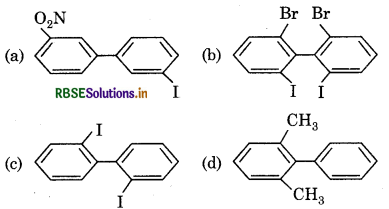
Answer:
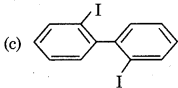
Question 11.
Which of the following is optically active?
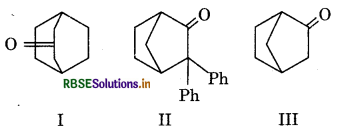
(a) Both II and III
(b) Only III
(c) Both I and III
(d) Both I and II
Answer:
(b) Only III
Question 12.
Enolic form of ethyl acetate is given below?
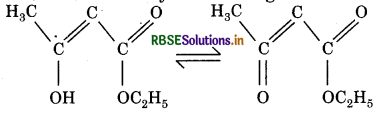
The correct option is
(a) 16 sigma- and 1 pi-bond
(b) 9 sigma- and 2 pi-bonds
(c) 9 sigma- and 1 pi-bond
(d) 18 sigma- and 2 pi-bonds
Answer:
(d) 18 sigma- and 2 pi-bonds
Question 13.
Which of the following electron displacement is more accurate for nucleophillic reactions?
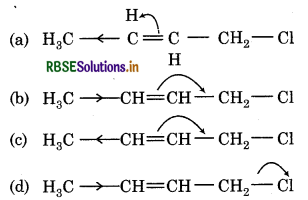
Answer:
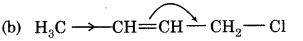

Question 14.
Which of the following compound gives largest number of ions by ionisation of C-Cl bond?
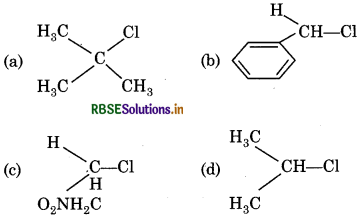
Answer:
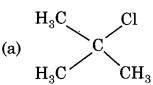
Question 15.
Which of the following, compound /compounds possess hyperconjugation?
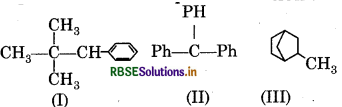
(a) Only II
(b) Only III
(c) Only I and III
(d) Only I
Answer:
(c) Only I and III
Question 16.
Which of the following is not a product of dihydration of:
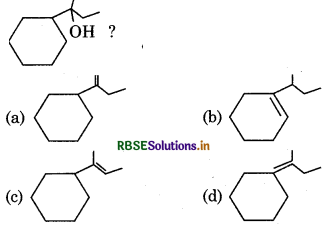
Answer:
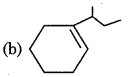
Question 17.
In SN1 reaction, of chiral centre:
(a) 100% racemisation taken place
(b) partial racemisation takes place
(c) 100% superimpositron
(d) 100% inversion
Answer:
(d) 100% inversion
Question 18.
Which of the following shows tautomerism?
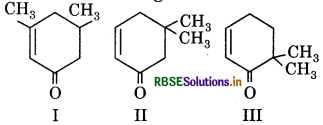
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) I, II and III
(d) I and III
Answer:
Question 19.
CH3CHOH COOH; two possible stereo isomers of given compound which shows optical activity are:
(a) Diastereomers
(b) Atripisomer
(c) Enantiomers
(d) Mesomers
Answer:
Question 20.
Which of the following is not correct about nucleophiles?
(a) Nucleophiles are Lewis acids
(b) Ammonia is a nucleophile
(c) Nuclophile attacks on less electron density area
(d) Nucleophile does not search for electrons
Answer:
Question 21.
Which of the following is product S ?
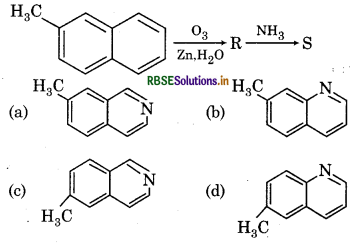
Answer:
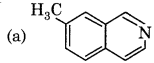
Question 22.
Isomers of hexane are classified into three groups as shown in figure
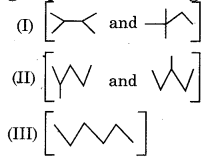
Correct order of their boiling points is:
(a) I > II > III
(b) III > II > I
(c) II > III > I
(d) III > I > II
Answer:
(a) I > II > III

Question 23.
Hybridisation in benzyl carbonium ion:
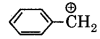
(a) sp2
(b) spd2
(c) sp2d
(d) sp2
Answer:
(a) sp2
Question 24.
The order of stability of following carbanions is:
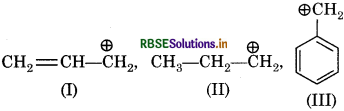
(a) III > II > I
(b) II > III > I
(c) I > II > III
(d) III > I > II
Answer:
(b) II > III > I
Question 25.
Arrange the following compounds on the basis of decreasing acidity?
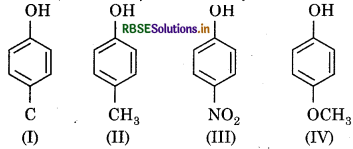
(a) II > IV > I > III
(b) I > II > III > IV
(c) III > I > II > IV
(d) IV > III > I > II
Answer:
(c) III > I > II > IV
Question 26.
Type of hybridisation in carbon atoms of alkyne C3H4:
(a) sp and sp3
(b) sp and sp2
(c) only sp2
(d) sp2 and sp3
Answer:
(b) sp and sp2
Question 27.
Which of the following does not show optical isomerism?
(a) Maleic acid
(b) a-amino acid
(c) Lactic acid
(d) Tartaric acid
Answer:
(a) Maleic acid
Question 28.
The correct increasing order of bond length of C-H, C-O, C-C and C = C is
(a) C-HC-O < C-C < C=C
(b) C-H < C=C < C-O < C-C
(c) C-C < C=C < C-O < C-H
(d) C-O < CH < C-C < C = C
Answer:
(b) C-H < C=C < C-O < C-C

Question 29.
Keeping hybridisation of carbon atom in mind, identify the molecule which is linear:
(a) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3
(b) CH3-CH=CH-CH3
(c) CH3-C=C-CH3
(d) CH2=CH-CH2-C CH
Answer:
(c) CH3-C=C-CH3
Question 30.
Which of the following electrophillic reagent is most active?
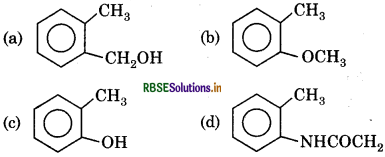
Answer:
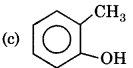

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter