RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 Important Questions The p-Block Elements
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Which element is added with copper and zinc to form bronze?
(a) Fe
(b) Mn
(c) Sn
(d) Me
Answer:
(c) Sn
Question 2.
White lead is:
(a) Basic lead nitrate
(b) Acidic lead carbonate
(c) Basic lead carbonate
(d) Basic lead hydroxide
Answer:
(c) Basic lead carbonate

Question 3.
Glass is a:
(a) Liquid
(b) Solid
(c) Supercooled liquid
(d) Transparent organic polymer
Answer:
(c) Supercooled liquid
Question 4.
Method used for obtaining highly pure silicon used as semiconductor material is:
(a) Oxidation
(b) Electrochemical reduction
(c) Crystallization
(d) Zone refining
Answer:
(d) Zone refining
Question 5.
Galena is an ore of:
(a) Gallium
(b) Lead
(c) Tin
(d) Germanium
Answer:
(b) Lead
Question 6.
When a mixture of air and steam is passed over red hot coke, the outgoing gas is:
(a) Producer gas
(b) Water gas
(c) Coal gas
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Water gas
Question 7.
Which of the following has most density?
(a) Fe
(b) Cu
(c) B
(d) Pb
Answer:
(d) Pb
Question 8.
Carborundum is obtained when silica is heated at high temperature with:
(a) Carbon
(b) Carbon monoxide
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Calcium carbonate
Answer:
(a) Carbon
Question 9.
The shape of gaseous SnCl2 is:
(a) Tetrahedral
(b) Linear
(c) Angular
(d) T-shaped
Answer:
(c) Angular

Question 10.
The most stable +2 oxidation state is exhibited by:
(a) Fe
(b) Sn
(c) Pb
(d) Si
Answer:
(c) Pb
Question 11.
Which of the following is the most electronegative ?
(a) Pb
(b) Si
(c) C
(d) Sn
Answer:
(c) C
Question 12.
Select the incorrect statement:
(a) In three dimensional network each silicon share three oxygen
(b) In Si2O6 there is one shared electron Si2
(c) In SiO there no oxygen shared 4
(d) There are three shared electron for three dimensional network silica
Answer:
(d) There are three shared electron for three dimensional network silica
Question 13.
Percentage of lead in lead pencil is:
(a) Zero
(b) 20
(c) 80
(d) 70
Answer:
(a) Zero
Question 14.
Which of the following is not acidic?
(a) PCl3
(b) SbCl3
(c) BiCl3
(d) CCl4
Answer:
(d) CCl4

Question 15.
Which of the following conceivable structures for CCl4 will have a zero dipole moment?
(a) Square planar
(b) Square pyramid (Carbon at apex)
(c) Irregular tetrahedron
(d) Regular tetrahedron
Answer:
(d) Regular tetrahedron
Question 16.
An alloy of Pb and Sn in equal proportion is called :
(a) Gun metal
(b) Horn silver
(c) Constantans
(d) Solder
Answer:
(d) Solder
Question 17.
Which of the following statement is correct with respect to the property of elements with increase in atomic number in carbon family?
(a) Their metallic character decreases
(b) The stability of +2 oxidation state increases
(c) Their ionisation enthalpy increases
(d) Their atomic size decreases
Answer:
(b) The stability of +2 oxidation state increases
Question 18.
In silicon dioxide:
(a) Each silicon atom is surrounded by four oxygen atoms and each oxygen atom is bounded to two silicon atoms
(b) Each silicon atom is surrounded by two oxygen atom and each oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms
(c) Silicon is bonded to two silicon atoms
(d) There are double bonds between silicon and oxygen atoms
Answer:
(a) Each silicon atom is surrounded by four oxygen atoms and each oxygen atom is bounded to two silicon atoms

Question 19.
Pb and and Sn are extracted froms their chief ores by:
(a) Reduction with carbon and self reduction respectively
(b) Self reduction and reduction with carbon respectively
(c) Electrolysis and self reduction respectively
(d) Self reduction and electrolysis respectively
Answer:
(b) Self reduction and reduction with carbon respectively
Question 20.
A yellow solid, known to be a single compound is completely insoluble in hot water but dissolves in hot dilute HCl to give orange red solution. When this solution is cooled a white crystalline precipitate is formed. Then compound is:
(a) Chromium silicate
(b) Copper oxide
(c) Lead chromate
(d) Ferric oxide
Answer:
(c) Lead chromate
Question 21.
The purification method of bauxite containing iron oxide as impurity is known as:
(a) Hoop's method
(b) Baeyer's process
(c) Electrolytic process
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Baeyer's process
Question 22.
Which of the following reaction will not give an anhydrous AICI?
(a) By heating AlCl3·6H2O
(b) By passing dry HCl on heated aluminium powder
(c) By passing dry chlorine on heated aluminium powder
(d) By passing dry chlorine overheated mixture of coke and alumina
Answer:
(a) By heating AlCl3·6H2O
Question 23.
In the aluminino thermite process, Al acts as a/an:
(a) Flux
(b) Oxidising agent
(c) Reducing agent
(d) Solder
Answer:
(c) Reducing agent

Question 24.
Aluminothermy used for on the spot welding of large iron structure is based upon the fact that:
(a) As compared to iron, aluminium has greater affinity for oxygen
(b) As compared to aluminium, iron has greater affinity for oxygen
(c) Reaction between aluminium and oxygen is endothermic
(d) Reaction between iron and oxygen is endothermic
Answer:
(a) As compared to iron, aluminium has greater affinity for oxygen
Question 25.
In the electrolysis of aluminium, cryolite is added to:
(a) Lower the melting point of alumina
(b) Increases the electrical conductivity
(c) Minimise anodic effect
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 26.
Which of the following statements is not true both for B and Al?
(a) They burn in oxygen to give oxide at high temperature
(b) Their halides are Lewis acids
(c) They combine with nitrogen to form nitrides
(d) They react with HCl to form chlorides
Answer:
(d) They react with HCl to form chlorides
Question 27.
Which is used in high temperature thermometry?
(a) Na
(b) Ga
(c) Ti
(d) Hg
Answer:
(b) Ga
Question 28.
The first ionisation enthalpies (kJ/mol) for Li, Be, B and C have following values. Which of these values corresponds to that of boron?
(a) 520
(b) 800
(c) 899
(d) 1086
Answer:
(b) 800
Question 29.
A particular element belongs to group13 and second period of the periodic table, it is:
(a) Gas, slightly metallic
(b) Liquid, non-metallic
(c) Solid, non-metallic
(d) Solid, less metallic
Answer:
(c) Solid, non-metallic

Question 30.
The metal ion M3+ loses 3 electrons. Its oxidation number will be:
(a) +3
(b) +6
(c) 0
(d) -3
Answer:
(b) +6
Question 31.
Which of the following statement is false?
(a) Boron trifluoride is a strong Lewis base
(b) Aluminium is a good reducing agent
(c) Boron resembles in many properties with silicon
(d) Boron shows +3 oxidation state
Answer:
(a) Boron trifluoride is a strong Lewis base
Question 32.
Aluminium oxide is not reduced by chemical reactions since:
(a) Aluminium oxide is highly stable
(b) Aluminium oxide is reactive
(c) Reducing agent contaminates
(d) The process pollutes the environment
Answer:
(a) Aluminium oxide is highly stable
Question 33.
A layer of coke is spread over bauxite during extraction of aluminium. This acts as a/an:
(a) Flux
(b) Slag to remove impurities
(c) Reducing agent
(d) Insulation and does not allow heat to escape
Answer:
(d) Insulation and does not allow heat to escape

Question 34.
Aluminium reacts with caustic soda to form:
(a) Sodium meta aluminate
(b) Aluminium hydroxide
(c) Sodium tetraaluminate
(d) Aluminium oxide
Answer:
(a) Sodium meta aluminate
Question 35.
Which of the of the following properties of aluminium makes it useful for food packing?
(a) Good thermal conductivity
(b) Good electrical conductivity
(c) Low density
(d) Non-toxicity
Answer:
(d) Non-toxicity
Question 36.
Which one is a non-metal in group 13 (IIIA)?
(a) B
(b) Al
(c) Ga
(d) In
Answer:
(a) B
Question 37.
Which of the following statements about anhydrous aluminium chloride is correct?
(a) It exist as AlCl3 molecule
(b) It is not easily hydrolyzed
(c) It sublimes at 100°C under vacuum
(d) It is a strong Lewis base
Answer:
(c) It sublimes at 100°C under vacuum
Question 38.
AICl3 fumes in moist air because:
(a) It sublimate
(b) It gives out HCl gas
(c) It is highly hygroscopic
(d) It is ionic
Answer:
(b) It gives out HCl gas

Question 39.
Aluminium (III) chloride forms a dimer because :
(a) Higher coordination number can be achieved by aluminium
(b) Aluminium has high ionisation energy
(c) Aluminium belong to 3rd group
(d) It cannot form a trimer
Answer:
(a) Higher coordination number can be achieved by aluminium
Question 40.
Which of the following statement is not correct? Boron differs from the members of the group because it:
(a) has much lower atomic radius
(b) is a non-metal
(c) has a maximum covalency 6
(d) is covalent in all its compound
Answer:
(c) has a maximum covalency 6
Question 41.
Which statement is wrong regarding nitrogen?
(a) Supporter of life
(b) Hydrogen bonding
(c) Lighter than air
(d) Low boiling point
Answer:
(a) Supporter of life

Question 42.
For the manufacture of NH3 by the following
reaction: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 + 22.4 kcal; the favorable conditions are :
(a) Low temperature, high pressure and catalyst
(b) High temperature, high pressure and catalyst
(c) High temperature, low pressure and catalyst
(d) Low temperature, low pressure and catalyst
Answer:
(a) Low temperature, high pressure and catalyst
Question 43.
NH4Cl solution is:
(a) neutral
(b) acidic
(c) basic
(d) amphoteric
Answer:
(b) acidic
Question 44.
Which is the most reactive species of phosphorus?
(a) White
(b) Red
(c) Scarlet
(d) Violet
Answer:
(a) White
Question 45.
Pure silicon doped with phosphorus is a:
(a) metallic conductor
(b) insulator
(c) n-type semiconductor
(d) p-type semiconductor
Answer:
(c) n-type semiconductor
Question 46.
Which of the following element occurs free in nature?
(a) N
(b) P
(c) As
(d) Sb
Answer:
(a) N

Question 47.
Phosphorus pentaoxide is widely used as:
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidizing agent
(c) dehydrating agent
(d) bleaching agent
Answer:
(c) dehydrating agent
Question 48.
The laughing gas is:
(a) Nitrous oxide
(b) Dinitrogen trioxide
(c) Nitric oxide.
(d) Nitrogen peroxide
Answer:
(a) Nitrous oxide
Question 49.
In aqua-regia the ratio of conc. HNO3 and conc. HCl present is:
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 2 : 3
(d) 3 : 2
Answer:
(a) 1 : 3
Question 50.
N forms NCl, whereas P can form PCl3 and PCl5 why?
(a) P contains 3d-orbitals, which can be used for bonding but N does not have 3d-orbitals in its valance shell
(b) N atoms is larger than P in size
(c) P is more reactive towards Cl than N
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) P contains 3d-orbitals, which can be used for bonding but N does not have 3d-orbitals in its valance shell
Question 51.
The bond present in N2O5 are:
(a) Only ionic
(b) Covalent and coordinate
(c) Only covalent
(d) Covalent ionic
Answer:
(b) Covalent and coordinate
Question 52.
The P-P-P bond angle in white phosphorus is:
(a) 120°
(b) 109° 28′
(c) 90°
(d) 60°
Answer:
(d) 60°
Question 53.
Which one of following substance has highest proton affinity:
(a) H2O
(b) H2S
(c) NH3
(d) PH3
Answer:
(c) NH3

Question 54.
Red P can be obtained from white P by:
(a) Heating in an atmosphere
(b) Distilling it in a inert atmosphere
(c) Dissolving it in CS2 and crystallizing
(d) Melting it and pouring the liquid into water
Answer:
(a) Heating in an atmosphere
Question 55.
When excess of water is added to BiCl5 solution:
(a) Ionisation of BiCl, is increased
(b) A white ppt of Bi(OH)3 is obtained
(c) BiCl5 is hydrolysed to give white ppt of BioCl
(d) BiCl5 is precipitated
Answer:
(c) BiCl5 is hydrolysed to give white ppt of BioCl
Question 56.
Structure of white phosphorus is:
(a) Square planar
(b) Pyramidal
(c) Tetrahedral
(d) Trigonal planar
Answer:
(c) Tetrahedral
Question 57.
Phosphide ion has the electronic structure similar to that of:
(a) Nitride ion
(b) Fluoride ion
(c) Sodium ion
(d) Chloride ion
Answer:
(d) Chloride ion
Question 58.
In nitrogen family, the H-M-H bond angle in the hydrides gradually becomes closer to 90% on going from N to Sb. This shows that gradually :
(a) The basic strength of the hydrides increases
(b) Bond energies of M-H bonds increases
(c) Almost pure p-orbitals are used for M-H bonding
(d) The bond pairs of electrons become nearer to the central atom
Answer:
(c) Almost pure p-orbitals are used for M-H bonding
Question 59.
The oxyacid of phosphorus in which phosphorus has lowest oxidation state is:
(a) Hypophosphrous acid
(b) Orthosphosphoric acid
(c) Pyrophosphoric acid
(d) Metaphosphoric acid
Answer:
(a) Hypophosphrous acid

Question 60.
Which shows maximum valency?
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Tin
(c) Antimony
(d) Bismuth
Answer:
(a) Phosphorus
Question 61.
Which of the following sets gives the correct arrangement of the compounds involved based on their bond strengths?
(a) HF > HCI > HBr > HI
(b) HI > HBr > HCl > HF
(c) HF > HCI > HBr > HI
(d) HCl > HF > HBr > HI
Answer:
(a) HF > HCI > HBr > HI
Question 62.
Which of the following has the strongest bond?
(a) F-B
(b) F-Cl
(c) F-Br
(d) Cl-Br
Answer:
(a) F-B
Question 63.
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Silicon exhibits 4 coordination number in its compounds
(b) Bond energy of F2 is less than Cl2
(c) Mn(III) oxidation state is more stable than Mn(II) in aqueous state
(d) Elements of 15th group shows only +3 and +5 oxidation states
Answer:
(b) Bond energy of F2 is less than Cl2
Question 64.
Which one of the following elements shows different oxidation states?
(a) Sodium
(b) Fluorine
(c) Chlorine
(d) Potassium
Answer:
(c) Chlorine
Question 65.
Which of the following elements exhibits the most basic properties?
(a) F
(b) Cl
(c) Br
(d) I
Answer:
(d) I
Question 66.
In the manufacture of bromine from sea water, the mother liquor containing bromine is treated with:
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Chlorine
(c) Iodine
(d) Sulphur dioxide
Answer:
(b) Chlorine

Question 67.
Which of the following elements is extracted commercially by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its compound?
(a) Cl
(b) Al
(c) Br
(d) Na
Answer:
(a) Cl
Question 68.
Which of the following arrangement for the three halogens Cl, Br and I when placed in the order of their increasing electron affinity is correct?
(a) Cl, Br, I
(b) I, Br, Cl
(c) Br, Cl, I
(d) I, Cl, Br
Answer:
(b) I, Br, Cl
Question 69.
Which of the following is a false statement?
(a) Halogens are strongly oxidising agents
(b) Halogens shows only-1 oxidation state
(c) HF molecules form intermolecular hydrogen bonding
(d) Fluorine is highly reactive
Answer:
(b) Halogens shows only-1 oxidation state
Question 70.
Which of the following has greatest reducing power?
(a) HI
(b) HBr
(c) HCl
(d) HF
Answer:
(a) HI
Question 71.
Among noble gases from He to Xe only xenon reacts with fluorine to form stable xenon fluorides because xenon:
(a) has the largest size
(b) has the lowest ionisation enthalpy
(c) has the highest heat of vaporization
(d) is the most readily available noble gas
Answer:
(b) has the lowest ionisation enthalpy
Question 72.
The element which has not yet been reacted with F2 is:
(a) Ar
(b) Xe
(c) Kr
(d) Rn
Answer:
(a) Ar

Question 73.
Molecular shape of SF4, CF4 and XeF4 are:
(a) The same, with 2,0 and 1 lone pairs of electrons respectively
(b) The same, with 1,1 and 1 lone pairs of electrons respectively
(c) Different, with 0,1 and 2 lone pairs of electrons respectively
(d) Different, with 1,0 and 2 lone pairs of electrons respectively
Answer:
(d) Different, with 1,0 and 2 lone pairs of electrons respectively
Question 74.
Which of the following noble gas is not present in atmosphere ?
(a) He
(b) Ne
(c) Ar
(d) Rn
Answer:
(d) Rn
Question 75.
Which of the following noble gas is least polarisable?
(a) He
(b) Xe
(c) Ar
(d) Ne
Answer:
(a) He
Question 76.
Argon is discovered by:
(a) Ramsay
(b) Rayleigh
(c) Rutherford
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Ramsay
Question 77.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of the noble gases in their group in the periodic table?
(a) Ar, He, Kr, Ne, Rn, Xe
(b) He, Ar, Ne, Kr, Xe, Rn
(c) He, Ne, Kr, Ar, Xe, Rn
(d) He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
Answer:
(d) He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
Question 78.
Which of the following statements about noble gases is false?
(a) They are used to provide inert atmosphere in many chemical reactions
(b) They are only sparingly soluble in water
(c) They form diatomic molecules
(d) Some of them are used to fill discharge tube used for advertising signs
Answer:
(c) They form diatomic molecules
Question 79.
Gradual addition of electronic shells in the noble gases causes a decrease in their:
(a) Ionisation energy
(b) Atomic radius
(c) Boiling point
(d) Density
Answer:
(a) Ionisation energy
Question 80.
The oxidation number of Xe in XeOF2 is :
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 4
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Which element of group 13 forms amphoteric hydroxide?
Answer:
Al and Ga

Question 2.
What is the general electronic configuration of carbon family?
Answer:
ns2np2
Question 3.
What are boranes?
Answer:
Stable hydrides of boron having analogy with alkanes are called boranes.
Question 4.
Which of the two elements C or Si forms multiple bonds?
Answer:
Due to smaller size and higher electronegativity, carbon undergoes рπ -рπ оverlap to form multiple bonds but silicon does not.
Question 5.
Name two elements which exhibit allotropy?
Answer:
Carbon and silicon.
Question 6.
What is the formula of carborundum?
Answer:
Silicon carbide (SiC).
Question 7.
What is dry ice? Why is it called so?
Answer:
Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice. It is called so because solid carbon dioxide can sublimate directly to gaseous state without passing through liquid state.
Question 8.
Which of the two Sn or Pb has greater ionization energy?
Answer:
Pb has greater ionization energy because of poor shielding effect and increasing atomic size.
Question 9.
Why does boron not form B3+ ion?
Answer:
Boron has very small size and has very high sum of three ionization enthalpies (IE1 + IE2 + IE3). Therefore, it cannot lose its three electrons to form B3+ ion.
Question 10.
What is the maximum covalency of silicon in its compounds?
Answer:
Silicon shows maximum covalency of six. Example: Na2SiF6·
Question 11.
[SiF6]-2 Explain is known but [CF6] is not known.
Answer:
Silicon has vacant d-orbitals and can form complexes like [SiF6]-2 because Si can extend its coordination number beyond four. But C has no vacant d-orbitals in its valence shell; it cannot form [CF6].

Question 12.
Diamond is a covalent compound, yet it has very high melting point. Explain.
Answer:
Diamond has three dimensional network structure involving strong carbon-carbon bonds. These bonds are difficult to break and therefore have high melting point.
Question 13.
How sodium boron hydride reacts with iodine?
Answer:
Di-borane is obtained.
2NaBH4 + I2 → B2H6 + 2NaI + H2
Question 14.
Why does BCl3 act as Lewis acid?
Answer:
Boron tri-chloride is an electron deficient compound, since B atom has only six electrons in its valence shell. In order to complete its octet, it can accept an electron pair and hence acts as Lewis acid.
Question 15.
Why is diamond a bad conductor of electricity but a good conductor of heat?
Answer:
Diamond has rigid three dimensional structure in which there is no free electron. Thus, diamond is bad conductor of electricity because movement of electrons is necessary for conduction of electric current but this is not necessary for conduction of heat.
Question 16.
What is the reason of anomalous behavior of certain elements?
Answer:
The reason for anomalous behavior is:
- Smallest size
- High electronegativity
- Absence of d-orbitals.
Question 17.
Which oxide of carbon is an anhydride of carbonic acid?
Answer:
Since carbonic acid decomposes to give carbon dioxide and water, therefore carbon dioxide is regarded as an anhydride of carbonic acid.
H2CO3 → H2O + CO2
Question 18.
Why AlCl3 exists as dimer?
Answer:
In AlCl3, there are six electrons around Al atom which are two less than octet. In the dimeric structure, A each aluminium atom completes its octet by accepting a us lone pair of electron from chlorine atom of another E aluminium chloride molecule.
Question 19.
What is the function of BF3 in industrial th processes?
Answer:
BF3 is an electron deficient compound. Thus, acts a as a catalyst in industrial processes. T20 The +1 oxidation state is more stable than +3 de oxidation state for thallium. Explain. Ans. Valence shell configuration of thallium is 6s2 6p1. Therefore, it can show oxidation state of +1 and +3. But due to inert pair effect 6s2 electrons are more tightly m attached to nucleus and are not available for bond th formation. Thus, thallium shows oxidation state of +1.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Why BBr3 is stronger Lewis acid as ac compared to BF3 though fluorine is more TH electronegative than bromine?
Answer:
In both the molecules: BF3 or BBr3, boron has only O six electrons in its outermost shell and can accept two ea electrons to complete its octet. Hence, both are Lewis ex acids. In BBr3, size of overlapping orbitals i.e. 2p orbital ha of boron and 4p orbital of bromine differ. Hence, fo overlapping does not occur to a great extent and as a result electron deficiency of boron does not decrease to a great extent. But in BF, size of 2p orbital of boron and 2p orbital of fluorine is almost same. Hencе, рë-рë bonding occurs effectively (Back bonding) which ca decreases electron density on boron. Thus, BBr3 is he stronger Lewis acid than BF3.

Question 2.
CO2 is a gas while SiO2 is a solid. Explain. to
Answer:
Carbon due to its small size and higher electronegativity than silicon forms рл-рл double bonds with oxygen atoms to form CO2 molecule. These molecules are held together by weak Vander Waals forces of attraction which can be easily overcome by collision of molecules at room temperature. Consequently, carbon dioxide is a gas. On the other hand, silicon due to its bigger size and lower net electronegativity than carbon has little tendency to form рл-рл double bonds with oxygen atoms. Instead, each silicon atom forms four single covalent bonds with O atoms which are tetrahedrally arranged around it leading to formation of three dimensional network An structures. To break these bonds large amount of energy is needed and hence SiO2 is a solid.
Question 3.
Explain why boron halides referred to as electron deficient compounds.
Answer:
In boron halides, boron involves sp2 hybridization sing one s and two p-orbitals. Each of the sp2 hybrid orbital overlaps with 2porbital of alogen to form B-X bonds. As 2p orbital is left vacant in e valence shell. In these compounds, octet of boron is ot complete because they have only six electrons round boron. Therefore, these halides are referred to as electron eficient compounds.
Question 4.
BCl3 is trigonal planar while AICl3 is tetrahedral in dimeric state. Explain.
Answer:
Both BCl3, and AlCl3 are electron deficient olecules having six electrons in its valence shell of eir respective central atoms. To complete their octet, ntral atom in each case can accept a pair of electron om chlorine atom of another molecule forming dimeric ructures. However, due to small size of boron, it cannot commodate four big sized Cl atoms around it. herefore, BCl3, prefers to exist as a monomeric planar molecule. On the other hand, Al because of its bigger size can sily accommodate four Cl atoms. As a result, AlCl3 its as a dimer. In this dimer, since the covalency of Al s increased to 4. Therefore, Al is sp3 hybridized and ur Cl atoms are held tetrahedrally around it.
Question 5.
Why does elemental silicon not form graphite like structure as carbon does? Explain.
Answer:
In graphite, carbon is sp2 hybridized and each rbon is linked to other three carbon atom by forming xagonal rings. Each carbon is now left with one bridized p-orbital which undergoes sidewise overlap form three рл-рл double bonds. Thus, graphite has two mensional sheets like structure consisting of a number benzene rings fused together. Silicon, on the other nd, due to bigger size and smaller electronegativity es not undergo sp2 hybridization and hence does not m рл-рл double bonds needed for graphite structure. stead it prefers to undergo only sp3 hybridization and nce silicon has diamond like three dimensional work structure.
Question 6.
Identify the compounds A, X and Z in the following reactions:
A + 2 HCl + 5H2O → 2NaCl + X
X → HBO2 → Z
Answer:
Na2B4O7 → X: H3BO3 → Z: B2O3
Na2B4O7 + 2HCl + 5H2O → 2NaCl + H3BO3
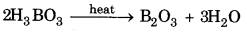
Question 7.
A compound X of boron reacts with NMe3 give an adduct B which on hydrolysis give compound C and hydrogen gas. C is an ad Identify the compounds X, B and C. Give reaction involved.
Answer:
The compound X is diborane which reacts NMe3 to form an adduct B2H6.NMe3 (B). ↑ hydrolysis of compound X gives boric acid (C) a hydrogen gas. The reactions are
B2H6 + NMе3 → B2H6NMe3
B2H6NMe3 + 6H2O → 2H3BO3 + 6H2 + NMe

Question 8.
Give reasons:
1. Graphite is used as lubricant.
2. Aluminium vessels should not be kept water overnight.
3. Conc. nitric acid can be transported aluminium container.
Answer:
- In graphite, the carbon atoms are arranged flat parallel layers as regular hexagons. Each layer is bonded to adjacent layers by weak Vand Waals forces. This allows each layer to slide over other easily. Due to this type of structure graphite is s and slippery, and can act as a lubricant.
- Aluminium reacts with water and dissolved oxygen forms a thin layer of aluminium oxide. A very sm amount of aluminium oxide dissolves to give Al3+ ions solution. Since Al3+ is injurious to health. Therefo drinking water should not be kept in aluminium utens overnight.
- Aluminium reacts with conc. nitric acid a becomes passive due to the formation of very thin film aluminium oxide on its surface which protects it fro further action. Therefore, aluminium containers can used to transport conc. nitric acid.
Question 9.
Explain the following reactions:
A. Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in presence of copper.
B. CO is heated with ZnO.
C. Hydrated alumina is treated with aqueous NaOH.
Answer:
A. Dichloro di-methyl silicon is formed.
2CH3Cl + Si → (CH3)2 SiCl2
B. ZnO is reduced to zinc.
ZnO + CO → Zn + CO2
C. Alumina dissolves to form sodium meta-aluminate
Al2O3 · 2H2O + 2NaOH + H2O → 2Na[Al(OH)4]
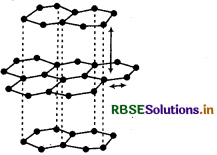
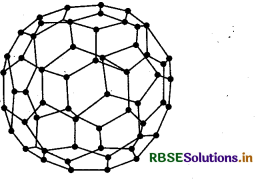
Question 10.
Draw the structure of:
1. Graphite
Answer:
(1) Graphite:
(2) Fullerene:
Question 11.
How carbon differs from other members of the group?
Answer:
Carbon differs from rest of the family members due der to smallest size, high electronegativity and absence of the d-orbitals. Some of the dissimilar properties are:
- Melting and boiling point of carbon is very high as compared to other family members.
- Carbon in its diamond form is hardest substance known.
- It has maximum tendency of catenation.
- It has high tendency to form pr-pr multiple bonds with other elements like nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur etc. i. a. C = C, C = C, CO, C = N.
- CO2 is a gas while other dioxides are solids.
- Carbon is not affected by alkalis.

Question 12.
Give reason:
1. PbX2 is more stable than PbX4.
2. PbCl is less stable than SnCl4 but PbCl2 is more stable than SnCl2.
3. PbO2 is a stronger oxidizing agent than SnO2
Answer:
- Due to inert pair effect, the +2 oxidation state of Pb is more stable than +4. Hence, PbX2 is more stable than PbX4·
- Stability of +4 oxidation state decreases down the group while that of +2 oxidation state increases due to inert pair effect.
- In PbO2 and SnO2, both lead and tin are present in +4 oxidation state. But due to strong inert pair effect, Pb +2 ion is more stable than Sn +2 ion. In other words, PbO2 is more easily reduced than SnO2. Thus, PbO2 is a stronger oxidizing agent than SnO2.
Question 13.
Discuss the following among group 14 elements:
1. Oxidation states
2. Atomic size
3. Reactivity with oxygen.
Answer:
1. Oxidation state:
- Carbon has oxidation state of +4.
- Ge, Sn and Pb exhibit +2 oxidation states due to inert pair effect.
- The tendency to form +2 ionic state increases down the group.
2. Atomic size :
- Atomic radius of group 14 increases down the group.
- Increase in atomic size is due to increase in number of shells.
3. Reactivity with oxygen:
- All the elements of carbon family react with oxygen to form oxides.
- Carbon forms five oxides: CO, CO2, C3O2, C5O2 is and C12O9.
- When heated with oxygen, Pb forms red oxide di called litharge and yellow oxide called massicot.
- Silicon forms SiO2.

Question 14.
Suggest reasons why B-F bond length in BF3 and BF-4 differ?
Answer:
BF is a planar molecule in which B is sp2 hybridized. It has empty 2p orbital. Because of similar sizes of B and F, back bonding occurs in which a lone pair is transferred from F to empty ea p-orbital of B forming рл-рл bоnd. As a result, B-F bond ca acquire some double bond character. On the other hand, gr in BF ion, B is sp3 hybridized and forms four B-F single 4 bonds. It does not have vacant p-orbital available to accept the electrons from F atom and hence B-F bond is purely single bond. Since double is shorter than single bond, therefore B-F bond lengths in BF3 is shorter than An in BF4.
Question 15.
SiF is known but SiCl2 is not known Explain.
Answer:
This is due to following reasons:
- Silicon being small in size can accommodate 6 F atoms but cannot accommodate larger 6 Cl atoms.
- Due to smaller size of F, stearic repulsion will be less in SiF62-
- Interaction of lone pair electrons of F with Si is stronger than that of Cl lone pairs.
Question 16.
C and Si are almost tetravalent but Ge, Sn and Pb shows divalency. Why?
Answer:
Carbon does not have d or f-electrons. Therefore, it Des not show inert pair effect. Consequently, it shows n oxidation state of +4 due to the presence of two ectrons in the s-orbital and two electrons in p-orbital of e valence shell. In contrast, all other elements from Ge Pb contain either d or both d and felectrons and hence now oxidation states of +2 and +4 due to inert pair fect. Further as the number of d and f electrons increases; the inert pair effect becomes more and more rominent. In other words, as we move down the group om Ge to Pb, the stability of +2 oxidation state increases and that of +4 oxidation state decreases. Therefore, the tendency of Ge, Sn and Pb to exhibit +2 idation state increases with increasing atomic number group 14.
Question 17.
How is excess of carbon dioxide responsible for global warming?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is produced during combustion. It utilized by plants during photosynthesis and oxygen is leased into the atmosphere. As a result of this carbon oxide cycle, a constant percentage of 21% oxygen is aintained in the atmosphere. However, if the ncentration of carbon dioxide increases beyond 0.03% volume in the atmosphere due to combustion, some of CO2 remain unutilized. This excess of CO2 absorbs at radiated by the earth. Some of it is dissipated into e atmosphere while the remaining part is radiated to earth and other bodies present on the earth. As a result, temperature of the earth and other bodies on rth increases. This is called green house effect and rbon dioxide is called as green house gas. As a result of een house effect, global warming occurs which harious consequences.
Question 18.
Which of the following is not hydrolyzed by water and why?
BF3, BCl3, BBr3
Answer:
BF3 is not easily hydrolyzed by water because with ter it forms an adduct BF3OH2 whereas BCl3, BBr3 hydrolyzed to boric acid and HCl or HBr respectively. This because the B-F bond in BF3 is very strong due extensive рл-рл back bonding. As a result, it is not drolyzed by water. The B-F bond energy is far larger an B-OH bond energy and cannot be compensated. whnever in BCl3, and BBr, the corresponding B-Cl and Br bond energy is relatively less than B-F because of sufficient рл-рлr bonding. B-Cl or B-Br bond energy sily compansated with new B-OH bond energy Therefore, these are not hydrolyzed.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is the difference between diamond and graphite?
Answer:
|
Diamond |
Graphite |
|
It occurs naturally in free state. |
It occurs naturally and is manufactured artificially. |
|
It is the hardest natural substance known. |
It is soft and greasy to touch. |
|
It has high relative density (about 3.5). |
Its relative density is 2.3. |
|
It is transpraent and has high refractive index (2.45). |
It is black in colour and opaque. |
|
It is non-conductor of heat and electricity. |
Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity. |
|
It burns in air at 900C to give CO2. |
It burns in air at 700-800C to give CO2. |
|
It occurs as octahedral crystals. |
It occurs as hexagonal crystals. |
|
It is insoluble in all solvents. |
It is insoluble in all ordinarý solvents. |
Question 2.
What are silicones? State the uses silicones.
Answer:
Silicones are inorganic polymers, that is, there ar no carbon atoms in the backbone chain. The backbone i a chain of alternating silicon and oxygen atoms. Eac silicone has two groups attached to it, and these can b any organic groups.
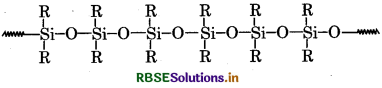
properities:
Some of the most useful properties of silicones include:
Uses:
- Low thermal conductivity.
- Low chemical reactivity
- Low toxicity.
- Thermal stability
- The ability to repel water and form watertigh .seals.
- Does not stick to many substrates, but adhere very well to others, e.g. glass.
- Does not support microbial growth.
- Silicones have excellent resistance to oxyger ozone, and ultraviolet light.
- Good electrical insulation.
Uses:
- Silicones are used in the construction industr (e.g. coatings, fire protection, glazing seals) an the automotive industry (external gaskets, external trim).
- Silicones are ingredients in many hair conditioners, shampoos and hair gel products.
- For making water proof papers, wool, textiles, wood etc. by coating them with a thin film of silicone.
- Silicone is becoming an important product in the cookware industry; particularly bake ware and kitchen utensils.
- Silicones are used as active compound in defoamers due to their low water solubility and good spreading properties.

Question 3.
(a) Carbon monoxide is readily absorbed by ammonical cuprous chloride solution but carbon dioxide is not. Why?
(b) Unlike ordinary fire, thermite reaction cannot be stopped by pouring water. Explain.
Answer:
(a) Due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on carbon in CO, it acts as a Lewis base and thus forms a soluble complex with ammonical cuprous chloride solution.
CuCl + NH3 + : CO → [Cu(CO)NH3] Cl
On the other hand, carbon dioxide does not act as a Lewis base since it does not have a lone pair of electrons on the carbon atom and hence does not dissolve in ammonical cuprous chloride solution.
(b) In ordinary fire, water not only decreases e temperature of the burning material, it also cuts off the supply of oxygen. But in case of thermite reaction:
2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The oxygen needed for reaction is supplied by metal oxide; therefore cutting off the supply of atmospheric oxygen has no effect. Further at high temperature Al react with water to produce hydrogen gas which helps to spread rather than extinguishing the fire.
2Al + 3H2O → Al2O3 + 3H2
Question 4.
(a) What is inorganic benzene ? Why is it so called? How will you get it from diborane?
(b) Identify A, B, C and D in the following sequence of reactions.
Metal (A) + N2 → (B) + C (white ppt.) + D (g) White ppt. (C) dissolves in NaOH solution while gas (D) gives white fumes with HCl.
Answer:
(a) Borazine or borazole is known as inorganic benzene because its structure is similar to that of benzene. It is also iso-electronic or isostructural with y benzene. Like carbon in benzene, both N and B, in d borazine are sp2 hybridized. Each N has a p-orbital which is perpendicular to the sigma bonding orbital and contain a lone pair of electron. In contrast, each B has an empty p-orbital which is also perpendicular to plane of the ring. Thus, the pi-bonding in borazine is dative and it arises from the sidewise overlapping of fully filled orbitals of N and empty orbitals of B.
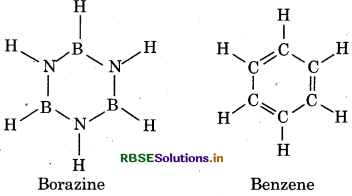
(b) (i) since gas (D) gives white fumes with HCl it must s be ammonia (NH3).
(ii) Since metal (A) on heating reacts with nitrogen to form compound B, which on hydrolysis with water gives white ppt.(C) which dissolves in NaOH along with evolution of NH3 (D) p therefore, metal (A) must be Al, (B) must be it aluminium nitride (AIN) and (C) must be p aluminium hydroxide Al(OH)3.
2Al + N2 → 2AIN
AIN + 3H2O → Al(OH)3 + NH3
AK(OH)3 + NaOH → NaAlO2 + 2H2O
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
Arrange the following group 13 elements increasing atomic radius :
(a) Al < Ga < In < Tl
(b) Ga < Al< In < Tl
(c) Al < In < Ga < Tl
(d) Al < Ga < Tl < In
Answer:
(b) Ga < Al< In < Tl
Question 2.
Which of the following order is not accordance to the property given?
(a) B < C < N < O (Increasing ionisation energy)
(b) I < Br < C < F (Increasing electron ga enthalpy)
(c) Li< Na < K < Rb (Increasing metallic radius)
(d) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < F (Increasing atomic size]
Answer:
(a) B < C < N < O (Increasing ionisation energy)
Question 3.
The order of stability of +1 oxidation state is
(a) Al < Ga < In < Tl
(b) Tl < In < Ga < Al
(c) In < Tl < Ga < Al
(d) Ga < In < Al < Tl
Answer:
(a) Al < Ga < In < Tl
Question 4.
Calumniate is:
(a) Ca[B2O4 (OH)2] · 2H2O
(b) Ca2B62H2O
(c) Ca(OH)2
(d) Na2B4O7 · 2H2O
Answer:
(b) Ca2B62H2O
Question 5.
When aqueous solution of aluminium chloride is heated to dryness, it gives :
(a) AlCl3
(b) Al2Cl6
(c) Al2O3
(d) Al (OH) Cl2
Answer:
(c) Al2O3
Question 6.
Which of the following is electron deficient compound?
(a) B2H6
(b) C2H6
(c) PH3
(d) SiH4
Answer:
(a) B2H6
Question 7.
The compound which exists as dimer is:
(a) LiCl
(b) MgCl2
(c) AlCl3
(d) SiCl4
Answer:
(c) AlCl3
Question 8.
Which of the following has same structure as graphite?
(a) B2H6
(b) BN
(c) B
(d) B4C
Answer:
(b) BN

Question 9.
The essential number of electrons required to form bridging bond in diborane is :
(a) 6
(b) 2
(c) 8
(d) 4
Answer:
(d) 4
Question 10.
The number of B-O-B bond and B-OH bonds present in borax are :
(a) 5 and 4
(b) 4 and 5
(c) 3 and 4
(d) 5 and 5
Answer:
(a) 5 and 4
Question 11.
Which liquid solidification:
(a) Ga
(b) Al
(c) In
(d) Cu
Answer:
(a) Ga
Question 12.
The products obtained on hydrolysis of diborane are:
(a) B2O3 and H2 BO3
(b) Only B2O3
(c) HBO3 and H2
(d) Only H2 BO3
(e) B2O3 and H2
Answer:
(c) HBO3 and H2
Question 13.
Boron cannot form BF3 because:
(a) Electronegativity of boron is high
(b) Electronegativity of fluorine is high
(c) Absence of d-orbitals in boron
(d) The difference in electronegativity is less between B and F.
Answer:
(c) Absence of d-orbitals in boron
Question 14.
The correct formula of aluminium nitride is:
(a) AIN
(b) AIN2
(c) AIN3
(d) Al3N2
Answer:
(a) AIN

Question 15.
The decreasing order of ability of BF3, BCl3, BBr3 to behave as Lewis acid is :
(a) BF3 > BCl3 > BBr3
(b) BCl3 > BF3 > BBr3
(c) BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3
(d) BBr3 > BF3 > BCl3
Answer:
(c) BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3
Question 16.
The product obtained on mixing ammonia with diborane at 120°C is :
(a) B2H6 NH3
(b) B2H6 2NH3
(c) B2H6 3NH3
(d) B2H6·4NH3
Answer:
(b) B2H6 2NH3
Question 17.
Which of the following anion is not formed by boron?
(a) BF63-
(b) BH4-
(c) B(OH)-4
(d) BO2-
Answer:
(a) BF63-
Question 18.
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) Aluminium reacts in excess of NaOH and forms Al(OH)3·
(b) NaHCO3 gives Na2CO3 on heating.
(c) Pure sodium metal dissolves in ammonia to give blue solution.
(d) NaOH reacts with glass and forms sodium silicate.
Answer:
(a) Aluminium reacts in excess of NaOH and forms Al(OH)3·
Question 19.
Which of the following gives silicon oil on hydrolysis and polymerisation?
(a) Trimethyl chlorosilane and dimethyl chlorosilane
(b) Trimethyl chlorosilane and methyl chlorosilane
(c) Methyl trichlorosilane and dimethyl chlorosilane
(d) Trimethyl chlorosilane and diethyl dichlorosilane
Answer:
(a) Trimethyl chlorosilane and dimethyl chlorosilane
Question 20.
Which sulphide is soluble in yellow ammonium sulphide?
(a) HgS
(b) PbS
(c) Cds
(d) SnS
Answer:
(d) SnS
Question 21.
Red lead is:
(a) Pb3O4
(b) PbO
(c) PbO2
(d) Pb4O3
Answer:
(a) Pb3O4
Question 22.
Which of the following is not a monomer for high molecular weight silicon polymer?
(a) PbSiCl3
(b) MeSiCl3
(c) Me2 SiCl2
(d) Me3SiCl
Answer:
(d) Me3SiCl

Question 23.
Choose the element which do not form double bond?
(a) N
(b) S
(c) Si
(d) P
Answer:
(c) Si
Question 24.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Beryl is an example of cyclic silicate.
(b) MgSiO4 is an orthosilicate.
(c) The fundamental unit in silicates is tetrahedron SiO2 unit.
(d) Feldspar is not an aluminosilicate.
Answer:
(d) Feldspar is not an aluminosilicate.
Question 25.
The basic structural unit of silicates is:
(a) SiO2-
(b) SiO4-
(c) SiO44-
(d) SiO2-
Answer:
(c) SiO44-
Question 26.
Which element in p-block does not show property of catenation?
(a) C
(b) Si
(c) Ge
(d) Pb
(e) Sn
Answer:
(d) Pb

Question 27.
Pb + conc. HNO3 gives:
(a) Pb (NO3 )2 + NO2
(b) PbNO3 + NO
(c) Pb (NO3) + NO3
(d) Pb (NO3)3 + N2O
Answer:
(a) Pb (NO3 )2 + NO2
Question 28.
Which of the following has lowest tendency of catenation?
(a) C
(b) Si
(c) Ge
(d) Sn
Answer:
(d) Sn

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter