RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 Important Questions The s-Block Elements
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Which property of alkali metal increase with increase in atomic number?
(a) electronegativity
(b) ionic radius
(c) first ionisation energy
(d) melting point
Answer:
(b) ionic radius

Question 2.
Sodium metal can be stored under:
(a) kerosene
(b) benzene
(c) toluene
(d) alcohol
Answer:
(a) kerosene
Question 3.
The process of industrial preparation sodium carbonate is known as:
(a) Castner process
(b) Haber's process
(c) Le-blanc process
(d) Chamber process
Answer:
(c) Le-blanc process
Question 4.
Alkali metals are strong reducing agen because:
(a) These are mono-valent
(b) Their ionisation potential is very high
(c) Their E° values are negative
(d) These are metals
Answer:
(c) Their E° values are negative
Question 5.
Which of the following s-block element forms nitride ?
(a) Ba
(b) Be
(c) Ca
(d) Li
Answer:
(d) Li
Question 6.
Potassium nitrate is called:
(a) Mohr's salt
(b) Gypsum
(c) Indian salt petre
(d) Chile salt petre
Answer:
(c) Indian salt petre
Question 7.
A substance X is a compound of an element IA. It gives violet colour in flame test, X is.
(a) LiCl
(b) NaCl
(c) KCl
(d) none
Answer:
(a) LiCl
Question 8.
Which of the following is most electropositive element?
(a) calcium
(b) chlorine
(c) potassium
(d) carbon
Answer:
(b) chlorine
Question 9.
Which of the following is a false statement?
(a) Fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine
(b) Nitrogen has greater IE1 than oxygen.
(c) Lithium is amphoteric
(d) Chlorine is an oxidising agent.
Answer:
(d) Chlorine is an oxidising agent.
Question 10.
When NaOH crystals are left in open air, they acquire a fluid layer around each crystal as:
(a) They starts melting
(b) They absorb moisture from air.
(c) They react with air to form a liquid compound
(d) They absorb CO2 from air
Answer:
(b) They absorb moisture from air.

Question 11.
Which of the following metal is found in green colouring pigment chlorophyll of plants?
(a) Fe
(b) Mg
(c) Na
(d) Al
Answer:
(c) Na
Question 12.
For bleaching powder, which is incorrect?
(a) React with dilute acid to release chlorine
(b) Oxidising agent
(c) Light yellow coloured powder
(d) Highly soluble in water
Answer:
(b) Oxidising agent
Question 13.
The dark red colour of bombs in fireworks is due to the presence of:
(a) Na
(b) Ba
(c) Sr
(d) K.
Answer:
(d) K.
Question 14.
Setting of cement is an:
(a) Exothermic reaction.
(b) Endothermic reaction
(c) Neither exothermic nor endothermic
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Exothermic reaction.
Question 15.
The correct order of increasing ionic character is:
(a) BeCl2 < MgCl2 < CaCl2 < BaCl2
(b) BeCl2 < MgCl2 < BaCl2 < CaCl2
(c) BeCl2 < BaCl2 < MgCl2 < CaCl2
(d) BaCl2 < CaCl2 < MgCl2 < BeCl2
Answer:
(b) BeCl2 < MgCl2 < BaCl2 < CaCl2
Question 16.
A certain metal M is used to prepare an antacid, which is used as a medicine for acidity. This metal accidently catches fire which cannot be put out by using CO2 based extinguisher. The metal M is:
(a) Ca
(b) C
(c) Mg
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these

Question 17.
Among alkaline earth metals, the element forming predominantly covalent compound is :
(a) Barium
(b) Strontium
(c) Calcium
(d) Beryllium
Answer:
(a) Barium
Question 18.
Peroxide bond is present in :
(a) MgO
(b) CaO
(c) Li2O
(d) BaO2
Answer:
(b) CaO
Question 19.
A sodium salt on treatment with MgCl2 gives white precipitate only on heating. The anion of sodium salt is :
(a) HCO3
(b) CO2-
(c) NO3
(d) SO2-
Answer:
(b) CO2-
Question 20.
Bleaching action of CaOCl2 is due to:
(a) Nascent oxygen
(b) Chlorine
(c) HCIO
(d) HCl
Answer:
(a) Nascent oxygen
Question 21.
The correct order of stability for the following super oxides is:
(a) Na2O
(b) Na2O2
(c) K2O
(d) KO2
Answer:
(d) KO2
Question 22.
The elements which are very abundant in earth crust are :
(a) Si and Al
(b) Ca and Mg
(c) B and Al
(d) All
Answer:
(a) Si and Al

Question 23.
The oxides of beryllium BeO is:
(a) Acidic
(b) Basic
(c) Amphoteric
(d) Neutral
Answer:
(c) Amphoteric
Question 24.
Some of the group-2 metal halides are Among the following metal halides, the one which is soluble in ethanol is covalent and soluble in organic solvents.
(a) BeCl2
(b) MgCl2
(c) CaCl2
(d) SrCl2
Answer:
(a) BeCl2
Question 25.
Which is not an ore of Ca ?
(a) Lime stone
(b) Flurospar
(c) Dolomite
(d) Epsomsalt
Answer:
(d) Epsomsalt
Question 26.
The order of decreasing polarity in the compounds CaO, CSF, KCl, MgO is :
(a) CaO, CSF, KCl, MgO
(b) MgO, KCl, CaO, CsF
(c) KCl, CaO, CSF, MgO
(d) CsF, KCl, CaO, MgO
Answer:
(d) CsF, KCl, CaO, MgO
Question 27.
Which of the following is not known?
(a) KO3
(b) KO4
(c) KO2
(d) K2O2
Answer:
(b) KO4
Question 28.
Which of the following acts as reducing as well as oxidising agent?
(a) NaNO3
(b) Na2O2
(c) Na2O
(d) KNO3
Answer:
(c) Na2O
Question 29.
The salt that is added to table salt to make it flow freely in rainy season is :
(a) KCl
(b) Kl
(c) Cag (PO4)2
(d) Na3PO4
Answer:
(c) Cag (PO4)2

Question 30.
Which of the following alkaline earth metal sulphates is least soluble in water?
(a) MgSO4
(b) CaSO4
(c) BaSO4
(d) SrSO4
Answer:
(c) BaSO4
Question 31.
The hydration energy of Mg2+ is greater than that of:
(a) Al3+
(b) Be2+
(c) Na+
(d) Mg
Answer:
(c) Na+
Question 32.
The active constituent of bleaching powder is:
(a) Ca(OCI)2
(b) Ca(OCI)Cl
(c) Ca(CIO2)2
(d) Ca(ClO2)Cl
Answer:
(a) Ca(OCI)2
Question 33.
KO2 is used in oxygen cylinders in space and submarines because it:
(a) absorbs CO2 and increase O2 content
(b) eliminates moisture
(c) produces ozone
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) absorbs CO2 and increase O2 content
Question 34.
Flame test is not given by:
(a) Be
(b) Sr
(c) K
(d) Ca
Answer:
(a) Be
Question 35.
Which of the following is radioactive ?
(a) Ca
(b) Fr
(c) Rb
(d) Li
Answer:
(b) Fr
Question 36.
Caesium oxide is:
(a) strong basic
(b) acidic
(c) weak base
(d) amphoteric
Answer:
(a) strong basic
Question 37.
Which of the following is lightest element?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Li
(d) Mg
Answer:
(c) Li

Question 38.
When K is heated, we obtain:
(a) K2O
(b) KO2
(c) K2O2
(d) KO
Answer:
(b) KO2
Question 39.
The group which forms peroxide is:
(a) Li, Na, K
(b) Na, K, Mg
(c) H, Na, Ba
(d) H, Li, Mg
Answer:
(c) H, Na, Ba
Question 40.
Which of the following is strongest reducin agent in aqueous solution in terms o electrode potential?
(a) Li
(b) Na
(c) K
(d) Rb
Answer:
(a) Li
Question 41.
Covalent chloride is:
(a) BaCl2
(b) NaCl
(c) CaCl2
(d) BeCl2
Answer:
(d) BeCl2
Question 42.
Amphoteric oxide is:
(a) MgO
(b) Na2O
(c) BeO
(d) BaO
Answer:
(c) BeO
Question 43.
Which of the following is used as dehydrating agent in laboratory?
(a) NaCl
(b) CaCl2
(c) MgCl2
(d) KCl
Answer:
(b) CaCl2
Question 44.
Baking soda is :
(a) Sodium carbonate
(b) Sodium bicarbonate
(c) Sodium sulphate
(d) Potassium carbonate
Answer:
(b) Sodium bicarbonate
Question 45.
In Solvay's method, the reason for the precipitate is:
(a) Reaction with ammonia
(b) Low temperature
(c) common ion effect in brine solution
(d) reaction of carbon dioxide.
Answer:
(c) common ion effect in brine solution

Question 46.
An element of alkaline earth metals whic generally forms covalent compounds is:
(a) Ba
(b) Sr
(c) Ca
(d) Be
Answer:
(d) Be
Question 47.
Gypsum is :
(a) MgSO4 ·7H2O
(b) CuSO4.5H2O
(c) CaSO4 2H2O
(d) Na2SO4 · 10H2O
Answer:
(c) CaSO4 2H2O
Question 48.
Weakest base is
(a) Be(OH)2
(b) Mg(OH)2
(c) NaOH
(d) KOH
Answer:
(a) Be(OH)2
Question 49.
The boiling point of Mg is:
(a) 1023 K
(b) 1272 K
(c) 1373 K
(d) 1473 K
Answer:
(c) 1373 K
Question 50.
The electronic configuration of alkaline earth metals is:
(a) ns2
(b) ns1
(C) np6
(d) ns2 (nd)d 10
Answer:
(a) ns2

Question 51.
Which of the following is most positive alkaline earth metal?
(a) Be
(b) Mg
(c) Ca
(d) Ba
Answer:
(d) Ba
Question 52.
Which of the following has highest ionisation potential?
(a) Be
(b) Mg
(c) Ca
(d) Ba
Answer:
(a) Be
Question 53.
Which colour is given by calcium in flame test?
(a) red
(b) green
(c) white
(d) pink
Answer:
(a) red
Question 54.
Which of the following has outermost electronic configuration of 3p6 4s2?
(a) Ca
(b) Zn
(c) Mg
(d) Cu
Answer:
(a) Ca
Question 55.
Which of the following is insoluble in acetic acid?
(a) calcium oxide
(b) calcium carbonate
(c) calcium oxalate
(d) calcium hydroxide
Answer:
(c) calcium oxalate
Question 56.
Which of the following metal is found in chlorophyll?
(a) Mg
(b) Be
(c) Ca
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) Mg

Question 57.
Magnesium is burnt in:
(a) N2
(b) CO
(c) NO2
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) N2
Question 58.
Out of Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs, how many of them directly form superoxides on heating with oxygen?
(a) 5
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 59.
Carbonates of lithium are not stable like that of sodium due to :
(a) Low electronegativity
(b) Low electropositivity
(c) Low charge density
(d) Not known yet
Answer:
(b) Low electropositivity
Question 60.
Which one of the following is not an alkali metal?
(a) Francium
(b) Caesium
(c) Rubidium
(d) Radium
Answer:
(d) Radium
Question 61.
Crystals of Na2CO3 10H2O when exposed to air:
(a) Lose water and remain solid
(b) Gain water and remain solid
(c) Gain water and become liquid
(d) Remains unchanged
Answer:
(a) Lose water and remain solid
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Which metal floats on water without any apparent reaction with it?
Answer:
Lithium.

Question 2.
Which of the following and why can be used for storage of alkali metals? H2O, C2H5 OH, benzene.
Answer:
Benzene can be used to store alkali metals because Ans other substances react with alkali metals as:
Na + H2O → NaOH + 1/2 H2
Na + C2H5OH → C2H5ONa + 1/2 H2
Question 3.
What is dead burnt plaster?
Answer:
When Plaster of Paris is heated above 393 K, whole Ans of the water of crystallization is lost. The resulting its anhydrous calcium sulphate is called as dead burnt But plaster as it loses the property of setting with water.
Question 4.
Why are halides of beryllium polymeric?
Answer:
The halides of Be are electron deficient as their octets are incomplete. Therefore to complete their octet, the halides polymerize.
Question 5.
Which element in group 2 forms amphoteric oxide and water soluble sulphate? To which period does it belongs?
Answer:
Beryllium. It belongs to second period.
Question 6.
Arrange the alkaline earth metal carbonates in decreasing order of thermal stability.
Answer:
The decreasing order of thermal stability is:
BaCO3 > SrCO3 > CaCO3 > MgCO3 > BeCO3.
Question 7.
Which of the alkali metal is smallest in size?
Answer:
Lithium.
Question 8.
Which metal salts gives deep pink colour to the flame?
Answer:
Strontium.
Question 9.
What is the order of solubility of sulphates of alkaline earth metals in water?
Answer:
BeSO4 > MgSO4 > CaSO4 > SrSO4 > BaSO4·
Question 10.
Why alkaline earth metals have a great tendency to form complexes than alkali metals?
Answer:
Because of smaller size and higher charge on aline earth metal cations as compared to responding alkali metal cations, alkaline earth metal
ons have a greater tendency to form complexes.

Question 11.
The second ionisation enthalpy of calcium is more than that of first and yet calcium forms CaCl2 and not CaCl. Why?
Answer:
The higher enthalpy of lattice formation of Ca2+ is re that compensates the second ionization enthalpy uired for formation of divalent Ca2+ ions.
Question 12.
What is the difference between milk of lime and lime water?
Answer:
A suspension of slaked lime, i.e. Ca(OH), in water alled milk of lime and a clear decanted solution of ked lime is called lime water.
Question 13.
Why BaSO4 is insoluble whereas BeSO4 is soluble in water?
Answer:
The lattice enthalpy of BaSO is much more than ydration enthalpy and hence it is insoluble in water. hydration enthalpy of BeSO4 is much higher than lattice enthalpy because of small size of beryllium. Therefore, it is highly soluble in water.
Question 14.
It is necessary to add gypsum in the final stages of preparation of cement. Explain why?
Answer:
Gypsum is added in the final stage of preparation ement since when water is added to cement it slows n the process of setting of cement so that it gets iciently hardened thereby imparting greater ngth to it.
Question 15.
Why does beryllium show similarity with aluminium?
Answer:
Due to same electronegativity and very similar rizing power of their ions.
Question 16.
Alkali and alkaline earth metals cannot be obtained by chemical reduction metho Explain.
Answer:
Since they are themselves stronger reducin agents than majority of common reducing agents used.
Question 17.
Why lithium hydride is used as a source of hydrogen?
Answer:
Lithium hydride has low molecular weight and o reacting with water it evolves highest percentage hydrogen by weight. Hence it is used as a source hydrogen for military purposes and for fillin metrological balloons.
Question 18.
Why lithium cannot be used in making photoelectric cells?
Answer:
Lithium cannot be used in making photoelectr cells because out of all alkali metals, it has highe ionization enthalpy and cannot emit electrons whe exposed to light.

Question 19.
LiI3 is less stable than CsI3. Why?
Answer:
This is due to lattice energy effects. The larg cation stabilizes a large anion in its lattice. Therefor CsI is more stable because Cs being larger cation ca stabilizes large Ig ion.
Question 20.
Arrange the following in decreasing order ionic mobility:
Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+.
Answer:
Rb+ > K+ > Na+ < Li+.
Question 21.
Arrange the following in decreasing order melting point: Be, Mg, Ca, Sr.
Answer:
Be > Ca > Sr > Mg
Question 22.
Arrange the following in decreasing order enthalpy of formation: BeO, MgO, CaO.
Answer:
CaO > MgO > BeO
Question 23.
Arrange the following in decreasing order metallic radius: Be, Mg, Ca (metallic radius).
Answer:
Ca > Mg > Be.
Question 24.
Write the name of alkali metal which a found in liquid state.
Answer:
Cs and Fr.
Question 25.
Why density of alkali metals is low?
Answer:
Because of large size and weak metallic bond.
Question 26.
What are group 1 elements called?
Answer:
Alkali metals.
Question 27.
Which element shows diagonal relationshi with Mg?
Answer:
Li.
Question 28.
Write the main ores of sodium and potassium.
Answer:
Na-NaCl and K-KCl.

Question 29.
Why alkali metals are used in photoelectric cells?
Answer:
Because their ionisation enthalpy is low.
Question 30.
Why melting and boiling points of alkali metals are low?
Answer:
Because their size is large and bonds present in them is also weak.
Question 31.
Which alkali metal ion has highest polarising power?
Answer:
Lithium.
Question 32.
Why beryllium chloride is soluble in organic solvents?
Answer:
Because it is a covalent compound.
Question 33.
On moving down the group, density of group IA elements increases but at which element this order disturbs?
Answer:
At potassium.
Question 34.
Which elements have density less than water?
Answer:
Li, Na-and K.
Question 35.
Which metal is hard in group IA elements?
Answer:
Lithium.
Question 36.
Which metal is soft in group IA elements?
Answer:
Caesium.
Question 37.
Which element in group LA cannot be cut with a knife?
Answer:
Lithium.

Question 38.
Which hydroxide in group IA is strongest alkali?
Answer:
CsOH.
Question 39.
Which element of group IA reacts with nitrogen and form nitride?
Answer:
Lithium.
Question 40.
Alkali metals are conductors of heat and electricity. Explain.
Answer:
Because its valence electron is loosely attached to nucleus.
Question 41.
Pure NaCl is not deliquescent but salt used in homes becomes wet in rainy season. Why?
Answer:
Magnesium chloride is mixed as impurity in ip common salt used at homes which is a deliquescent compound.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
How do following properties vary among alkali metals?
1. Atomic radius
2. Ionization energy
3. Metallic character
Answer:
- Atomic Radius: Atomic radius of alkali metals increases down the group because on moving down the group, with increase in nuclear charge, number of shells also increases. This results in increase in atomic radius.
- lonization Energy: Alkali metals have lowest ionization energy in a period. The ionization energy of alkali metals decreases down the group. Decrease in ionization energy is due to increase in atomic size which results in lesser attraction of electrons by nucleus.
- Metallic Character: All alkali metals are strongly electropositive or metallic in nature. Metallic character increases down the group due to decrease in ionization energy down the group.
Question 2.
Lithium differs from other alkali metals. Explain with examples.
Answer:
Lithium shows anomalous behaviour due to its smallest size, high polarization power and non-availability of d-orbital. Some of them are as follows:
- Lithium is hardest of all the alkali metals.
- The melting and boiling point of lithium are much br higher than other alkali metals.
- Lithium is deliquescent and crystallizes as a hydrate, LiCl 2H2O while other alkali metals do Ar not.
- It forms only monoxide with oxygen while others form peroxides and super oxides.
- It readily forms nitride with nitrogen while other alkali metals do not form nitride.
- Li + N2 → 2LigN

Question 3.
How is Plaster of Paris prepared? Describe its main property due to which it is widely used.
Answer:
Plaster of Paris is prepared by heating gypsum to 393 K.
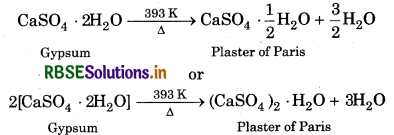
It is widely used due to its property of setting with water. mixing with water, it forms a plastic mass which sets co a hard solid in 5-15 minutes. This is called as setting Plaster of Paris. The setting is due to hydration of aster of Paris into gypsum.
Question 4.
When an alkali metal is dissolved in liquid ammonia the solution acquire different colours. Explain the reason for this type of colour change.
Answer:
In solution the alkali metal atom readily loses the lence electron. Both the cation and electron combine th ammonia to form ammoniated cation and
moniated electron as:
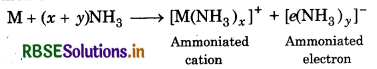
Where M = alkali metal
Ammoniated electron is responsible for blue colour of the lution. When light falls on these ammoniated ectrons, they get excited to higher energy levels by sorbing energy corresponding to red region of visible ht. As a result, transmitted light is blue in colour. The lution becomes blue in colour which is paramagnetic. hen the concentration increases, the ammoniated etal ion get bound by free unpaired electron known as panded metals. As a result, the solution becomes onze in colour which is diamagnetic.
Question 5.
Why fluorides of alkali metals are most stable and iodides are least stable? ·
Answer:
The alkali metal halides are high melting lourless crystalline solids. All these halides have high gative enthalpies of formation. The enthalpies of mation for fluorides become less negative as we move wn the group. While reverse is true for iodides. For a ven metal, enthalpy of formation becomes less gative from fluoride to iodide. Thus, fluorides of alkali etals are most stable and iodides are least stable.
Question 6.
Give reasons:
(i) Alkaline earth metals always form divalent cations even though the second ionization energy of these metals is almost double their first ionization energy.
(ii) A piece of burning magnesium ribbon continues to burn in SO2.
Answer:
(i) In solid state, the divalent cations form stronger ctices than monovalent cations and therefore, a lot of energy called lattice energy is released. It is the greate lattice enthalpy of E2+ ion which compensates for hig second ionization energy and is responsible for it greater stability as compared to E.
(ii) Magnesium continues to burn in SO2 because reacts with it to form MgO and S.
2Mg + SO2 → 2MgO + S
The reaction is exothermic and it keeps the piece magnesium burning.

Question 7.
State as to why:
(i) Lithium on being heated in air mainly form monoxide and not peroxide.
(ii) Alkaline earth metals cannot be obtained reduction of their oxides with carbon.
Answer:
(i) Lithium ion is very small ion and therefore, ha strong positive field around it. Therefore, it can stabiliz only a small anion, O2- . In other words, because of sma size of lithium ion, the spreading of negative charg towards another oxygen atom is prevented an therefore, it cannot combine with another oxygen ator to form peroxide ion.
(ii) Alkaline earth metals are themselves stron reducing agents (high reduction potential values] Therefore, they cannot be obtained by reduction of thei oxides by carbon.
Question 8.
What is the order of stability of carbonates alkaline earth metals? Why?
Answer:
The order of stability of alkaline earth meta
carbonates is as follows:
BeCO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 < SrCO3 < BaCO3
Stability of alkaline earth metal carbonates increase down the group as the electropositive character of th metal or the basicity of the metal hydroxide increase down the group. Hence, BeCO3 is unstable and can b kept only in atmosphere of CO2.
Question 9.
Explain diagonal relationship of lithium with magnesium.
Answer:
Lithium resembles magnesium due to similarity in sizes of their atoms and ions. The main points o similarity are:
1. Both have almost similar electronegativities.
2. Both LiOH and Mg (OH), are weak bases.
3. Lithium and magnesium react with nitrogen to form nitride.
6Li + N2 → 2Li3N
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
4. The carbonates of both these metals decompose on heating to form oxide and evolve carbon dioxide.
Li2CO3 → Li2O + CO2
MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
5. Both combine with oxygen to form monoxides.
Other forms peroxides or superoxide.
4Li + O2 → 2Li2O
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
6. Chlorides of both are deliquescent and crystallize from aqueous solution as hydrates.
Question 10.
What is cement? How is it prepared? What are important components of Portland cement?
Answer:
Cement is a mixture of finely grinded mixture of calcium silicates and aluminates which sets to a hard e mass when treated with water. It is known as Portland d cement because it resembles with famous building stone found near Portland in England.
The important components of Portland cement are:
- Di-calcium silicate (Ca2SiO4): 26%
- Tri-calcium silicate (Ca3SiO): 51%
- Tri-calcium aluminate (Ca3Al2O6): 11%
Question 11.
How do following properties vary among alkaline earth metals?
1. Atomic radius
2. Metallic character
3. Melting and boiling point
Answer:
- Atomic Radius : The atomic radius of alkaline s earth metals is fairly large and it increases down the e group. Their atomic radius is smaller than alkali metals. On moving down the group, due to the addition of an extra shell of electrons in each succeeding element and increasing screening effect, atomic radius increases.
- Metallic Character: Alkaline earth metals are highly electropositive elements. These elements have low ionization energy; they have high tendency to lose both the valence electrons to form di-positive ion. The metallic character increases down the group because ionization energy decreases and atomic size increases down the group.
- Melting and Boiling Point: The melting and o boiling point of alkaline earth metals are high as compared to alkali metals. However, down the group there is no regular trend in their melting and boiling point.

Question 12.
Explain the formation and properties of oxides of alkaline earth metals:
Answer:
(i) Formation of Oxides : BeO, MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO
Oxides of alkaline earth metals are obtained by heating the metal in di-oxygen or decomposition of their carbonates.
2M + O2 → 2MO
MCO3 → MO + CO2
(M = Be, Mg, Ca)
Properties:
1. The oxides have high melting point and have low vapour pressure.
2. The enthalpies of formation of these oxides are quite high and are very stable.
3. Except BeO, all other oxides of alkaline earth metals are basic in nature. BeO is amphoteric.
4. The solubility, thermal stability and basic character of these oxides increase with increasing atomic number.
Question 13.
Explain formation and properties of hydroxides of alkaline earth metals.
Answer:
Formation of hydroxides : Be(OH)2, Mg(OH)2,
Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2.
Hydroxides are formed by reacting metal with cold water or by reacting corresponding oxides with water.
M + 2H2O → M(OH)2 + H2
MO + H2O → M(OH)2
Properties:
- Except Be(OH)2, all other hydroxides are basic in nature.
- These hydroxides are less soluble than alkali metals and solubility increases with increase in atomic number down the group.
- Solubility and thermal stability increase down the group.
Question 14.
Why lithium is strongest reducing agent in aqueous solution?
Answer:
Lithium is strongest reducing agent because it has lowest value of electrode potential (-3.04 V). Electrode potential is a measure of tendency of an element to lose electrons in aqueous solutions. More negative is the value of electrode potential, higher is the tendency to lose electrons and stronger is the reducing agent. Electrode potential depends upon :
(a) Ionization enthalpy : M(g) → M+ (g) + e-
(b) Enthalpy of sublimation → Asub H
(c) Hydration enthalpy: M+(g) + H2O → M-(aq)
Li+ has the smallest size and is hydrated to maximum extent. Therefore, large amount of energy called hydration energy is released in hydration of lithium. The amount of energy released is so large that it compensates the energy needed to remove electron i.e ionization energy. The net effect is that it has greater tendency to lose electron in solution than alkali metals.
Li (s) → Li+(aq) + e-
Thus lithium is strongest reducing agent because of its greater hydration energy.

Question 15.
How beryllium shows similarity with aluminium?
Answer:
Beryllium shows similarities with aluminium due to diagonal relationship. Some of them are:
1. Both the metals are weakly electropositive in nature.
2. Both Be and Al have same electronegativity and their charge/radius ratio are similar.
3. Both form covalent bonds.
4. Both BeO. and Al2O3 are amphoteric i.e., the dissolve in acids and bases.
BeO + 2HCl → BeCl2 + H2O
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
BeO + 2NaOH → Na2 BeO2 + H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
5. Carbides of both Be and Al liberate methane with water.
Be2C + 2H2O → 2BeO + CH4
Al4C3 +12H2O → 4Al(OH)3 + 3CH4
Question 16.
When heated in air alkali metals form various oxides. Mention the oxides formed by Li, Na and K.
Answer:
Lithium forms only lithium oxide, sodium forms nainly sodium peroxide along with a small amount of odium oxide and potassium forms only potassium uperoxide.
4Li + O2 → 2Li2O (Lithium oxide)
2Na + O2 → Na2O2 (Sodium peroxide)
K + O2 → KO2 (Potassium superoxide)
Reason 1. As the size of metal cation increases, positive eld around it becomes weaker and weaker thereby ermitting initially formed oxide ion to combine with another oxygen to form first peroxide ion and then uperoxide. Since larger cation stabilizes larger anions due to igher lattice energy, therefore, stability increases from oxide to superoxide as size of metal cation increases down the group.
Question 17.
Sodium fire in laboratory should not be extinguished by pouring water. Why?
Answer:
Sodium reacts violently with water producing hydrogen which also catches fire. Therefore, the fire increases on adding water instead instead of getting extinguished. Hence, water should not be used for extinguishing sodium fire. It can be extinguished by pyrene.
Question 18.
The crystalline salts of alkaline earth metals contain more water of crystallization than the corresponding alkali metal salts. Explain.
Answer:
Alkaline earth metals have smaller size and higher nuclear charge than alkali metals. Therefore, alkaline earth metals have higher tendency to attract water molecules and hence contain more water of crystallization molecules than alkali metals. For example: MgCl2 · 6H2O. However among alkali metals only lithium because of its small size forms hydrated salts such as LiCl · 2H2O.

Question 19.
Explain why?
a. LiH is more stable than NaH.
b. Alkali metals are soft and have low melting points.
c. Salts of alkaline earth metals are colourless and diamagnetic.
Answer:
(a) Both Lit and H have small size and their combination has high lattice energy. Therefore, LiH is stable as compared to NaH.
(b) Alkali metals have only one electron per metal atom. As a result, the binding energy of alkali metal ion in the close-packed metal lattices is weak. Therefore, these are soft and have low melting point.
(c) Alkaline earth metals form di-positive ions in their salts. These di-positive ions have noble gas configurations with no unpaired electrons. Therefore, these compounds are colourless and diamagnetic.
Question 20.
How will you distinguish between:
1. Magnesium and calcium?
2. Sodium sulphate and barium sulphate?
3. Lithium nitrate and potassium nitrate?
Answer:
- Calcium and Magnesium: Calcium when heated imparts brick red colour to flame but magnesium does not.
- Sodium sulphate is soluble in water but barium. sulphate is insoluble.
- Lithium nitrate on heating gives reddish brown vapours of NO2 but potassium nitrate gives colourless oxygen gas.
Question 21.
Calcium burns in nitrogen to produce a white powder which dissolves in sufficient water to produce a gas (A) and an alkaline solution. The solution on exposure to air produces a thin solid layer of (B) on the surface. Identify the compounds (A) and (B).
Answer:
Ca burns in air to form CaO and Ca2N2
2Ca + O2 → 2CaO
3Ca + N2 → Ca3N2
and
Calcium nitride on hydrolysis with water gives ammonia (A)
CaзN2 + 6H2O → 3Ca(OH)2 + 2NH3
The alkaline solution of calcium hydroxide thus formed reacts with carbon dioxide present in air to form calcium carbonate which being insoluble forms a thin solid layer on the surface.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Describe Solvay-Ammonia process for preparation of sodium carbonate.
Answer:
By Solvay process sodium carbonate can be prepared.
It has following steps:
(a) Ammoniation Tower: Ammonia and saturated solution of brine is introduced into this.
(b) Carbonating Tower: In this, carbon dioxide is passed through ammoniated brine to form sodium bicarbonate.
(c) Filtration: Here filtration is done through vacuum filters.
(d) Calcination of Sodium Bicarbonate: Sodium carbonate is formed by calcination as:
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
(e) Ammonia recovery Tower Here ammonia is recovered which is reused in ammoniation tower.
The whole process can be represented as:
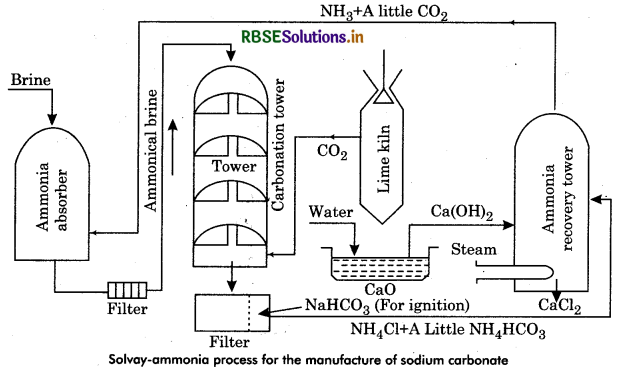

Question 2.
Write the physical properties of alkaline earth metals. (in tabular form).
Answer:
|
Property |
Alkaline Earth models |
|
1. Appearance |
Silvery white, lustrous and relatively soft. |
|
2. Valence electrons |
Two |
|
3. Melting and boiling point Nature |
Higher than alkali metals Electropositive; metallic nature increases down the group. |
|
4. Reactivity |
Highly reactive |
|
5. Nature of compounds formed |
Ionic compounds |
|
6. Density |
Denser than alkali metals |
|
7. Electrical conductivity |
Good conductors |
|
8. Oxidation state |
+2 |
Competitive Exam Questions:
Question 1.
In the formation of potassium dichromate by chromite ore, how sodium chromate is converted to sodium dichromate?
(a) By reaction of conc. sulphuric acid
(b) By soda ash
(c) By the reaction of NaOH
(d) By reaction of lime stone.
Answer:
(a) By reaction of conc. sulphuric acid
Question 2.
Low solubility of LiF and CsI in water is due to which property of alkali metal ions?
(a) High hydration enthalpy of Li+, high lattice enthalpy of Cs+
(b) Low hydration enthalpy of Li+, high lattice enthalpy of Cs
(c) Low lattice enthalpy of Li+, low lattice enthalpy
(d) High lattice enthalpy of Li+, low lattice enthalpy of Cs+
(e) High lattice enthalphy of Li+, low hydration enthalpy of Cs+
Answer:
(e) High lattice enthalphy of Li+, low hydration enthalpy of Cs+

Question 3.
Oxides formed by Li, Na and K by burning in air are respectively :
(a) LiO2, Na2O2 and K2O
(b) Li2O2, Na2O2 and KO2
(c) Li2O, Na2O2 and KO2
(d) Li2O, Na2O and KO2
Answer:
(c) Li2O, Na2O2 and KO2
Question 4.
Bleaching powder is a compound whose molecular formula is:
(a) CaOCl3
(b) Ca(CIO)2
(c) CaClO
(d) CaClO
Answer:
(b) Ca(CIO)2
Question 5.
The correct order for solubility of sulphates of alkaline earth metals in water is:
(a) Be > Ca > Mg > Ba > Sr
(b) Mg > Be > Ba > Ca > Sr
(c) Be > Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba
(d) Mg > Ca > Ba > Be > Sr
Answer:
(c) Be > Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba
Question 6.
Which of the following has maximum second ionisation enthalpy?
(a) Ba
(b) Mg
(c) Ca
(d) Sr
(e) Be
Answer:
(e) Be
Question 7.
Which of the following element do not form acidic oxide?
(a) Carbon
(b) Phosphorous
(c) Chlorine
(d) Barium
Answer:
(d) Barium

Question 8.
Which of the following statement is not true?
(a) Mg2+ ion forms complex with A.T.P.
(b) Ca2+ ion is necessary for blood clotting.
(c) Ca2+ ion is necessary for maintaining the heart rate.
(d) Mg2+ ion is necessary for green parts of the plants.
Answer:
(c) Ca2+ ion is necessary for maintaining the heart rate.
Question 9.
Which of the following statement is not true regarding beryllium?
(a) Its hydride is electron deficit and polymeric.
(b) It is made inactive by nitric acid.
(c) It forms Be C.
(d) Its salt hydrolysed with difficulty.
Answer:
(d) Its salt hydrolysed with difficulty.
Question 10.
The final solution obtained on electrolysis of concentrated solution of NaCl is:
(a) Turns red litmus to blue
(b) Turns blue litmus red
(c) Colourless with phenolphthalein
(d) Colour of red and blue litmus paper do not change
Answer:
(a) Turns red litmus to blue
Question 11.
Which of the following pair is not found in solutions?
(a) NaHCO3 and NaOH
(b) Na2CO3 and NaOH
(c) Na2CO3 and NaCl
(d) NaHCO3 and NaCl
Answer:
(a) NaHCO3 and NaOH
Question 12.
An alkali metal hydride 'A' react with diborane and gives a tetrahedral compound 'B' which is used extensively as a reducing agent in the synthesis of organic compounds. The compounds 'A' and 'B' are:
(a) C6H6 and NaBH4
(b) C2H6 and C2H5Na
(c) C2H2O and NaBH4
(d) CH3COCH, and B3N3H6
Answer:
(c) C2H2O and NaBH4
Question 13.
Carbon dioxide is obtained easily by heating which of the following compound?
(a) K2CO3
(b) Na2CO3
(c) MgCO3
(d) CaCO3
Answer:
(c) MgCO3
Question 14.
Decreasing order of solubility of sulphates of alkaline earth metals is :
(a) Ca > Sr > Ba > Mg
(b) Sr > Ca > Mg > Ba
(c) Ba > Mg > Sr > Ca
(d) Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba
Answer:
(d) Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba

Question 15.
The function of "Sodium pump" is a biological process operating in all living beings. Which of the following essential biological ion is an important component of this pump?
(a) Mg2+
(b) K+
(c) Fe2+
(d) Ca 2+
Answer:
(b) K+
Question 16.
Which of the following alkaline earth metal sulphate has more lattice enthalpy than hydration energy?
(a) CaSO4
(b) BeSO4
(c) BaSO4
(d) SrSO4
Answer:
(b) BeSO4
Question 17.
Match the colour of flame in bunsen burner and salts of alkaline earth metal:
(A) Calcium
(B) Strontium
(C) Barium
(p) brick red
(q) apple green
(r) Crimson
(a) A-p, B-r, C-q
(b) A-r, B-p, C-q
(c) A-q, B-r, C-p
(d) A-p, B-q, C-r
Answer:
(a) A-p, B-r, C-q
Question 18.
Decreasing order of basic properties of K2O, BaO, CaO and MgO is:
(a) K2O > BaO > CaO > MgO
(b) K2O > CaO > BaO > MgO
(c) MgO > BaO > CaO > K2O
(d) MgO > CaO > BaO > K2O
Answer:
(a) K2O > BaO > CaO > MgO
Question 19.
Salts dilute and that reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid are :
(a) Na2SO4
(b) CaF2
(c) Na3PO4
(d) Ba(NO3)2
Answer:
(d) Ba(NO3)2
Question 20.
Metal that cannot be obtained by the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of its salts is:
(a) Ag
(b) Ca
(c) Cu
(d) Cr
Answer:
(b) Ca

Question 21.
Which of the following is obtained when carbon dioxide gas is passed through aqueous solution of sodium dichromate?
(a) Cr(OH)3 is precipitated.
(b) Yellow solution of Cr2 (CO3)3 is obtained.
(c) Orange solution of Na2 Cr2O7 is obtained.
(d) No reaction takes place.
Answer:
(c) Orange solution of Na2 Cr2O7 is obtained.
Question 22.
What is obtained when sodium hydride is dissolved in water?
(a) Acidic solution
(b) Basic solution
(c) Neutral solution
(d) Cannot say sodium hydroxide in
Answer:
(b) Basic solution
Question 23.
For production of Castner-Kelner cell:
(a) Electrolysis of brine takes place by graphite electrodes
(b) electrolysis of molten sodium chloride takes place
(c) sodium amalgam is formed at mercury cathode
(d) Electrolysis of brine takes place by platinum electrodes
Answer:
(c) sodium amalgam is formed at mercury cathode
Question 24.
The correct order of solubility in aqueous solution is:
(a) Na2S > ZnS > CuS
(b) CuS > ZnS > Na2S
(c) ZnS > Na2S > CuS
(d) Na2S > CuS > ZnS
Answer:
(a) Na2S > ZnS > CuS
Question 25.
Potassium is kept in:
(a) in alcohol
(b) in water
(c) in kerosene
(d) in liquid ammonia
Answer:
(c) in kerosene
Question 26.
Sodium metal is kept in :
(a) Benzene
(b) Kerosene
(c) Alcohol
(d) Toluene
Answer:
(b) Kerosene
Question 27.
Which of the following has maximum basic strength?
(a) CSOH
(b) KOH
(c) NaOH
(d) LiOH
Answer:
(a) CSOH
Question 28.
Which of the following gives metallic hydroxide, H2O2 and O2 on hydrolysis?
(a) Li2O
(b) Na2O2
(c) NaO2
(d) Na2O
(e) BeO
Answer:
(c) NaO2

Question 29.
Which metal in alkali metal oxides gives normal oxide M2O?
(a) Rb
(b) K
(c) Li
(d) Na
Answer:
(c) Li
Question 30.
The order of ease of adsorption of hydrated alkali metal ions on ion exchange resins is :
(a) Li+ < K+ < Na+ < Rb+
(b) Rb < K < Na+ < Li+
(c) K+ < Na+ < Rb+ < Li
(d) Na+ < Li < K+ < Rb
Answer:
(b) Rb < K < Na+ < Li+
Question 31.
In the replacement reaction:
→ C- I+ MF → CF + MI
The reaction will be most favourable if M happens to be:
(a) Na
(b) K
(c) Rb
(d) Li
Answer:
(c) Rb
Question 32.
The strength of reaction between sodium and water can be reduced by:
(a) reducing temperature
(b) By taking less amount of alcohol
(c) by amalgamate sodium
(d) by taking less amount of acetic acid
Answer:
(c) by amalgamate sodium
Question 33.
Plaster of Paris is:
(a) CaSO4 ·2H2O
(b) CaSO4·3H2O
(c) CaSO4 · H2O
(d) CaSO4 1/2H2O
Answer:
(d) CaSO4 1/2H2O
Question 34.
Which of the following gives acidic oxides with basic oxide on thermal decomposition?
(a) KClO3
(b) Na2CO3
(c) NaNO3
(d) CaCO3
(e) NH4NO3
Answer:
(d) CaCO3
Question 35.
Chile saltpeter is:
(a) NaNO3
(b) Na2SO4
(c) KNO3
(d) Na2SO3
Answer:
(a) NaNO3

Question 36.
Which of the following order is not correct?
(a) Hydration energy: Li > Na > K > Rb
(b) Ionisation energy: Li > Na > K > Rb
(c) Density: Li < Na < K < Rb
(d) Atomic size: Li < Na < K < Rb
Answer:
(c) Density: Li < Na < K < Rb
Question 37.
Which of the following compound has lowest melting point?
(a) CaF2
(b) COCl2
(c) CaBr2
(d) Cal2
Answer:
(d) Cal2
Question 38.
The decreasing order of stability of alkaline earth metal carbonates MgCO3, CaCO3, BaCO3, and SrCO3 is:
(a) CaCO3 > SrCO3 > MgCO3 > BaCO3
(b) BaCO3 > SrCO3 > MgCO3 > CaCO3
(c) BaCO3 > SrCO3 >CaCO3 > MgCO3
(d) MgCO3 > CaCO3 > SrCO3 > BaCO3
Answer:
(a) CaCO3 > SrCO3 > MgCO3 > BaCO3

- RBSE Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 States of Matter