RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions
RBSE Class 8 Science Cell – Structure and Functions InText Questions and Answers
Page90
Question 1.
A hen’s egg can be seen easily. Is it a cell or a group of cells?
Answer:
The egg of hen represents a single cell which is big enough to be seen by the unaided eyes.

Page 92
Question 2.
What advantage does amoeba derive by changing shape?
Answer:
By changing the shape amoeba get movement and help in capturing food.
Page 93
Question 3.
Are the cells in an elephant larger than the cells in a rat?
Or
Does the size of cell depend on the size of animal?
Answer:
The size of the cell has no relation with the size of the body of the animal or plant. It is not necessary that the cells in the elephant are much bigger than those in a rat. The size of the cell is related to its function. For example, nerve cells, both in the elephant and rat, are long and branched. They perform the same function, that of transferring messages.

Page 94
Question 4.
I want to know why plant cells need cell walls?
Answer:
Plant cells need protection against variations in temperature, high wind speed, atmospheric moisture, etc. for these purposes plant cells need cell walls.
Page 95
Question 5.
Paheli wants to know if the structure of nucleus is the same in cells of plants, animals and bacteria?
Answer:
No, the structure of nucleus is not the same as in cells of plants, animals and bacteria. In plants and animals cells have well organised nucleus with a nucleur membrane while the nucleus of the bacteria cells are not well organised and without nuclear membrane.
RBSE Class 8 Science Cell – Structure and Functions Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
(a) Unicellular organisms have one - celled body. (T/F)
(b) Muscle cells are branched. (T/F)
(c) The basic living unit of an organism is an organ. (T/F)
(d) Amoeba have irregular shape. (T/F)
Answer:
(a) True
(b) False
(c) False
(d) True
Question 2.
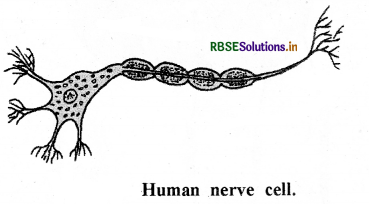
Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
Answer:
Function of nerve cell: The nerve cell receives and transfers messages, thereby helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body.

Question 3.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus of a cell
Answer:
(a) Cytoplasm:
The jelly - like substance between the nucleus and the cell membrane is called cytoplasm. Various other components, or organelles, of cells are present in the cytoplasm. They are mitochondria, golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc. They help in different activities of cell.
(b) Nucleus of a cell:
It is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell. Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. This membrane is also porous and allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus. There is a smaller spherical body in the nucleus.
It is called the nucleolus. In addition, nucleus contains thread - like structures called chromosomes. These carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring. Nucleus acts as control centre of the activities of the cell.
Question 4.
Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Answer:
The organelles of cell are present in the cytoplasm.

Question 5.
Make sketches of animal and plant cells. State three differences between them.
Answer:
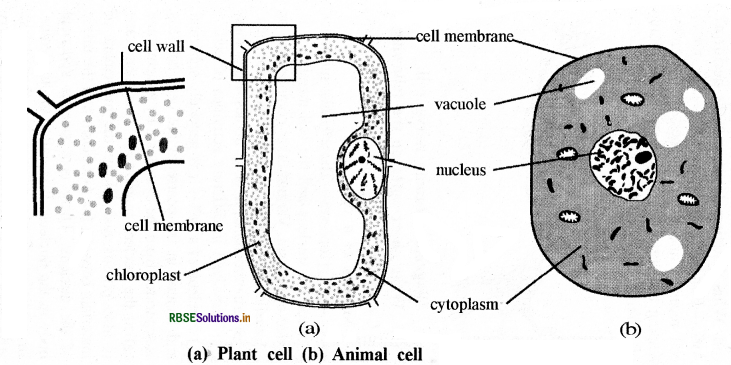
|
Plant Cell |
Animal Cell |
|
1. Outside the cell membrane, there is cell wall, which is made up of cellulose. |
1. It is surrounded by cell membrane. It is proteinaceous. Cell wall is absent. |
|
2. Vacuoles are main and large in size. |
2. Vacuoles are small in size or absent. |
|
3. Plastids are present. |
3. Plastids are absent. |
Question 6.
State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Answer:
|
Eukaryotes |
Prokaryotes |
|
1. They are having well organised nucleus with a nuclear membrane. |
1. They are not having well organised nucleus and nuclear membrane is absent. |
|
2. Cell organelles are covered by membrane. |
2. Cell organelles are not covered by membrane. |
|
3. Example: (i) Bacteria, (ii) Blue green algae. |
3. Example : (i) Onion peel, (ii) Cheek cells. |
Question 7.
Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their functions.
Answer:
Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of cell. Functions of chromosomes:
- They carry genes.
- They help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
- Help in cell division.
Question 8.
'Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms'. Explain.
Answer:
Cell builds the body of organisms. Due to this cell it is called the structural unit. Each living cell is capable to do living function. Unicellular organism performs all living activities in a single cell. But in multicellular organisms for doing different functions cells become specialised. Cell performs the specialised function due to organelles. Due to this cell it is called the basic structural unit of organisms.

Question 9.
Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
Answer:
Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells. They provide green colour to the leaves. Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of leaves, is essential for photosynthesis (process of food manufacture).
Question 10.
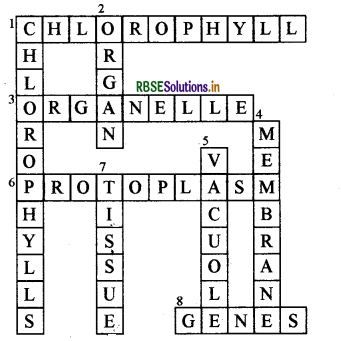
Complete the crossword with the help of clues given below:
Across
1. This is necessary for photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the cell.
8. Units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down
1. Green plastids.
2. Formed by collection of tissues.
4. It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding medium.
5. Empty structure in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells.
Answer: