RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8. Students can also read RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 8 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 8 science chapter 14 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Light
RBSE Class 8 Science Light InText Questions and Answers
Page 200
Question 1.
What would happen if I threw the light on the mirror along the normal?
Answer:
If a light beam fells normally on a mirror, the light would retrace the path and both the angles of incidence and angle of reflection will be zero.

Page 203
Question 2.
I have a question. Can the reflected rays be further reflected if incident on another mirror?
Answer:
Yes, these rays will be reflected again.
Eg: seeing our image formed by a mirror in another mirror
RBSE Class 8 Science Light Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room. Explain.
Answer:
No, we cannot see anything in the dark room. We can see objects only if die light from those objects enter our eyes. Yes, we can see objects outside that room because light is emitted and reflected from the objects and so we can see the objects.

Question 2.
Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
Answer:
Regular Reflection:
- Reflection occurs from a smooth surface like that of a mirror.
- Reflected rays are parallel.
Diffused Reflection:
- Reflection from an irregular surface is called diffused reflection.
- Reflected rays are in different directions. Diffused reflection is not the failure of laws of reflection. It occurs due to the irregularities of rough surface.
Question 3.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
(a) Polished wooden table
(b) Chalk powder
(c) Cardboard surface
(d) Marble floor with water spread over it
(e) Mirror
(f) Piece of paper
Answer:
(a) Polished wooden table:
Regular reflection will take place because surface of wood becomes smooth due to polishing.
(b) Chalk Powder:
Diffused reflection because chalk powder provides irregular surface.
(c) Cardboard surface:
Diffused reflection because irregular reflection is caused due to irregular rough surface of card board.
(d) Marble floor with water spread over it:
Regular reflection because water forms regular surface.
(e) Mirror:
Regular reflection because mirror forms regular / smooth surface.
(f) Piece of paper:
Regular reflection if paper is smooth and diffused reflection if paper is rough.

Question 4.
State the laws of reflection.
Answer:
Laws of reflection:
- The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Question 5.
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Answer:
Working:
Spread a sheet of white paper on a table. Make a straight line MM'. Make a mirror stand parallel to this line and perpendicular to the plane of paper.
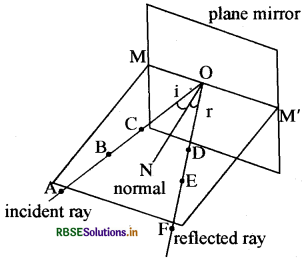
With the help of torch, throw the light on the mirror in such a way that the reflected ray of light is parallel to the table. Mark three points A, B and C on the incident light ray and mark three points D, E and F on.the reflected light ray. Now switch off the light. Remove the mirror. Now join the points and extend them to the mirror.
Line joining A, B and C meets MM' at 0. D, E and F also meets MM' at O. OA is an incident light and OF is reflected light ray. Draw a perpendicular on point O, ON: It proves that incident, reflected and normal lie on same plane.

Question 6.
Fill in the blanks in the following:
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be ...................... m from his image.
(b) If you, touch your ...................... ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with ...................... .
(c) The size of the pupil becomes ...................... when you see in dim light.
(d) Night birds have ...................... cones than rods in their eyes.
Answer:
(a) 2
(b) left, left
(c) large
(d) lesser
Choose the correct option in Question 7 & 8
Question 7.
Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
(a) Always
(b) Sometimes
(c) Under special conditions
(d) Never
Answer:
(a) Always
Question 8.
Image formed by a plane mirror is
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
(c) real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged
(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Answer:
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.

Question 9.
Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Answer:
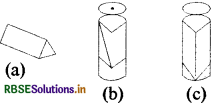
To make a kaleidoscope, get three rectangular mirror strips each about 15 cm long and 4 cm wide. Join them together to form a prism as shown in figure. Fix this arrangement of mirrors in a circular cardboard tube or tube of a thick chart paper. Make sure that the tube is slightly longer than the mirror strips.
Close one end of the tube by a cardboard disc having a hole in the centre, through which you can see. To make the disc durable, paste a piece of transparent plastic sheet under the cardboard disc. At the other end, touching the mirrors, fix a circular plane glass plate (fig. c).
Place on this glass plate several small pieces of coloured glass (broken pieces of coloured bangles). Close this end of the tube by a ground glass plate. Allow enough space for the colour pieces to move around. Your kaleidoscope is ready.
Question 10.
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.
Answer:
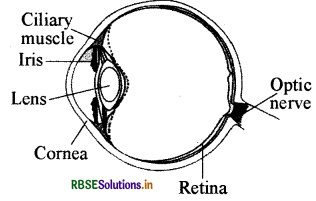
Question 11.
Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher's advise?
Answer:
Light produced from the laser torch harms our retina. That is why teacher denied the use of laser torch.

Question 12.
Explain how you can take care of your eyes?
Answer:
We can take care of our eyes by the following methods:
- Use the appropriate spectacles if adviced.
- Both poor as well as bright light is harmful for our eyes. Insufficient light develops stress in eyes and headache. Excess light from sun or any powerful lamp or laser torch harms the retina.
- Sun or any powerful light source must not be seen with naked eyes.
- Do not rub your eyes if any dust or sand particle had fallen into eyes. Rinse eyes with fresh water. Consult a doctor if there is no improvement.
- Rinse eyes regularly with fresh water.
- Books must be kept at an appropriate distance. Books must not be kept very close or very far from our eyes while reading.
- Vitamin A enriched food must be taken.
Question 13.
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Answer:
Angle between incidence ray, reflected ray is 90°, i.e.
∠i+∠r = 90°
According to law of reflection:
∠i = ∠r
∠i + ∠r = 90°
2∠ i = 90° (since ∠r =∠i)
∠i = \(\frac{90^{\circ}}{2} \)
∠i = 45°
Hence, the angle of incidence will be 45°.
Question 14.
How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
Answer:
Infinite number of images.

Question 15.
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
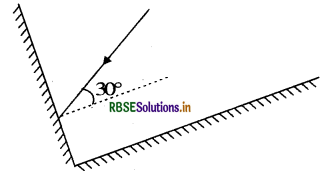
Answer:
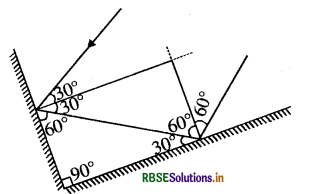
Question 16.
Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror a Can he see himself in the mirror ? Also can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q and R ?

Answer:
Boojho cannot see himself because mirror lies outside the boundary. He will be able to see the reflection of P and Q but not of R.

Question 17.
(a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (Fig.).
(b) Can Paheli at B see this image?
(c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?

Answer:
(a) A is at a distance Ao from the mirror. Reflected image of A will be formed A' such that Ao = A'o.
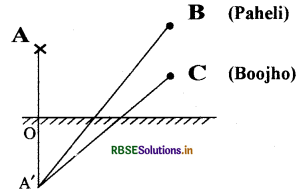
(b) Paheli can see reflection from position B.
(c) Boojho can see reflection from position A.
(d) Reflection of A won’t shift anywhere. When Paheli moves from B to C, reflection of A will then also be at its original position.

- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame