RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8. Students can also read RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 8 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 8 science chapter 14 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
RBSE Class 8 Science Chemical Effects of Electric Current InText Questions and Answers
Page 175
Question 1.
When the free ends of the tester do not touch each other, there is an air gap between them. Paheli knows that air is a poor conductor of electricity. But she has also read that during lightning, an electric current passes through air.
She wonders if air is indeed a poor conductor under all conditions. This makes Boojho ask whether other materials classified as poor conductors also allow electricity to pass under certain conditions.
Answer:
No, in all conditions air is not a poor conductor of electricity. At the time of lightning it becomes a conductor of electricity due to humidity (present of water molecules in air) of air.

Page 178
Question 12.
After doing the electroplating activity, Paheli interchanged the electrodes and repeated the activity. What do you think she would observe this time?
Answer:
In electroplating activity copper is always deposited on negative electrode. Thus, the plate which is to be coated of metal layer is always connected to negative terminal of battery. Therefore on exchanging electrodes electroplating will be affected because deposition will not take place on the that metal which is to be electroplated.
RBSE Class 8 Science Chemical Effects of Electric Current Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of .................... , .................... and .................... .
(b) The passage of an electric current through a solution causes .................... effects.
(c) If you pass current through copper sulphate solution, copper gets deposited on the plate connected to the .................... terminal of the battery.
(d) The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material by means of electricity is called .................... .
Answer:
(a) acids, bases and salts
(b) chemical
(c) -ve (negative)
(d) electroplating.

Question 2.
When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution, the magnetic needle shows deflection. Can you explain the reason?
Answer:
When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution electric current flows in the solution. Due to flow of current in the solution the magnetic needle deflects.
Question 3.
Name three liquids, which when tested in the manner shown in Fig. 14.9, may cause the magnetic needle to deflect.
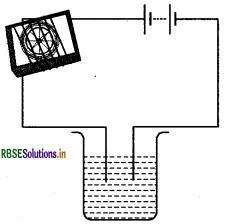
Answer:
- Lemon juice
- Salt solution
- Copper sulphate solution.

Question 4.
The bulb does not glow in the setup shown in Fig. 14.10. List the possible reasons. Explain your answer.
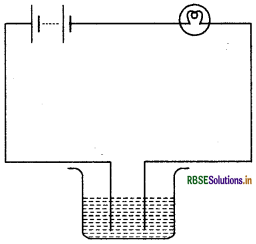
Answer:
In the given figure the bulb doesn't glow. The possible reason may be that the solution in the beaker may not be an electrolyte. The bulb also doesn't glow when there is glucose solution, alcohol or distilled water in the beaker. It can also happen that the electric current is weak. Therefore LED can be used which lights even when there is weak current.
Question 5.
A tester is used to check the conduction of electricity through two liquids, labelled A and B. It is found that the bulb of the tester glows brightly for liquid A while it glows very dimly for liquid B. You would conclude that
(i) liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.
(ii) liquid B is a better conductor than liquid A.
(iii) both liquids are equally conducting.
(iv) conducting properties of liquid cannot be compared in this manner.
Answer:
(i) liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.

Question 6.
Does pure water conduct electricity? If not, what can we do to make it conducting?
Answer:
No, pure water doesn't conduct electricity. To make it conducting we add few drops of diluted sulphuric acid to it.
Question 7.
In case of a fire, before the firemen use the water hoses, they shut off the main electrical supply for the area. Explain why they do this.
Answer:
Water is a conductor of electricity. To save themselves from electric shock firemen shut off the main electrical supply of the area.
Question 8.
A child staying in a coastal region tests the drinking water and also the seawater with his tester. He finds that the compass needle deflects more in the case of seawater. Can you explain the reason?
Answer:
Seawater comprises of dissolved salts. Therefore seawater is a conductor of current, which means that current passes through it. Exactly opposite to it, drinking water is bad conductor. Current doesn't pass easily through it. Thus for seawater magnetic needle shows more deflection.

Question 9.
Is it safe for the electrician to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during heavy downpour? Explain.
Answer:
No, it is not safe for the electrician to carry out repair work during heavy downpour because water is a good conductor of electricity. The lineman can experience an electric shock.
Question 10.
Paheli had heard that rainwater is as good as distilled water. So she collected some rainwater in a clean glass tumbler and tested it using a tester. To her surprise she found that the compass needle showed deflection. What could be the reasons?
Answer:
It is true that rainwater is as pure as distilled water. But rainwater dissolves many of the impurities from atmosphere such as carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide etc. which makes it a conductor. Thus on testing, a compass needle shows deflection.
Question 11.
Prepare a list of objects around you that are electroplated.
Answer:
List of electroplated objects are as follows:
- Bathroom taps, gas burner and rims of cycle wheels are chromium plated.
- Ornaments made of cheap metals are electroplated with silver and gold.
- Iron articles are electroplated with tin to avoid rusting.
- Iron buckets are coated with zinc.
- Kitchen utensils are also electroplated with appropriate metals.

Question 12.
The process that you saw in Activity 14.7 is used for purification of copper. A thin plate of pure copper and a thick rod of impure copper are used as electrodes. Copper from impure rod is sought to be transferred to the thin copper plate. Which electrode should be attached to the positive terminal of the battery and why?
Answer:
The impure copper electrode which, acts as anode, is connected to the positive terminal of battery. On passing current through copper sulphate the positive ions move towards cathode and pure metal deposits on cathode, impurities settle under anode in the electrolyte.

- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame