RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8. Students can also read RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 8 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 8 science chapter 14 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
RBSE Class 8 Science Crop Production and Management InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Boojho want to know where and how we use these tools.
Answer:
We use khurpi, shovel, plough tools etc. in the field for agricultural work.
Khurpi: With the help of khurpi we prepare beds, dig soils and remove weals.
Sickle: With the help of sickle we harvest the crop.
Shovel: It is used for filling soil, food grains, etc. in the baskets.
Plough: It is used for tilling, adding manure / fertilisers and scraping of soils.

Question 2.
Since we all need food, how can we provide food to a large number of people in our cuntiry?
Answer:
We can provide food for the large population on a large scale by regular production, proper managment and distribution.
Page 2.
Question 3.
Why paddy can not be grown in the winter season?
Answer:
Paddy requires plenty of water. So it can not be grown in the winter season. It is grown in the rainy season.
Page 4
Question 4.
One day I saw my mother put some gram seeds in a vessel and pour some water on them. After a few minutes some seeds started to float on top. I wonder why some seeds float on water!
Answer:
Some damaged seeds become hollow and become lighter. Therefore, they float on the water.
Page 5
Question 5.
There is a nursery near my school. I found that little plants were kept in small bags. Why are they kept like this?
Answer:
These small plants are kept in bags to protect them from outer environment and pamper them with suitable growth conditions and when these plants have grown sufficiently they will be grown in field conditions.

Question 6.
I saw a healthy crop growing in a farm. In the neighbouring farm, the plants were weak. Why do some plants grow better than others?
Answer:
Those plants which get water, minerals, manure and fertilisers in sufficient quantity, grow better in comparision to those plants which do not get these substances in sufficient quantity.
Page 10
Question 7.
Have these other plants been planted purposely?
Answer:
No, these other plants do not grow with crop with a special object. These are undesirable plants which grow naturally along with the crop. They are called weeds.
Question 8.
Do weedicides have any effect on the person handling the weedicide sprayer?
Answer:
Yes, weedicides can have an effect on the health of the person spraying it. These are the toxic chemicals. Hence he should cover his nose and mouth with a piece of cloth during spray of the chemicals.

Page 11
Question 9.
I saw my mother putting some dried neem leaves in an iron drum containing wheat. I wonder why?
Answer:
Dried neem leaves are kept in an iron drum containing grains to keep them safe from pests.
RBSE Class 8 Science Crop Production and Management Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called .....................
(b) The first step before growing crops is ..................... of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would ..................... on top of water
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and ..................... and ..................... from the soil are essential.
Answer:
(a) crop
(b) preparation
(c) float
(d) nutrients, water.
Question 2.
Match items in column A with those in column B.
|
A |
B |
|
(i) Kharif crops |
(a) Food for cattle |
|
(ii) Rabi crops |
(b) Urea and super phosphate |
|
(iii) Chemical fertilisers |
(c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
|
(iv) Organic manure |
(d) Wheat, gram, pea |
|
|
(e) Paddy and maize |
Answer:
|
A |
B |
|
(i) Kharif crops |
(e) Paddy and maize |
|
(ii) Rabi crops |
(d) Wheat, gram, pea |
|
(iii) Chemical fertilisers |
(b) Urea and super phosphate |
|
(iv) Organic manure |
(c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |

Question 3.
Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop.
Answer:
(a) Kharif crop:
(i) Paddy
(ii) Maize.
(b) Rabi crop:
(i) Wheat
(ii) Gram.
Question 4.
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Answer:
(a) Preparation of soil:
Before growing crop the soil is prepeared. For this purpose it is important to turn the soil and loosen it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. This process is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by ploughing. The crop plant roots obtain sufficient amount of oxygen from air present in pores of loose soil. The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. These organisms are friends of the farmer since they further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it. By turning and loosing of the soil brings the nutrient - rich soil to the top. Therefore the plants can easily use these nutrients.
(b) Sowing:
The process in which seeds are put in soil for cultivation of crops is known as sowing. Seeds of the crop are sown after ploughing the land of the field, levelling and adding manure. There are two methods for sowing in fields:
(i) By traditional tools: This is a funnel like in shape. The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends. These ends pierce into the soil and placed seed into the soil.
(ii) By seed drill: Seed drill tool is used for sowing seeds. This tool sows the seeds uniformly at equal distances and depths. Quality of seeds and method of sowing of seeds both play important role of cultivation of crops.
(c) Weeding:
The removal of weeds from field in known as weeding. Weeding is essential in the field because weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the crop. The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds. The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them near to ground, from time to time. This work is done in the field in the standing crop. Tilling before sowing the crops enables in uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. This is done with the help of khurpi and harrow.
(d) Threshing:
From harvested crop, the grain seeds are separated from the chaff. This process is called threshing. This is carried out with the help of a machine called 'combine' which is in fact a combined harvester and thresher. Small holding farmers separate the grain with chaff by winnowing.

Question 5.
Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer:
|
Fertiliser |
Manure |
|
1. A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. |
Manure is a natural (organic) substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues. |
|
2. A fertiliser is prepared in factories. |
Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
|
3. A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. |
Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
|
4. Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. |
Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Question 6.
What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer:
Irrigation: The supply of water to crops at different and regular intervals is called irrigation.
Water conserving methods of irrigation:
(i) Sprinkler System :
This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. Sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil.
(ii) Drip system :
In this system, the water falls drop by drop directly near the roots. So it is called drip system. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. The system provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all.
Question 7.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer:
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, they will not grow because they need not require more water for growing. In rainy season seeds are damaged due to excess water.
Question 8.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer:
Due to continuous growing of crops in the field, there is a deficiency of some nutrients in the soil. This reduces soil fertility. Therefore, to compensate this farmers have to add manure in the field. Improper or insufficient manuring results in weak plants or improper growth of plants.

Question 9.
What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer:
In a field many other undesirable plants (or wild plants) may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds.
Control on weeds: For this purpose weeding is done in the field. In this process such plants are removed from the field. Following methods are used for removal of weeds:
(1) Removal of weeds by harrow:
Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. Now if in the field harrow or comb like equipment is used, these uprooted weeds entangled with rods of harrow are removed from the field.
(2) By use of chemicals:
Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides, like 2 , 4 - D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds. They do not damage the crops. The weedicides are diluted with water to the extent required and sprayed in the fields with a sprayer.
Question 10.
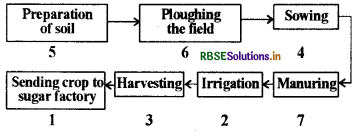
Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
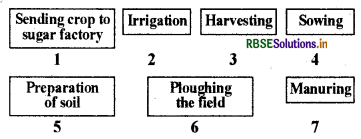
Answer:
Question 11.
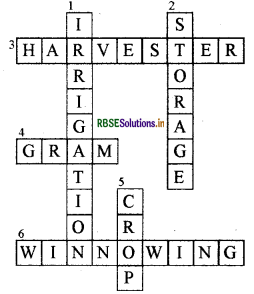
Complete the following words puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi. crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
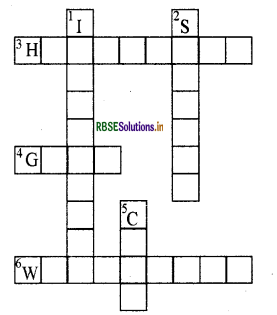
Answer:

- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame