RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Bank Reconciliation Statement
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 Bank Reconciliation Statement Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Solutions Chapter 5 Bank Reconciliation Statement
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Bank Reconciliation Statement Textbook Questions and Answers
Test Your Understanding I
I. Read the following transactions and identify the cause of difference on the basis of time gap or errors made by business firm/bank. Put a sign (✓) for the correct cause.
|
S. No. |
Transactions |
Time gap |
Errors made by business/bank |
|
1. |
Cheques issued to customers but not presented for payment. |
✓ |
|
|
2. |
Cheque amounting to ₹ 5,000 issued to M/s. XYZ but recorded as ₹ 500 in the cash book. |
|
✓ |
|
3. |
Interest credited by the bank but yet not recorded in the cash book. |
✓ |
|
|
4. |
Cheque deposited into the bank but not yet collected by the bank. |
✓ |
|
|
5. |
Bank charges debited to firm’s current account by the bank. |
✓ |
|

II. Fill in the blanks:
(i) Passbook is a copy of ............. as it appears in the ledger of the bank.
(ii) When money is with drawn from the bank, the bank ............. the account of the customer.
(iii) Normally, the cash book shows a debit balance, passbook shows ................ balance.
(iv) Favourable balance as per the cash book means ................ balance in the bank column of the cash book.
(v) If the cash book balance is taken as starting point the items which make the cash book balance smaller than the passbook must be ................ for the purpose of reconciliation.
(vi) If the passbook shows a favourable balance and if it is taken as the starting point for the purpose of bank reconciliation statement then cheques issued but not presented for payment should be ................ to find out cash balance.
(vii) When the cheques are not presented for payment, favourable balance as per the cash book is than that of the passbook.
(viii) When a banker collects the bills and credits the account passbook overdraft shows ................ balance.
(ix) If the overdraft as per the passbook is taken as the starting point, the cheques issued but not presented are to be ................ in the bank reconciliation statement.
(x) When the passbook balance is taken as the starting point items which makes the passbook balance ................ than the balance in the cash book must be deducted for the purpose of reconciliation.
Answer:
(i) Customer account
(ii) Debit
(iii) Credit
(iv) Debit
(v) Added
(vi) Deducted
(vii) loss
(viii) Loss
(ix) Added
(x) Higher
Test Your Understanding II
Select the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
A bank reconciliation statement is prepared by: ...................
(a) Creditors
(b) Bank
(c) Account holder in a bank
(d) Debtors
Answer:
(b) Bank
Question 2.
A bank reconciliation statement is prepared with the balance:
(a) Passbook
(b) Cash book
(c) Both passbook and cash book
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both passbook and cash book
Question 3.
Passbook is a copy of: ............
(a) Copy of customer Account
(b) Bank column of cash book
(c) Cash column of cash book
(d) Copy of receipts and payments
Answer:
(a) Copy of customer Account
Question 4.
Unfavourable bank balance means:
(a) Credit balance in passbook
(b) Credit balance in cash book
(c) Debit balance in cash book
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Credit balance in passbook

Question 5.
Favourable bank balance means:
(a) Credit balance in the cash book
(b) Credit balance in passbook
(c) Debit balance in the cash book
(d) Both b and c
Answer:
(c) Debit balance in the cash book
Question 6.
A bank reconciliation statement is mainly prepared for:
(a) Reconcile the cash balance of the cash book.
(b) Reconcile the difference between the bank balance shown by the cash book and bank passbook
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Reconcile the difference between the bank balance shown by the cash book and bank passbook
Test Your Understanding III.
State whether each of the following statements is True or False:
1. Passbook is the statement of account of the customer maintained by the bank.
2. A business firm periodically prepares a bank reconciliation statement to reconcile the bank balance as per the cash book with the passbook as these two show different balances for various reasons.
3. Cheques issued but not presented for payment will reduce the balance as per the passbook.
4. Cheques deposited but not collected will result in increasing the balance of the cash book when compared to passbook.
5. Overdraft as per the passbook is less than the overdraft as per cash book when there are cheques deposited but not
collected by the banker.
6. The debit balance of the bank account as per the cash book should be equal to the credit balance of the account of the
business in the books of the bank.
7. Favourable bank balance as per the cash book will be less than the bank passbook balance when there are unpresented cheques for payment.
8. Direct collections received by the bank on behalf of the customers would increase the balance as per the bank passbook when compared to the balance as per the cash book.
9. When payments made by the bank as per the standing instructions of the customer, the balance in the passbook will be more when compared to the cash book.
Answers:
1. True
2. True
3. False
4. True
5. False
6. True
7. True
8. True
9. False

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the need for the preparation of bank reconciliation statement.
Answer:
Need of preparing bank reconciliation statement.
(1) Helps in locating errors: it helps in locating and rectifying errors committed by bank or business.
(2) Credibility of information: Customers become sure of the bank balance as shown in the cash book.
(3) Facilitation in preparing amended cash book: With the help of bank reconciliation statement, corrected/amended cash book can be prepared easily.
Question 2.
What is a bank overdraft?
Answer:
Bank overdraft: It is a facility given by the bank to the business organisation and it happens when the cash withdrawn exceeds the cash available in the bank account. The facility to overdraw is available after an agreement is signed between bank and business person(s). Bank charges nominal charges on the overdrawn balance.
Question 3.
Briefly explain the statement ‘wrongly debited by the bank’ with the help of an example.
Answer:
Statement ‘wrongly debited by the bank’ means wrong entry is passed by the banker. This happens due to the similarity of names of the customers or because of clerical error on the part of the clerks of the bank. This again creates problem of difference in the balances of the cash book and the pass book.
In order to reconcile the above difference, a reconciliation statement is prepared. If the bank reduce our deposit with the transaction of any other party, it is called wrongly debited by bank.
Example: A Cheque issued for ₹ 10,000 was shown as ₹ 1,000 on the debit side of passbook or instead of debiting Suchee’s Account, clerk debits Sachee’s Account.

Question 4.
State the causes of difference occurred due to time lag.
Answer:
The causes of difference in the balances of cash book and passbook due to time lag:
(1) Cheques deposited into bank but not collected by bank
(2) Cheques issued but not presented for payment
(3) Direct payments made by customers in our account.
(4) Bank charges made by bank but not appearing in the cash book
(5) Dividend and interest collected by bank but not appearing in the cash book
(6) Cheques deposited into the bank but returned dishonoured.
Question 5.
Briefly explain the term ‘favourable balance as per cash book’.
Answer:
Favourable balance of cash book means the deposits in the bank are more than the withdrawals and there is credit balance in the passbook or debit balance in cash book. This balance means the sum owed by the bank to the customer.
Question 6.
Enumerate the steps to ascertain the correct cash book balance.
Answer:
Bank reconciliation statement is prepared at the end of each month but when it is prepared at the end of the financial year, we need to show correct bank balance in the balance sheet. The bank balance as given in the cash book needs to be corrected.
Correct bank balance in the cash book may be obtained by taking following steps:
Step 1: Take closing balance as given in the cash book
Step 2: Add those transactions which appear on the credit side of passbook but not in cash book [Bank Reconciliation Statement)
Step 3: Deduct those transactions which appear on the debit side of passbook but not in the cash book.
Step 4: Add/less errors took place in the cash book.
Step 5: Find out correct bank balance which may be taken in the balance sheet.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a bank reconciliation statement? Why is it prepared?
Answer:
Meaning of bank reconciliation statement: A statement prepared at the end of each month showing the items of difference between the bank statement and the bank column of Cash Book is known as Bank Reconciliation Statement.
Need of Preparing Bank Reconciliation Statement:
(1) Helps in Locating Errors: It helps in locating and rectifying errors committed by bank or business.
(2) Credibility of Information: Customers become sure of the bank balance as shown in the cash book.
(3) Facilitation in Preparing Amended Cash Book: With the help of bank reconciliation statement, corrected/ amended cash book can be prepared easily.
(4) Reduction in Embezzlement of Cash: It helps in detecting financial frauds done by the staff members.
(5) Check on Movement of Cheques: Through bank reconciliation statement, a status of Cheques clearance and payments can easily be known.
(6) Avoidance of errors: Through bank reconciliation statement, business firms come to know about the errors and can prepare well for the future.
Question 2.
Explain the reasons where the balance shown by the bank passbook does not agree with the balance as shown by the bank column of the cash book.
Answer:
The causes of difference in the pass book balance and cash book balance may be classified into two categories:
(a) Difference due to timing of transaction


(b) Difference due to errors committed either by bank or business

Question 3.
Explain the process of preparing bank reconciliation statement with amended cash balance.
Answer:
Bank reconciliation statement is prepared at the end of each month but when it is prepared at the end of the financial year, we need to show correct bank balance in the balance sheet. The bank balance as given in the cash book needs to be corrected.
Correct bank balance in the cash book may be obtained by taking following steps:
Step 1: Take closing balance as given in the cash book.
Step 2: Add those transactions which appear on the credit side of passbook but not in cash book.
Step 3: Deduct those transactions which appear on the debit side of passbook but not in the cash book.
Step 4: Add/less errors took place in the cash book.
Step 5: Find out correct bank balance which may be taken in the balance sheet.
Step 6: Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement with the help of adjusted bank balance.
Step 7: Deduct Cheques deposited in the bank but not collected by bank.
Step 8: Add Cheques issued but not presented for payment.
Step 9: Deduct any wrong credit given by bank, if any.
Step 10: Add any wrong debit charged by bank, if any.

Numerical Questions
Question 1.
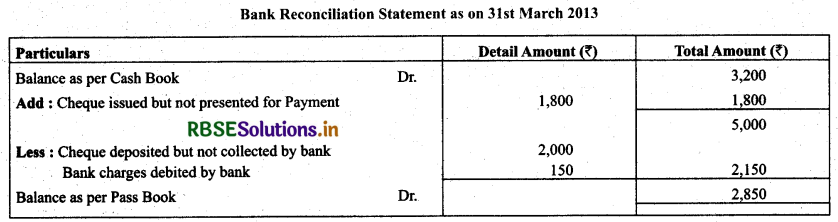
From the following particulars, prepare a bank reconciliation statement as at March 31,2013:
(i) Balance as per cash book -- ₹ 3,200
(ii) Cheque issued but not presented for payment -- ₹ 1,800
(iii) Cheque deposited but not collected upto March 31,2013 -- ₹ 2,000
(iv) Bank charges debited by bank -- ₹ 150
Solution.
Question 2.
On March 31, 2013 the cash book showed a balance of ₹ 3,700 as cash at bank, but the bank passbook made up to same date showed that cheques for ₹ 700, ₹ 300 and ₹ 180 respectively had not presented for payment, Also, cheque amounting to ₹ 1,200 deposited into the account had not been credited. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement.
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 31st March 2013
Solution:
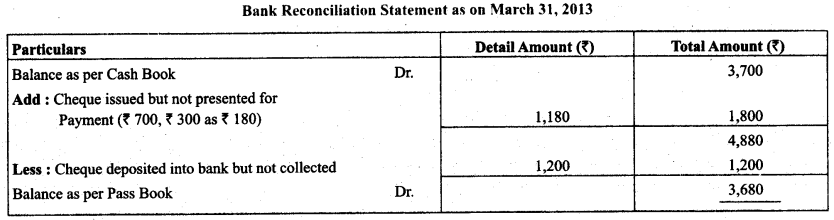

Question 3.
The cash book shows a bank balance of ₹ 7,800. On comparing the cash book with pass book the following discrepancies were noted:
(a) Cheque deposited into bank but not credited -- ₹ 3,000
(b) Cheque issued but not yet presented for payment -- ₹ 1,500
(c) Insurance premium paid by the bank -- ₹ 2,000
(d) Bank interest credit by the bank -- ₹ 400
(e) Bank charges -- ₹ 100
(f) Directly deposited by a customer -- ₹ 4,000
Solution:
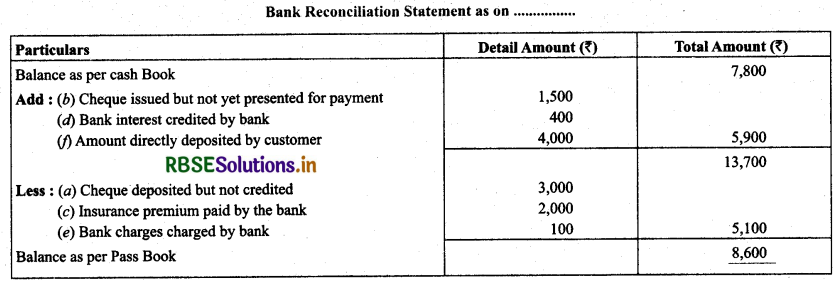

Question 4.
Bank balance of ₹ 40,000 showed by the cash book of Atul on December 31, 2014. It was found that three cheques of ₹ 2,000, ₹ 5,000 and ₹ 8,000 deposited during the month of December were not credited in the passbook till January 02,2014. Two cheques of ₹ 7,000 and ₹ 8,000 issued on December 28, were not presented for payment till January 03, 2014. In addition to it bank has credited Atul for ₹ 325 as interest and had debited him with ₹ 50 as bank charges for which there were no corresponding entries in the cash book. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on December 31, 2014.
Solution:
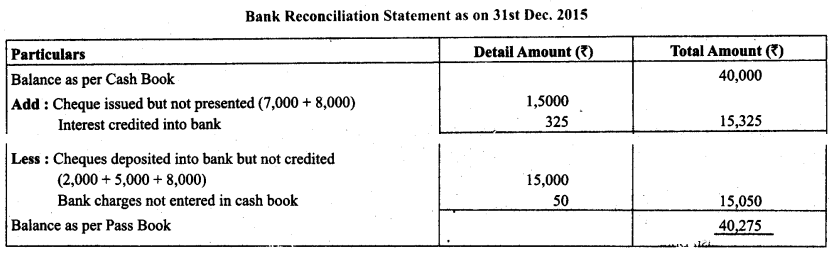
Question 5.
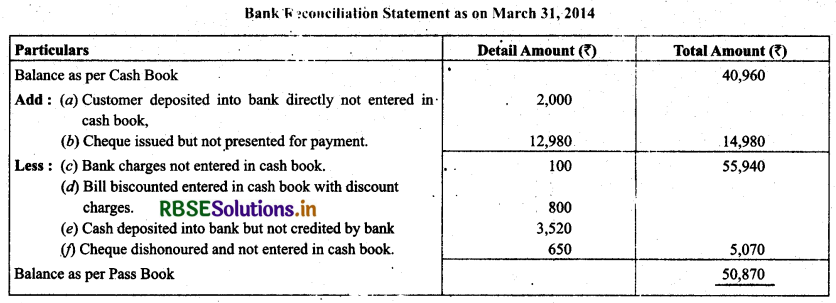
On comparing the cash book with pass book of Naman it is found that on March 31, 2014, bank balance of ₹ 40,960 showed by the cash book differs from the bank balance with regard to the following:
(a) Bank charges 100 on March 31, 2014, are not entered in the cash book.
(b) On March 21,2014, a debtor paid ₹ 2,000 into the company’s bank in settlement of his account, but no entry was made in the cash book of the company in respect of this.
(c) Cheques totaling ₹12,980 were issued by the company and duly recorded in the cash book before March 31,2014, but had not been presented at the bank for payment until after that date.
(d) A bill for ₹ 6,900 discounted with the bank is entered in the cash book with recording the discount charge of ₹ 800.
(e) ₹ 3,520 is entered in the cash book as paid into bank on March 31st, 2014, but not credited by the bank until the following day.
(f) No entry has been made in the cash book to record the dishonour on March 15,2014 of a cheque for ₹ 650 received from Bhanu.
Prepare a reconciliation statement as on March 31,2014.
Solution:
Question 6.
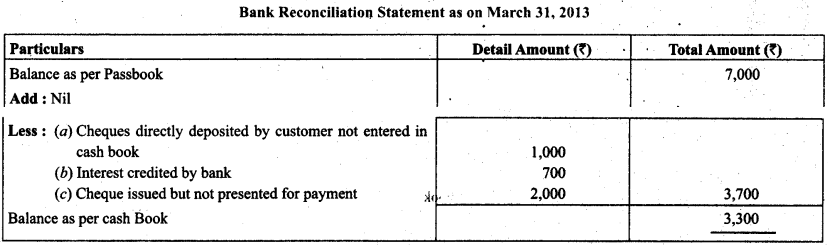
Prepare bank reconciliation statement as on December 31,2013. On this day the pass book of Mr. Himanshu showed a balance of ₹ 7,000.
(a) Cheques of ₹ 1,000 directly deposited by a customer.
(b) The bank has credited Mr. Himanshu for ₹ 700 as interest.
(c) Cheques for ₹ 3000 were issued dining the month of December but of these cheques for ₹ 1,000 were not presented during the month of December.
Solution.

Question 7.
From the following particulars prepare a bank reconciliation statement showing the balance as per cash book on December 31,2015:
(a) Two cheques of ₹ 2,000 and ₹ 5,000 were paid into bank in October, 2015 but were not credited by the bank in the month of December.
(b) A cheque of ₹ 800 which was received from a customer was entered in the bank column of the cash book in December 2015 but was omitted to be banked in December, 2015.
(c) Cheques for ₹ 10,000 were issued into bank in January 2014 but not credited by the bank on December 31,2014.
(d) Interest on investment ₹ 1,000 collected by bank appeared in the passbook.
Balance as per Pass book was ₹ 50,000
Solution:

Question 8.
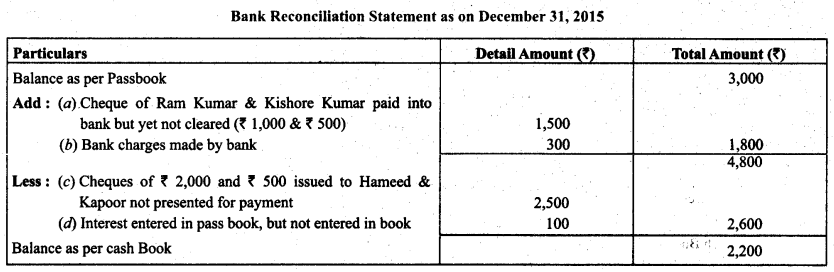
Balance as per pass book of Mr. Kumar is 3,000.
(a) Cheque paid into bank but not yet cleared Ram Kumar ₹ 1,000 Kishore Kumar ₹ 500
(b) Bank Charges ₹ 300
(c) Cheque issued but not presented Hameed ₹ 2,000 Kapoor ₹ 500
(d) Interest entered in the pass book but not entered in the cash book ₹ 100. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement.
Solution:
Question 9.
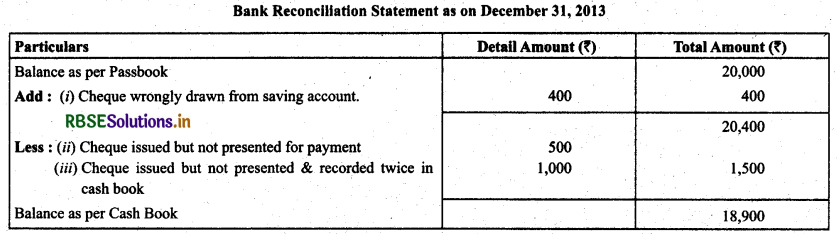
The pass book of Mr. Mohit current account showed a credit balance of ₹ 20,000 on dated December 31,2013. Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement with the following informations:
(i) A cheque of ₹ 400 drawn on his saving account has been shown on current account.
(ii) He issued two cheques of ₹ 300 and ₹ 500 on of December 25, but only the 1st cheque was presented for payment.
(iii) One cheque issued by Mr. Mohit of ₹ 500 on December 25, but it was not presented for payment whereas it was recorded twice in the cash book.
Solution.

Question 10.
On 1st January 2015, Rakesh had an overdraft of ₹ 8,000 as showed by his cash book. Cheques amounting to ₹ 2,000 had been paid in by him but were not collected by the bank by January 01, 2015. He issued cheques of ₹ 800 which were not presented to the bank for payment up to that day. There was a debit in his pass book of ₹ 60 for interest and ₹ 100 for bank charges. Prepare bank reconciliation statement for comparing both the balance.
Solution:
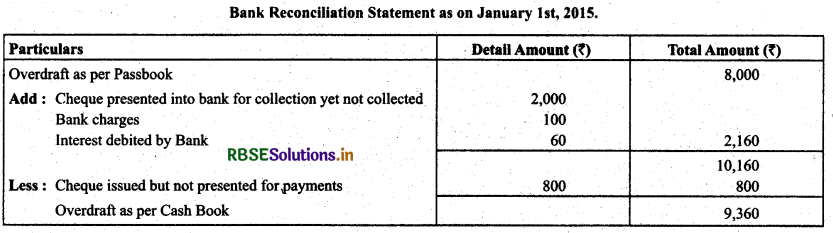
Question 11.
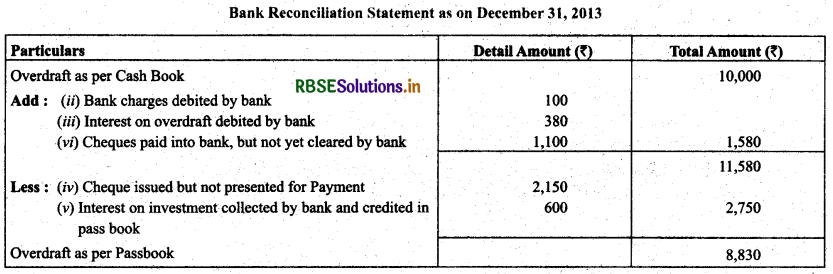
Prepare bank reconciliation statement with the help of following informations:
(i) Overdraft shown as per cash book on December 31,2013 -- ₹ 10,000.
(ii) Bank charges for the above period also debited in the pass book -- ₹ 100.
(iii) Interest on overdraft for six months ending December 31,2013 ₹ 380 debited in the pass book.
(iv) Cheques issued but not encashed prior to December 31, 2013 amounted to -- ₹ 2,150.
(v) Interest on investment collected by the bank and credited in the pass book -- ₹ 600.
(vi) Cheques paid into bank but not cleared before December, 31,2013 were -- ₹ 1,100.
Solution:
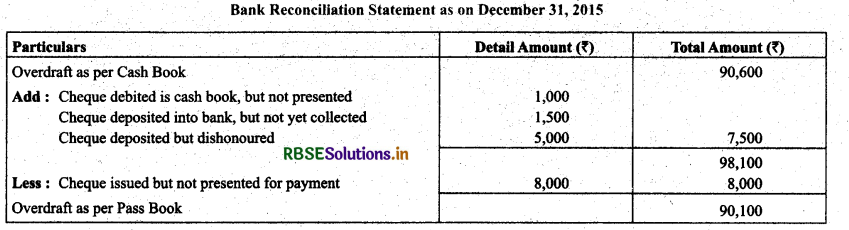
Question 12.
Kumar find that the bank balance shown by his cash book on December 31,2015 is ₹ 90,600 (Credit) but the pass book shows a difference due to the following reason: A cheque (post dated) for ₹ 1,000 has been debited in the bank column of the cash book but not yet presented for payment. Also, a cheque for ₹ 8,000 drawn in favour of Manohar has not yet been presented for payment. Cheques totaling ₹ 1,500 deposited in the bank have not yet been collected and cheque for ₹ 5,000 has been dishonoured.
Solution:

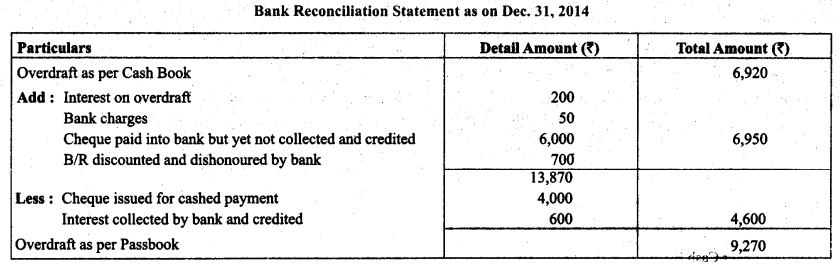
Question 13.
On December 31,2014, the cash book of Mittal Bros., showed an overdraft of ₹ 6,920. From the following particulars prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement and ascertain the balance as per pass book:
(i) Debited by bank for ₹ 200 on account of Interest on overdraft and ₹ 50 on account of charges for collecting bills.
(ii) Cheques drawn but not encashed before December 31,2014 for ₹ 4,000.
(iii) The bank has collected interest and has credited ₹ 600 in pass book.
(iv) A bill receivable for ₹ 700 previously discounted with the bank had been dishonoured and debited in the pass book,
(v) Cheques paid into bank but not collected and credited before December 31,2014 amounted ₹ 6,000.
Solution.
Question 14.
Prepare bank reconciliation statement of Shri Bhandari as on December 31,2013.
(i) Debited by bank for ₹ 200 on account of interest on overdraft and ₹ 50 on account of charges for collecting bills.
(ii) Withdrawal column of the pass book under cast by ₹ 200.
(iii) A cheque of ₹ 200 has been debited in the bank column of the cash book but it was not sent to bank at all.
(iv) A cheque of ₹ 300 debited to bank column of the pass book was not sent to the bank.
(v) ₹ 500 in respect of dishonoured cheque were entered in the pass book but not in the cash book.
Solution.
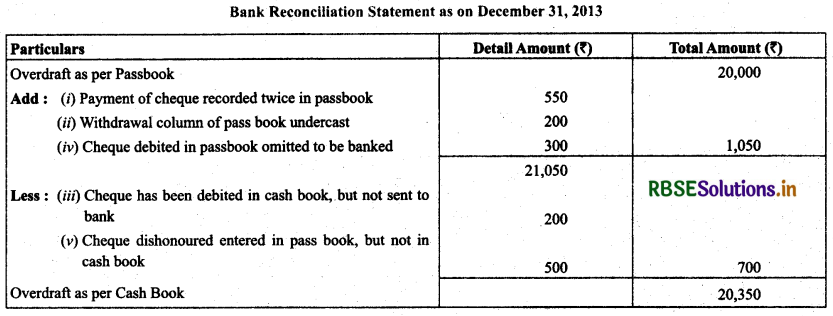

Question 15.
Overdraft shown by the pass book of Mr. Murli is ₹ 20,000. Prepare bank reconciliation statement on dated December 31,2013.
(i) Bank charges debited as per passbook ₹ 500.
(ii) Cheques recorded in the cash book but not sent to the bank for collection ₹ 2,500.
(iii) Received a payment directly from customer ₹ 4,600.
(iv) Cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 6,980.
(v) Interest credited by the bank ₹ 100.
(vi) Cheque of ₹ 2,500 deposited into Bank for payment of LIC but not cleared.
(vii) Cheques deposited with the bank but not collected ₹ 3,500.
Solution.

Question 16.
Raghav & Co. have two bank accounts. Account No. 1 and Account No. 2. From the following particulars relating to Account No. 1, find out the balance on that account of December 31,2015 according to the cash book of the firm.
(i) Cheques for ₹ 10,000 paid into bank perior to December 31,2015, but not credited.
(ii) Transfer of funds from Account No. 2 to Account No. 1 recorded by the bank on December 31,2015 but entered in the cash book after that date for ₹ 8,000.
(iii) Cheques issued prior to December 31,2015 but not presented until after that date for ₹ 7,429.
(iv) Bank charges debited by bank not entered in the cash book for ₹ 200.
(v) Interest debited by the bank not entered in the cash book ₹ 580.
(vi) Overdraft as per Pass book ₹ 18,990.
Solution.
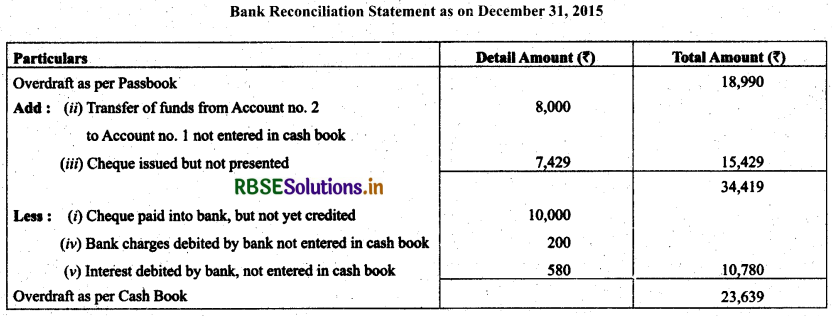
Question 17.
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement from the following particulars and show the balance as per cash book.
(i) Balance as per pass book on December 31,2015 overdrawn ₹ 20,000.
(ii) Interest on bank overdraft not entered in the cash book ₹ 2,000.
(iii) ₹ 200 insurance premium paid by bank has not been entered in the cash book.
(iv) Cheques drawn in the last week of December, 2015, but not cleared till date for ₹ 3,000 and ₹ 3,500.
(v) Cheques deposited into bank on November, 2005, but yet to be credited on dated December 31,2015 ₹ 6,000.
(vi) Wrongly debited by bank ₹ 500.
Solution.
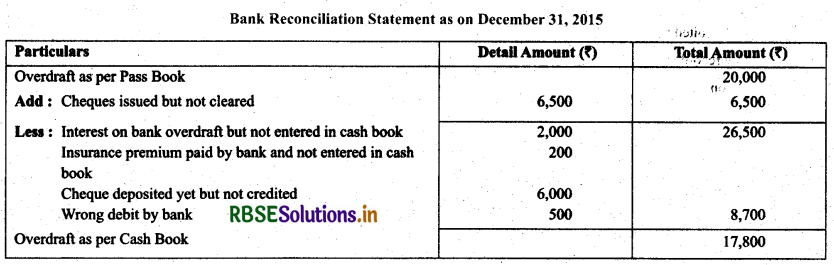

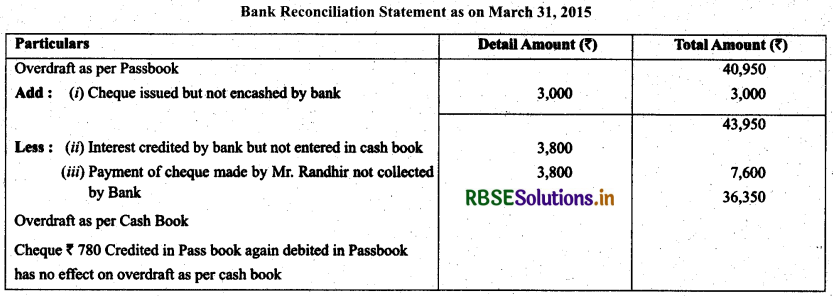
Question 18.
The pass book of Mr. Randhir showed an overdraft of ₹ 40,950 on March 31,2013. Prepare bank reconciliation statement on March 31,2013.
(i) Out of cheques amounting to ₹ 3,000 drawn by Mr. Randhir on March 27 was encashed on April 03.
(ii) Credited by bank with ₹ 3,800 for interest collected by them, but the amount is not entered in the cash book.
(iii) ₹ 10,900 paid in by Mr. Randhir in cash and by cheques on March, 31 cheques amounting to ₹ 3,800 were collected on April, 07.
(iv) A Cheque of ₹ 780 credited in the pass book on March 28 being dishonoured is debited again in the pass book on April 01,2013. There was no entry in the cash book about the dishonour of the cheque until April 15.
Solution.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 बैंक समाधान विवरण
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 लेन-देनों का अभिलेखन-2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 तलपट एवं अशुद्धियों का शोधन
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors