RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Solutions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting Textbook Questions and Answers
Test Your Understanding I
Fill in the correct words :
1. The user oriented programmes designed and developed for performing certain specific tasks are called as ................
2. Language syntax is checked by software called as ................
3. The people who write programmes to implement the data processing system design are called as ................
4. ............... is the brain of the computer.
5. ................ and ................ are two of the important requirements of an accounting report.
6. An example of responsibility report is ................
Answers:
1. Application Software
2. Language Processor
3. Programmer
4. CPU
5. Timeliness, Relevance
6. Management Responsibility.

Test Your Understanding II
1. The framework of storage and processing of data is called as ................
2. Database is implemented using ................
3. A sequence of actions taken to transform the data into decision useful information is called ................
4. An appropriate accounting software for a small business organisation having only one user and single office location would be ................
Answers:
1. Operating environment
2. DBMS
3. Data Processing
4. Ready to use
Test Your Understanding III
A. Indicate against each of the following statements are True or False :
(a) Every relation has at least one super key by default, which is the combination of all its attributes.
(b) Data transformation is called information.
(c) Referential integrity constraint arises because of relationships between various entities.
(d) The complete absence of WHERE clause in SELECT statement implies that no tuples of a relation shall be selected.
(e) ER model is an example of representational data model.
Answer:
(a) True
(b) True
(c) True
(d) False
(e) False
B. Fill in the blanks, an appropriate word(s)
(a) A ............. does not have key attributes of its own.
(b) The ............. for binary relationship specifies the number of relationship instances that an entity can participate in.
(c) Each simple attribute of an entity type is associated with a value set called ............. of values.
(d) When structure of AIS is based on both human and computer resources, it is called ............ AIS.
(e) An ............. is a collection of all entities of a particular entity type.
(f) A weak entity type always has a ............. constraint with respect to its identifying relationship.
(g) When a relation has more than one attribute with unique values, each such attribute is called .............
Answers:
(a) Weak entity
(b) Computer based
(c) Time ware
(d) Live ware
(e) Total participation
(f) Multi-valued
(g) Full functional
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the different elements of a computer system.
Solution:
(a) Hardware
(b) Software
(c) People
(d) Procedure
(e) Data
(f) Connectivity
Elements of Computer System
(a) Hardware: Hardware of computers include monitor, printer, key board, processor, mouse, processor etc.
(b) Software: In order to solve a particular problem, a computer needs to be given specific instructions written in a particular language. Set of instructions is known as program and set of different programs is known as ‘software’.
Example: By installing ‘Accounting software’, accounts can be prepared, through ‘Pay roll software’, the attendance of employees can be monitored, through ‘GST software’, Input GST and Output GST can be maintained.
(c) People: The individuals working on the computer systems by using hardware and software are also called live-ware of the computer. They are three types, systems analysts, programmers and operators.
(d) Procedure: Series of operations exercised by the people to achieve desired results. They are three types: software oriented, hardware oriented and internal procedure. These procedures are of three types: hardware oriented, software oriented and internal procedure.
(e) Data: These are the facts in terms of number or text, gathered and entered into a computer system.
Examples, data of attendance of students, data on the pay to employees etc.
(f) Connectivity: The way the computers are connected through internet, satellite links, microwave transmission etc.

Question 2.
List the distinctive advantages of a computer system over a manual system.
Solution:
(a) Speed
(b) Accuracy
(c) Reliability
(d) Upto date information
(e) Real time user interface
Advantages of computerised accounting system
(a) Speed: It is always faster than in manual accounting.
(b) Accuracy: Possibility of errors is eliminated
(c) Reliability: They are immune to tiredness, boredom and fatigue, the information are always reliable.
(d) Upto date information: The accounting records are always updated when the data is entered and stored.
(e) Real time user interface: Most of the compuer systems are interlinked, they provide real time information to the users.
Question 3.
Draw block diagram showing the main components of a computer.
Solution:
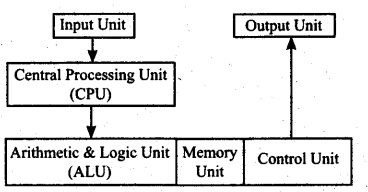
Question 4.
Give three examples of a transaction processing system.
Solution:
Transaction Processing System (TPS) has many steps e.g., Data Entry, Data validation, Processing and Revalidation, Storage, Information and Reporting.
Following are the examples of TPS :
1. ATM (Automatic Transaction System)
2. E/Net Banking Transaction
3. Payments through Debit/Credit Card.
Question 5.
State the relationship between information and decision.
Solution:
All decisions are made in the light of available information. So, decision-making completely depends upon the available information. We can say that information are the input and decision is output. Well settled information system is the only system which influence the decision making process of an organisation. So, information and decision are complementary of each other.
Question 6.
What is Accounting Information System?
Solution:
Accounting Information System: It is a sub-system of Management Information System. It collects, processes, summarises, and reports about a business organisation in monetary terms.

Question 7.
State the various essential features of an accounting report.
Solution:
Essential features of an accounting report:
(a) Relevance
(b) Timeliness
(c) Accuracy
(d) Completeness
(e) Summarisation
Question 8.
Name three components of a Transaction Processing System.
Solution:
Thre components of Transaction Processing System are:
1. Input : Data Entry
2. Processing : Data Validation, Data Manipulation (Processing and Revalidation) and Storage.
3. Output : Information and Reporting.
Question 9.
Give example of the relationship between a Human Resource Information System and MIS.
Solution:
Human Resource Information System (HRIS) provides details of employees, their categories and remuneration/salaries to MIS. MIS takes necessary steps to control the number of employees and their allowances and remuneration. Hence, both of MIS and HRIS are interrelated with each other. This is clear from the under mentioned diagram:

Question 10.
State the four basic requirements of a database applications.
Solution:
1. Front-end interface : With the help of front end interface user communicates to the back-end interface.
e.g., accounting treatment for goods sold is maintained by sale voucher and this data is entered by the operator in computer system.
2. Back-end database :Only authorised users can enter in this database and they can use only such data for which they are authorised. In other words, we can say that data is not opened for all types of users.
3. Data Processing : A stored data is not purposeful/important if it is not further processed. Data processing is a group of activities which convert the data in such a manner that it becomes helpful in decision making.
4. Reporting system : This system is related to those decisions/informations which are presented in the form of summary.
Question 11.
Name the various categories of accounting package.
Solution:
Accounting packages may be categorised as under:
1. Ready to use:These packages are used by small organisation and available in the market every time. Busy, Tally are the examples of ready to use packages.
2. Tailor-made Software (Tailored) : These packages are developed as per the order and requirement of users. These are not easily available in the market. These packages are customised for special requirements.
3. Customised : These software, are designed to meet the special requirement of users and high level of secrecy is used : Users of these software need a training of high level.

Question 12.
Give examples of two types of operating system.
Solution:
Operating system is the system of computer used by the users according to their need. Followings are the examples of operating system:
1. Personal Computer with Standardised Software : This system is used by small organisations because number of transactions in these organisations are comparatively less.
2. Multi-User Operating System : This system is used by those organisations which are large in size and their business is scattered in different type of geographical conditions.
Question 13.
List the various advantages of computerised accounting systems.
Solution:
Advantages of computerised accounting system:
1. Economical : A computerised accounting system helps in producing the financial reports at a comparatively lower cost than manual system of accounting.
2. Quick reporting : The speed with which the decision can be taken depends on how quickly the information can be obtained.
3. Accuracy : The information content of reports and queries searched out by computerised accounting systems are accurate and therefore reliable for decision making.
4. Lesser paper work : in computerised system the quest of reducing paper work and dispensing of large volumes of books of accounts can be easily achieved.
5. On-line Facility : With the advent of internet, the online facility allows for working on computerised accounting systems miles and miles away from the office.
6. Scientific research : with the help of computerised accounting systems, millions of calculations can be done within few minutes.
7. Flexible reporting : The reports of a manual accounting system reveals balances of accounts on periodic basis, as originally planned while the computerised accounting system is capable of reporting as and when required.
Question 14.
Give two examples of each of the organisations where ‘ready-to-use’, ‘customised’, and ‘tailored’ accounting packages respectively suitable to perform the accounting activity.
Solution:
Ready to use and tailored accounting packages:
1. Ready to use: Accounting package is used by small organisations, Traditional/Conventional Organisations, not- for-profit organisations, etc.
2. Tailor made accounting packages are used by those organisations which operate large and tipical business. ‘Tailor made’ packages are used by purchase/sale/finance departments of such organisations.
3. Customised accounting package is used by those organisations whose business/branches are scattered at large

Question 15.
Distinguish between a ‘ready-to-use’ and ‘tailored’ accounting software.
Solution:
Main difference between ‘ready-to-use’ and ‘tailored’ accounting software are as under:

Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
‘An organisation is a collection of interdependent decision-making units that exists to pursue organisational objectives’. In the light of this statement,
(a) Explain the relationship between information and decisions.
(b) Also explain the role of Transaction Processing System in facilitating the decision-making process in business organisations.
Answer:
(a) Relation between information and decisions: (Refer Q5 SAQ)
(b) Role of Transaction Processing System: Every organisation whether it is small in size or medium or large have to develop a well-defined information system to make effective decisions because, if information are not purposeful, the decision will serve no purpose.
The following is the role of Transaction Processing System:
1. To Record: Various data are collected from various sources and these are entered into the system with the help of input device.
2. Validation of Data: After entering the data into system there accuracy, relevancy and reliability are compared with predetermined standard data.
3. Processing: After validation of data, action is taken by the system and necessary calculations are performed.
4. Storage/Memory: Processed data are sorted in memory of systems.
5. Information/Reporting: With the help of stored data, necessary information is derived from the system and a summary report is prepared, which will be helpful in decision-making.

Question 2.
Explain, using examples, the relationship between the organisational MIS and the other functional information system in an organisation. Describe how AIS receives and provides information to other functional MIS.
Answer:
Interaction of AIS with other Information Systems: Basically, all systems of an organisation which either generate funds or spend funds have interfaces with accounting information systems. For example, the purchasing system exchanges data with accounting information system because it uses funds and for which it has to maintain the purchase books used to prepare the accounts of business. The following figure describes the interaction of accounting information system with other information systems.
A brief description of these systems interfaces is as follows:
(a) Marketing Systems. Marketing system plays a role in the firm’s Accounting Information System by providing sales order data. Sales representatives enter the data from customer offices, using laptops or sales order personnel at headquarters may take order data over the phone or by mail and enter into keyboard terminals. In some cases customers enter the data directly into the firm’s computer.
(b) Manufacturing Systems. The task of interaction between Accounting Information System and manufacturing system also plays an important role in the AIS of the organisation. It describes that how the raw materials are received and its data is entered into the computers or database, and how the shipment of finished goods is sent to the customers for their use.
(c) Human Resource Systems. The data that is handled by the human resource system is a blending of personnel and accounting data elements. Personnel data elements are relatively permanent and are non-financial in nature like employees name, sex, date of birth, education etc. Accounting data elements on the other hand, are primarily financial.
(d) Financial Information System. Accounting Information System provides a record of everything of monetary
importance that happens in the firm. A record is made of each transaction that describes, what, when, it happened and how much money was involved.
(e) General Ledger Systems. The general ledger system is the accounting system that combines data from accounting systems for presenting a composite financial picture of the firm’s operations. The file that contains the combined accounting data is the general ledger.

Question 3.
‘An accounting report is essential a report which must be able to fulfill certain basic criteria1. Explain. List the various types of accounting reports.
Answer:
Given below are the main essentials of a good report:
1. Relevance : The matter of report should be according to the title/heading of report.
2. Timeliness: Report submitted late after the predetermined time, importance of that report goes down.
3. Accuracy: All the information provided by the report should be real and true.
4. Completeness: Reports are always in the form of summary but all facts must be included in the report.
5. Conciseness : Only important and necessary facts should be included in the report. The items which are not compulsory for that report, those items must be rejected. It will enhance the importance of a report.
Types of accounting reports:
1. Summary Reports: Trading and P & L A/c and Balance sheet of any organisation are the example of summary report.
2. Demand Reports: These reports are prepared on the demand of higher authorities. Report about the forcasting of demand of a new product is the example of demand report.
3. Customer Report: As per the requirements of higher authorities, reports about the customer is to be called the customer report.
4. Supplier Reports : As per the requirements of manager reports about the supplier of the firm is to be called the supplier report.
5. Exception Reports : These reports are prepared in particular situations not in normal condition.
Question 4.
Describe the various elements of a computer system and explain the distinctive features of a computer system and manual system.
Answer:
Elements of computer system:
(a) Hardware: Hardware of computers include monitor, printer, key board, processor, mouse, processor etc.
(b) Software: In order to solve a particular problem, a computer needs to be given specific instructions written in a particular
language. Set of instructions is known as program and set of different programs is known as ‘software’.
Example: By installing ‘Accounting software’, accounts can he prepared, through ‘Pay roll software’, the attendance
of employees can be monitored, through ‘GST software’, Input GST and Output GST can be maintained.
(c) People: The individuals working on the computer systems by using hardware and software are also called live-ware of the computer. They are three types, systems analysts, programmers and operators.
(d) Procedure: Series of operations exercised by the people to achieve desired results. They are three types: software oriented, hardware oriented and internal procedure. These procedures are of three types: hardware oriented, software oriented and internal procedure.
(e) Data : These are the facts in terms of number or text, gathered and entered into a computer system. Examples, data of attendance of students, data on the pay to employees etc.
(f) Connectivity: The way the computers are connected through internet, satellite links, microwave transmission etc.

Features of Computer System:
1.Fast/High Speed: Many of today’s computers can perform hundreds of millions of processing operations in one second. Computer takes less time than human being does to perform any task, calculation etc.
2. Reliability : Today’s computers may run day in and day out for year without failure. Computer is away from tiredness, boredom or fatigue. So, these are more reliable than human being.
3. Accuracy : Computers physical processing circuits rarely make errors. Computers make errors, of course, but they are usually due to faulty programs or incorrect data input which human beings give. Therefore, computers are much accurate than human beings.
4. Versatility: Computers has no likes and dislikes. It works in all field/area of life equally e.g., Science, health,
medical education, technology, statistics etc. It can perform all the works whether they are easy for a man or complex.
5. Storage Capacity: Today personal computers can be equipped with disk capable of storing more than one billion characters. That capacity is enough to store the complete works of William Shakespeare, an unabridged English dictionary and all your written work from the third grade to graduate level-with zoom for more.
6. Transfer of Information: It can move information very quickly from one place to another. One computer can send the entire text of the Encyclopedia Britannica to another linked computer in less than one second.
Features of Manual System :
Some features of manual system can’t be developed in computer system. These features are as under:
1. Common Sense : Manual system has common sense. However, computer has no common sense. Man can think at your own level but computer thinks only according to the installed program.
2. I.Q : Manual system supersede in the terms of I.Q. Man can work after thinking its merits and demerits but computer will perform according to program.
3. Decision Making Power: Manual System has good decision-making power. If any error remain in the software the result/decision taken by the computer will be faulty but man has own decision-making power.
4. Practical Knowledge: Man becomes pained by experience and practical work. This experience helps him to take correct decision in all situations. However, computers have no such type of knowledge.
Question 5.
Define a computerised accounting system. Distinguish between a manual and Computerised Accounting System.
Answer:
Accounting has been defined as the art of recording, classifying and summarising in a significant manner and in the terms of money, transactions and events which are of financial nature and interpreting the results thereof.
Difference between manual accounting and computerised accounting system:
(1) Identifying: The identification of transactions is common to both manual and computerised accounting system.
(2) Recording : In manual accounting system, the recording is done through books of original entries while in the computerised accounting system, transactions are stored in a well-designed accounting database.
(3) Classification : In a manual accounting system, there is duplicity of transactions as these are recorded in the journal book and then ledger book whereas duplication does not happen in case of computerised accounting.
(4) Summarising : In the manual accounting, transactions are summarised to produce trial balance whereas in the computerised accounting, The generation of ledger accounts is not a necessary condition for producing trial balance in a computerised accounting system.
Question 6.
Discuss the advantages of computerised accounting system over the manual accounting system.
Answer:
Advantages of computerised accounting system:
1. Economical: A computerised accounting system helps in producing the financial reports at a comparatively lower cost than manual system of accounting.
2. Quick reporting: Computerised systems, because of their speed and accuracy are capable of offering quick and qualitative reports.
3. Accuracy: The information content of reports and queries turned out by computerised accounting systems are accurate and therefore reliable for decision making.
4. Lesser paper work: In in computerised system the quest of reducing paper work and dispensing of large volumes of books of accounts can be easily achieved.
5. On-line facility: With the advent of internet, the online facility allows for working on computerised accounting systems miles and miles away from the office.
Question 7.
Describe the various types of accounting software along with their advantages and limitations.
Answer:
Types of accounting softwares:
1. Ready to use: These packages are developed for common users not for a particular user. These packages are used by small organisation and available in market every time. Busy, Tally are the examples of ready to use packages. Advantages:
1. These packages can be used easily by small organisations.
2. Cost of installation of these packages are very low.
Limitations:
1.These packages are not so beneficial for large organisation.
2. Level of secrecy of these software is very low.
Tailor-made Software (Tailored): These packages are developed as per the order and requirement of users. These are not easily available in the market. These package are customised for special requirements.
Advantages:
1. These softwares have high, level of security and secrecy.
2. These softwares fulfil the special requirements of the users.
Limitations:
1. Cost of these softwares are comparatively high.
2. These softwares cannot be used by small organisations.
Customised : These packages are also available in the market but can be changed according to the requirements of users.
Advantages:
1. Data remain more secure comparatively.
2. These softwares fulfil the special requirement of its users.
Limitations:
1. These softwares are comparatively costly.
2. Not appropriate for small organisations.
‘Accounting software is an integral part of the computerised accounting system’ Explain briefly list the generic considerations before sourcing an accounting software.

Generic considerations before sourcing an accounting software:
1. Cost of installation and maintenance: The software/packages which is selected by the organisation must be according to the financing capacity of the firm itself.
2. Size of organisation: Size of the organisation, volume of the transaction and prosperity of development of organisation must be considered at the time of selection of a package.
3. Flexibility: Requirement of flexibility in capacity of accounting package must be considered at the time of selection of package.
4. Adaptability: This software is used by competitive firm’, this is not a good method of adapting a accounting package.
5. Level of vendors: Level of vendors is the main determinant for selection of accounting package. Their levels will decide the level and quality of package.
6. Needs of Training: Before selection of any accounting package needs of training must be considered because affordability of training expenses will depend upon the organisation sources. ‘Computerised Accounting System are best form of accounting system’. Do you agree? Comment. Yes, I agree to the above statement that computerised system is the best form of accounting system if we understand the benefits accrue from the computerised system of accounting.
Computerised Accounting: The term computerised accounting implies that when various stages of accounting process - recording, classification and summarising are done with the help of computers, it is known as computerised accounting. In case of computerised accounting manual system is completely replaced with computerised system of book-keeping with the help of certain accounting packages. Through such packages the computer is instructed to do the routine bookkeeping and to produce financial statements by calculations and balances.
Benefits of computerised system:
A typical computerised accounting system is capable of offering the following advantages to justify its need:
1. Economical : Competition forces the production of quality goods at the least possible cost. A computerised accounting system helps in producing the financial reports at a comparatively lower cost than manual system of accounting.
2. Quick reporting : Computerised systems, because of their speed and accuracy are capable of offering quick and qualitative reports.
3. Accuracy : The information content of reports and queries turned out by computerised accounting systems are accurate and therefore reliable for decision making.
4. Lesser paper work : In computerised system the quest of reducing paper work and dispensing of large volumes of books of accounts can be easily achieved.
5. On-line facility : Computerised accounting systems offer online facility to store and process transaction data so as to retrieve information to produce and view financial reports.
6. Scientific research : With the help of computerised accounting systems, millions of calculations can be done within few minutes. Therefore, the computerised accounting has given a big boost to scientific research.
Objective Type Questions
A. Fill in the blanks with correct word:
1. Drawings accounts should be placed under ................. section of gateway of Tally.
2. Analysis of ratio is available under ................. section of gateway of Tally.
3. Elements of AIS are Accounting,................. and System.
4. Printing of vouchers and ................. of ledger accounts are the two activities of automat accounting system.
5. .................. softwares are designed to suit the need of the general users.
Answers:
1. Capital
2. Reports
3. Information
4. Grouping
5. Readymade

B. State whether the following statements are True or False:
1. Tally is an accounting software.
2. One cannot pass contra entry in tally
3. System is a set of related components that work independently
4. Combination of keyboard and monitor is called terminal.
5. Specially programmed softwares are called tailor-made softwares.
Answers:
1. True
2. False
3. False
4. True
5. True
C. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Information is stored and transmitted inside a computer in:
(a) Binary form
(b) ASCI code form
(c) Decimal form
(d) Alphanumeric form.
Answer:
(a) Binary form
Question 2.
Which of the following is not part of the processor?
(a) The ALU
(b) The CU
(c) The registers
(d) The system bus.
Answer:
(a) The ALU
Question 3.
Multi-programming is a prerequisite for:
(a) Multitasking
(b) An operating system
(c) To run more than one program at the same time
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) To run more than one program at the same time
Question 4.
An accounting information system adds value to an organisation in many ways. Which of the following is not a way in
which the AIS add value?
(a) Monitoring outputs for defects to increase product quality
(b) Providing more timely information
(c) Providing more accurate information
(d) All of the above are ways in which an AIS adds value to the organisation.
Answer:
(d) All of the above are ways in which an AIS adds value to the organisation.

Question 5.
Financial statements are prepared:
(a) Only for publicly owned business organisations.
(b) For corporations, but not for sole proprietorships or partnerships.
(c) Primarily for the benefit of persons outside of the business organisation.
(d) In either monetary or no montary terms, depending upon the need of the decision maker.
Answer:
(c) Primarily for the benefit of persons outside of the business organisation

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 बैंक समाधान विवरण
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 लेन-देनों का अभिलेखन-2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 तलपट एवं अशुद्धियों का शोधन
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors