RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8. Students can also read RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 8 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 8 science chapter 14 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Important Questions Cell – Structure and Functions
Objective Questions
Question 1.
It is absent in animal cell:
(a) Plasma membrane
(b) Cell wall
(c) Cytoplasm
(d) Nucleus
Answer:
(b) Cell wall

Question 2.
Example of largest cell is
(a) White blood cell
(b) Red blood cell
(c) Egg of ostrich
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Egg of ostrich
Question 3.
Largest cell of the human body is
(a) Nerve cell
(b) Muscle cell
(c) Blood cell
(d) Cheek cell
Answer:
(a) Nerve cell
Question 4.
Performs the function of transfer of hereditary characters from parents to offspring
(a) Vacuole
(b) Cell membrane
(c) Centrosome
(d) Chromosome
Answer:
(d) Chromosome

Question 5.
A group of similar cells performing a specific function is called
(a) Tissue
(b) Cell
(c) Organ
(d) Living
Answer
(a) Tissue
Fill in the blanks
1. Hen's egg is a single ........................
Answer:
cell
2. ........................ separates the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Answer:
Nuclear membrane

3. ........................ cell is having one large central vacuole.
Answer:
Plant
4. Gree plastids in which ........................ found, called chloroplast.
Answer:
chlorophyll.
True/False
Indicate whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F)
1. Hen's egg is a single cell.
Answer:
True
2. The number of cells is equal in all organisms.
Answer:
False

3. In large organisms large cells and in small organisms small cells are present.
Answer:
False
4. Amoeba is a multicellular organism.
Answer:
False
5. Nuclear membrane separates the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Answer:
True
6. Plant cell is different from animal cell.
Answer:
True
Match the words given in ’Column-A' 'Column-B'
Question 1.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Blood cell |
(a) Cylindrical |
|
(ii) Nerve cell |
(b) Flat |
|
(iii) Muscle cell |
(c) Oval |
|
(iv) Skin cell |
(d) Long |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Blood cell |
(c) Oval |
|
(ii) Nerve cell |
(d) Long |
|
(iii) Muscle cell |
(a) Cylindrical |
|
(iv) Skin cell |
(b) Flat |

Question 2.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Cell membrane |
(a) Protect the cell |
|
(ii) Cell wall |
(b) Control the cell |
|
(iii) Nucleus |
(c) Photosynthesis |
|
(iv) Plastid |
(d) Transport regulation |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Cell membrane |
(d) Transport regulation |
|
(ii) Cell wall |
(a) Protect the cell |
|
(iii) Nucleus |
(b) Control the cell |
|
(iv) Plastid |
(c) Photosynthesis |
Question 3.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Gene |
(a) Living structural unit |
|
(ii) Prokaryotic |
(b) Unit of heredity |
|
(iii) Eukaryotic |
(c) Nucleus membrane absent |
|
(iv) Cell |
(d) Nucleus membrane present |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Gene |
(b) Unit of heredity |
|
(ii) Prokaryotic |
(c) Nucleus membrane absent |
|
(iii) Eukaryotic |
(d) Nucleus membrane present |
|
(iv) Cell |
(a) Living structural unit |
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question 1.
Write the name of two unicellular organisms.
Answer:
- Amoeba
- Paramecium.

Question 2.
Write the name of main components of cell.
Answer:
Basic component of cell:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus.
Question 3.
What is meant by protoplasm?
Answer:
Protoplasm:
Total components of a living cell is called protoplasm. This is the living material of a cell.
Question 4.
Write the names of two prokaryotic cell organisms.
Answer:
- Bacteria
- Blue green , algae.

Question 5.
What is the function of pseudopodia in Amoeba?
Answer:
Amoeba moves and feeds with the help of pseudopodia.
Question 6.
Amoeba and white blood cells are unicellular, are both similar.
Answer:
Amoeba is well developed organism, which is having independent existence while white blood cell is a part of blood, it is not independent. So both are not similar.
Question 7.
Usually what type of shape is of the cell?
Answer:
Generally, cells are round, spherical or elongated.

Question 8.
In comparision to animal cell, the plant cells can easily tolerate the external atmospheric variations, why?
Answer:
Due to the presence of cell wall in plant cells, they easily tolerate the atmospheric variations.
Question 9.
What is the function of chloroplasts in plants?
Answer:
Chloroplast helps in the process of photosynthesis in plants.
Question 10.
Write the name of two organelles found in cytoplasm.
Answer:
- Mitochondria
- Ribosome.
Short Answer type Questions
Question 1.
Being an unicellular organism, how does Amoeba move from one place to another? Draw the labelled diagram of Amoeba also.
Answer:
Amoeba being an unicellular organism can move from one place to another. For this pseudopodia help them. From the main body of Amoeba some projections of varying lengths protruding out of its body, these are called pseudopodia. These projection appear and disappear as amoeba moves.
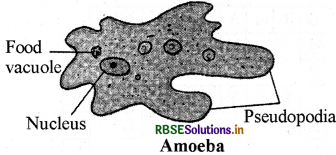

Question 2.
How was the cell discovered? Explain.
Answer:
Discovery of cell:
Robert Hooke in 1665 observed slices of cork under a simple magnifying device. He observed many partitioned boxes or compartments in the cork slice. These boxes appeared like a hony - comb. He also noticed that one box was separated from the other by a wall or partition. Hooke coined the term ’cell1 for each box. Hooke observed boxes or cells in the cork which were actually dead cells.
Question 3.
Explain the multicellular and unicellular organisms.
Answer:
Multicellular organisms:
Organisms made of more than one cell are called multicellular organism. The number of cells being less in smaller organisms does not, in any way, affect the functioning of the organisms. All multicellular organisms begin life as a single cell which is the fertilized egg. The fertilized egg cell multiplies and the number of cells increase as development proceeds.
Unicellular organism:
The single - celled organisms are called unicellular organisms. A single celled organism performs all the necessary functions that multicellular organisms perform.
Question 4.
Unicellular amoeba is having irregular shape. What benefit he is having by this?
Answer:
Formation of pseudopodia makes the shape of the amoeba irregular. Amoeba moves with the help bf pseudopodia and it helps in capturing the food.

Question 5.
Who performs the function in giving the shape of cell?
Answer:
Membrane provides the shape to the cells. This membrane besides providing the shape of cell, also protect the organelles and control the movement of materials both inwards and outward. In plant cells outside the membrane there is one covering layer, called cell wall. This gives the shape to the plant cell and it also provides rigidity to it.
Question 6.
Explain the structure and function of cell wall.
Answer:
Cell wall: In plant cells outside the cell membrane there is one more layer, called cell wall. It is made up of cellulose.
Function: Cell wall helps in giving the fixed shape and size to plant cells. Cell wall protects the cell from external injuries. It also protects from atmospheric variations.
Question 7.
Explain the differences between cell wall and cell membrane.
Answer:
|
Cell wall |
Cell membrane |
|
1. Only found in plant cell. |
1. Mainly found in animal cells. |
|
2. Made up of cellulose. |
2. Made up of protein, lipid and water. |
|
3. It is thick and hard. |
3. Very thin and flexible in habit. |
|
4. It is not selectively by permeable. |
4. It is selectively by permeable |
Question 8.
What are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Or
Define prokaryotic cell. Write the names of the two prokaryotes.
Answer:
Prokaryotic cells:
In this type of cells the nucleus is not well organised and nuclear membrane is absent. Organelles are not covered by membrane. Examples are bacteria and blue - green algae. Such cell organisms are called prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic cells:
In these cells well organised nucleus with a nuclear membrane is present and organelles are covered by membrane. As in peel of onion and cheek cells eukaryotic cells are present. Such cell organisms are called eukaryotes.

Question 9.
Write definition of following words
(a) Protoplasm
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Nucleoplasm.
Answer:
(a) Protoplasm:
The entire content of living cell is known as protoplasm. Protoplasm is the basis of life and enclosed by cell membrane. It consists of both cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. This is called living material of cell.
(b) Cytoplasm:
It is found in between nucleus and cell membrane. It consists of many small organelles. Here protein synthesis and process of glycolysis take place.
(c) Nucleoplasm:
It is found in nucleus. It consists of chromatin material and nucleolus. It forms spindle at the time of cell division.
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the structure of cell on the basis of following components :
(a) Cell membrane
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Nucleus.
Or
Describe the structure of cell.
Answer:
Structure of cell:
Structure of cell has three main components
(a) cell membrane
(b) cytoplasm and
(c) nucleus.
Description of these components are as under:
(a) Cell membrane:
Cytoplasm and nucleus are covered by cell membrane. Cell membrane separates one cell to other cell and from surrounding medium. Cell membrane is also called plasma membrane. This is porous and regulates the movements of materials in cell. In plants outside the cell membrane one additional layer is present, called cell wall.
(b) Cytoplasm:
It is the jelly - like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various other components or organelles of cell are present in the cytoplasm.
(c) Nucleus:
It is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell. Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. This membrane is also porous and allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus. There is a smaller spherical body in the nucleus.
It is called the nucleolus.In addition, nucleus contains thread - like structures called chromosomes. These carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring. Nucleus acts as control centre of the activities of the cell.

Question 2.
On the basis of following points compare the plant and animal cell:
(i) Cell membrane
(ii) Cell wall
(iii) Nucleus
(iv) Nuclear membrane
(v) Cytoplasm
(vi) Plastid and
(vii) Vacuole.
Answer:
Comparision between plant cell and animal cell:
|
Parts of cell |
Plant cell |
Animal cell |
|
Cell membrane |
Present |
Present |
|
Cell wall |
Present |
Absent |
|
Nucleus |
Present near the cell wall |
Present in center |
|
Nuclear membrane |
Present |
Present |
|
Cytoplasm |
Present |
Present |
|
Plastid |
Present |
Absent |
|
Vacuole |
Present, distinct and large size |
Usually absent or very small |

- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame