RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Important Questions Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
Objective Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is non - metal?
(a) Iron
(b) Sulphur
(c) Aluminium
(d) Copper
Answer:
(b) Sulphur

Question 2.
Which of the following is not malleable?
(a) Iron
(b) Aluminium
(c) Lead pencil
(d) Silver
Answer:
(c) Lead pencil
Question 3.
Active non - metal which catches fire when exposed to air is
(a) Sodium
(b) Potassium
(c) Zinc
(d) Phosphorous
Answer:
(d) Phosphorous

Question 4.
Non - metal which is essential for our life and taken by all living organisms during respiration is
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Hydrogen
Answer:
(a) Oxygen
Question 5.
The liquid in which sodium metal is preserved at room temperature is
(a) Petrol
(b) Water
(c) Kerosene oil
(d) Lemon juice
Answer:
(c) Kerosene oil
Fill in the blanks
1. ................... and ................... metals are soft and can be cut with a knife.
Answer:
Sodium, Potassium
2. Generally metallic oxides are ................... in nature.
Answer:
basic

3. Iron reacts with water ...................
Answer:
slowly
4. ................... reacts with water vigorously.
Answer:
sodium.
True/False
Mark 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if it is false.
1. Sulphur is good conductor of electricity.
Answer:
False
2. Mercury is liquid at room temperature.
Answer:
True
3. Magnesium oxide is basic in nature.
Answer:
True

4. Iron reacts with water vigorously.
Answer:
False
5. Generally non-metals do not react with acids.
Answer:
True
6. Phosphorous reacts with water vigorously.
Answer:
False
Match the words given in 'Column-A' with 'Column-B'
Question 1.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) CuSO4 |
(a) Iron sulphate |
|
(ii) ZnSO4 |
(b) Copper sulphate |
|
(iii) FeSO4 |
(c) Sulphuric acid |
|
(iv) H2SO4 |
(d) Zinc sulphate |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) CuSO4 |
(b) Copper sulphate |
|
(ii) ZnSO4 |
(d) Zinc sulphate |
|
(iii) FeSO4 |
(a) Iron sulphate |
|
(iv) H2SO4 |
(c) Sulphuric acid |

Question 2.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) 'Pop' sound |
(a) Mercury |
|
(ii) Liquid metal |
(b) Copper sulphate |
|
(iii) Blue colour |
(c) Hydrogen gas |
|
(iv) Soft metal |
(d) Potassium |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) 'Pop' sound |
(c) Hydrogen gas |
|
(ii) Liquid metal |
(a) Mercury |
|
(iii) Blue colour |
(b) Copper sulphate |
|
(iv) Soft metal |
(d) Potassium |
Question 3.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Oxygen |
(a) Antibiotic |
|
(ii) Nitrogen |
(b) Fertilizer |
|
(iii) Ozone |
(c) Breathing |
|
(iv) Iodine |
(d) Water purification |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Oxygen |
(c) Breathing |
|
(ii) Nitrogen |
(b) Fertilizer |
|
(iii) Ozone |
(d) Water purification |
|
(iv) Iodine |
(a) Antibiotic |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by malleability?
Answer:
The property of metals by which they can be beaten into thin sheets is called malleability.
Question 2.
What is ductility?
Answer:
The property of metal by which it can be drawn into wires is called ductility.

Question 3.
Complete the following reaction of magnesium with oxygen.
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → ?
Answer:
2 Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → Magnesium oxide (2 MgO)
Question 4.
Complete the following reaction of iron with oxygen.
Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (O2) + 2 Water (H2O) → ?
Answer:
2 Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (O2) + 2 Water (H2O) → Iron hydroxide 2[Fe(OH)2]
Question 5.
What is meant by POP sound?
Answer:
The sound released during the burning of hydrogen gas is called POP sound.
Question 6.
Which gas is produced by the reaction of metals with sodium hydroxide?
Answer:
Hydrogen.

Question 7.
Name the non - metal which is used in fertilizers for the growth of plants?
Answer:
Nitrogen.
Question 8.
Name the non - metal, violet colour solution of which is used as antibiotic on wounds?
Answer:
Iodine.
Question 9.
Which non - metal is used in the purification process of water?
Answer:
Ozone.
Question 10.
Name two metals which can be cut with a knife easily.
Answer:
- Sodium
- Potassium.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is malleability? Due to this one. metal is used to decorate sweets. Write the name of that metal.
Answer:
Malleability:
The property of metals by which it can be beaten into thin sheets is called malleability. Due to this property silver foil is prepared and used for decorating sweets.

Question 2.
What is metal? Explain with examples.
Answer:
Some materials are hard, lustrous, malleable, ductile, sonorous and good conductors of heat and electricity. The materials which generally possess these properties are called metals. The examples of metals are iron, copper, aluminium, etc.
Question 3.
What is non - metal? Explain with examples.
Answer:
The materials which are soft and dull in appearance, break down into powdery mass on tapping with hammer. They are not sonorous and are bad conductors of heat and electricity. These materials are called non - metals. The examples of non - metals are sulphur, carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, etc.
Question 4.
Metals are sonorous, what do you mean by this?
Answer:
The things made of metals produce ringing sound like bells of temples when struck hard. Since metals produce ringing sounds, they are said to be sonorous.

Question 5.
Metallic oxides are acidic or basic in nature. Explain.
Answer:
Metallic oxides are basic in natrue. This can be explained by this experiment.
Experiment:
A magnesium ribbon is burned and the ash obtained is dissolved in water and tested with red litmus which turns blue. So oxide of magnesium is basic in nature.
Question 6.
Oxides of non - metals are acidic in nature, explain it.
Answer:
Generally oxides of non - metals are acidic in natrue which can be explained by this experiment, small amount of powdered sulphur is taken in a deflagrating spoon and it is heated. As soon as sulphur starts burning the spoon is introduced into a glass tumbler and tumbler is covered with a lid to ensure that the gas produced does not escape.
After sometime the spoon is removed and a small quantity of water is added into the tumbler, lid is replaced quicky and the tumbler is shaked well. The product formed in the reaction of sulphur and oxygen is sulphur dioxide gas. When sulphur dioxide is dissolved in water sulphurous acid is formed. The reaction can be given as follows:
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) + Water (H2O) → Sulphurous acid (H2SO3).
The sulphurous add turns blue litmus paper to red which proves that oxides of non - metals are generally acidic in nature.
Question 7.
Do metals and non - metals react with water? Explain.
Answer:
Reaction of metals with water:
Some metals like sodium react with water vigorously and form sodium oxide but some other metals do not do so. For example, iron reacts with water slowly.
Reaction of non - metals with water:
Generally, non - metals do not react with water though some may be very reactive in air. Such non - metals are stored in water. For example, phosphorous is a very reactive non - metal. So it is stored in water.

Question 8.
How the reaction of metals with acids occurs?
Answer:
Generally metals reacts with acids and produce hydrogen gas that bums with a 'pop' sound. The reaction of iron with sulphuric acid can be given as follows:

Non - metals generally do not react with acids.
Question 9.
Explain the reaction of metals with bases.
Answer:
Metals reacts with bases and produce hydrogen gas, which can be explained by this experiment.
Experiment:
A freshly prepared solution of sodium hydroxide is taken in a test tube and a piece of aluminium foil is droped in it. Now bring a burning match stick near the mouth of the test tube, then a pop sound is heard. Which proved the presence of hydrogen gas. So it can be concluded that metals produce hydrogen gas by the reaction with bases.
Question 10.
How will you prove the chemically silver is less reactive than copper?
Answer:
A rod of silver metal is kept in blue solution of copper nitrate for some time. It is observed that there is no displacement reaction, silver rod and blue solution of copper nitrate remain as such. It means silver metal can not displace the copper metal from the solution of copper sulphate which proves that silver metal is less reactive than copper metal.
Question 11.
Explain if there is any reaction of following metals with copper sulphate solution.
(i) Copper
(ii) Zinc.
Answer:
(i) Copper metal does not react with solution of salt of copper (copper sulphate solution).
(ii) Zinc metal is more reactive than copper metal, so it displaces the copper metal from the solution of copper sulphate. During this process blue colour of copper sulphate solution disappears.
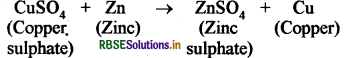
Question 12.
Write the important uses of metals.
Answer:
Uses of metals are as follows:
- Metals are used in the manufacturing of machines, vehicles, aeroplanes, rail, etc.
- Metals are used in the manufacturing of satellites.
- Industrial gadgets, cooking utensils are made from metals.
- Water boilers are also made from metals.

Question 13.
What are the uses of non - metals in our life?
Answer:
Uses of non - metals:
- Oxygen is non - metal which is essential for our life which all living beings inhale during breathing.
- Nitrogen and phosphorous are non - metals, which are used in fertilisers to enhance the growth of plants.
- Ozone is used in the purification of water.
- Sulphur is used as fungicides and gun powder is also prepared from it which is used in crackers.
Question 14.
What will happen if phosphorous is kept open in air instead of water?
Answer:
Phosphorous is a very reactive metal. If kept open in air it will react with oxygen and catches fire. Therefore, phosphorous is kept in water.
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Sulphur dioxide gas is formed by the reaction of substance A and B, which gives C, when dissolved in water. Write the chemical equations with the names of substances A, B and C.
Answer:
Substance A = Sulphur, B Oxygen, C = Sulphurous acid.
Equation
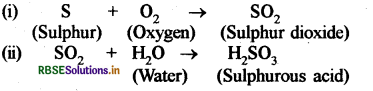
Question 2.
Explain the displacement reactions in metals.
Answer:
Displacement reactions in metals:
One metal displaces another metal from the aqueous solution of its compound but this reaction is not general. A more reactive metal can replace a less reactive metal, but a less reactive one cannot replace a more reactive metal. This can be explained by the following experiment:
5 beakers of 100 ml are taken and labelled A, B, C, D and E. 50 ml of water is taken in each beaker. In beaker A one tea spoonful copper sulphate + Zinc granule, in beaker B copper sulphate + Iron nail, in beaker C Zinc sulphate + copper turnings, in beaker D iron sulphate + copper turnings and in beaker E zinc sulphate + Iron nail are taken. These solutions are stirred with spoon and kept undisturbed for some time.
It is observed that in beaker A zinc (Zn) replaces copper (Cu) from copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution. That is why the blue colour of copper sulphate solution disappears and a powdery red mass of copper is deposited at the bottom of the beaker. Similarity the blue colour of copper sulphate solution also disappears in beaker B. The reactions are as under:
CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu (Red)
CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu (Red)
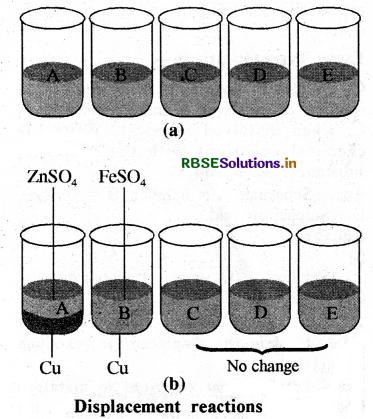
But there is no change in beakers C, D and E in beaker C, copper is not able to replace zinc from zinc sulphate where as zinc can replace copper. Because zinc is more reactive than copper and iron a more reactive metal can replace a less reactive metal but a less reactive one cannot replace a more reactive metal that is why there is no displacement reactions in beakers D and E also.

Question 3.
Differentiate between the metals and non - metals.
Answer:
Difference between metals and non - metals
|
Metals |
Non - metals |
|
1. Metals are good conductor of heat and electricity. |
1. Non - metals are bad conductors of heat and electricity, exception is graphite which is non - metal although it is good conductor of heat and electricity. |
|
2. Metals are malleable and ductile. |
2. Non - metals are not malleable and ductile but these are brittle. |
|
3. Metals are lustrous and can be polished. |
3. Non - metals are generally not lustrous and cannot be polished. |
|
4. Metals are solids (exception is mercury which is liquid). |
4. Non - metals may be solid, liquid or gases. |
|
5. Melting and boiling points of metals are generally high. |
5. Melting and boiling points of non - metals are comparatively low. |
|
6. Metals form basic oxides. |
6. Non - metals forms acidic or neutral oxides. |
|
7. Metals generally displace the hydrogen from dilute acids. |
7. Non - metals do not displace the hydrogen from dilute acids. |
|
8. Metals generally do not react with hydrogen only some very reactive metals react with hydrogen and form hydrides. |
8. Non - metals forms stable hydrides by the reaction with hydrogen. |
