RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
These comprehensive RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Notes Financial Statements-I
Financial Statements:
Meaning: Financial statement refer to the end results of financial transactions taken place during a particular period. The end results are in the form of profit or loss and financial statements.
Types of Financial Statements
(a) Trading, Profit and Loss Account: It is prepared to find out gross profit, net profit and operating profit for the year ended.
(A) Balance Sheet: It is prepared to know financial position in the form of assets and liabilities at the end of the year.

Receipts & Payments
(а) Receipts: Receipts can be in the form of cash or through banking. They are mainly classified into two categories:
- Revenue Receipts: The receipts received in usual course of business are known as revenue receipts. They are recurring in nature like interest received, rent received, net sales, commission received, discount received etc. Treatment in Financial Statements: Revenue incomes are treated as Revenue Incomes and are taken on the credit side of either Trading Account or Profit & Loss Account.
- Capital Receipts: The receipts which not usual in the business are known as capital receipts. These receipts include capital introduced, loan received etc.
- Treatment in Financial Statements: Normally such receipts are treated Capital Incomes and are taken on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
(b) Payments: Payments can also be made in cash or through banking. They are also classified into two categories:
- Revenue Payments: The payments which are made to receive services of different kind of persons working for an organisation and to the supplier of goods like, payment of salaries, wages, interest paid, commission paid, rent paid, purchases etc.
- Treatment in Financial Statements: Revenue payments are treated as revenue expenditures and are taken on the credit side of either trading account or profit or loss account.
- Capital Payments: Capital payments are those payments which provide the benefit for more than one financial year. They are treated as capital expenditures. These are non-recurring in nature. These include, purchase of fixed assets, expenses incurred to increase or improve the value of fixed assets.
- Treatment: Capital payments are taken on the assets side of balance sheet.
Incomes and Expenditures
(a) Incomes: Incomes are of two types.
1. On the Basis of Nature
These are capital incomes and revenue incomes.
- Capital Incomes: all capital receipts are capital incomes
- Revenue Incomes: All revenue receipts are revenue incomes.
2. On the Basis of Accounting
- Direct Incomes: All those incomes which are directly related with the production are known as direct incomes. Examples: like net sales, royalty from production, sale of scrap etc.
- Indirect Incomes: All those incomes which are indirectly related with the production or incidental to production are known as indirect incomes.
Examples: Discount received, interest received, rent received etc.
3. On the Basis of Production Process
- Operating Incomes: The incomes which are related with the production directly or indirectly are called operating incomes. These are further classified into two categories:
- Direct Operating Incomes: Like net sales, royalty from production, sale of scrap etc.
- Indirect/Other Operating Incomes: like discount received, interest received, rent received etc.
- Non-Operating Incomes: The incomes which do not have any relation with the production process are known as non-operating incomes.
Examples: Interest received on long term investments, profit on sale of fixed assets, rent received etc.
(b) Expenditures: Whenever any payment is made in return to services or any other purpose except to settle the liabilities, is called expenditure. These are mainly two types:
1. On the basis of nature
- Revenue Expenditure: The expenditure whose benefit is derived within a year.
Examples: Wages, salaries, commission paid, rent paid, insurance paid, discount allowed etc. - Capital Expenditure: The expenditure whose benefit is spread over a year.
Example: Purchase of assets. - Deferred Revenue Expenditure: It is a part of capital expenditure. The expenditure which are incurred to promote sales or to increase revenue are called deferred revenue expenditure.
Example: Advertisement expenditure for more than one year, research & development expenditure.
2. On the basis of accounting
- Direct Expenses: The expenses which are directly related with the production process.
Examples: Opening stock, net purchases, wages, manufacturing expenses etc. - Indirect Expenses: The expenses which are indirectly related with the production process.
Examples: Net sales, royalty from production, sale of scrap etc.
3. On the basis of production process
- Operating Expenses: All those expenses which are related with the production process directly or indirectly are called operating expenses.
- Direct Operating Expenses: Net purchases, wages, manufacturing expenses etc.
- Indirect/Other Operating Expenses: Salaries, discount allowed, commission allowed, legal expenses
- Non-Operating Expenses: The expenses which do not have any relation with the production process are known as non-operating expenses.
Examples: Loss due to damage to building, loss on sale of fixed assets, interest on long term loan etc.
Difference between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure
|
Basis |
Capital expenditure |
Revenue expenditure |
|
Earning capacity |
To increase earning capacity |
To maintain revenue capacity |
|
Purpose |
To acquire fixed assets |
To conduct day-to-day conduct of business |
|
Nature |
Non-recurring in nature |
Recurring in nature |
|
Period of benefit |
Its benefit extends for more than one year |
Its benefit accrues within an accounting year |

Process to Prepare Financial Statements
Accounting Process Involves the Following Steps:
- Identification of financial transactions
- Recording of transactions in the journal, cash book, other subsidiary books, and journal proper
- Posting of entries into ledger book
- Finding closing balances of all accounts in the ledger and cash book.
- Recording of all accounts with their balances in the trial balance Dr side or Cr side.
Process of Preparation of Financial Statements
Trial balance reflects three types of accounts:
(a) Personal Accounts: The personal accounts have either Dr balances or Cr balances. All debit balances are shown on the assets side of balance sheet and all Cr balances are shown on the liabilities side.
(b) Real Accounts : All real accounts have debit balances and are shown on the assets side of the balance sheet.
(c) Nominal Accounts: Nominal accounts represent expenses, losses, incomes and gains. The net result of all such accounts is either profit or loss.
Classification of nominal accounts
|
Nature |
Expenses and losses |
Incomes and gains |
|
Directly related with the production |
These are transferred to the debit side of trading account |
These are transferred to the credit side of trading account |
|
Indirectly related with the production
|
These are transferred to the debit side of profit and loss account |
These are transferred to the credit side of profit and loss account |
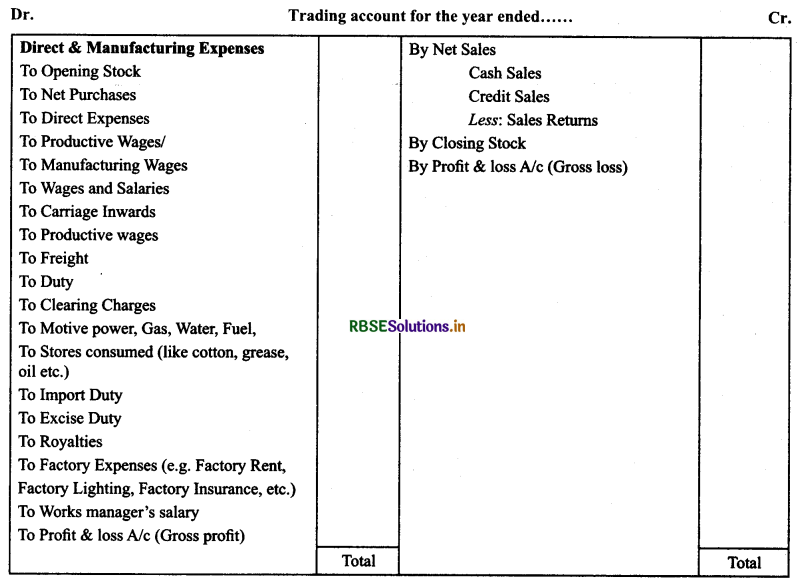
Preparation of Trading Account:
Meaning of Trading Account: First part of Income Statement is termed as Trading Account. In case of credit balance, it is profit and this profit is termed as ‘Gross Profit’. In case of debit balance, it is loss and is termed as ‘Gross Loss’.
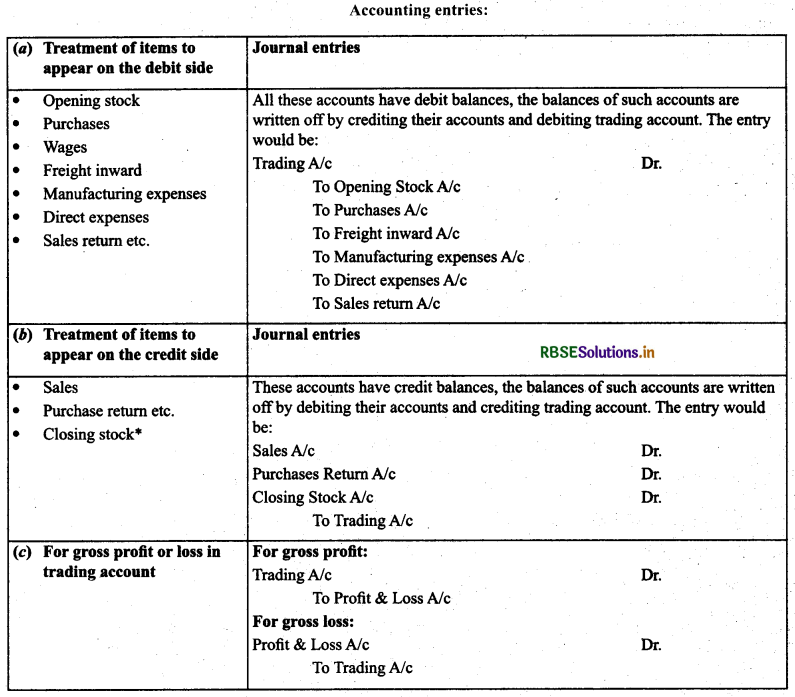
Procedure to Prepare Trading Account: From the list of nominal accounts, all expenses and losses directly related with the production process are transferred on the debit side of trading account and all incomes directly related with the production process are transferred to the credit side of trading account.
Accounting entries:

Valuation of closing stock
Closing stock is valued at the cost price or market price, whichever is less. It is vaiued at two stages:
(a) Before the preparation of trial balance: It appears on the debit side of trial balance and from there, it is taken on the assets side.
(b) After the preparation of fría! balance: It is shown on the credit side of trading account and on the assets side.
Format of Trading Account
 Calculation of Certain items from Trading Account
Calculation of Certain items from Trading Account
(a) Cost of goods sold/cost of sales
= Net sales - gross profit
Or
= Net sales + gross loss
Or
= Opening stock + net purchases + direct and manufacturing expenses - closing stock
Or
= Net purchases + direct and manufacturing expenses - increase in stock
Or
= Net purchases + direct and manufacturing expenses + decrease in stock
(b) Gross profit
= Net sales - cost of goods sold
Or
= Cost of goods sold + Net sales (i.e. gross loss)
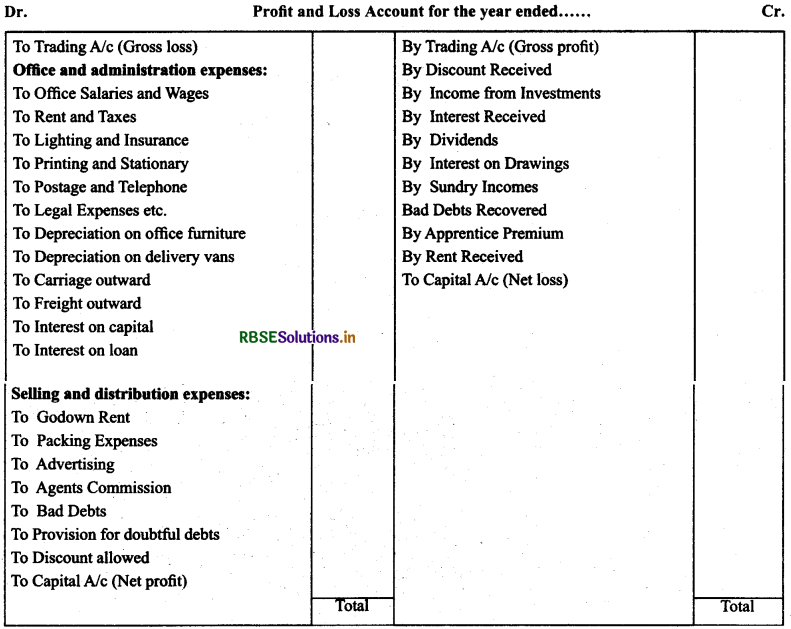
Preparation of Profit & Loss Account:
Meaning of Profit and Loss Account: Second part of income statement is known as profit and loss account. This account reveals net profit or net loss.
Procedure of Preparing Profit and Loss Account: From the list of nominal accounts, all nominal expenses and losses indirectly related with the production process are transferred on the debit side of profit and loss account and all incomes and gains indirectly related with the production process on the credit side of profit and loss account.
Note: All expenses in this account may be classified into two categories:
(a) Office and administration expenses
(b) Selling and distribution expenses

Accounting Entries:
|
(a) Treatment of items to appear on the debit side |
Journal entries |
|
Office and administration expenses:
|
All these accounts have debit balances, the balances of such accounts are written off by crediting their accounts and debiting profit and loss account. The entry would be: Profit and loss A/c Dr To Office Salaries and Wages To Rent and Taxes To Lighting and Insurance To Printing and Stationary To Postage and Telephone To Legal Expenses etc. |
|
(b) Treatment of items to appear on the credit side |
Journal entries |
|
Discount Received
|
These accounts have credit balances, the balances of such accounts are written off by debiting their accounts and crediting profit & loss account. The entry would be: |
Format of profit and Loss Account
 Calculation of Certain Items from Profit & Loss Account
Calculation of Certain Items from Profit & Loss Account
Operating Profit: I* refers to the normal profit earned by a business from the operations/manufacturing. It is the net result of incomes from operations reduced by its operating cost to achieve net sales.
= Net sales - cost of goods sold - indirect/other operating expenses + indirect/other operating incomes
Or
= Gross profit - indirect/other operating expenses + indirect/other operating incomes
Or
= Indirect/other operating incomes - Indirect/other operating expenses - Gross loss
Or
= Net profit + Non-operating expenses - other non-operating incomes
Net profit: It refers to final outcome of the business operations.
= Gross profit - other operating expenses - non operating expenses + other operating incomes + other non-operating incomes

Balance Sheet:
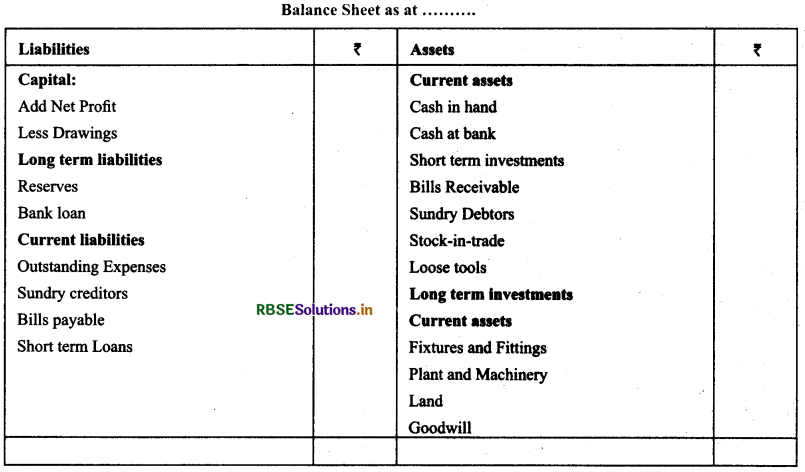
Meaning of Balance Sheet: Balance sheet is a statement of financial position of a concern at a given date. It is a list of assets and liabilities of a business concern on a particular date. Balance sheet is prepared from the trial balance.
Procedure to Prepare Balance Sheet: Balance sheet is prepared with the help of personal accounts and real accounts. All real accounts are shown on the assets side, personal accounts with credit balance are shown on the liabilities side and personal accounts with debit balance are shown on the assets side.
Marshalling of assets and liabilities: There are two ways to prepare balance sheet
(a) Order of Liquidity: Under liquidity order assets which are realisable in cash most easily are shown first and the assets which are most difficult to realise are shown in the end.
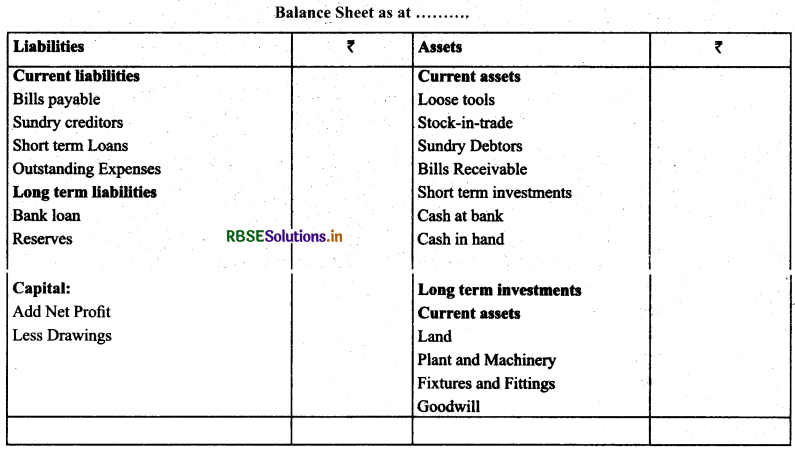 (b) Order of Permanence: On the basis of this order, fixed assets such as Land & Buildings, Plant & Machinery, Furniture, etc., are shown first, and these are followed by floating assets such as stock, debtors etc. The item which has practically no permanence is cash and it is shown at the end.
(b) Order of Permanence: On the basis of this order, fixed assets such as Land & Buildings, Plant & Machinery, Furniture, etc., are shown first, and these are followed by floating assets such as stock, debtors etc. The item which has practically no permanence is cash and it is shown at the end.