RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
These comprehensive RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 Notes Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
Trial Balance - Meaning, Objectives and Preparation
Meaning of Trial Balance:
It is a statement which shows the arithmetical accuracy of all debits and credits into the ledger accounts. It ensures both aspects of every transaction have been recorded accurately.
Objectives of preparing trial balance
- It helps to check the arithmetical accuracy of posting of all amounts in the ledger accounts.
- It helps to locate the errors which occur at various stages
- It helps to prepare financial statements
Format of Trial Balance
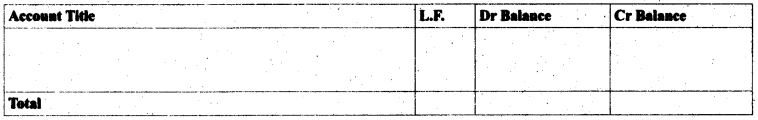
Preparation of trial balance:The following steps are taken to prepare the trial balance
- Ascertain the balance of each account in the ledger and cash book
- Place the balances in the trial balance. Debit balance in the debit column and credit balance in the credit column.
- Ignore the account if its balance is zero.
- Compute the total of debit balance column
- Compute the total of credit balance column
- Verify both sides of debit column and credit column agree.
Note: If both sides do not match, one must check correctness of all balances of all accounts. If still, the trial balance does not tally, the difference is put in a newly opened account, suspense account.

Types of Errors:
On the basis of nature, errors can be classified into four categories:
(a) Errors of Commission: Such type of errors include error due to wrong posting, wrong totaling, wrong, balancing of an account, wrong casting of subsidiary books, and wrong recording of amount in the books of original entry.
Note: Trial balance agrees if errors occurs due to recording in the correct book or there is the posting of an amount is done in the wrong account but on the correct side.
Trial balance does not agree if there is error in casting or error in carrying forwarding of amount or posting of an amount on the wrong side of correct account or posting is done with wrong amount in the correct account.
(b) Errors of Omission: These errors can be of two types:
(i) Errors due to Complete Omission: It happens when a transaction is not recorded anywhere in the original books of original entry or recorded in the journal book but not recorded in the ledger.
Example: Sales of ₹ 10,000 to Ram not recorded anywhere.
Note: Trial balance agrees.
(ii) Errors due to Partial Omission: It happens when a transaction is recorded in one account.
Example: Sales of ₹ 10,000 to Ram was not recorded in Ram’s account.
Note: Trial balance does not agree.
(c) Errors of Principle: It happens when accounting principles are not adopted while passing journal entries and no distinction between capital item and revenue item is made.
Example: Wages paid on the installation of machinery was debited to wages account.
Note: Trial balance agrees.
(d) Compensating Errors: Such errors happen when the effect of one error is nullified by another error and the effect of debit and credit is nil.
Example: Purchase of ₹ 10,000 was recorded as ₹ 1,000 whereas the sales of ₹ 10,000 was recorded as ₹ 1,000. In this case, debit side was short by ₹ 9,000 in first error whereas credit side was short by ₹ 9,000 in the second error. The second error nullified the effect of first error.
Note: Trial balance agrees.

Rectification of Errors not Affecting Trial Balance
Such errors are also called two sided errors. Examples of such errors are errors of principle, errors of complete omission, compensating errors and some errors of commission.
Procedure for rectification:
- Step 1: Pass the correct entry or the entry which should have been passed
- Step 2: Pass the incorrect entry or the entry which has already been passed
- Step 3: Match the common accounts debited and credited in each entry and cancel them.
- Step 4: See which account is left in the correct entry and in incorrect entry.
- Step 3: Pass rectifying entry by keeping the account left in the correct entry as it is and reverse the account left in the incorrect entry.
Example: ₹ 20,000 paid on buying laptop was debited to office expense account.

Rectification of Errors Affecting Trial Balance:
Such errors are also called one sided errors. Examples of such errors are errors of partial omission, errors of commission by which trial balance does not match.
(a) If such Error Occurs in the Books of Original Entry (journal book) before posting in the ledger, it can be corrected by crossing out the wrong amount by a single line and writing the correct amount with the initial of the accountant.
(b) If Such Occurs in the Ledger, the wrong amount in the concerned account may also be corrected in the same way by giving explanatory note in the particular column.
Example: Shyam’s Account was credited short by ₹ 190, such error may be corrected in the ledger in the following way:
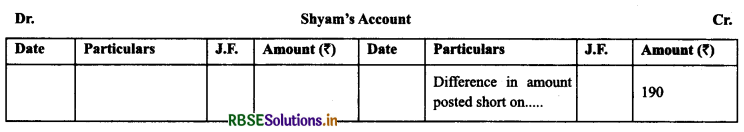
(c) If error is not Detected Before Preparing Trial Balance (use of Suspense Account): Trial balance is the basis of preparing financial statements which includes income statement and balance sheet. If the trial balance does not match and it is urgent to prepare financial statements, the difference in either side of trial balance is put in ‘Suspense Account’ for the time being.
Procedure to Correct the Errors using Suspense Account:
- Step 1: Identify the account affected due to error.
- Step 2: Debit or credit the account affected as required on the basis of original transaction
- Step 3: See the difference comes in either side of entry
- Step 4: Replace such difference with the suspense account and the effect of one sided errors get over gradually.
Note: After all one sided errors are rectified, there shall remain no balance in the suspense account.
Example 1: Credit sales of ₹ 10,000 to Nishant was not posted to his account. This is an error of partial omission.
Here in this case, Nishant Account was required to be debited but could not. We shall debit his account and credit suspense Account.

Example 2: Sales book was overcast by ₹ 5,000. This is the error of commission.
The total of sales book is transferred to the credit side of sales account. The balance of sales book was valued in excess by ₹ 5,000, so sales account got increase of ₹ 5,000 and now we need to reduce the sales account by debiting it.


Example 3: Furniture purchased for ₹ 5,000 was posted to purchase account as ₹ 500. This the error of commission. Here purchase account was wrongly debited by ₹ 500 instead of debiting furniture by ₹ 5,000. This error must have resulted the debit side of trial balance in deficit by ₹ 4,500 which would have been replaced by suspense account. Now we shall credit purchase account by ₹ 500, debit furniture account by ₹ 5,000 and the difference will be posted in the suspense account.


- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 बैंक समाधान विवरण
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 लेन-देनों का अभिलेखन-2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 तलपट एवं अशुद्धियों का शोधन
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors