RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
These comprehensive RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 11 Notes Accounts from Incomplete Records
Meaning, Features and Limitations
Meaning of Single Entry System: It is an incomplete system of accounting wherein no proper system of accounting is followed, for some transactions, proper debit and credit are followed, for some either side is followed or sometime no entry is passed.
Accounts under Single Entry System: Cash Book, Debtors Accounts and Creditors Accounts are prepared.
Features of Single Entry System
- Economical. This system is economic for those business which are of small size and where the transactions are few.
- Simple. This system is adopted by those businessmen who are not folly aware of the principles of double entry system,
- Incomplete Information: No complete information on expenses, losses, liabilities and assets.
- Lack of Uniformity: The accounts of different organisations following SES cannot be compared.
Limitations of Single Entry System
- Incomplete record. Under this system, only cash account & only personal accounts are maintained.
- No trial balance. Trial balance cannot be prepared due to incomplete records.
- Difficulty in locating and rectifying errors. Rectification of error also becomes difficult due to incomplete records.
- Difficulty in ascertaining Profit Due to non-availability of proper records of income and expenditure, accurate profit and loss cannot be ascertained.

Difference between Single Entry System and Double Entry System
|
Basis |
Double Entry System |
Single Entry System |
|
Aspect of recording |
Both aspects |
One aspect |
|
Accounts |
All accounts are prepared |
Only real and personal accounts are prepared |
|
Trial balance |
It can be prepared |
It cannot be prepared |
|
Final accounts |
Can be prepared |
Cannot be prepared |
|
Suitability |
Suitable for all types of organisations - |
Suitable for small business |
Ascertainment of Profit and Loss under Single Entry System
|
Particulars |
(₹) |
|
Capital at the end |
Xxx |
|
(-) Capital in the beginning |
Xxx |
|
(+) Drawings during the year |
Xxx |
|
(+) Capital withdrawn |
Xxx |
|
(-) Capital further introduced |
Xxx |
|
Profit / Loss |
Xxx/(xxx) |
Note: Positive figure will represent profit and negative figure will represent loss.
Calculation of Opening Capital:
In order to find out opening capital, we need to prepare ‘Statement of Affairs’ in which the book values of all assets and liabilities in the beginning of the year are shown and balancing figure on the either side is known as capital.
Calculation of Closing Capital:
In order to find out the closing capital, we prepare ‘Statement of Affairs’ with the book values of assets and liabilities with adjustments (if any) except capital further introduced, capital withdrawn and drawings and balancing figure on either side is known as closing capital.
Statement of Affairs resembles balance sheet but it is not called balance sheet as the data is not wholly based on ledger balances.
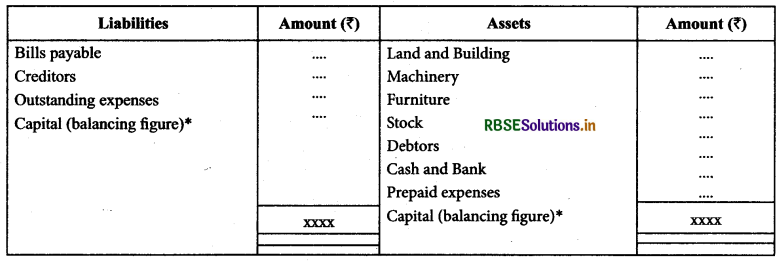
Note: Where the total of liabilities side is more than total of assets side, capital would be shown in assets side and it represent debit balance of capital.

Preparation of Trading, Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet
To convert the single entry system into double entry system, we need to arrive at the figures we require to prepare final accounts. Some items are easily available under single entry system through cash book, debtors’ book and creditors’ book but certain items have to be obtained by preparing various accounts. We need to prepare usually following accounts to find out various items:
(a) Cash account is prepared normally to find either of cash sales, cash purchase, cash received from debtors, cash paid to creditors, closing balance etc.
(b) Debtors account is prepared normally to find out credit sales, cash received, closing balance etc.
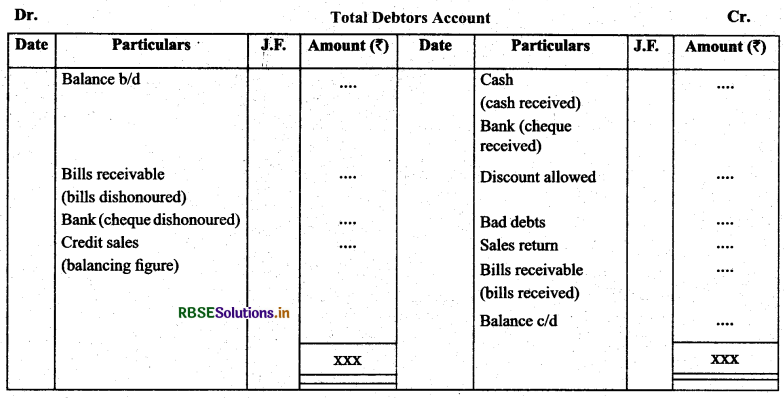
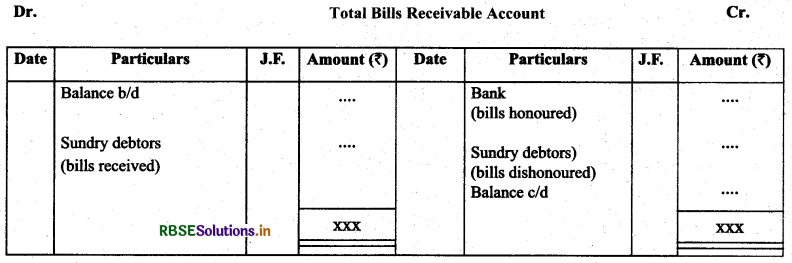
(c) Bills receivable account is normally prepared to find out bills receivable received, honoured, dishonoured, closing balance etc.
Note: Bills receivable account is closed before debtors account is closed.
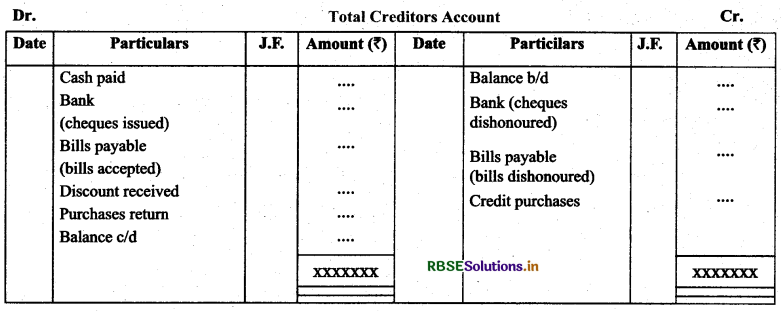
 (d) Creditors account is prepared normally to find out credit purchases, cash paid, closing balance etc.
(d) Creditors account is prepared normally to find out credit purchases, cash paid, closing balance etc.
(e) Bills payable account is normally prepared to find out bills payable issued, bills paid, closing balance etc. Note: Bills payable account is closed before debtors account is closed.
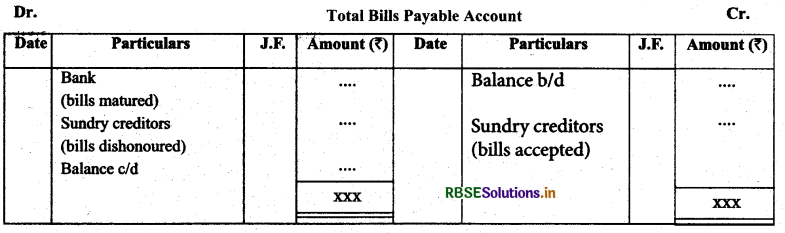

(f) Statement of affairs to find out capital in the beginning, (already discussed)
We prepare Trading Account, Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet simultaneously along with the working notes to find out the missing figures. We prepare final accounts in the usual way as we have learnt under financial statements chapter.
