RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
These comprehensive RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 10 Notes Financial Statements-II
Adjustments: Meaning and Need
Meaning of Adjustment: Financial statements are prepared on the basis of accrual concept of accounting. While preparing financial statements, adjustments means to adjust the expenses and incomes such that they may belong to financial year for which the accounts are to be prepared.
Need to Make Adjustments:Certain expenditures may not have been paid for the entire financial year and similarly incomes may not have been received for the entire financial year. So, we need to add outstanding expenses in the expense paid and add and accrued incomes in the incomes received.
Similarly, some expenditures may have been paid in advance and some incomes may have been received in advance. So, we need to deduct advance expense paid from the expense or deduct advance income received from the income concerned.

Important Adjustments
(1) Closing Stock: It is valued at cost price or market price whichever is lower. It is valued at two stages.
(a) Valuation before the Preparation of Trial Balance
Treatment: It appears inside the trial balance and it is shown directly on the assets side

(b) Valuation after the Preparation of Trial Balance
Treatment: It is shown on the credit side of trading account and on the assets side.

(2) Outstanding Expenses: It is the part of expense relating to one financial year which is yet to be paid.
Treatment: It is shown on the liabilities side and add in the respective expense either on the debit side of trading account or profit & loss account.
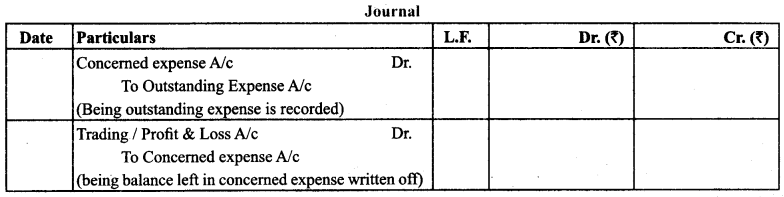
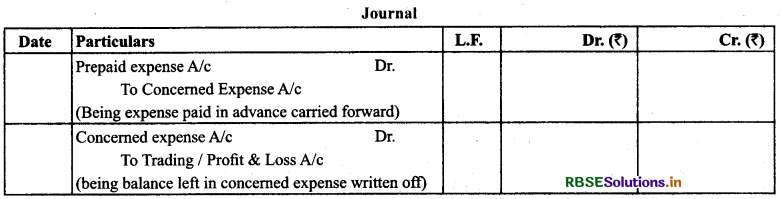
(3) Prepaid Expense/Unexpired Expense: It is the amount which has been paid in the accounting period for which the final accounts are being prepared but the actual expenditure relates to the next accounting period.
Treatment: Deduct from the concerned expense and show on the assets side.
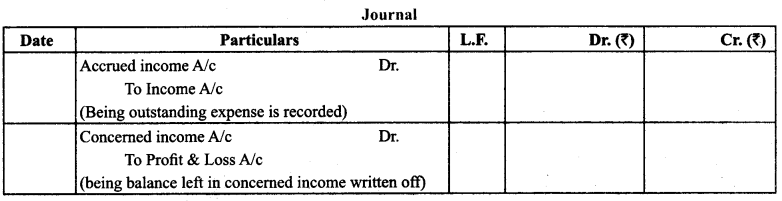
(4) Accrued Income: It is the income earned for the current financial year but not received.
Treatment: It is added in the concerned income and shown on the assets side.

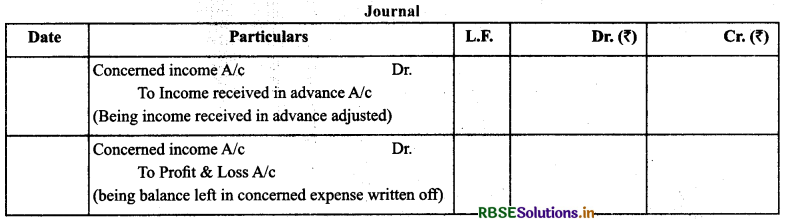
(5) Income Received in Advance/Unearned Income: The portion of income which belongs to next accounting year is known as income received in advance.
Treatment: Add in the concerned income and show on the assets side.
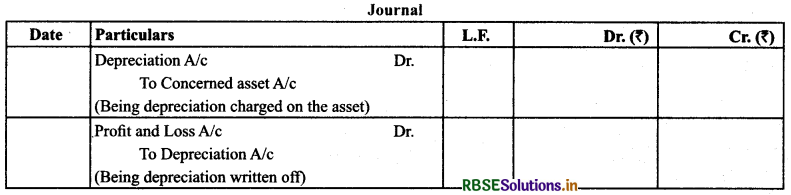
(6) Depreciation: Decline in the value of tangible assets due to normal wear and tear is known as depreciation.
Treatment: It is shown on the debit side of profit & loss account and deducted from the concerned asset in the balance sheet.
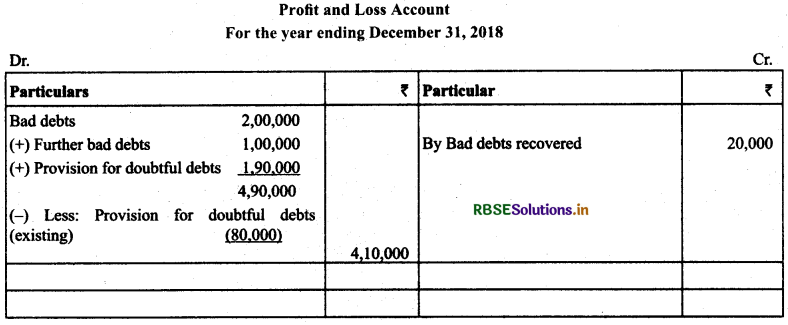
 (7) Bad Debts & Provision for Doubtful Debts: The amount due from the debtors not realised is known as bad debt. There are three stages when the bad debts can take place:
(7) Bad Debts & Provision for Doubtful Debts: The amount due from the debtors not realised is known as bad debt. There are three stages when the bad debts can take place:
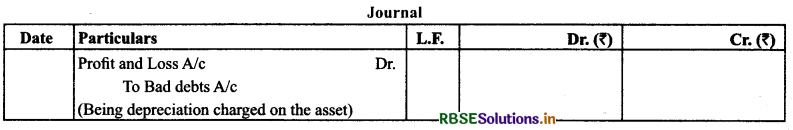
(a) Occurrence of Bad Debts before the Preparation of Trial Balance: It appear inside the balance which means some bad debts has already taken place.
Treatment: It is shown on the debit side of profit and loss account
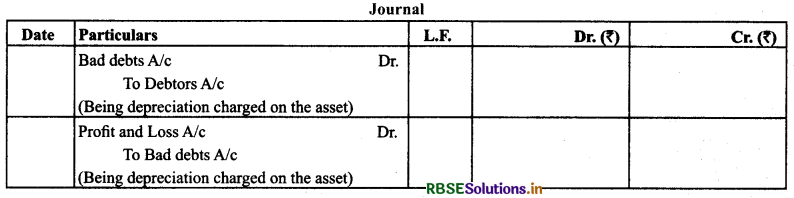
 (b) Occurrence of Bad Debts after the Preparation of Trial Balance: It is the bad debts which take place just after preparing the trial balance.
(b) Occurrence of Bad Debts after the Preparation of Trial Balance: It is the bad debts which take place just after preparing the trial balance.
Treatment: It is shown on the debit side of profit and loss account and deducted from the debtors.
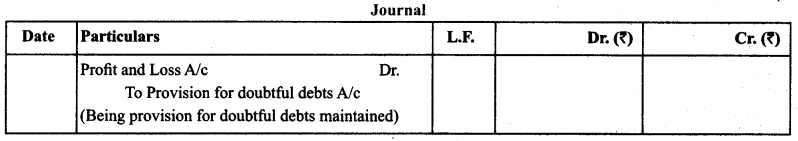
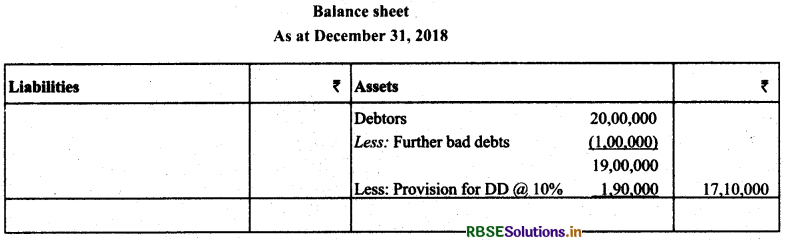
 (c) Possibility of Occurrence of Bad Debts in the Subsequent Year: It is the amount of likely bad debts in the subsequent year. It is also known as doubtful debts. To record such bad debts, a firm maintains provision for doubtful debts. Treatment: It is calculated on the debtors on the basis of percentage given, deducted from the debtors after deducting further bad debts and shown on the debit side of profit and loss account.
(c) Possibility of Occurrence of Bad Debts in the Subsequent Year: It is the amount of likely bad debts in the subsequent year. It is also known as doubtful debts. To record such bad debts, a firm maintains provision for doubtful debts. Treatment: It is calculated on the debtors on the basis of percentage given, deducted from the debtors after deducting further bad debts and shown on the debit side of profit and loss account.
 Example: The following example will help to understand the steps involved the treatment of bad debts and provision for doubtful debts.
Example: The following example will help to understand the steps involved the treatment of bad debts and provision for doubtful debts.
Trial balance
|
Name of the account |
Dr. Balances |
Cr. Balances |
|
Debtors |
20,00,000 |
|
|
Bad debts |
2,00,000 |
|
|
Provision for doubtful debts |
|
80,000 |
|
Bad debts recovered |
|
20,000 |

Adjustments:
(a) There were further bad debts amounting to ₹ 1,00,000 after the trial balance has been prepared.
Solution:
(b) Create provision for doubtful debts @ 10% of debtors.
Solution:
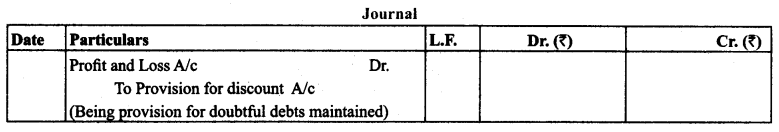
(8) Provision for Discount on Debtors:
Discount is allowed to debtors to encourage prompt payment. For the estimated amount of discount in the next financial year is estimated and profit is set aside by creating provision for doubtful debts.
Note: Provision for discount is calculated on the amount of debtors after ascertaining the amount for provision for doubtful debts.
Treatment: It will be shown on the debit side of Profit and Loss Account and shall be shown as deduction from the debtors.
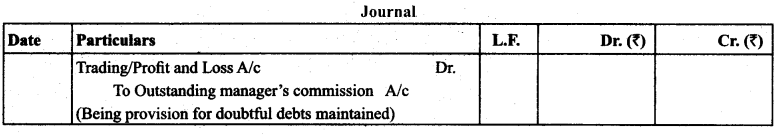
(9) Manager’s Commission: The manager may be given the commission on the net profit. It may be allowed in two ways:
(a) Commission on the Net Profit before Charging his Commission
Commission = Net profit × \(\frac{\text { Rate of commission }}{100}\)
(b) Commission on the Net Profit after Charging his Commission
Commission = Net profit × \(\frac{\text { Rate of commission }}{\text { Rate of commission }+100}\)
Treatment: It is shown on either debit side of trading account (if allowed to works/production manager) or on the debit side of profit and loss account (if allowed to sales manager) and then on the liabilities side as outstanding manager’s commission.

(10) Interest on Capital: Interest on capital is a notional expense which is considered to arrive at the accurate profit of the business presuming if the same amount of amount would have been raised from any other source, some amount of interest would have been paid.
Treatment: It is shown as expense on the debit side of profit and loss account add is added in the capital on the liabilities side.

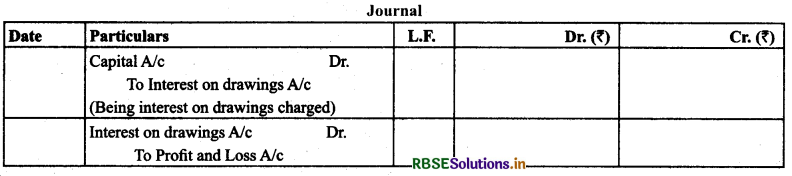
(11) Interest on Drawings: It is notional income which is calculated to arrive at the accurate profit presuming if the same amount would have been given to any outsider, some interest would have been earned by the business.
Treatment: It is shown on the credit side of profit and loss account and as deduction from the capital.
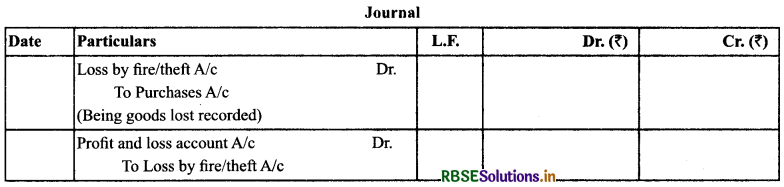
 (12) Abnormal Loss/ Loss of Goods by Fire/ Loss of Goods by Theft: Purchase account is reduced by the cost of goods lost. There can be three situations:
(12) Abnormal Loss/ Loss of Goods by Fire/ Loss of Goods by Theft: Purchase account is reduced by the cost of goods lost. There can be three situations:
(a) When the Goods Lost are not Insured
Treatment: It is shown as deduction from the purchases and shown on the debit side of profit and loss account
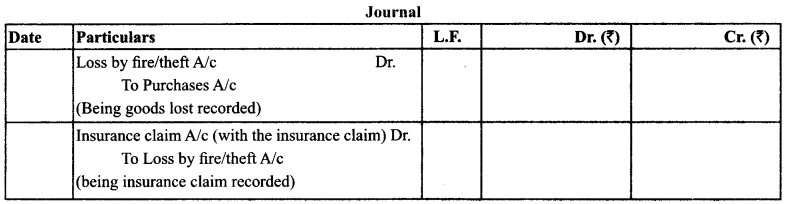
(b) When the Goods are Insured (Fully/Partially)
Treatment: It is shown as deduction from the purchases and the claim is shown on the assets side
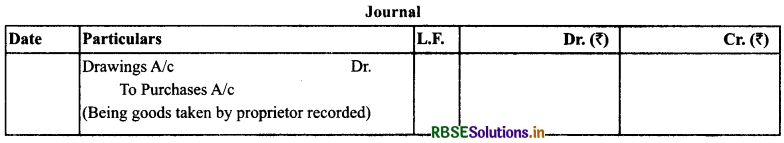
(13) Goods Taken for Personal Use: It is similar to drawings but in kinds.
Treatment: Purchases account is reduced by the cost of the goods and is shown as deduction from the capital as drawings of goods
Other Additional Adjustments

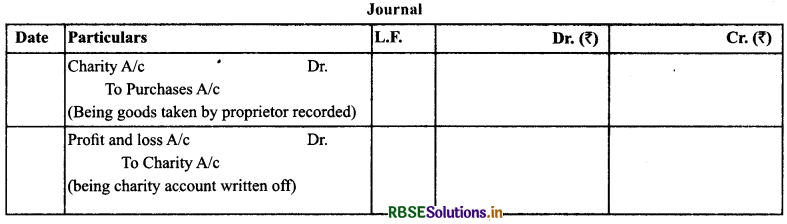
(14) Goods Given as Charity
Treatment: It is shown as deduction from the purchases and on the debit side of profit and loss.
 (15) Goods Distributed on Samples
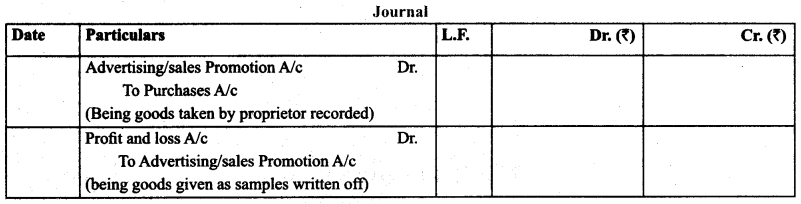
(15) Goods Distributed on Samples
Treatment: It is shown as deduction from the purchases and on the debit side of profit and loss.
 (16) Treatment of Deferred Revenue Expenditure/Capital Expenditure: Such expenditures are written off over the years of benefits accruing from such expenditure.
(16) Treatment of Deferred Revenue Expenditure/Capital Expenditure: Such expenditures are written off over the years of benefits accruing from such expenditure.
Treatment: Expenditure is divided by such number of years, the part to be written off is shown on the debit side of profit and loss account and balance is shown on the assets side.
 (17) Goods Sent on Sales or Return Basis Recorded as Actual Sales: Such goods refer to the goods which have been sent to customers subject to approval but recorded as actual sales and at the time of preparation of final accounts, no information is received from the customers.
(17) Goods Sent on Sales or Return Basis Recorded as Actual Sales: Such goods refer to the goods which have been sent to customers subject to approval but recorded as actual sales and at the time of preparation of final accounts, no information is received from the customers.
Treatment: Sales account is reduced by the sale price of such goods and from the debtors. Closing stock is increased by the cost price.
 Adjustments on GST
Adjustments on GST
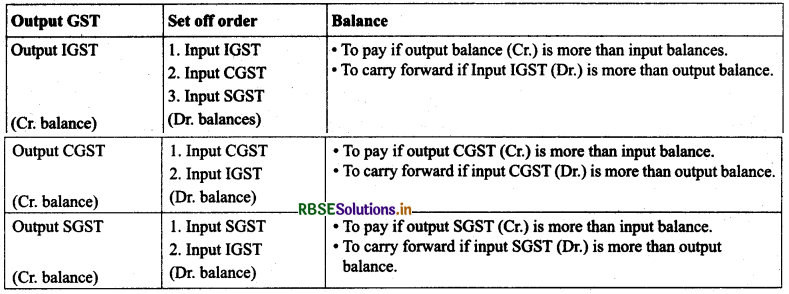
The trial balance may carry Input GST (IGST, CGST and SGST) and Output GST (IGST, CGST and SGST). Output GST is the tax collected and Input GST is the tax paid. Tax collected is used to set off tax paid. Two situations may arise:
(a) Net Balance Remains as Output GST (Cr) - It will be shown on the liabilities side under current liabilities as Output GST Payable.
(b) Net Balance Remains as Input GST (Dr) - It will be shown on the assets side under current assets to carry forward for settlement in the following month.
How to set off GST paid with GST Collected GST paid → Input GST (IGST/CGST/SGST) GST Collected → Output GST (IGST/CGST/SGST)

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 बैंक समाधान विवरण
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 लेन-देनों का अभिलेखन-2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 तलपट एवं अशुद्धियों का शोधन
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors