RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting
These comprehensive RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 1 Notes Introduction to Accounting
Meaning:
It is an art of recording, classifying and summarising and communicating the economic information for interpreting the Business Transactions.
Objectives:
Objectives of accounting can be classified into following two categories:
(a) Primary Objectives
(1) To Keep Systematic Records: Accounting is done to keep a systematic record of financial transactions. In the absence of accounting, there would have been too much burden on human memory. Businessman cannot remember all the transactions what he might have observed during the daily operations.
(2) To Ascertain Profit or Loss: Accounting helps in ascertaining the net profit earned or loss suffered on account of carrying the business. This information is available from the profit and loss statement. Profit is calculated by deducting expenses from the revenues. Profit is a measure of performance of the business.

(3) To Ascertain the Financial Position of the Business: This objective is served by the Balance Sheet. A Balance Sheet depicts the financial position of a business. The Balance Sheet is a statement of assets and liabilities of the business on a particular date. Balance Sheet serves as a barometer to ascertaining the financial position of the business.
(4) To Provide Information to Users: Businessman needs useful information for making different types of business decisions. The outside users have limited authority or resources to obtain information. They also need useful and timely information regarding the financial position of the business.
(b) Other Objectives
With the help of properly recorded transactions the books of accounts reveal the following:
- Amount of Profit or Loss during the period.
- Financial position as on a particular date.
- Amount owes to others by the business and amount owed by others to the business.
- Details of incomes and gains.
- Details of expenditure and losses.
- Details of assets.
- Details of liabilities.
All the above-mentioned information and details helps the business in making rational judgements and taking rational decisions for the success of business enterprise.
(c) Process of Accounting:
(1) Identify the Transactions & Events: Accounting help to identify the every transaction separately i.e. (financial or non-financial; whether internal or external) as a specific entity.
(2) Measurement of Transactions & Events: Every transaction is measured in common units (i.e. as per currency of concerned country). In India every transaction & events are measured in rupees.
(3) Recording of Business Transactions: The transactions are usually recorded manually. It is important function of accounting. It is concerned with recording of business transaction in a systematic manner. Recording is done in the Book (Journal) all Cash & Credit related transactions are recorded in orderly manner in appropriate books.
(4) Classifying the Business Transactions Classification is concerned with the systematic analysis of recorded data. The work of classification is done in Book (Ledger). It contains different account heads of all transaction of similar nature.
(5) Summarising the Business Transactions: Although business has thousands of transactions in an accounting period so it is necessary to summaries their effect upon financial conditions of the business to condense the information contained in Books of Account in meaningful figures for the guidance of proprietorship of the management through
- Trial Balances,
- Profit & Loss Account
- Balance Sheet.
(6) Interpreting the Business Transactions: The recorded data is interpreted in a manner that users can make meaningful judgement about financial position and profitability of business. This function should basically done by accountant who interprets the statements in meaningful manner for the facilitation of users.
(7) Communicating the Interpreting Information to Users: The data so collected should be communicated to the users through which users enable to take effective decisions.

Accounting as a Source of Information:
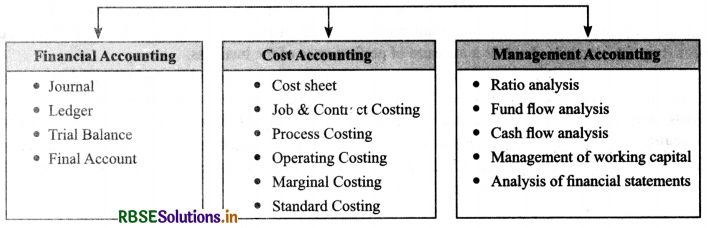
Branches of Accounting, Book-Keeping vs. Accounting Branches of Accounting:
- Financial Accounting The objective of financial accounting is to ascertain the profit or loss of a business concern for a particular period and to find out financial position on a particular data.
- Cost Accounting. The objective of cost accounting is to determine and control the cost of product and services.
- Management Accounting: The objective of management accounting is to provide information to the management for taking appropriate decisions for the efficient management of the concern.
Book-keeping: Book keeping is an art of recording Business dealing in a set of Books. It is a Branch of Knowledge which helps to know how to keep the records of Business transactions in systematic form.
|
Basic |
Book Keeping |
Accounting |
|
1. Meaning |
It is an art of Recording business dealing in set of books in orderly manner. |
It is an art of recording classifying, summarising the in transaction is systematic manner in terms of money & interpreting the results thereof. |
|
2. Level |
It is primary level of accountancy i.e., Starts before accounting. |
It is secondary level of accountancy. It starts where book keeping ends. |
|
3. Scope |
It contains recording, posting & balancing. |
It consists of preparation of final accounts. |
|
4. Working |
It records transaction in significant & orderly manner. |
It helps in classifying, summarising and interpreting the transactions in effective manner. |
|
5. Native |
It is preliminary in nature. |
Data is converted from primary to secondary nature. |
|
6. Error & Rectification |
No error & rectification is required. |
Errors are detected & rectified as well as adjustment and transfers. |
Qualitative Information of Accounting:
- Understandability Main qualitative essential of accounting information in financial statement must be understandable by users. Understandability means decision makers must Interpret accounting information in the same sense as it is prepared & conveyed to them.
- Comparability Comparability means users can be able to compare the financial reports over different time period. To be comparable, accounting reports must belong to a common period and use common unit of measurement and format of reporting for the comparison.
- Reliability: Reliability means the users must be able to depend on the information. Reliability is to be measured by the degree of correspondence between what the information conveys about the transactions or events that have occurred and displayed.
- Relevance: Relevance means information must be available according to time predictions and feedback must be possible.
Users of Accounting Information:
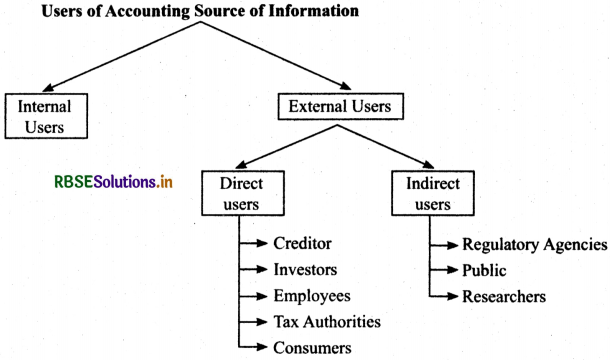
(a) Internal Users
- Proprietor/Owner/Partner(s)/Shareholders The person who invests his money as money’s worth and bears the risk in the business.
- Directors/Board of Directors: These persons compare, analyse the accounting information, make forecast, and compare its financial results with the result of industry.
(b) External users
- Creditors: The users may be short term creditors or long term creditors. They require accounting information to know the solvency of the firm.
- Government: Government make policies, prepare plans and formulate corporate law regarding Taxation, Labour etc. which is based on financial statements.
- Lenders and Bankers Before lending money to the business concern, the lender ascertain the soundness, liquidity and profitability of the concern for the safety of their investment and regular terms.
- Tax Authorities: Tax authorities whether Income tax, Services tax, Value added tax, Wealth tax, they need information the access the tax liability of the organisation.
- Public: Public is also interested in the financial information with the help of which public come to know about profit and non-profit enterprises.
- Researchers- Researchers having indirect interest in accounting information.
- Print and Electronic Media: TV, Magazine, Newspaper Channels related to finance and economic need for publishing and find solution for problem of company so accounting provide information to such channels and newspapers.
Basic Accounting Terms:
- Business Transaction: Event entered into by two parties in financial nature is recorded in the books of accounts. Such events are expressed in monetary terms. It is an agreement between two parties for exchange and transfer of goods and services.
- Account - The record of transaction relate to particular head at one place. It records two aspects i.e. debit and credit and their effect on each account.
- Capital- The amount invested by proprietor or partner in the business. It is liability of business which increases with fiirther investment and decreases when it is withdrawn (known as drawing) or loss is incurred in business. It is also called net worth of business.
- Drawings- It is the amount of cash or goods withdrawn by owner for personal use. It reduces the capital of the owner. It is deducted from capital at the time preparing financial statements.
- L labilities- The amount owned by the business is called liability. It is of two types: internal liability as well as external. Liability toward the owner is internal liability. Liability towards outsiders is external liability.
Liability is Further Classified as:
- Current Liability: It is payable within one year from the date of preparing balance sheet. Example: Bank overdraft, bills payable, creditors etc.
- Non-current Liability: It is payable after 12 months from the date of balance sheet. Example: Loans taken from the bank for a longer period, capital etc.

(6) Assets: Assets are valuable resources owned by business which are measurable in money terms. These are economic resources owned by proprietor for benefit in future.
- Current Assets: These are the assets which are held by the business with the purpose of converting them into cash within one year. For example: goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn profit, prepaid expenses, cash, stock, debtors etc.
- Non-Current Assets: The assets held by business not to resell for earning capacity. These are held for long term point of view. For Example: Long term loan and advances to outsiders, fixed assets.
Fixed Asset Further Classified into
- Tangible Assets: These are the assets which can be touched and seen and has physical existence. Example: Land and feuilding, Machinery etc.
- Intangible Assets: These are the assets which cannot be touched and seen and don’t have physical existence. Example: Goodwill, Trademark, Patents etc.
- Fictitious Assets: Fictitious assets are those which are neither tangible nor intangible. They are losses not written off in the year in which these are incurred. For Example: Deferred Revenue Expenditure, expenditure incurred on training of employees etc.
(7) Receipts: The amount received or receivable on selling goods and providing services. It is of two types:
- Revenue Receipt
- Capital Receipt.
(a) Revenue Receipts: It is the amount received against sale of goods and rendering services. Example. Sale of goods, interest received on fixed deposits, interest received on Investments.
(b) Capital Receipts: It is the amount received which is used by a business for a longer period of time, amount raised for a longer period of time or profit on sale of non-current assets. Example: Capital, long term borrowings etc.
(8) Expenditure. It is the amount spent for acquiring assets goods and services. It is of two types.
- Capital Expenditure: It is an expenditure incurred to acquire assets or improving the existing asset which will increases the earning capacity of the business. Example: Purchase a Computer for carry on business.
- Revenue Expenditure: It is expenditure which is incurred for maintain of capital assets i.e., whose benefit is exhausted or caused within one year. Example: rent, electricity, salary etc.
- Deferred Revenue Expenditure: It is an expenditure which is revenue in nature, but it written off in more than one accounting period. Example: Advertisement expenditure.
(9) Expense: The cost incurred for generating income is called expense. Example: Cash payment for wages, rent, and salary.
(10) Income: Income is the profit earned during a period. Example: Cash Received for Rent, Commission Income = Revenue - Expense
(11) Profit: Any income earned by business from any operating activity is called profit. Difference between cost and sales is called profit. It is of two types.
- Gross Profit: Sales - Revenue/Direct Cost
- Net Profit: Gross Profit -All Indirect Expenses

(12) Gain: Gain is also part of profit which is non-recurring in nature. Example: Gain from sale of fixed asset, long term investments.
(13) Losses: Losses decrease monetary value of owner’s equity i.e. losses incurred from operating activities. It is also non-recurring in nature. Example: Loss on sale of fixed assets.
(14) Purchases: The goods used to purchase for resale or producing the finished products which are also to be sold. It is one cash and credit basis. Goods purchased for cash called are cash purchases and goods purchased on credit basis called credit purchases.
(15) Purchases Return: Goods purchased may be returned to the seller as they are defective or any reason. It is called Purchase Return or Return Outward.
(16) Sales: The goods used for sale for cash and credit basis it is called sales. When goods sold for cash they termed as Cash Sales. When sold on credit called Credit Sales.
(17) Sales Return: When the goods sold when returned by the buyer, it is known as sales return or Return Inward.
(18) Goods: Goods are subject matter and main ingredients in physical terms of trade. This term is used for all sales, purchase, drawing, stock of business enterprise in selling, purchasing, manufacturing the operating activities of business. Example: Stationery, fridge, air conditioner.
(19) Stock/Inventory: It is current and tangible assets of an enterprise for the purpose of sale and earn profit. It is further classified as
- Opening Stock: Stock in hand in Beginning of accounting year.
- Closing Stock: Stock in hand at the end of accounting year.
It is classified under the head Current assets in Balance sheet on Asset side. It is valued at cost price or market price, whichever is lower. It can be valued in three forms:
(a) Stock/Inventory of Finished Goods: It is an inventory remain unsold in case of trading concern and goods manufactured for the purpose of sale is called Stock of Goods.
(b) Stock/Inventory of Raw Material: It is stock of Raw Material used for manufacturing goods. Example: Stock of wheat used for manufacturing bread.
(c) Stock of Work in Progress: It is stock which is partly finished goods. Example: Cost of Labour, Cost of Raw Material used.
All above stock/inventory valued at cost price/market price whichever is lower.

(20) Trade Receivables: These can be classified into two categories:
(a) Debtors: Person who owes amount of an enterprise against credit sales of goods and services is called debtor. It is classified in Balance Sheet under Current Asset.
(b) Bill Receivable: Bill of exchange accepted by debtor against credit sales and amount of which will be received on specific date is called bill receivable. It is classified in balance sheet under the head current assets.
(21) Trade Payables: These are classified into two categories:
(a) Creditors: The person who owes money against credit purchases for goods and services is called creditor. It is classified under the head of Current Liabilities in Balance Sheet.
(b) Bill Payable: Bill of exchange accepted by creditor and amount of which will be payable on specified date. It is classified under the Current Liabilities in Balance Sheet.
(22) Cost: It is an expenditure incurred on specified goods and services.
(23) Vouchers: Vouchers are the written documents prepared by accountants to prove the existence of a business transaction. Example: Debit voucher, credit voucher and transfer voucher.
(24) Discount: Reduction allowed to customers in the prices of goods by the business or amount paid by customers is known as Discount.
- Trade Discount: Trade discount is the concession* allowed by the seller on the basis on sales. The amount is deducted from sales. It is not recorded in books of accounts but are recorded in separate books.
- Cash Discount: Cash Discount is the concession allowed for timely payment of due amount., It is recorded in the books of account of both of parties.
