RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 3 Recording of Transactions-I
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 3 Recording of Transactions-I Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 3 Recording of Transactions-I
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is business transaction?
Answer:
Business transaction an exchange of money or money’s worth for buying of goods or availing or service.
Question 2.
What do you mean by source documents?
Answer:
The documents on the basis of which the transactions are recorded are known as source documents/source voucher.
These documents are the evidence/proof of transactions.

Question 3.
Give two examples of source document.
Answer:
Cash memo, Invoice, Sales bill, Pay-in-slip, Cheque, Salary slip etc.
Question 4.
Given an example of a transaction for which there may not be any evidence.
Answer:
Petty expenses are the examples of such transactions like payment to rickshaw puller.
Question 5.
How do vouchers help in accounting?
Answer:
Vouchers help in recording of all business transactions.
Question 6.
Classify the vouchers.
Answer:
These are two types: Source voucher and accounting voucher.
Question 7.
What is accounting voucher?
Answer:
The document which is usually based on source document and is prepared to record the business transaction in the system of accounting.
Question 8.
State the types of accounting vouchers.
Answer:
Cash voucher and non-cash voucher.

Question 9.
What is cash voucher?
Answer:
The accounting voucher which is prepared to record receipts and payments of cash.
Question 10.
Classify cash voucher.
Answer:
Cash vouchers are: debit voucher and credit voucher.
Question 11.
What is non cash voucher?
Answer:
The voucher which is prepared to all those transactions which do not involve cash or bank movement. Example: credit sales, outstanding expenses, depreciation, bad debts etc.
Question 12.
What is complex voucher?
Answer:
The voucher which is prepared to record multiple debits and multiple credits is known as complex voucher.
Question 13.
What another name is used for complex voucher?
Answer:
Journal voucher.
Question 14.
Give an example of a transaction for which there may not be any evidence.
Answer:
Petty expenses are the examples of such transactions like payment to rickshaw puller.
Question 15.
What is the rule of debit and credit for personal accounts?
Answer:
The account of receiver is debited and the account of giver is credited.
Question 16.
What is the journal?
Answer:
Journal is a book of prime entry in which transactions are copied in order of date from a memorandum or waste book.
Question 17.
What is the full form of G.S.T.?
Answer:
it is Goods and Services Tax.
Question 18.
Classify broadly the types of taxes under the GST.
Answer:
Central GST and State GST.
Question 19.
What is ledger?
Answer:
Meaning of ledger: It contains several accounts debited or credited in the journal and in other special purpose subsidiary books. It is known as principal book of entry.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between source vouchers and accounting vouchers.
Answer:
Source vouchers are also known as source documents meAnswer:the evidence of transaction being took place whereas accounting vouchers are the documents to record the accounting information on the basis of source documents.

Question 2.
Journalise:
1. Charge interest on capital of ₹ 10,00,000 @ 12% p.a. for 8 months.
2. Sunil who owed us ₹ 40,000 becomes insolvent and nothing is received from his estate.
3. Sold good to Brijesh costing ₹ 20,000 at 30% loss, trade discount @ 20% and cash discount @10%.
Answer:
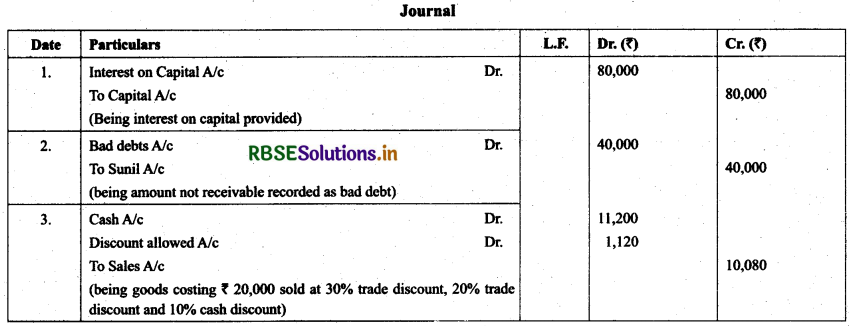
Question 3.
X started business on 1st April 2013 with a capital of ₹ 1,00,000 and a loan of ₹ 50,000 from the bank. During the year, he withdrew ₹ 20,000 and introduced Anther capital of ₹ 30,000. On 31st March 2014, his assets were ₹ 1,75,000. Find out his capital as on 31st March 2014 and profit earned during the year 2013-14.
Solution.
Closing capital = closing assets - closing liabilities (loan)
Closing capital = ₹1,75,000 - ₹ 50,000 = ₹ 1,25,000
Profit or loss = Closing capital + drawings - further Capital introduced - opening capital = ₹ 1,25,000 + ₹ 20,000
₹30,000 - ₹1,00,000 = ₹15,000
Question 4.
(GST transactions): pass journal entries for the following transactions:
(a) Goods costing ₹ 10,000 were given as charity, which were purchased after payment of CGST and SGST @ 6%,each.
(b) Goods costing ₹ 6,000 were used by the proprietor, which were purchased after the payment of CGST and SGST @12% each.
(c) Goods of ₹ 4,000 were destroyed by fire which were purchased after payment of CGST and SGST @ 6 % each.
Solution.
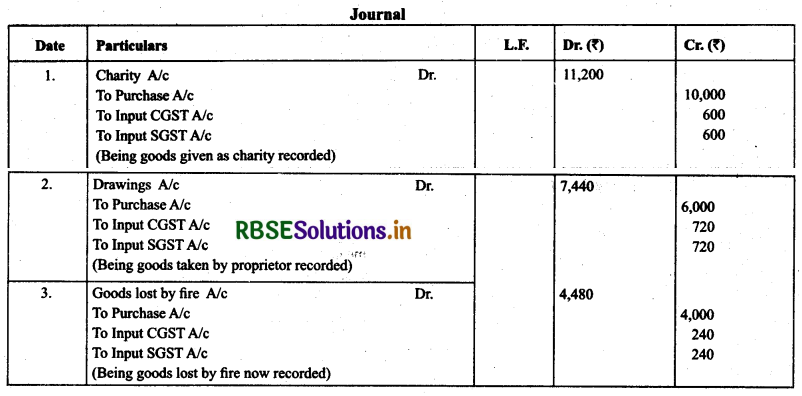

Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
(GST transactions): Journalise the following entries along with setting off entries on GST:
(a) Purchased goods costing ₹ 3,00,000 within state after paying CGST and SGST @ 6 % both.
(b) Sold goods for ₹ 6,00,000, CGST and SGST both levied on them @6%.
(c) Purchased goods for ₹ 4,00,000 from other state, IGST paid was 12 %.
(d) Sold goods for ₹ 2,40,000 to other states, IGST paid was 12 %.
Answer:
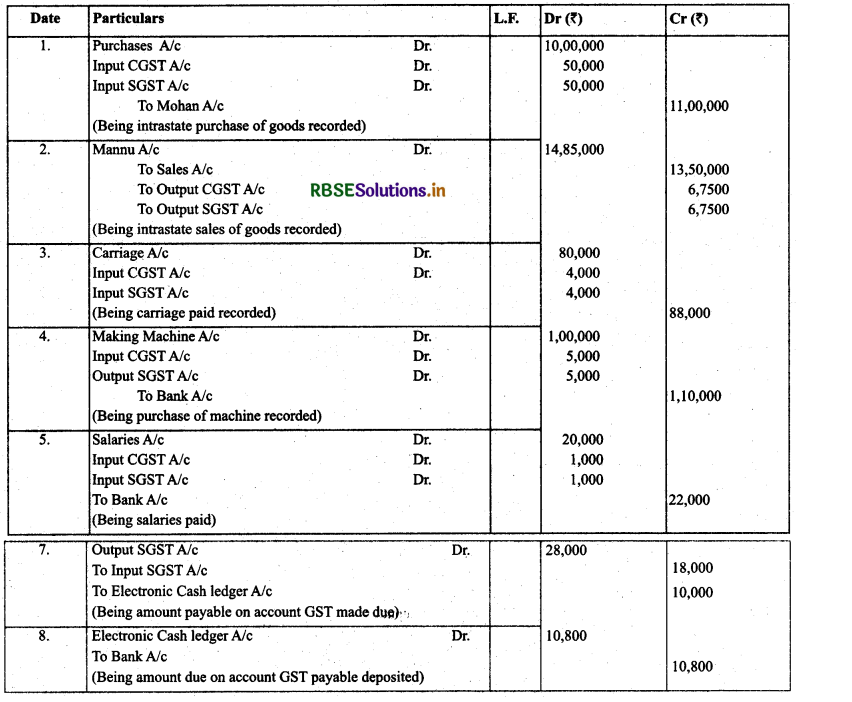
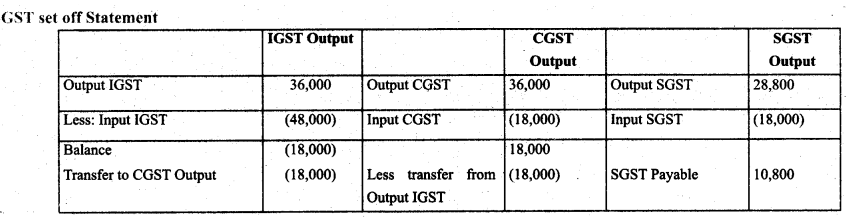
Question 2.
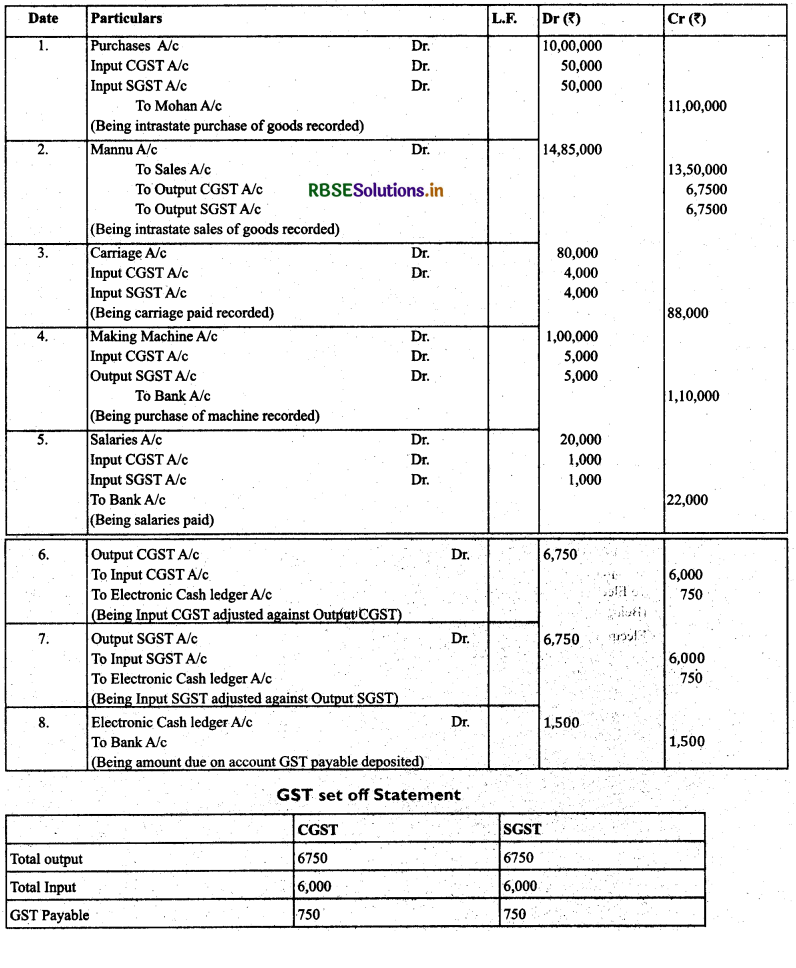
(GST transactions): Record necessary Journal entries assuming COST @ 5% and SGST @ 5% and all transactions are occurred within Delhi)
(1) Mohan bought goods ₹ 10,00,000 on credit
(2) He sold the goods for ₹ 13,50,000 within Delhi on credit to Mannu
(3) He paid for carriage and cartage for ₹ 80,000
(4) He bought making machine for ₹ 1,00,000
(5) Paid salaries for ₹ 20,000 Solution,
Answer:
Higher Order Thinking Skills Questions
Question 1.
How does recording of transaction is done in accountancy?
Answer:
Recording of transactions is done with the help of vouchers.
Question 2.
How the transactions are recorded when there is no evidence of transactions?
Answer:
Recording of transactions done with the help of a voucher which is got approved from a appropriate authority.

Question 3.
what is the base to prepare accounting voucher?
Answer:
Accounting voucher is prepared on the basis of source documents.
Question 4.
Which voucher is prepared to record cash payment?
Answer:
Debit voucher.
Question 5.
Which voucher is prepared to record cash receipt?
Answer:
Credit voucher.
Question 6.
What is another name of non-cash voucher?
Answer:
Transfer voucher.
Question 7.
Name the voucher which contains multiple debits and credits.
Answer:
Complex voucher.
Question 8.
If a firm pays salary to Ram, which account will be debited and why?
Answer:
Salary account will be debited as it is the expense for the firm. Ram being the receiver cannot be debited as he would become debtor and his account can be debited if we have made any credit sales.
Question 9.
Mention the name of document which is given by the seller to the buyer on goods purchased for cash.
Answer:
Cash memo.
Question 10.
in which type of sale is invoice issued by the seller?
Answer:
Credit sale
Question 11.
Narayan purchased goods worth ₹1,00,000 from Shivam on credit basis. Out of these, goods worth ₹ 5,000 were defective and returned to the seller. Which document should Narayan attach with goods returned?
Answer:
Debit note.
Question 12.
what is the difference between J.F. and L.F.?
Answer:
J.F. stands for Journal folio which is written in the account and L.F. stands for ledger account for ledger folio which is written in the journal book.
Question 13.
Monika received a cheque on May 12,2017. Date of the cheque was June 12,2013. Which type of cheque is it?
Answer:
Post-dated cheque.

Question 14.
State the transactions in the following transactions:
(a) Decrease in assets and decrease in capital (withdrawal by owner).
(b) Increase in one liability and decrease in another liability
(c) Increase in capital and decrease in liabilities
(d) Decrease and increase in capital
Answer:
(a) Withdrawal by the owner
(b) Converting creditors into bills payable
(c) Converting loan into capital
(d) Withdrawal and interest charged on withdrawal
Question 15.
On January 1,2013, Ashok started business with capital of ₹ 50,000 and loan of ₹ 20,000 taken from his friend. During 2013, Ashok earned a profit of ₹ 7,000. On December 31, 2013, his assets were ₹ 90,000. Calculate the amount of liabilities.
Solution.
For calculating liabilities at the end of accounting period, closing capital needs to be calculated.
Closing Capital = Opening Capital + Profit = ₹ 50,000+ ₹ 7,000 = ₹ 57,000
Liabilities = Assets - Closing capital
= ₹ 90,000 - ₹ 57,000 = ₹ 33,000
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The origin of a transaction is derived from the ______
(a) Source document
(b) Voucher
(c) Journal
(d) Ledger
Answer:
(a) Source document
Question 2.
Which of the equation is correct?
(a) Capital = Assets + Liabilities
(b) Capital = Assets — Liabilities
(c) Assets Liabilities — Capital
(d) Liabilities = Assets — Capital
Answer:
(b) Capital = Assets — Liabilities

Question 3.
Amount owned by the proprietor is called ______
(a) Assets
(b) Liabilities
(c) Capital
(d) Drawings
Answer:
(c) Capital
Question 4.
Accounting equation is connected with ______
(a) Assets only
(b) Liabilities only
(c) Assets, Liabilities and capital
(d) Assets and liabilities except capital
Answer:
(c) Assets, Liabilities and capital
Question 5.
Entry passed in the beginning of the accounting year is called ______
(a) Original entry
(b) Final entry
(c) Opening entry
(d) Compound entry
Answer:
(c) Opening entry
Question 6.
ledger is the book of_____
(a) original entry
(b) final entry
(c) all cash transactions
(d) all non cash transactions
Answer:
(b) final entry
Question 7.
The column of ledger, which links the entry with journal, is called ______ column.
(a) L.F
(b) 3F
(c) Particulars
(d) amount
Answer:
(b) 3F
Question 8.
Journalisam book of ______
(a) original entry
(b) final entry
(c) all cash transactions
(d) all non cash transactions
Answer:
(a) original entry
Question 9.
Cash discount is allowed when ______
(a) there is cash sales/purchases
(b) when there is credit sales/purchase
(c) when the payment due is made before the due date
(d) when the payment is made on the due date.
Answer:
(c) when the payment due is made before the due date

Question 10.
Which of the following can have either credit balance or debit balance?
(a) Cash account
(b) bank account
(c) capital
(d) purchases
Answer:
(b) bank account
II. State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. If creditors accept bill of exchange, the value of creditors reduces.
2. Outstanding expenses are deducted from the capital.
3. Prepaid expenses affect the assets side only.
4. The seller on the return of goods prepares credit note.
5. Transfer vouchers are prepared for cash transactions.
6. Cheque in hand is opened when a cheque is received which is later deposited.
7. Trade discount is recorded in the special purpose subsidiary books.
8. When bad debts are recovered, debtor’s account is credited.
9. Contra entries are those entries in which except cash or bank is debited or credited.
10. The book where the accounting transactions are recorded in chronological order for the first time is called journal book.
Answers:
1. True
2. False
3. True
4. True
5. False
6. True
7. True
8. False
9. False
10. True

III. Fill in the blanks with correct answer.
1. ................. is a written document in support of a transaction.
2. Every business transaction has ................. aspects.
3. Traditional approach of accounting is also called ................. approach.
4. Modem approach of accounting is also called ................. approach.
5. Interpersonal accounts are classified into ................. types.
6. Bank overdraft is an example of ................. account.
7. Outstanding expenses are expense of ................. account.
8. Source documents give the information about the nature of .................
9. Accounting equation ................. assets and liabilities.
10. Assets are always equal to liabilities plus .................
11. A transaction which increases the capital is called.................
12. Journal is a book of .................
13. Ledger is the ................. book of accounts.
14. Recording of transactions in the journal is called .................
15. The process of transfer of entries from journal to ledger is called .................
16. ................. column represents the place of posting of an entry in the ledger.
17. .................account is the account which represent amount not recovered from the customers.
18. ................ c/d means ................. and b/d means .................
19. Debit balance arises on the ................. side of the account.
20. L.F. column in the journal is filled at the time of .................
Answers:
1. voucher
2. Two
3. British
4. American
5. Two
6. Personal
7. Representative personal
8. Transactions
9. Equates
10. Capital
11. Income/gain
12. Original entry
13. Principal
14. Journalizing
15. posting
16. Ledger folio
17. Bad debt
18. carried down/brought down
19. Credit
20. Posting

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 बैंक समाधान विवरण
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 लेन-देनों का अभिलेखन-2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 तलपट एवं अशुद्धियों का शोधन
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors