RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through manav janan class 12 in hindi that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 14 Ecosystem
RBSE Class 12 Biology Ecosystem Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks.
(a) Plants are called as ........................... because they fix carbon dioxide.
Answer:
Autotrophs
(b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is ........................... type.
Answer:
Spindle
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is ...........................
Answer:
Sunlight
(d) Common detritivores in our ecosystem are ...........................
Answer:
Earthworm, bacteria and fungi of decay and vulture
(e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is ...........................
Answer:
Oceans

Question 2.
Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers
(d) Decomposers
Answer:
(d) Decomposers
Question 3.
The second trophic level in a lake is -
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Benthos
(d) Fishes
Answer:
(b) Zooplankton
Question 4.
Secondary producers are
(a) Herbivores
(b) Producers
(c) Carnivores
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 5.
What is,the percentage of photo synthetically act., radiation (PAR), in the incident solar radiation?
(a) 100%
(b) 50 %
(c) 1 - 5%
(d) 2 - 10%
Answer:
(b) 50 %
Question 6.
Distinguish between
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) Upright and inverted pyramid
(d) Food chain and Food web
(e) Litter and detritus
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
Answer:
The differences are as follows:
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
|
Grazing food chain |
Detritus food chain |
|
1. Energy is derived from the sun. |
1. Energy is derived from organic matter produced in trophic levels of the grazing food chain. |
|
2. It typically entails a large population. |
2. It is comparatively smaller. |
|
3. Starts with producers at the first trophic level. The plant biomass is then consumed by herbivores which is inturn are consumed by different carnivores. |
3. Starts with detritus such as dead bodies of fallen leaves and animals that are consumed by detritivores or decomposers which inturn are consumed by predators. |
(b) Production and decomposition
|
Production |
Decomposition |
|
1. Rate of producing food(organic matter) by producers is known as production. |
1. Disintegration of complex organic matter from the bodies of dead animals and plants with the help of decomposers into organic raw material namely water, carbon dioxide, other such nutrients is decomposition. |
|
2. For primary production, sunlight is required. |
2. Decomposition does not require sunlight. |
|
3. Dependent on the photosynthetic capacity of producers. |
3. Takes places with the help of decomposers. |
(c) Upright and inverted pyramid
|
Upright pyramid |
Inverted pyramid |
|
1. Pyramid of energy is always upright. |
1. Pyramid of numbers and biomass can be inverted. |
|
2. At the producer level of an ecosystem, this pyramid has the highest number and biomass of organisms which declines at each trophic level in a food chain. |
2. At the producer level of an ecosystem, this pyramid has the lowest number and biomass of organisms which rises at each increasing tropic level in a food chain. |
(d) Food chain and Food web
|
Food chain |
Food web |
|
1. Constitutes for a single linear sequence of entities. |
1. Consists of a number of interconnected food chains. |
|
2. Members inhabiting higher trophic levels feed only on one type of entity. |
2. Any given individual has alternate options for food sources. |
(e) Litter and detritus
|
Litter |
Detritus |
|
1. Comprises of all kinds of wastes above the ground level. |
1. Comprises of residues of dead animals and plants. |
|
2. Consists of biodegradable and non - biodegradable substances. |
2. Consists of biodegradable substances only. |
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
|
Primary productivity |
Secondary productivity |
|
It is the amount of organic matter generated |
It is the rate of generating organic matter by consumers over a span of time. |
Question 7.
Describe the components of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Ecosystem is an interacting unit involving both living components and the non - living components of a region. Both of these components interact with each other functioning as a unit which is apparent in the processes of energy flow, nutrient cycling, productivity, decomposition in ecosystems such as grasslands, forest, ponds etc.
Ecosystems have two components, they are:
1. Abiotic components: These constitute the non - living components of an ecosystem such as temperature, light, water, wind, soil, chemical nutrients etc.
2. Biotic components:
They form the living component of an ecosystem which include biotic factors such as decomposer, consumers, and producers. Plants and some algae form the producers as they contain chlorophyll to synthesize their own food through the process of photosynthesis carried out in the presence of light, hence they are also referred to as transducers or converters. The consumers or heterotrophs are dependent on producers either directly (primary consumers) or indirectly (secondary consumers) while decomposers are constituted by the microbes in the ecosystem, such as fungi and bacteria. They form the largest population in the food chain as they derive their nutrition by disintegrating the residues of dead animals and plants.

Question 8.
Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Answer:
An ecological pyramid can be defined as a graphical representation of different ecological parameters, namely the number of individuals found at each trophic level, the energy quantity or the biomass found in each trophic level. These pyramids depict the producers at the base whereas the apex depicts the top level consumers found in the ecosystem.
Pyramids are of three types:
1. Pyramid of numbers:
It gives the graphical representation of the number of individuals found at each trophic level in a food chain of an ecosystem. This pyramid can be inverted or upright depending on the crowd of producers. Example: In a Grassland ecosystem, this pyramid is upright where in the food chain, the number of producers is followed by the number of herbivores, which in turn is followed by number of secondary and tertiary consumers. Therefore, the number of individuals at the level of producers will be maximum, whereas the number of individuals at the top carnivores will be the least. The pyramid of numbers in a parasitic food chain is inverted, where in the food chain, producers provide food to fruit eating birds which in response support few species of insects.
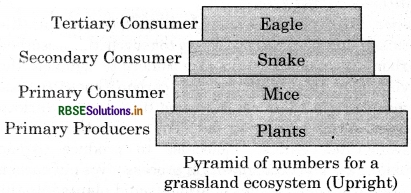
2. Pyramid of biomass:
It is a graphical representation of the total quantity of living matter found at each trophic level of an ecosystem and can either be inverted or upright. In grasslands and forest ecosystems it is upright as the quantity of biomass at the producer level is higher than at the carnivore level, at the top. This pyramid is inverted in a pond ecosystem as the biomass of fishes far surpass the biomass of zooplankton on which they feed.
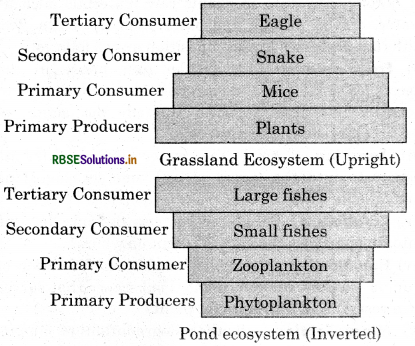
3. Pyramid of energy:
Energy pyramid is a graphical representation indicating flow of energy at each trophic level in an ecosystem. Pyramid of energy is always upright. It cannot be inverted, because when energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step. In the energy pyramid, each bar shows the amount of energy present at each trophic level in a given time or annually per unit area.
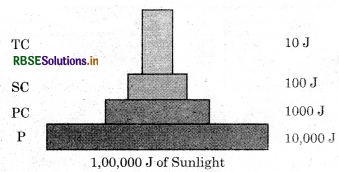
An ideal pyramid of energy. Observe that primary producers convert only 1% of the energy in the sunlight available to them into NPP
Question 9.
What is primary productivity? Give brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Answer:
Primary productivity can he defined as the amount of organic matter or biomass that is generated by producers per unit area over a span of time. It can be affected by factors such as rain, temperature, water, light etc. Primary productivity also depends on the availability of nutrients and that of plants to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
Question 10.
Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
Answer:
Decomposition can be defined as a process that involves the disintegration of complex organic matter from the body of dead animals and plants with the action of decomposers into inorganic raw materials such as water, carbon dioxide and other such nutrients. The different processes in decomposition are as follows:
- Fragmentation: It is the first phase in the decomposition process, it includes the disintegration of detritus into fine particles through the action of detritivores such as earthworms.
- Leaching: here, the water - soluble nutrients penetrate into the layers of soil and get sealed as unavailable salts
- Catabolism: Fungi and bacteria degrade detritus into fine particles through different enzymes
- Humification: this phase causes the formation of humus - a dark colored colloidal substance that serves as a reservoir of nutrients for plants
- Mineralization: further degradation of humus through the activity of microbes takes place in this stage wherein inorganic nutrients are finally released into the soil. This phenomena of releasing inorganic nutrients from the humus is known as mineralization. Humus degrades to release inorganic raw materials such as water, carbon dioxide, and other nutrients in the soil.
Question 11.
Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
Answer:
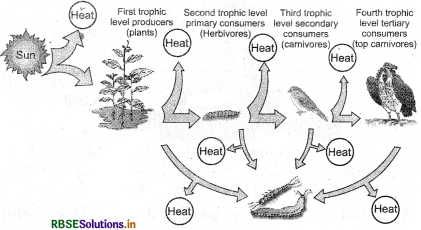
In an ecosystem, energy enters from the ultimate source of energy - the Sun. These solar rays pass through the atmosphere to be absorbed by the surface of the earth, which help plants in performing photosynthesis. Additionally, they also help in maintaining the temperature of the earth so that living entities survive. Some of these incident rays are reflected by the surface of the earth and only close to 2 - 10% of the solar energy is captured by the producers (green plants) during the photosynthesis process in order to convert it into food.
Gross primary productivity is the rate at which the biomass is generated by plants during the process of photosynthesis. Just 10% of the stored energy is transferred to herbivores from the producers when plants are consumed by herbivores. The rest of 9094 of the energy is used for different processes by plants such as growth, respiration and reproduction. Likewise, a mere 10% of the energy of herbivores is conveyed to carnivores. This is referred to as the ten percent law of energy flow.
Question 12.
Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Sedimentary cycles have reservoirs in the crust of earth or rocks. Nutrient elements such as phosphorus, sulphur, potassium and calcium are present in the sediments of the earth. These sedimentary cycles are unhurried, and slow. It takes a long time to complete their circulation and are deemed to be less perfect cycles. It is because when recycling, the nutrient elements may get sealed in the reservoir pool taking a long time to come out and continue circulation. Hence, they typically go out of circulation for a long period of time.
Question 13.
Outline salient features of carbon cycling in an ecosystem.
Answer:
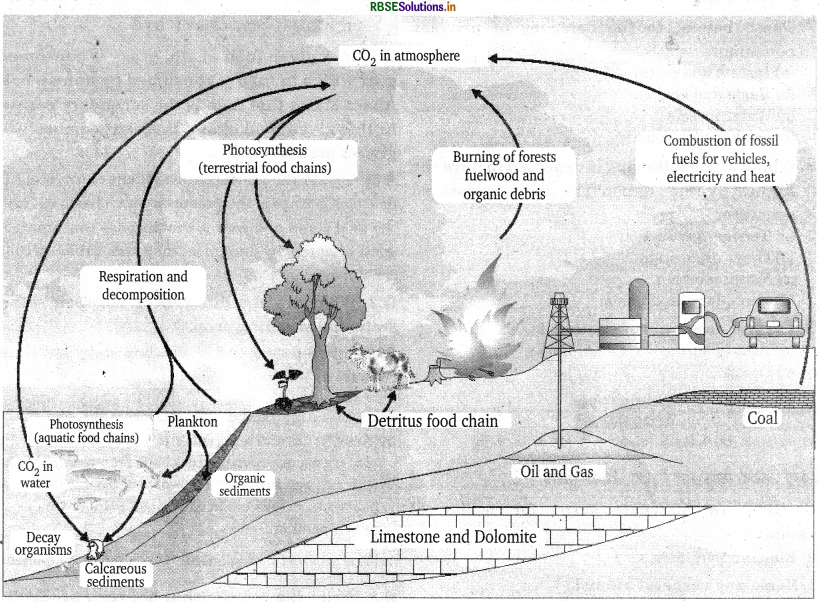
The carbon cycle is an essential gaseous cycle which has its reservoir pool in the atmosphere. All of the living entities consist of carbon as a major constituent of the body. This carbon is a basic element present in all the living forms. Biomolecules such as lipids, carbohydrates, proteins etc that are crucial for - life processes are made of carbon. Living forms are incorporated with carbon through the basic process of photosynthesis that is carried out by plants, the primary producers. The process of photosynthesis uses up atmospheric carbon dioxide and sunlight to produce a carbon compound known as ‘glucose’, this in turn is used by other living entities.
Hence, atmospheric carbon gets incorporated into life forms. It now becomes necessary to recycle this absorbed carbon dioxide back to the atmosphere to complete the cycle. For this recycling of carbon back to the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide gas, various processes can be carried out. The respiration process disintegrates glucose molecules to produce carbon dioxide gas. The decomposition process gives out carbon dioxide from dead bodies of animals and plants into the atmosphere. Some other sources of carbon dioxide are industrialization, combustion of fuels, deforestation, forest fires, volcanic eruptions and so on.

- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 16 पर्यावरण के मुद्दे
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 15 जैव-विविधता एवं संरक्षण
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 14 पारितंत्र
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 13 जीव और समष्टियाँ
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 12 जैव प्रौद्योगिकी एवं उसके उपयोग
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 11 जैव प्रौद्योगिकी-सिद्धांत व प्रक्रम
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 10 मानव कल्याण में सूक्ष्मजीव
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 9 खाद्य उत्पादन में वृद्धि की कार्यनीति
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 8 मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 7 विकास
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 6 वंशागति के आणविक आधार