RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations
RBSE Class 12 Biology Organisms and Populations Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How is diapause different from hibernation?
Answer:
Difference between Dipause and Hibernation:
|
Dipause |
Hibernation |
|
1. Under unfavourable conditions, many species in lakes and ponds are known to enter a stage of suspended development called diapause. |
1. Under unfavourable conditions, the animals that fail to migrate avoid the stress by escaping in time and showing winter sleep is called hibernation. |
|
2. It occurs both in summer and winter. |
2. It occurs usually in winters. |
|
3. Example, Zooplanktons undergo diapause in lakes and ponds under unfavourable conditions. |
3. Example, beer goes into hibernation during winter. |

Question 2.
If a marine fish is placed in a fresh water aquarium, will the fish be able to survive? Why or why not?
Answer:
If a marine fish is placed in a fresh water aquarium, will not be able to survive because:
- Water will enter the body of fish through endosmosis.
- It does not have mechanism of salt absorption as in fresh water fishes.
- Its drinking water habit will cause excess of water to enter the body. So the marine fish will fail to maintain the osmolarity and hence will die.
Question 3.
Most living organisms cannot survive at temperature above 45°C. How are some microbes able to live in habitats with temperature exceeding 100°C?
Answer:
Tolerance power to the extremes of temperature varies from species to species e.g., certain bacteria and cyanobacteria have thermal resistant enzymes and peculiar cell wall (having branched chain lipids).
Question 4.
List the attributes that populations possess but not individuals.
Answer:
The attributes that populations possess but not individuals are:
- Population density.
- Population growth.
- Natality or birth rate.
- Mortality or death rate.
- Sex ratio.
- Age distribution.
Question 5.
If a population growing exponentially double in size in 3 years, what is the intrinsic rate of increase (r) of the population?
Answer:
t=\(\frac{\log ^{2} N}{\dot{r}}\)
or
r= \(\frac{\log ^{2} N}{t}=\frac{0.7931}{3}\)
= 0.2643
In trinsic rate of increase = 0.2643 x 100 = 26.43%
Question 6.
Name important/ defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory.
Answer:
Defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory:
1. Morphological traits:
- Thorns, spines.
- Sticky glandular hairs.
- Resemblance to dread animals (mimicry).
- Harbouring ants.
- Latex.
2. Chemical defence:
- Poisonous cardiac glycosides.
- Offensive smell
- Tannins
- Bitter taste
- Alkaloids.
Question 7.
An Orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and the mango tree?
Answer:
The interaction between an ‘orchid and the mango tree is commensalism, because orchid is benefited by getting shelter from mango tree whereas the mango tree is neither harmed nor benefited.
Question 8.
What is the ecological principle behind the biological control method of managing with past insects?
Answer:
The ecological principle operating in the biological control method of managing with pest insect is through their natural enemies, i.e., predators and parasites.

Question 9.
Distinguish between the following:
(a) Hibernation and Aestivation.
(b) Ectotherms and Endotherms.
Answer:
(a) Difference between Hibernation and Aestivation
|
Hibernation |
Aestivation |
|
1. It is the condition of passing winter in a resting or dorment condition. |
1. It is the condition of inactivity during hot dry summer. |
|
2. It losts usually for the whole winter season. |
2. It lasts usually for hot dry day time because nights are often colder. |
|
3. Animals rest in warm place. |
3. Animals rest in a cool and shady place. |
|
4. It is also called winter sleep. |
4. It is also called summer sleep. |
(b) Difference between Ectotherms and Endotherms
|
Ectotherms |
Endotherms |
|
1. They are cold – blooded animals. |
1. They area warm – blooded animals. |
|
2. They exhibit both hibernation and aestivation. |
2. Their activities are uncommon. |
|
3. They are less active animals. |
3. They are more active animals. |
|
4. They are unable to regulate their body temperature which change with temperature of environment. |
4. They can regulate their body temperature. |
Question 10.
Write a short note on:
(a) Adaptation of desert plants and animals.
(b) Adaptation of plants to water scarcity.
(c) Behavioral adaptation in animals.
(d) Importance of light plants.
(e) Effect of temperature or water scarcity and adaptations of animals.
Answer:
(a) Adaptations of desert plants are as follows:
- Desert plants have thick cuticle to minimise water loss.
- In some desert plants, leaves are modified into spines to minimise loss of water.
- These plants have long root and adaptations to reduce transpiration.
Adaptations of desert animals are as follows:
- Desert animals have concentrated their urine for minimum loss of water, e.g., Kangaroo rat.
- They absorb heat from the sun, when the body temperature drops below the comfort zone.
- They live in burrows during hot day time and have little water requirement.
(b) Adaptations of Plants to Water Scarcity:
- Some desert plant adopt special photosynthetic pathway (CAM) to minimise the loss of water.
- Some plants have sunken stomata to minimise loss of water.
- They have thick cuticle on the leaves and stems to minimise transpiration.
- Roots are deep seated.
- Some plant bear linear leaves to reduce transpiration.
(c) Behavioral adaptation in animals:
- Some animals are capable to burrowing into the soil to hide and escape from ground heat.
- Hibernation and aestivation is quite common in ectothermal animals.
- Desert lizards bask in the sun and absorb heat when their body temperature drops below the comfort zone, but move into shade when ambient temperature starts increasing.
(d) Importance of light to plants:
- For manufacturing food by photosynthesis.
- Light determinates flowering and fruiting.
- Essential for growth and development.
(e) Effect of temperature or water scarcity and the adaptation of animals:
- Animals living in arid areas reduce water loss to minimum.
- The requirement of water is often compensated by food and metabolic water. Water loss is prevented by burrowing into the soil to hide and escape from the above ground heat.
- Concentration of urine to minimise water loss.
- Animals protect themselves from excessive cold by deposition of fat, fur etc.
Questin 11.
List the various abiotic environmental factors.
Answer:
- Atmospheric Factors: Light, temperature, wind and water.
- Hydrosphere: Pond, river, lake and ocean.
- Lithosphere: Rock, soil.
- Edaphic Factors: Soil texture, soil water, soil air, soil pH.
- Topographic Factors: Slope, altitude, latitude, valley.
Question 12.
Give an example for:
(a) An endothermal animal.
(b) An ectothermal animal.
(c) An organism of banthic zone.
Answer:
(a) Goat
(b) Lizard
(c) Angler fish.

Question 13.
Define population and community.
Answer:
Population: It is a group of individuals of same species, which can reproduce among themselves and occupy a particular area in given time.
Community: It is an assemblage of several populations in a particular area and time and exhibit interaction and interdependence through trophic relationships.
Question 14.
Define the following terms and give one example for each:
(a) Commensalism
(b) Parasitism
(c) Camouflag
(d) Mutualism
(e) Interspecific Competition.
Answer:
(a) Comhiensalism: It is a relationship between two different species where one is benefited and other remains unaffected. Example : Clown fish and sea anemone. Here the clown fish gets protection from predators which stay away from stinging tentacles of anemone but anemone does not derive any benefit from fish.
(b) Parasitism: It is an interaction between two organism in which one is benefited and the other is harmed, e.g., Cuscuta plant absorbs food from host plant.
(c) Camouflage: It is a phenomenon of blending of an organism with the surrounding due to similar colour, marking and shape so as to avoid the predators, e.g., leaf - like insect such as grasshopper.
(d) Mutualism: It is the interaction between two species in which both organisms are benifited. e.g., Lichen, the combination of algae and fungi.
(e) Interspecific competition: It is the competition among. the members of different species for limited natural resources.
Example: Tiger and Leopard, both are required same food and compete each other.
Question 15.
With the help of suitable diagram describe the logistic population growth curve.
Answer:
Logistic Growth:
- The resources become limited at certain point of time, so no population can grow exponentially.
- This growth model is more realistic.
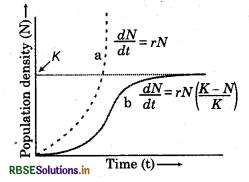
- Every ecosystem or habitat has limited resources to support a particular maximum number of individuals called its carrying capacity.
- When N is ploted in relation to time t, the logietic growth show sigmoid curve and is also called Verhulst - Pearl logistic growth.
It is given by following equation:
\(\frac{d N}{d t}=r N\left(\frac{k-N}{k}\right)\)
where N = Population density at time t
r = interinsic rate of natural increase
k = carrying capacity.
Question 16.
Select the statement which explains best parasitism:
(a) One organism is benefited
(b) Both the organisms benefited
(c) One organisms is benefited, other is not affected
(d) One organism is benefited, other is affected.
Answer:
(d) One organism is benefited, other is affected.
Question 17.
List any three important characteristics of a population and explain.
Answer:
1. Population density: Population density of a species is the number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume.
PD = \(\frac{N}{S}\)
where PD = Population density
N = Number of individuals in an area
S = Number of unit area in a region
2. Birth Rate: It is expressed as the number pf birth per 1000 individuals of a population per year.
3. Death Rate: It expressed as the number ofideaths per 1000 individuals of a population per year.
