RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through manav janan class 12 in hindi that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 15 Important Question Biodiversity and Conservation
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
One of the ex situ conservation methods for endangered species is
(a) Wild life sanctuaries
(b) Biosphere reserves
(c) Cryopreservation
(d) National parks
Answer:
(c) Cryopreservation

Question 2.
Which of the following is not done in a wild life sanctuary?
(a) Fauna is conserved
(b) Flora is conserved
(c) Soil and flora is utilised
(d) Hunting is prohibited
Answer:
(c) Soil and flora is utilised
Question 3.
First National park developed in India is
(a) Gir
(b) Kaziranga
(c) Jijn Corbett
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Jijn Corbett
Question 4.
Which one of the following pairs of geographical areas show maximum biodiversity in our country?
(a) Sunderbans and Rann of Kutch
(b) Eastern Ghats and West Bengal
(c) Eastern Himalayas and Western Ghats
(d) Kerala and Punjab
Answer:
(c) Eastern Himalayas and Western Ghats
Question 5.
Genetic biodiversity in agricultural crops in threatened by
(a) introduction of high yielding varieties
(b) intensine use of fertilizers
(c) extensive intercropping
(d) intensive use of biopesticides
Answer:
(a) introduction of high yielding varieties
Question 6.
In your opinion, which is the most effective way to conserve the plant diversity of an area?
(a) By creating Biosphere reserve
(b) By creating Botanical gardens
(c) By developing seed banks
(d) By tissue culture method
Answer:
(a) By creating Biosphere reserve
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by heterogeneity?
Answer:
Immense diversity.

Question 2.
Where are the largest Amazonian main forests found?
Answer:
South America.
Question 3.
More than 70 percent of all the species recorded on earth are.
Answer:
Animals.
Question 4.
22 percent of the total species on earth comprise of.
Answer:
Plants.
Question 5.
Name one country located near the equator which has nearly 1,400 species of birds.
Answer:
Colombia.
Question 6.
The graph between species - area relationships is
Answer:
Hyperbola.
Question 7.
Who found that plots with more species showed less year to year variation in total biomass?
Answer:
Tilman.
Question 8.
More than 25 percent of the drugs currently sold in the market worldwide are derived from
Answer:
Plants.
Question 9.
In which year was the historic Convention of Biological Diversity held?
Answer:
1992
Question 10.
Where was the World Summit on Sustainable Development held in 2002?
Answer:
Johennesburg.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
What are biological hotspot? Name the main hotspots in India.
Answer:
Biological hotspot is an area where the species richness is great. The species diversity of that region is very much. Many species of plants and animals are endemic to such area owning to such a great biological diversity these areas are called biological hotspots. The main hotspots of India are:
- The Western Ghats
- The Himalayas
- Indo - Burma Region
- Sundaland

Question 2.
What is biodiversity?
Answer:
Biodiversity is defined as the presence of different types of genes, gene pools, species, habitats and ecosystem in a given area at a given point of time. The term biodiversity was given by a sociobiologist Edward Wilson to describe the combined diversity at all levels of biological organisation. There are mainly three types of biodiversity:
- Genetic diversity
- Species diversity
- Ecological diversity
Question 3.
List any four techniques where the principle of ex situ conservation of biodiversity has been employed.
Answer:
There are four techniques where the principle of ex situ conservation of biodiversity has been employed are:
- Tissue culture
- Cryopreservation
- Botanical gardens
- Zoological parks.
Short Answer Type Questions - II
Question 1.
Give four causes of loss in biodiversity. Explain the adverse effects on native species on invasion of Alien species in a habitat.
Answer:
There are mainly four causes of biodiversity loss. These are as follows:
1. Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: The main cause of extinction of species is the destruction of their habitat. The degradation of habitats by any reason like due to pollution. Some species need larger habitat to survive but due to any reason or human interferance these large habitats are broken into smaller habitats.
2. Over exploitation: Over exploitation is the excessive use of any natural resource by human beings because of its greedy needs results into the extinction of many aperies.
3. Alien (Exotic) species invasions: When some exotic or Alien species introduces into an entirely new areas unintentionally or deliberately some becomes invasive and cause harmful impact or extinction of the native or indigenous species. For example, Nile perch (Predator fish).
4. Co - extinctious: When a species becomes extinct the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory manner also becomes extinct.
The adverse effects on native species on invasion of Alien species in a habitat: When some exotic or alien species introduces into an entirely new area unintentionally or deliberately sometimes it becomes invasive and started causing harmful impact or extinction df the native or indigenous species. For example,
- Nile Perch: It is a large predator fish when introduced in lake victoria it causes the extinction of an ecologically endemic species of cichlid fish in the lake.
- Invasive weeds species like Parthenium (Carrot grass), Lantana and Eichhornia (water hyacinth) caused environmental damage and pose threat to native species on the area.

Question 2.
Why are sacred groves highly protected?
Answer:
Sacred groves basically the forest areas in particular which are set aside by the government in order to protect the biodiversity with special religious importance in a particular culture. These are also mythologically important. These are undisputed and undisturbed forests without any human interventions because these are highly protected hence they includ many rare, endangered and endemic species of that area.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How is conservation of biodiversity done? How will we conserve an animal to save it from extinction.
Answer:
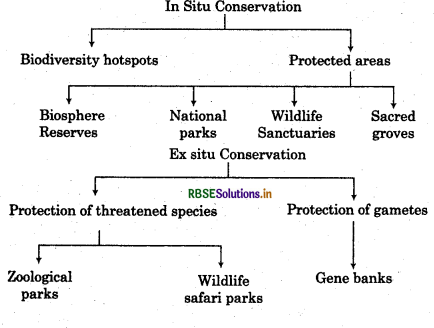
Conservation of biodiversity is the need of the hour. There are various reasons for conservation of biodiversity. There are two basic approaches of biodiversity conservation:
- In situ conservation (on site conservation)
- Ex situ conservation (off site conservation)
In situ conservation: In situ means on site. It involves the protection of any species in its natural habitat. In this conservation stratagy we protects the animal in its original environmental ecololgy.
It can be done in following areas:
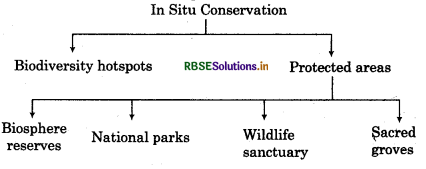
Boidiversity Hotspots: These are the specific areas with highest levels of species richness and high degree of endemism (which means that an endemic species does not found at any other place). Hotspots covers less than 2% of earth’s land area. There are 34 biodiversity hotspots in the world and in India there are 4 hotspots which are as follows:
- Wester Ghats
- Sri Lanka
- Sund Land
- Himalaya
Protected Areas: These are ecologically unique and biodiversitywise rich areas. These are called so because these are legally protected by their respective countries. Accordingly these are called:
- Biosphere reserves
- National Parks
- Sanctuaries
India has 14 biosphere reserves, 90 national parks and 448 wildlife sanctuaries.
Sacred Groves: These are basically the forest areas in particular which are set aside by the governments in order to protect the biodiversity. These many be religious and cultural places which are protected. For example,
Western ghat regions of kamataka and Maharasthtra. Khasi and Jaintia hills in Meghalaya.
Aravalli hills of Rajasthan.
Sarguja, Chanda and Bastar areas of Madhya Pradesh.
Ex Situ Conservation: In this conservation strategy threatened animals and plants are taken out from their natural habitats and they are placed in special care units for their protection and survival.
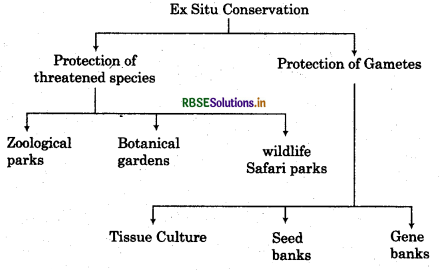
Cryopreservation: Cryopreservation means to preserve sperms, eggs, animal cells, tissue, seeds of different genetic strains and embryo at minus -190°C for longer times in viable and fertile conditions in gene banks, seed banks etc.
In Vitro Propagation: This method is used for plants propagation by using tissue culture techniques. In order to conserve an animal to save it from extinction a 3 way conservation strategy will be adopted.

- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 16 पर्यावरण के मुद्दे
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 15 जैव-विविधता एवं संरक्षण
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 14 पारितंत्र
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 13 जीव और समष्टियाँ
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 12 जैव प्रौद्योगिकी एवं उसके उपयोग
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 11 जैव प्रौद्योगिकी-सिद्धांत व प्रक्रम
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 10 मानव कल्याण में सूक्ष्मजीव
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 9 खाद्य उत्पादन में वृद्धि की कार्यनीति
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 8 मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 7 विकास
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 6 वंशागति के आणविक आधार