RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 14 Ecosystem
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 14 Ecosystem Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Important Question Ecosystem
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Given below is one of the types of ecological pyramids. This type represents
(a) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland
(b) Pyramid of biomass in a follow land
(c) Pyramid of biomass in a lake
(d) Energy pyramid in a spring
Answer:
(c) Pyramid of biomass in a lake

Question 2.
Energy transferred from one trophic level to another
(a) 5%
(b) 10%
(c) 15%
(d) 20%
Answer:
(b) 10%
Question 3.
Maximuni absorption of rainfall water is done by
(a) Tropical deciduous forest
(b) Tropical evergreen forest
(c) Tropical savannah
(d) Scrule forest
Answer:
(b) Tropical evergreen forest
Question 4.
Which of the following is called as a detrivore?
(a) An animal feeding on decaying organic matter
(b) An animal feeding on a plant
(c) A plant feeding on an animal
(d) An animal feeding on another animal
Answer:
(a) An animal feeding on decaying organic matter
Question 5.
The pyramid of energy is always upright for any ecosystem. This situation indicates the fact that:
(a) producers have the lowest energy conversion efficiency
(b) carnivores have a better energy conversion efficiency
(c) energy, conversion efficiency is the same in all trophic levels
(d) herbivores have a better energy conversion efficiency than carnivores.
Answer:
(d) herbivores have a better energy conversion efficiency than carnivores.
Question 6.
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
(a) Tundra - permafrost
(b) Savanna - Acacia trees
(c) Praire - epiphytes
(d) Coniferous forest - evergreen trees
Answer:
(c) Praire - epiphytes
Question 7.
These belong to the category of primary consumers
(a) Insects and cattle
(b) Eagle and snakes
(c) Water insects
(d) Snakes and frogs
Answer:
(a) Insects and cattle
Question 8.
Which of the following is expected to have the highest value (gm/m2/yr) in a grassland ecosystem?
(a) Tertiary production
(b) Gross production
(c) Net production
(d) Secondary production
Answer:
(b) Gross production
Question 9.
Largest reservoir of sulphur is
(a) Atmosphere
(b) Rocks
(c) Ocean
(d) Lake
Answer:
(b) Rocks
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give an alternate term for ecological pyramids.
Answer:
Eltonian pyramids.

Question 2.
Name any vesperal animal.
Answer:
Rabbit.
Question 3.
How deep in sea, producers are present?
Answer:
Upto 200 m.
Question 4.
Name any one Eutrophic lake.
Answer:
Dal lake in Kashmir.
Question 5.
Name any denitrifying bacteria.
Answer:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Question 6.
For how long the entire CO2 of the air can last with its use in photosynthesis by green plants?
Answer:
1 year.
Question 7.
Name the dark coloured amorphorus substance accumulated as a result of humification.
Answer:
Humus.
Question 8.
What is unit of energy measurement for energy pyramids?
Answer:
Kcalm yr.
Question 9.
Which is the most stable ecosystem?
Answer:
Oceans.
Question 10.
In a food chain, the maximum population is of which organisms?
Answer:
Producers.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
In a given food chain, grass is consumed by goat which in turn is consumed by human beings. Anant states that man is the secondary consumer in this given food chain. Is Anant correct? If yes, give explanation.
Answer:
Yes, in the given context Anant is correct. In this food chain grass is the producer which feeds energy into the food chain and goat is the primary consumer. Since goat is eaten by humans, they are called secondary consumers.

Question 2.
What are the differences between standing state and standing crop.
Answer:
Differences between standing state and standing crop are as follows:
|
Standing State |
Standing Crop |
|
1. Amount of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium etc. present in the soil of an ecosystem at any given point of time. |
1. It is the amount of living biomass available at a given trophic level at a given point of time. |
|
2. It is an abiotic component. |
2. It is a biotic component. |
Question 3.
Write the relationship between productivity, Gross primary productivity, net primary productivity and secondary productivity.
Answer:
The rate of biomass production is called productivity in terms of gm-2yr-1 for an ecosystem, it can be divided in gross primary productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP). GPP of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. NPP is the available biomass for the consumption of heterotrophs i.e., herbivores and decomposers. Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Short Answer Type Questions - II
Question 1.
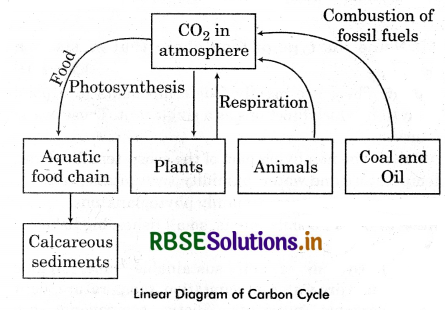
Explain carbon cycle in ecosystem. Give a linear diagram of carbon cycle.
Answer:
It is the most common nutrient or biogeochemical cycle of an ecosystem. Carbon constitutes 49% of dry weight of an organism. About 71% of carbon is found dissolved in oceans which is responsible for it regulation in atmosphere. Carbon cycle occurs through atmosphere, ocean and through living and dead organisms. Fossil fuels also represents a reservoir of carbon. Green plants fixes the atmospheric carbon into organic molecule with the help of photosynthesis.
A considerable amount of carbon is returned to atmosphere as CO2, released by the animals and plants during respiration and by the activities of decomposers. The additional sources of carbon release in atmosphere are burning of wood, forest fire and combustion of organic matter, fossil fuel, volcanic activity. Human reduced activities like deforestation, massive burning of fossil fuel for energy and transport have significantly increased the rate of release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Question 2.
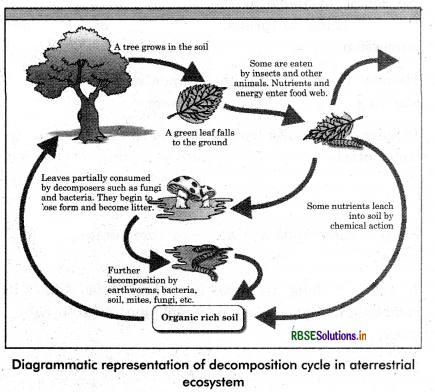
What is decomposition? Write down its steps. Give a diagrammatic representation of decomposition cycle in a terrestrial ecosystem.
Answer:
It is the process in which decomposers breakdown complex organic matter into simpler inorganic substances like carbondioxide, water and mineral nutrients. The dead plant remain like leaves, branches, flowers and dead animal remain are acts as raw material called detritus. The process of decomposition have multiple steps. These are:
- Fragmentation
- Leaching
- Catabolism
- Humification
- Mineralisation.
The process of decomposition depends on the following:
- Oxygen availability
- Chemical composition of detritus
- Climate factors
- Temperature and soil moisture
Decomposition rate is slow in low temperature and anerobic conditions while speeds up in warm and aerobic conditions.
Question 3.
Describe the inter - relationship between productivity gross primary productivity and net productivity.
Answer:
The rate of biomass production is called productivity. It is expressed in terms of g -2yr-1 or (k cal m-2 )yr-1. Productivity of an ecosystem can be categorised as primary and secondary productivity. Primary Productivity (PP) is the amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by the plants during photosynthesis. It can be divided further into:
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP): It is defined as the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. A considerable amount of GPP is utilised by plant in respiration.
Inter relationship between GPP and NPP: Gross primary productivity minus the respiration losses is net primary productivity. It is actually the available mass for consumption by heterotrophs. Hence,
GPP - R = NPP
where, R = Respiration losses.

Question 4.
Differentiate between primary and secondary succession. Give one example of each.
Answer:
|
Primary Succession |
Secondar Succession |
|
1. It occurs in the barren area. |
1. It occurs in land denuded recently. |
|
2. No soil is available at the time of being of primary succession. |
2. Soil is present at the beginning of secondary succession. |
|
3. Humus is absent in the begining. |
3. Humus is present from the begning. |
|
4. Pioneer community comes from outside. |
4. Pioneer community develops partly from previous occupants and partly from migrants. |
|
5. Serai communities are many. |
5. Serai communities are few. |
|
6. It takes a long time for completion, 1000 years or more. |
6. It takes less time for completion., 50 - 200 years. |
|
7. e.g., bare land, cooled lava. |
7. e. g., burnt grassland. |
Question 5.
The pyramid of energy is always upright. Explain with the help of labelled diagrams the difference between an upright pyramid of biomass and an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Answer:
Pyramid of energy represents the total energy of the organism at each trophic level. Pyramid of energy is always upright i.e., it can never be inverted because energy is transferred from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step.
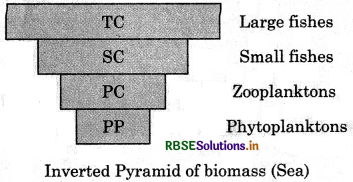
The pyramid of biomass in a sea ecosystem is inverted. Because the sum total of the phytoplanktons is for less than a few fishes feeding at higher trophic levels.
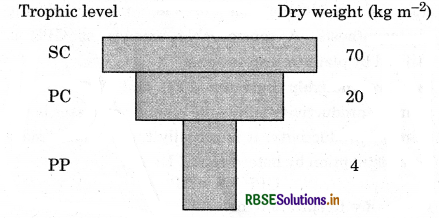
Pyramid of biomass in a forest ecosystem is upright because producers are more in biomass than primary consumers. Primary consumers are more than secondary consumers and secondary consumers are more than tertiary consumers.
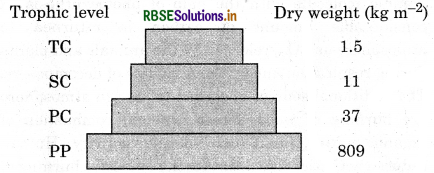
Question 6.
(i) Taking example of a small pond, explain how the four components of an ecosystem function as a unit.
(ii) Name the type of food chain that exists in a pond.
Answer:
(i) There are mainly four components in a pond ecosystem which functions as a single unit. These are as follows:
Abiotic: The non living part of the ecosystem like light, temperature and water, humidity, precipitation etc.
Autotrophs: Producers, mainly phytoplanktons.
Heterotrophs: Zooplanktons, small fishes, big fishes.
Decomposers: Bacteria and fungi.
Pond ecosystem is self sustainable unit. Abiotic components are water, precipitation, temperature, light and inorganic nutrients. Biotic components are producers, like algae, and aquatic plants.
Consumers are zooplanktons, larvae, tadpole and some fishes. Primary carrivores are water beetles, scorpions, dragon fly larvae, hydra and some fishes.
Decomposers includes fungi, bacteria and some flag ellates.
This pond ecosystem performs all the function of an ecosystem which are explained below.
Autotrophs: They convert inorganic materials with the help of sun’s energy.
Heterotrophs: They consume food upon autotrophs.
Decomposers: They decomposes and mineralise dead organic materials to release them back for reuse by the autotrophs. The above sequence of events repeats again and again in the ecosystem.
(ii) Grazing food chain (GFC) occurs in a pond.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define food chain. How many types of food chain are there? Give difference between food chain and food web. Draw a linear diagram of food chain.
Answer:
In any ecosystem there is transfer of food from one organism to another organism. One organism act as an food source for anpther organism. This transfer of food in a sequence forming a chain referred to as food chain. This chain is the result of interdependency. There are mainly two types of food chain exists in an ecosystem. These are:
(a) Grazing food chain (GFC): This food chain starts with the green plants i.e., producers at the first trophic level in any ecosystem. In case of aquatic ecosystem, the GFC is the major system for energy flow. In this food chain energy comes from the sun. A simple grazing food chain is shown below:

(b) Detritus Food Chain (PFC): At starts with the dead organic matter with the decomposers. These organisms are called saprophytes at first trophic level for example bacteria and fungi. In an terrestrial ecosystem a large amount of energy flows through this type of food chain. In this type of food chain energy comes from organic matter or detritus. Detritus food chain is connected with the grazing food chain at various levels.
Difference between Food chain and Food web:
|
Food Chain |
Food Web |
|
1. It represents the linear flow of food energy from one organism to another. |
1. It represents the many inter connecting food chains in an ecosystem. |
|
2. It is single undirectional energy flow. |
2. It is a connection of, several interconnected food chains. |
|
3. It consists of 4-5 trophic levels. |
3. It consists of many more number of trophic levels. |
|
4. Whole food chain is disturbed of one disturbance occurs at any level. |
4. It does’nt affected by a single disturbance in a single trophic level. |
|
5. It can be of two main types grazing and detritus food chain. |
5. No such type of differentiation occurs in a food web. |
Diagram of Food Chain:
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle

Question 2.
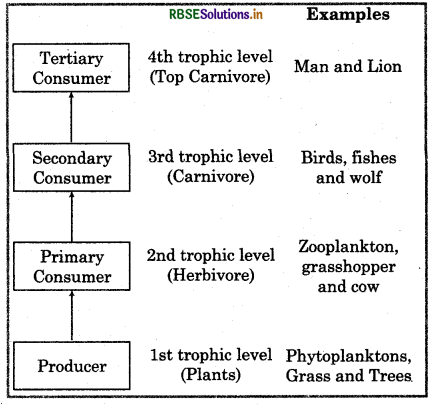
What is ecosystem? Explain the structure of ecosystem and draw a diagram of trophic levels of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Ecosystem is defined as an functional unit of nature. Where living organisms interact with each other and with their surrounding physical environment. The word ecosystem was coined by Sir AG Tansley (1935). The size of any ecosystem various greatly from a small pond to a large forest or a sea.
Ecosystem can be classified into two main types:
- Terrestrial Ecosystem : Example forest, grassland, desert etc.
- Aquatic ecosystem: For example pond, lake, river, wet land, estuary etc.
There are some man made ecosystem e.g., Fish aquarium.
Structure of Ecosystem: Each and every ecosystem consists of biotic (living component of the ecosystem like autotrophs, herbivores and cornivores and abiotic components non living component of the ecosystem like soil, air etc. and their interactions with each other result in a physical structure, that is the characteristic for each type of ecosystem. Identification and enumeration of plant and animal species of an ecosystem gives its species composition vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called stratification. For example, trees occupy top vertical starta or layer of a forest, shrubs the second and herbs and grasses occupy the bottom layer. The other main functional components of an ecosystem are
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Energy flow
- Nutrient lycling.
In an ecosystem the transfer of food energy taken place from one organism to another organism, this transfer of food making a sequence of events in unidirectional way is called food chain. The many interconnected food chains together forms food web. The specific position occupied by an organism in a food chain in an ecosystem is called trophic level. There are many trophic levels in ecosystem like:
- producer (Ist trophic level)
- Herbivores (IInd trophic level)
- Carnivore (IIIrd trophic level)
- Top carnivore (IVth trophic level)
Diagrammatic representation of trophic levels in an ecosystem is given below:
Question 3.
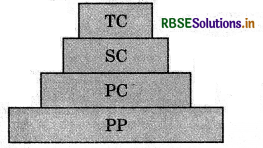
What are ecological pyramids? What precautions should be kept in mind in calculating its different aspects? Draw the diagrams of pyramids of grassland ecosystem and energy flow ecosystem.
Answer:
In any ecosystem the transfer of food energy takes place from one organism to another Organism in the form of food chain. The graphical representation of relationship between producers and consumers in terms of biomass and energy in the form of a pyramid or ecological pyramids. In simple words pyramid can reflects the relationship between different trophic level in an ecosystem based on biomass, number and energy parameters.
Certain precautions should be kept in mind while calculating its different aspects like the pyramid structure is broader at its base which represents the producers or the first trophic level and the apex is narrower which represents to P level consumer or last trophic level. After considering these precautions different types of pyramids can be possible in an ecosystem like Pyramid of number. It represents the relationship in terms of number, between the producers and consumers in an ecosystem. Thus it can be of upright e.g., in grassland ecosystem and may be inverted e.g., in tree ecosystem.
Pyramid of Biomass: It represents the relationship between produces and consumers in terms of biomass. It can be upright e.g., in grassland ecosystem and may be inverted e.g., in pond ecosystem.
Pyramid of Energy: It reflects the relationship between the producers and consumers in an ecosystem in terms of flow of energy. Each bar in the energy pyramid indicates the amount of energy present at each trophic level in a given time or annually per unit area. It is always upright because energy is always lost at each successive trophic level.
These ecological pyramids have some limitations like it does not take into account the Same species belonging to two or more trophic levels, it assumes a simple food chain, which never exists in nature i.e., it does not accomodate the food web, saprophytes/decomposers are not given any position in ecological pyramids.
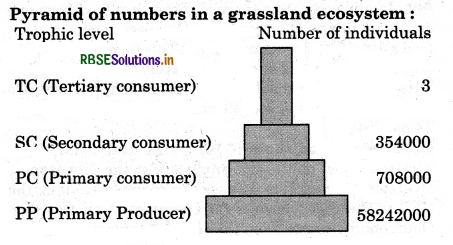
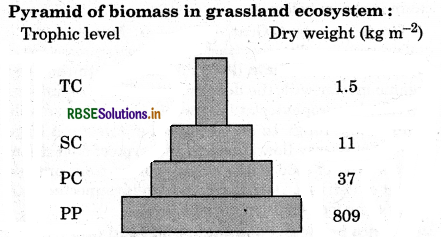
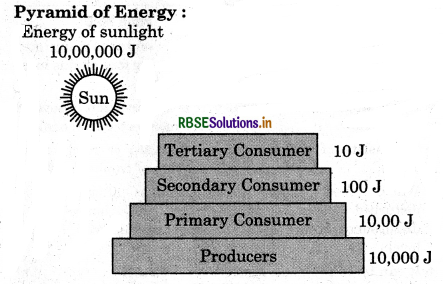
Question 4.
What is ecological succession. Mention its different steps. Explain Hydrach and Xerarch succession with diagrammatic representation.
Answer:
The gradual, sequential and predictable changes in the species composition of an given area are called ecological succession. During the succession some species adopts and colonise an area and their population becomes more numerous whereas the population of other species declines and gradually disappears from that area.
The entire sequence of communities that successfully and successively changes in a given area is called sere. The species that invades a bare area and starts the ecological succession are called pioneer species. The ecological changes leads finally to a community that is in equilibrium with the existing environment and this is called climax community. It is the most stable stage. All the existing present day communities in the world have to be because of succession that has accurred over millions of years since life started on the plant Earth. Types of ecological succession:
- Hydrarch succession
- Xerarch succession.
Types of Ecological succession:
Primary succession begins in an area where no previous living organisms are presents. It is a very slow process as it includes soil formation which takes thousands of years for climax to be reached. For example cooled lava, bare rock, newly formed pond etc.
Secondary succession begins in an area where natural biotic communities have been destroyed because of any reason man-made or natural for example abandoned form land, burned or cut forests, it is faster process as soil is already available for succession.
Hydrarch Succession: It occurs in wet area or water, leading to successional series that progress from hydric to the mesic conditions.
In hydrarch succession pioneers are phytoplankton. These phytoplanktons with time are replaced by free floating angiosperms followed by rooted hydrophytes, sedges, grasses and finally the trees, leading to mesic conditions.
Xerarch Succession: It occurs in dry areas and the series progresses from xeric to mesic condition. The climax community remains stable as long as environment remains unchanged. With time, the xerophytes habitat gets converted into mesophytic conditions.
Stages of xerarch succession are:
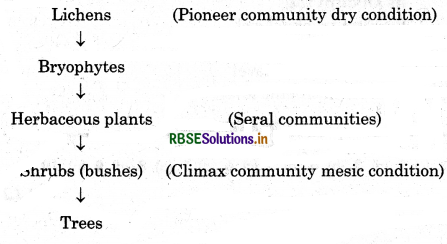
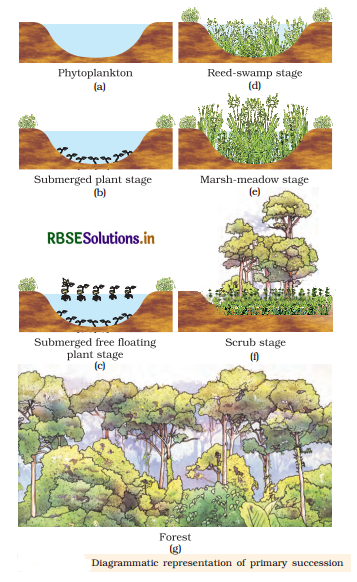

Question 5.
(i) What is an ecological pyramid? Compare the pyramids of energy, biomass and number.
(ii) Write any two limitations, of ecological pyramids.
Answer:
(i) Ecological pyramids are the diagrammatic illustration of connection between different trophic levels in terms of energy, biomaSs and number of organisms. The base of each pyramid represents the producers or the first tropic level. Apex represents tertiary or top level consumers. In general, all pyramids are upright, but there are few exceptions.
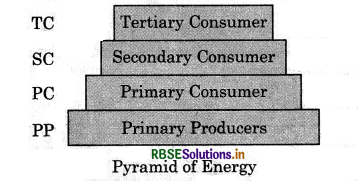
Pyramid of energy: It represents total energy of the organisms in each trophic level.
Pyramid of energy is always upright because when energy is transferred from a particular trophic level to next some energy is always lost.
It can be inverted:
Pyramid of Biomass : It represents the total weight of the organisms in each tropic, level.
It is upright in case of terrestrial ecosystem. It is inverted for aquatic ecosystem.
Pyramid of number : It represents the total number of organisms at each trophic level.
Pyramid of number is upright, in most ecosystems. In a tree ecosystem, pyramid of number is inverted.
(ii) Limitations of Ecological Pyramids :
- It never takes into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
- Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramid even though, they play an important role in ecosystem.
