RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through manav janan class 12 in hindi that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Important Question Biotechnology and its Applications
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
We can get desired characters of plant and animals through:
(a) genetic engineering
(b) chromosomal engineering
(c) bonsai technology
(d) ekabana technology
Answer:
(a) genetic engineering

Question 2.
Which one is not related to agriculture biotechnology?
(a) Increase crop production
(b) Inhibition of a Innate gene
(c) To get better flavor
(d) Improve nutritional value
Answer:
(b) Inhibition of a Innate gene
Question 3.
First transgenic crop was:
(a) cotton
(b) rice
(c) tobacco
(d) pea
Answer:
(c) tobacco
Question 4.
Bt toxin produced from:
(a) Virus
(b) Insects
(c) E. coli
(d) B. thuringiensis
Answer:
(d) B. thuringiensis
Question 5.
Cry gene found in:
(a) B. thuringiensis
(b) tobacco
(c) rice
(d) insulin
Answer:
(a) B. thuringiensis
Question 6.
Green revolution relates to:
(a) fertilizer
(b) GM Crops
(c) advanced mechines
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 7.
Midgut epithelium breakdown can be done by:
(a) protoxic
(b) activated protein crystals
(c) protoplast fusion
(d) dehydration
Answer:
(b) activated protein crystals
Question 8.
dsRNA in RNAi is cut by:
(a) dicer protein
(b) endonucleas
(c) analine
(d) ligas
Answer:
(a) dicer protein
Question 9.
Bt toxin in bacteria do not kill itself because:
(a) toxip enclosed in a poutch
(b) toxin is inactive
(c) bacteria is resistant
(d) toxin separate from body
Answer:
(b) toxin is inactive

Question 10.
Transgenic bacteria used to produce insulin:
(a) B. thuringiensis
(b) Brassica napus
(c) Agrobacterium hizogenes
(d) E. coli
Answer:
(d) E. coli
Question 11.
Gene, that encode the structure of Insulin located on:
(a) small arm of chromosome 11
(b) long arm of chromosome 11
(c) small arm of chromosome 12
(d) long arm of chromosome 12
Answer:
(a) small arm of chromosome 11
Question 12.
Nematode specific genes auere introduced into the tobacco host plant using a vector
(a) pBR 322
(b) Plasmid
(c) Bacteriophage
(d) Agrobacterium
Answer:
(d) Agrobacterium
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by green revolution?
Answer:
Period from 1930 to 1960 when agriculture field adopted to modern methods and technology such as fertilizers, pesticides, high yielding variety.
Question 2.
When was green revolution started in India?
Answer:
The green revolution in India was initiated in 1960s by introducing high yielding varieties.
Question 3.
What are agrochemicals?
Answer:
It includes insecticides, herbicides, fungicides and nematicides.

Question 4.
Write the full name of GMO.
Answer:
Genetically modified organism.
Question 5.
Define genetically modified organism.
Answer:
Organisms, whose DNA or genes are artificially designed and altered with desired gene are called Genetically modified organism (GMO).
Question 6.
Write the scientific name of the bacteria that produce Bt toxin.
Answer:
Bacillus thuringiensis.
Question 7.
What is Bt toxin?
Answer:
Bt toxin is a intracellular crystal protein produced by Bacillus thuringiensis.
Question 8.
What is the use of Bt toxin?
Answer:
Used to produced insecticide plants with the help of rDNA technology.
Question 9.
The Bt toxin produced by Bt does not kill bacillus but kill insects. Why?
Answer:
Bacteria produce inactive Bt toxin, which gets activated only when it enters in mid gut of insects.
Questoin 10.
Write the name of Boll worm resistance genetically modified variety of cotton plant.
Answer:
Bt cotton is a genetically modified variety of pest resistance plant.
Question 11.
What are ‘cry gene’? In which organism they are present?
Answer:
Cry genes are Bt toxic genes, which produces toxic protein crystals.
Question 12.
Write the two specific ‘cry’ genes that encode the proteins which control cotton bollworms.
Answer:
Cry IAC and Cry IIAb genes control the cotton bollworms.
Question 13.
Which gene control the corn borer?
Answer:
Cry IAb controls corn borer.
Question 14.
Name the source organism of the gene Cry IAc and its target pest.
Answer:
Cry IAc gene control the cotton bollworm isolate from bacteria bacillus thuringiensis.
Question 15.
Write the possible source of RNA interference (RNAi) gene.
Answer:
The source of RNAi may be viruses which have RNA genome or mobile genetic elements e.g., transposons.
Question 16.
State the role of transposons in silensing of mRNA in eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
Transposons are mobile genetic elements that act as a complementary RNA that is used to stop translation.
Question 17.
How does dsRNA gain entry into eukaryotic cell to cause RNA interference?
Answer:
The small piece of mRNA which cause RNAi can be alien source or infection of viruses it is mobile genetic elements (transposones).
Question 18.
Write the name of pest controlled by RNAi method.
Answer:
Meloidogyne incognita.
Question 19.
Give one use of biotechnology in the field of medicine.
Answer:
Production of genetically modified affected therapeutic drugs e.g., Insulin.
Question 20.
Which bacteria is used to produce genetically enginured insulin?
Answer:
E. coll
Question 21.
How the two polypeptides of insulin bond each other?
Answer:
Two polypeptides chain A and B of insulin are bond with disulfide linkage (—S—S).
Question 22.
Mention the chemical changes that proinsulin undergoes, to be able to act as mature insulin.
Answer:
When pro - insulin get processed to be mature, that C peptide chain separate out from the insulin.
Question 23.
Which american company designed insulin?
Answer:
In 1983, American company, Eli - Lilly, designed two DNA sequence, similar to A and B chain of insulin.
Question 24.
Define gene therapy.
Answer:
Therapy of defective genes, which are replaced by healthy genes.

Question 25.
Why is adenosine deaminas (ADA) enzyme essential for children?
Answer:
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency leads to an accumulation of toxic purin, which most potently affects on lymphocytes and serves immunodeficiency in children.
Question 26.
Name any two techniques that serve the purpose of early diagnosis of some bacterial/viral human diesease.
Or
Name a molecular diagnostic technique to detect the presence of pathogen in its early stages of infection.
Answer:
Techniques that serve the purpose of early diagnosis of some bacterial/viral human diseases are as follow:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- DNA recombinant technology.
- ELISA.
Question 27.
Write two harmful effects of transgenic plants on human health.
Answer:
Harmful effects of transgenic plants on human health:
- Causes allergic reactions.
- Cause immuno - suppression.
Question 28.
What are IIIrd generation vaccines?
Answer:
Synthesized vaccines with high potency of purity and potential.
Question 29.
Name the Indiant variety of rice patented by an American company.
Answer:
Basmati.
Question 30.
Define biopiracy.
Answer:
Use of biological resources or biochemicals of another country without permission and information. It is a kind of ‘theft’.

Question 31.
Write the full form of 'GEAC'
Answer:
Genetic Engineering Approval Committee.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
Explain the role of biotechnology in agriculture by giving an example.
Answer:
Agriculture biotechnology has been producing countless new products, that have change our live for the better role of biotechnology which are followed to increase the food production.
- Agriculture based on Agrochemical.
- Organic agriculture.
- Agriculture based on genetically engineered crop.
Question 2.
List any four ways by which GMO’s have been useful for enhanced crop output?
Answer:
- GMO’s are resistant to pest so reduced in dependency on agrochemicals.
- GMO’s have high yield so due to resistancy post harvest losses are greatly reduced.
- GM crops are able to use maximum minerals of soil.
- GM crops have increased nutritional value of food.
Question 3.
Write any two uses of'genetically modified plants.
Answer:
Two uses of genetically modified plants are:
- Enhance nutritional value of food e.g., vitamin A enriched rice (golden rice).
- Increase the quantitative production of crops.
Question 4.
Why do the toxic insecticidal proteins secreted by bacillus thuringiensis kill the insect and not the bacteria itself?
Answer:
In bacteria, toxic proteins present in inactive form that is protoxic which is not toxic. Once this protein is eaten by insect larvae, toxin get activated in gut of insect and kill the bacteria.
Question 5.
What makes the protoxin to activated toxin?
Answer:
Protein crystals of Bt toxin in bacteria are insoluble and no longer harmful but when these crystals reached to the alkaline medium of larvae gut, crystals solubilised in epithelial cell and get activated so that insecticidal protein kill the insect larvae.

Question 6.
What do ‘cry genes’ in Bacillus thuringiensis code for? State its importance for cotton crop.
Or
Name the soil bacterium that produces a protein/chemical that is toxic to insect pest. Show with example that these are encoded by different forms of the gene.
Answer:
Bt cotton is genetically modified plant contain a gene ‘cry gene’ of Bacillus thurengiensis (Bt) which control lepidopteran insects by producing toxin protein. e.g., Cry IAc and Cry IIAb kill cotton boll worms. Cry genes inserted into cotton plant through DNA technology. Bacterial gene get cloned inside the cotton plant (Bt cotton plant) to produced large quantity of protoxic in plant cell. When insects feed on plant protein get activated in insect gut and kill the insects.
Question 7.
Explain the process of RNA interference.
Or
How does ‘RNA interference’ takes place in Eukaryotes? Mention its importance.
Answer:
To control the infection oiMeloidogyne incognita, a novel strategy has been used which is known as RNA interference. It is a biological process in all eukaryotic organism, where RNA molecule silence a gene by inhibit a gene translation due to the presence of complementry dsRNA. Which kinds to and prevent translation of the mRNA by forming dsRNA. RWAi used to produce pest resistant plants specially for nematodes or cotton root knot nematode.
Question 8.
Explain the brief “Biotechnology applications in medicine”.
Answer:
Biotechnology has proved to be a boon in the field of medicine which has worked at a very high level to fight disease like corona virus and pandemic. The applications of genetic engineering has made to produce many hormones such as insulin, steroid hormones, sex hormones, relaxine hormones etc. These genetic engineering hormones and growth factors are highly purified, effective and have very few side effects.
Question 9.
What were the conventional methods to produce insulin.
Answer:
Initially, insulin given to a diabetic patient was extracted from the pancreas by killing animals such as cow and pig. This insulin, taken from animals was injected into the human body, was less beneficial and cause allergies, they had to suffer many kind of problems.
Question 10.
What is the difference between pro - insulin and mature insulin?
Or
How pro - insulin undergoes for maturation?
Or
Why is proinsulin so called? How is proinsulin different from functional insulin in humans?
Answer:
Pro - insulin is naturally synthesised by human and other mammals contain a c - peptide chain that does not found in mature insulin. Pro - insulin contain three chains A, B and C, when pro - insulin undergoes maturation c - peptide separate out from insulin and fully mature insulin only contain two A and B chains, bonded with di - sulfide bond.
Question 11.
Explain how Eli Lilly, an American company, produced insulin by recombinant DNA technology?
Or
Who designed artificial insulin and how?
Answer:
In 1983, American company Eli Lilly designed two DNA sequence, similar to A and B chain of insulin. E. coli bacteria used to produce A and B chains in culture medium separately. Though disuifide linkage both the chains are exactly like mature insulin. This artifically synthesised insulin is named humulin, which is very safe and cause no ellergy.
Question 12.
Name the source used to produce hepatitis B vaccine using rDNA technology.
Answer:
In 1984 on the advise of Geneva, WHO organization used yeast (Sabcharomyces cerevisiae) for the production of hepatitis B vaccine using rDNA technology.
Question 13.
State the role of C peptide in insulin.
Answer:
C - peptide chain is a small middle part of proinsulin of 31 - amino acid having the chain sequence B—C—A. It is also called connecting peptide. When we intake food, blood glucose level increase, in response ß - cells of pancreas release mature insulin into blood, which regulated by C - peptide.
Question 14.
What is gene therapy? Name the first clinical case in which it was used.
Or
Name the first disease and how it was cured by the help of gene therapy?
Answer:
Gene therapy, is the therapy of defective genes which are replaced by healthy gene. In the child or fetue, get corrects the defect of malfunctioning gene before it grow older than the disease will no longer grow in body. So “Gene therapy is a medical field which focuses on the utilization of the therapeutic delivery of nucleic acid (gene) into a patient’s cell as a drug to treat disease.” Very first experiment of gene therapy performed on 4 years old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Question 15.
Mention the cause and the body system affected by ADA deficiency in humans.
Answer:
ADA deficiency is caused by the mutation or malfunctioning of ADA gene. Which is responsible for making an enzyme that found in white blood cells (lymphocytes). This enzyme is very crucial for the well functioning of immune system. ADA deficiency affects lymphocytes, lungs, kidney and also affect the skin.
Question 16.
What are the advantage of molecular diagnosis over conventional methods?
Or
What is molecular diagnosis and it use to early detection of infectious disease?
Answer:
Molecular diagnosis is a great advantage in which you can detect the disease in time before it spreads to the whole body. Initially blood test, urine test, serum test was the conventional methods to detect the infection through virus, bacteria they are very less and small, due to which they are not detected with conventional method. Molecular diagnostics detect the presence of genetic material or proteins associated with specific health disease, even when they are present in very small number or non - symptomatic. The advanced diagnostic techniaues like recombinant DNA, ELISA, PCR used to check the early symptoms.
Question 17.
State the principle on which ELISA technique is based. How it is help in early detection of a disease?
Or
Explain any technique used for early detection of a disease.
Answer:
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a molecular diagnosis technique used to identify the viral, fungal, bacterium and mycoplasma etc. It is highly specific disease requires a very small amount of factors. When a pathogen enters our body, our immune response produces antibodies against it, by ELISA technique, these antibodies are detected and pathogen is identified at the early stage.
Question 18.
Explain the role of transgenic animals in production of biological products.
Answer:
The production of transgenic animals is to improve human health and increase animal welfare by decreasing livestock disease.
- The main purpose of transgenic animals to produce is to study the regulation of genes in body.
- Transgenic animals contribute a great deal to the study of disease.
- A major objective of transgenic animals is produce biological products.

Question 19.
What are probes? How does they used in Molecular diagnosis.
Answer:
Single stranded DNA or RNA molecules which are tagged with radioactive molecules are called probes. DNA probes are small piece of ssDNA used to detect the presence of complementary DNA sequence by hybridization. DNA probes are radioactively labelled with radioisotopes, flurophores etc.
Question 20.
What is biopiracy? Why should nations develop laws against biopiracy?
Answer:
Biopiracy is a kind of theft of biological resources. Biopiracy is the use of biological resources or biochemicals of another countary without permission and information. Injustic between developed and developing nations have developing a feeling of inadequate compensation and profit sharing, due to this, some native have made restriction on the use of their pocket resources and traditional knowledge without prior permission. The India patent bill was also made in the parliament of India, in which disputes related to biopiracy are taken care of.
Short Answer Type Questions - II
Question 1.
How.Bt cotton plant is protected against bollworm infestation?
Or
Why do lepidopterans die when they feed on Bt cotton plant? Explain how does it happen.
Answer:
Bt cotton plants are transgenic plants having the gene of Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria produce a toxic protein that kill insects of lepidopterons (tobacco, budworms) beetles, flies, moth etc. This toxin is actually a protein crystals which are formed in bacteria in certain phase of growth. Bacteria produced protein crystals are insoluble in bacteria and no longer harmful but when these crystals reached to the alkaline medium of larvae gut, crystals solubilised in epithelial cell and get activated. So that insecticidal protein kill the insect larvae.
Question 2.
How is Bt cotton plant created as a GM plant? How it is different from normal cotton plant?
Or
Write down the procedure to producing Bt cotton plant by the help of recombinant DNA technology.
Or
How has the study of biotechnology helped in development of pest - resistance cotton crop?
Answer:
Bt cotton is a genetically modified plant contain a gene (Cry IAc, Cry IIAb) cry genes of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). Which control lepidopteran insects by producing toxin protein. Normal cotton plant do not consists such genes. These cry gqnes which produced toxic protein crystals produce different strains of toxins. That cry gene isolated from bacteria and inserted into cotton plant DNA through rDNA technology where bacterial gene get cloned inside the cotton plant to produced large quantity of pro - toxic in plant cell. Specific cry gene are inserted to produce resistancy for particular insects according to the region of world.
Question 3.
Name the nematode that infects and damages tobacco roots.
Answer:
Nematodes are thread like, round worms which can be parasitise for plants, animals and for human being also. Most common nematode parasite is Meloidogyne incognita also know as southern root nematode or cotton root - knot nematode belong to heteroderidae family, it is world wide species and mostly affected roots of tobacco plants. A novel strategy has been used to protect plant against pest is RNA interference. The process RNA interference (RNAi) involves silencing of a specific mRNA. To control the infection oiMeloidogyne incognita, a novel strategy has been used which is known as RNA interference. It is a biological process in all eukaryotic organism, where RNA molecule silence a gene by inhibit a gene translation due to the presence of complementry dsRNA. Which kinds to and prevent translation of the mRNA by forming dsRNA. RWAi used to produce pest resistant plants specially for nematodes or cotton root knot nematode.

Question 4.
Explain the various steps involved in the production of artificial insulin.
Or
Explain the application of rDNA technology to produce insulin.
Answer:
An american company produced insulin via recombinant DNA technology in 1983. Company designed two DNA sequence, similar to A and B chain of insulin and introduced in E. coli bacteria via following steps:

Question 5.
How has the use of Agrobacterium as vector helped in controlling Melodoigyne incognita infestation in toboacco plants? Explain in correct sequence.
Or
How has RNAi technique helped to prevent the infestation of roots in tobacco plants by a nematode meloidogyne incognita?
Answer:
To control the infection of meloidogyne incognita a novel strategy has been used which is RNAi.
- Firstly we isolate those genes from nematode which are important for the survival and introduce into Agrobacterium vector to form rDNA.
- This rDNA how infected to the plant cell, where it produce both sense and anti - sense RNA in plant cell.
- We ensurely take only those gene from M. incognita that have ability to form dsRNA.
- dsRNA formed in plant cell, cut by dicer enzyme into small dsRNA, having RNAi specific sequence.
- When nematode eat such cells, these RNAi silenced the mRNA of nematode and stop protein translation.
- Without protein or enzyme nematode get dies.
Question 6.
Recombinant DNA technology is of great importance in the field of medicine, with the help of a flow chart, show now this technology has been used in preparing genetically engineered human insulins.
Or
How Eli Lilly, an american company produced insulin by recombinant DNA technology?
Answer:
To control the infection of meloidogyne incognita a novel strategy has been used which is RNAi.
- Firstly we isolate those genes from nematode which are important for the survival and introduce into Agrobacterium vector to form rDNA.
- This rDNA how infected to the plant cell, where it produce both sense and anti - sense RNA in plant cell.
- We ensurely take only those gene from M. incognita that have ability to form dsRNA.
- dsRNA formed in plant cell, cut by dicer enzyme into small dsRNA, having RNAi specific sequence.
- When nematode eat such cells, these RNAi silenced the mRNA of nematode and stop protein translation.
- Without protein or enzyme nematode get dies.
Question 7.
What was the convenstional method to obtained insulin and what kind of problems had to be faced to produced genetically engineered insulin?
Answer:
Insulin is,naturally secreted by pancreas through ffcells of islets of langerhence. Insulin control the blood glucose level. When pancreas failed to produce enough insulin, it causes diabetes. This problem could only be controlled by giving insulin to the body. Initially, insulin gives to a diabetic patient wax extracted from pancreas by killing animals such as cow and pig. This insulin injected to human create allergies other kind of problems. Naturally synthesised pro - insulin made by mammals contain a C - peptide that insulin undergoes maturation and C - peptide separate out when blood glucose level increases. When insulin was produced using rDNA techniques, this separation of C - peptide become a major challange to get mature insulin artificially.
Question 8.
Explain enzyme replacement therapy to treat adenosine deaminase deficiency. Mention two disadvantage of this procedure.
Answer:
In enzyme replacement therapy, the patient is given functional ADA (Adenosine deaminas) through injection. ADA is a crucial enzyme produced by lymphocytes and important for the immune system of body. Enzyme replacement therapy consist following steps:
- In first step, lymphocytes of patient isolated from the blood and cultured in external medium.
- ADA genes fom lymphocytes of healthy person also isolated from blood.
- These active ADA genes are introduce into retrovirus (vector).
- Retrovirus with recombinant genetic material copied into the genome of host cell.
- These cells are now produced ADA into the body.
Disadvantage of this therapy is that these genetically modified lymphocytes are mortal, so it has to be removed time to time from patient body so this therapy was not permanent and patient did not recover completely.
Question 9.
Mention the cause of ADA deficiency in human. How has genetical engineering helped patient suffering from it?
Answer:
Cause of ADA deficiency:
ADA deficiency is caused by the mutation or malfunctioning of ADA gene. Which is responsible for making an enzyme that found in white blood cells (lymphocytes). This enzyme is very crucial for the well functioning of immune system. ADA deficiency affects lymphocytes, lungs, kidney and also affect the skin.
The first approved gene therapy given to 4 years old girl a regular injection of ADA enzyme was performed every two months. Some children with ADA deficiency cured with bone marrow transplantation and other treated with injection, enzyme replacement therapy, which active ADA was injected to patient. Roth these procedure are temperary and not fully successed permanent gene therapy can be done by replacement of ADA gene from bone marrow cells of early embryonic stages.

Question 10.
Why is molecular diagnosis preferred over conventional methods? Name any two techniques used in molecular diagnosis. Explain how PCR is used to diagnostic technique to detect mutation or cancer?
Answer:
Molecular diagnosis is a great advantage in which you can detect the disease in time before it spreads to the whole body. Initially blood test, urine test, serum test was the conventional methods to detect the infection through virus, bacteria they are very less and small, due to which they are not detected with conventional method. Molecular diagnostics detect the presence of genetic material or proteins associated with specific health disease, even when they are present in very small number or non - symptomatic. The advanced diagnostic techniaues like recombinant DNA, ELISA, PCR used to check the early symptoms.
PCR is currently the most widely used method for detection of cancer and HIV AIDS:
- Radioactively labelled probes or ssDNA used to detect the presence of complementary DNA sequence by hybridization.
- It is allowed to hybridise with its complementary DNA in a clone of cells, followed by detection using autoradiography.
- Healthy or normal dsDNA clone cells are detectable on autoradiography plate, but mutant gene will not detected on photographic film, don’t have any radioactive probe.
Question 11.
What are transgenic animals, give some advantages of transgenic animals. How is ‘Rosie’ considered different from a normal cow? Explain.
Answer:
Transgenic animals are animals whose gene or DNA altered and manipulated with foreign desire gene. They are simply created by the microinjection of DNA into the fertilised egg of surrogate mother.
Advantage:
- The main purpose of producing transgenic animals is to study the regulation of gene in body.
- Transgenic animals contribute a great deal to study of disease. We can find out how gene fight against disease.
- A major objective of transgenic animals is also to produce biological products, e.g. ,milk, blood, urine, silk.
- Genetic engineering has the biggest hand in the line of making vaccine e.g., corona vaccine, BCG, DPT, Polio vaccine etc.
- Transgenic animals are more sensitive to certain chemicals and drugs, so they used for chemical safety testing.
Rosie was a transgenic cow which contain 2.4 gram of protein per leter which is more than a normal cow. This milk contain human α - lectalbumine which is a very balance nutrient for the human body.
Question 12.
How many documented varieties of Basmati rice are grown in India? How has this variety of rice been exploited?
Answer:
There are 27 documented varieties of Basmati rice are grown in India.
- In 1997, an american company got patent righ on Basmati to through US patent and trademark office.
- While all the varieties of Basmati were developed via the cross between Indian Basmati rice with semi - dwarf variety.
- They claimed this new variety as invented by them.
- This allowed the company to sell a ‘new’ variety of Basmati rice in the US and abroad.
Question 13.
Expand GEAC. Why was GEAC established? Mention the responsibilities assigned to this organisation.
Or
GEAC is one of the organisation set up by Indian government. Write it’s full form. Give it’s two objectives.
Answer:
GEAC = Genetic Engineering Approval Committee.
The reasons and responsibilities of GEAC:
- To keep the experimenters with in a boundary, due to which they do not go beyond the limitation of marality of human activities.
- Some ethical standards are required to test on living beings which can be useful or unprotective for animals.
Responsibilities:
- To make dicisions regarding the validity of GM research.
- Protection of the organism for the legal and public survives.
Question 14.
What is a GMD? List any five possible advantage of a GMD to a farmer.
Answer:
Genetically modified organism (GMO) are any cell of plants, bacteria, algae, fungi and animals, whose DNA or genes are artificially designed and altered with desired gene. GM crops, are those whose DNA has been modified to get desired effects.
Advantage of GM crops has following:
- Genetically modified crops are more tolerant to abiotic stresses such as heat, salt, cold, drought etc.
- Because they are resistant to pest so reduced in dependency on agrochemicals e.g., pesticides.
- Genetically modified crops have high yield so due to resistancy post harvest losses are greatly reduced.
- GM crops are able to use maximum minerals of soil, which prevents fertility of soil by early exhaustion and keep the soil healthy.
- The second generation GM crops have increases nutritional value of food and beneficial for consumers, e.g. golden rice are enriched in vitamin A, soyabeans with increased oleic acid.
- Second generation GM crops can be transfered and stored for long time without decaying of product.
The purpose of genetic engineering is to produce Tailor made plants, which means plants grow for specific purpose with high yield, good nutritional value and resistant from several diseases. Tailor made plants supply enough alternative resources to industries in means of fuels, pharmaceuticals, starches, carbohydrates, proteins etc.

Question 15.
Differentiate between diagnostics and therapeutics. Give one example for each category.
Answer:
Diagnostic technique helps us to identify a disease. It have complex equipment that produce image such as X - rays or scans. When body fails to function properly, professionals typically order diagnostic procedures. In diagnostic technique many complex steps of biotechnology performes. Example: ELISA is a diagnostic test for HIV.
Once a cause in identified, therapeutic procedure performed to the disease therapeutic radiographers use radiation to treat cancer and tissue defects. Simply a therpeutic agents helps in the treatment of disease. Example: Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the application of biotechnology in producing Bt cotton.
Answer:
The main objective of biotechnology in the field of agriculture is to produce some such crops which are pest resistant and in which we can use pesticides to a minimum. So they are called genetically modified organisms GMO or GM crops, e.g., Bt - Crops.
Bt cotton plants are transgenic plants having the gene of Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria produce a toxic protein that kill insects of lepidopterons (tobacco, budworms) beetles, flies, moth etc. This toxin is actually a protein crystals which are formed in bacteria in certain phase of growth. Bacteria produced protein crystals are insoluble in bacteria and no longer harmful but when these crystals reached to the alkaline medium of larvae gut, crystals solubilised in epithelial cell and get activated. So that insecticidal protein kill the insect larvae.
Bt cotton is a genetically modified plant contain a gene (Cry IAc, Cry IIAb) cry genes of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). Which control lepidopteran insects by producing toxin protein. Normal cotton plant do not consists such genes. These cry gqnes which produced toxic protein crystals produce different strains of toxins. That cry gene isolated from bacteria and inserted into cotton plant DNA through rDNA technology where bacterial gene get cloned inside the cotton plant to produced large quantity of pro - toxic in plant cell. Specific cry gene are inserted to produce resistancy for particular insects according to the region of world.
Question 2.
Insulin in the human body is secreted by pancreas as prohormone/proinsulin. The schematic polypeptide structure of proinsulin is given below. This proinsulin needs to undergo processing before it becomes functional in the body. Answer the questions that follow:
(a) State the change the proinsulin undergoes at the time of its processing to become functional.
(b) Name the technique the American company Eli Lilly used for the commercial production of human insulin.
(c) How are the two polypeptide of a functional insulin chemically held together?
Or
Explain the applications of rDNA technology to produce insulin. Give well define diagram producing humulin via genetic engineering.
Answer:
(a) Pro - insulin is naturally synthesised by human and other mammals contain a c - peptide chain that does not found in mature insulin. Pro - insulin contain three chains A, B and C, when pro - insulin undergoes maturation c - peptide separate out from insulin and fully mature insulin only contain two A and B chains, bonded with di - sulfide bond.
(b) In 1983, American company Eli Lilly designed two DNA sequence, similar to A and B chain of insulin. E. coli bacteria used to produce A and B chains in culture medium separately. Though disuifide linkage both the chains are exactly like mature insulin. This artifically synthesised insulin is named humulin, which is very safe and cause no ellergy.
(c) Two separately produced A and B chains of insulin are bond with disulfide linkage (—S—S—).
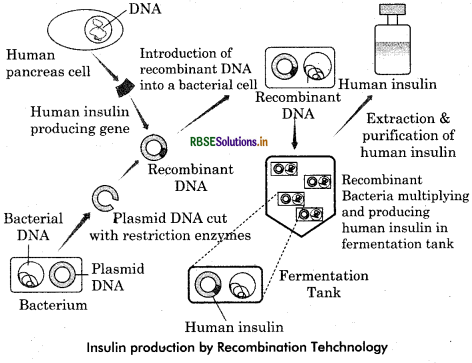
Question 3.
(i) Name the source from which insulin was extracted earlier. Why is this insulin no more in use by diabetic people?
(ii) Explain the process of synthesis of insulin by Eli Lilly company. Name the technique used by the company.
(iii) How is the insulin produced by human body different from the insulin produced by the above mentioned company?
Answer:
(i) Insulin is,naturally secreted by pancreas through ffcells of islets of langerhence. Insulin control the blood glucose level. When pancreas failed to produce enough insulin, it causes diabetes. This problem could only be controlled by giving insulin to the body. Initially, insulin gives to a diabetic patient wax extracted from pancreas by killing animals such as cow and pig. This insulin injected to human create allergies other kind of problems. Naturally synthesised pro - insulin made by mammals contain a C - peptide that insulin undergoes maturation and C - peptide separate out when blood glucose level increases. When insulin was produced using rDNA techniques, this separation of C - peptide become a major challange to get mature insulin artificially.
(ii) In 1983, American company Eli Lilly designed two DNA sequence, similar to A and B chain of insulin. E. coli bacteria used to produce A and B chains in culture medium separately. Though disuifide linkage both the chains are exactly like mature insulin. This artifically synthesised insulin is named humulin, which is very safe and cause no ellergy.
(iii) Insulin naturally produced by pancreas through ß - cells of islets of langerhence naturally insulin produced in the form of proisulin having 3 chains A, B and C, chain C is interlinking between A and B chains. When pro - insulin undergoes maturation, C peptide separate out from insulin due to the increased blood level, but insulin produced artifically do not have that C chain because artificial proinsulin can not be produced in such way. Company only produce mature insulin having two A and B chains.

Question 4.
Explain:
(i) What are the three options that can be thought of, to increase food production?
(ii) Mention the reasons for the success of Green revolution in increasing food production.
Answer:
(i) Option to Increase food production:
- Agro chemical based Agriculture: This is a good option to increase food supply. These method is and cheap for the farmers, e.g., Insecticides, pesticides, urea etc.
- Organic Agriculture: This is a novel method producing system that sustains the health of soil, ecosystem and people without using any insectiside, agro chemical, growth hormones, it only uses compost.
- Agriculture based on Genetically Engineered Crop: By using genetically modified crops we can enhance the quality and quantity of agriculture e.g., Bt cotton, Bt brinjal.
(ii) During this period agriculture adopted to modern methods and technology and increased use of fertiliser, pesticides, tractor, advance machine etc. Which leads the agriculture to green revolution and tremendously food production increases.

- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 16 पर्यावरण के मुद्दे
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 15 जैव-विविधता एवं संरक्षण
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 14 पारितंत्र
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 13 जीव और समष्टियाँ
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 12 जैव प्रौद्योगिकी एवं उसके उपयोग
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 11 जैव प्रौद्योगिकी-सिद्धांत व प्रक्रम
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 10 मानव कल्याण में सूक्ष्मजीव
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 9 खाद्य उत्पादन में वृद्धि की कार्यनीति
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 8 मानव स्वास्थ्य तथा रोग
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 7 विकास
- RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 6 वंशागति के आणविक आधार