RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Maths in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5
Question 1.
\(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}=\frac{A}{x+1}+\frac{B}{x+2}\)
⇒ x = A(x + 2) + B(x + 1)
⇒ x = (A + B)x + 2A + B
Comparing the coefficients of x and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B = 1, 2A + B = 0
Now, solving these equations, we get
A = - 1 and B = 2
∴ \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}=\frac{-1}{x+1}+\frac{2}{x+2}\)
∴ \(\int \frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)} d x=-\int \frac{d x}{x+1}+\int \frac{2}{x+2}\) d x
= - log |x + 1| + 2 log |x + 2| + C
= - log |x + 1| + log |x + 2|2 + C
= log\(\frac{(x+2)^{2}}{|x+1|}\) + C (∵ (x + 2)2 > 0)

Question 2.
\(\frac{1}{x^{2}-9}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{1}{x^{2}-9}=\frac{1}{(x-3)(x+3)}\)
= \(\frac{A}{x-3}+\frac{B}{x+3}\)
⇒ 1 = A(x + 3) + B(x - 3)
⇒ 1 = A(A + B)x + 3A - 3B
Comparing the coefficients of x and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B = 0 and 3A - 3B = 1
Now, solving these equations, we have
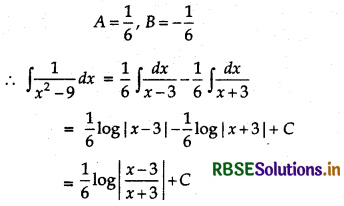
Alternative:
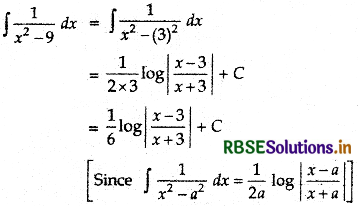
Question 3.
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
= \(\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{x-2}+\frac{C}{x-3}\)
⇒ 3x - 1 = A(x - 2) (x - 3) + B(x - 1) (x - 3) + C(x - 1) (x - 2)
⇒ 3x - 1 = A(x2 - 5x + 6) + B(x2 - 4x + 3) + C(x2 - 3x + 2)
⇒ 3x - 1 = (A + B + C)x2 + (- 5A - 4B - 3C)x + 6A + 3B + 2C
Comparing the coeffcients of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B + C = 0
- 5A - 4B - 3C = 3
and 6A + 3B + 2C = - 1
Now, solving these equations, we get
A = 1, B = -5, C = 4
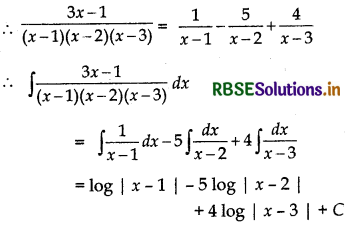
Alternative:
(3x - 1) = A(x - 2) (x - 3) + B(x - 1) (x - 3) + C(x - 1) (x - 2)
Putting x = 1
3 × 1 - 1 = A(1 - 2) (1 - 3)
⇒ 2 = A(- 1)(- 2)
⇒ 2 = 2A
⇒ A = 1
Putting x = 2
3 × 2 - 1 = B(2 - 1) (2 - 3) = B(- 1)
⇒ 6 - 1 = - B
∴ B = - 5
Putting x = 3
3 × 3 - 1 = C(3 - 1)(3 - 2)
⇒ 9 - 1 = C × 2 × 1
⇒ 8 = 2C
∴ C = 4
Values of A, B and C also obtain in this method.

Question 4.
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
Answer:
Let
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{x-2}+\frac{C}{x-3}\)
⇒ x = A(x - 2) (x - 3) + B(x - 1) (x - 3) + C(x - 1) (x - 2) .... (1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
1 = A(1 - 2) (1 - 3) + 0 + 0
⇒ 1 = A( - 1) (- 2) = 2A
∴ A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Putting x = 2 in equation (1), we get
2 = B(2 - 1) (2 - 3)
⇒ 2 = B(1) (- 1)
⇒ 2 = - B
∴ B = - 2
Putting x = 3 in equation (1), we get
3 = C(3 - 1) (3 - 2) = C(2) × 1
⇒ 3 = 2C
C = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
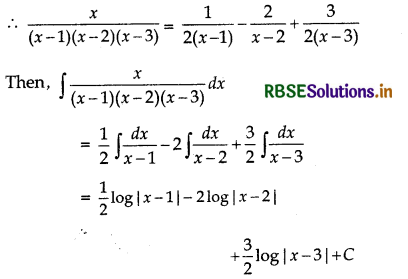
Question 5.
\(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=\frac{2 x}{(x+1)(x+2)}\)
⇒ \(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=\frac{A}{(x+1)}+\frac{B}{(x+2)}\)
⇒ 2x = A(x + 2) + B(x + 1)
Putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × (- 1) = A(- 1 + 2)A
- 2 = A
∴ A = - 2
Putting x = - 2 in equation (1). we get
2 × (- 2) = B(- 2 + 1) = - B
⇒ - 4 = - B
∴ B = 4
∴ \(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=\frac{-2}{x+1}+\frac{4}{x+2}\)
∴ \(\int \frac{2 x d x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=-2 \int \frac{d x}{x+1}+4 \int \frac{d x}{x+2}\)
= - 2 log |x + 1| + 4 log |x + 2| + C
= 4 log |x + 2| - 2 log |x + 1| + C

Question 6.
\(\frac{1-x^{2}}{x(1-2 x)}\)
Answer:
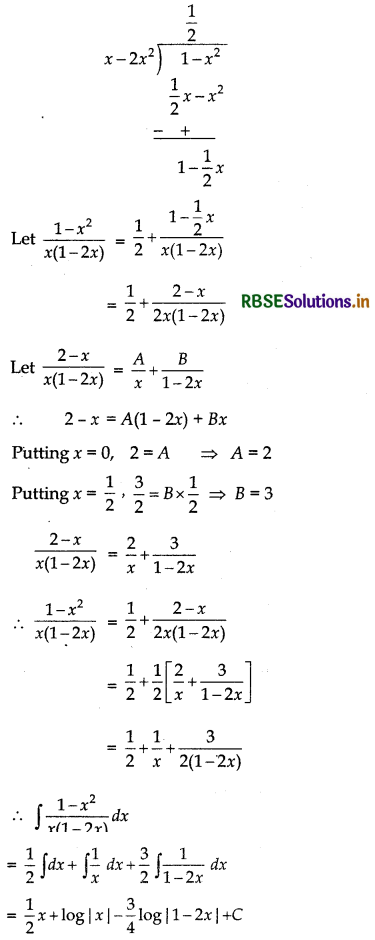
Question 7.
\(\frac{x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B x+C}{x^{2}+1}\)
⇒ x = A(x2 + 1) + (Bx + C) (x - 1)
⇒ x = A(x2 + 1) + (Bx2 + Cx - Bx - C)
⇒ x = (A + B)x2 + (C - B)x + A - C
Comparing the coefficeint of x2, and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B = 0, C - B = 1, A - C = 0
Now, solving these equation, we get
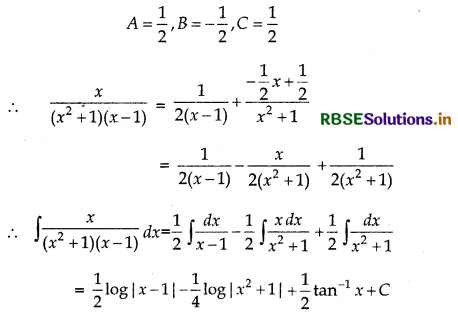
Alternative: ∫\(\frac{x d x}{x^{2}+1}\)
Putting x2 + 1 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ x dx = \(\frac{d t}{2}\)
∴ \(\int \frac{x d x}{x^{2}+1}=\frac{1}{2} \int \frac{d t}{t}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)log |t| + C1
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)log |x2 + 1| + C1

Question 8.
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x+2)}\)
Answer:
Let
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x+2)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{(x-1)^{2}}+\frac{C}{x+2}\)
⇒ x = A(x - 1) (x - 2) + B(x + 2) + C(x - 1)2 ......... (1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
1 = B(1 + 2) = 3B
∴ B = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Putting x = - 2 in equation (1), we get
- 2 = C(- 2 - 1)2
⇒ - 2 = C(- 3)2 = 9C
∴ C = - \(\frac{2}{9}\)
Again, from equation (i), we have
x = A(x2 + x - 2) + B(x + 2) + c(x2 - 2x + 1)
⇒ x = (A + C)x2 + (A + B - 2C)x - 2A + 2B + C
Comparing the coefficients of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A + C = 0
A + B - 2C = 1
and - 2A + 2B + C = 0
On solving these equations, we get
Then A = \(\frac{2}{9}\)
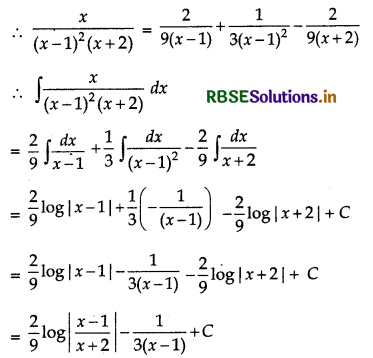
Question 9.
\(\frac{3 x+5}{x^{3}-x^{2}-x+1}\)
Answer:
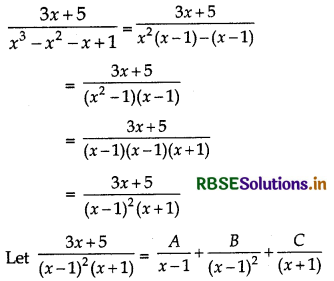
⇒ 3x + 5 = A(x - 1) (x + 1) + B(x + 1) + C(x - 1)2
⇒ 3x + 5 = A(x2 - 1) + B(x + 1) + C(x2 - 2x + 1)
⇒ 3x + 5 = (A + C)x2 + (B - 2C)x - A + B + C
Comparing the coefficeints of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A + C = 0, B - 2C = 3, - A + B + C = 5
Now, solving these equations, we get
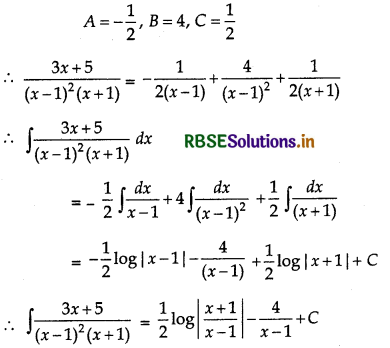

Question 10.
\(\frac{2 x-3}{\left(x^{2}-1\right)(2 x+3)}\)
Answer:
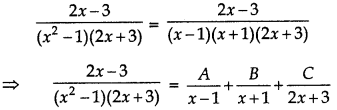
⇒ 2x - 3 = A(x + 1) (2x + 3) + B(x - 1) (2x + 3) + C(x - 1) (x + 1) ..... (1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × 1 - 3 = A(1 + 1) (2 × 1 + 3)
⇒ 2 - 3 = A × 2 × 5 = 1OA
⇒ - 1 = 10A
⇒ A = - \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × (- 1) - 3 = B( - 1 - 1) (2 × (- 1) + 3)
⇒ - 2 - 3 = B(- 2) (- 2 + 3) = - 2B
⇒ 2B = 5 ⇒ B = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Putting x = -\(\frac{3}{2}\) in equation (1), we get
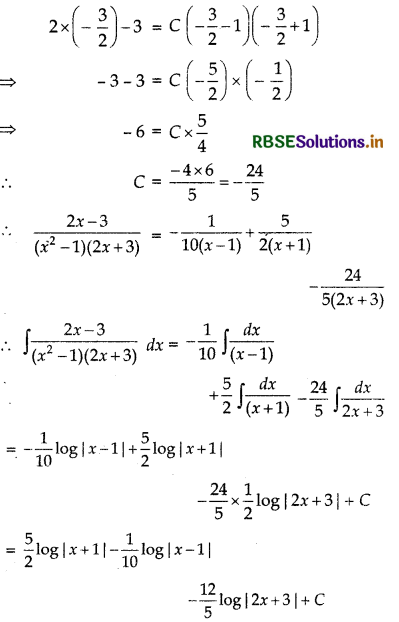
Question 11.
\(\frac{5 x}{(x+1)\left(x^{2}-4\right)}\)
Answer:
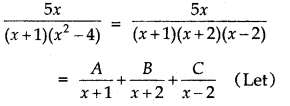
∴ 5x = A(x - 2) (x + 2) + B(x + 1) (x - 2) + C(x + 1) (x + 2) ...... (1)
Putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
5 × (- 1) = A(- 1 - 2) (- 1 + 2)
⇒ - 5 = A(- 3)(1) = - 3A
∴ A = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Putting x = -2 in equation (1), we get
5 × (- 2) = B(- 2 + 1) (- 2 - 2)
⇒ - 10 = B(- 1) (- 4) = 4B
∴ B = - \(\frac{10}{4}\) = - \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Putting x = 2 in equation (1), we get
5 × 2 = C(2 + 1) (2 + 2)
⇒ 10 = c(3) (4)
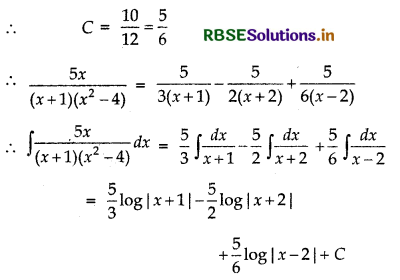

Question 12.
\(\frac{x^{3}+x+1}{x^{2}-1}\)
Answer:
Here, the given integrand is an improper rational function.
Divide x3 + x + 1 by x2 - 1, we get
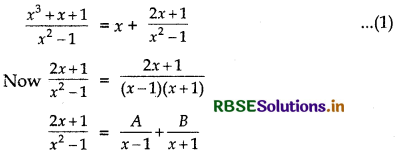
⇒ 2x + 1 = A(x + 1) + B(x - 1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × 1 + 1 = A(1 + 1) + 0
⇒ 3 = 2A
∴ A = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Again putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
2(- 1) + 1 = B(- 1 - 1) = - 2B
⇒ - 2 + 1 = - 2B .
⇒ - 1 = - 2B
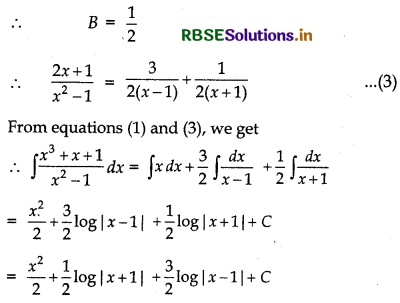
Question 13.
\(\frac{2}{(1-x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{(1-x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}=\frac{A}{(1-x)}+\frac{B x+C}{1+x^{2}}\)
⇒ 2 = A(1 + x) + (Bx + C) (1 - x)
⇒ 2 = A + Ax2 + Bx - Bx2 + C - Cx
⇒ 2 = (A - B)x2 + (B - C)x + A + C
Comparing the coefficients of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A - B = 0, B - C = 0, A + C = 2
Now, solving these equation, we get
A = 1, B = 1, C = 1
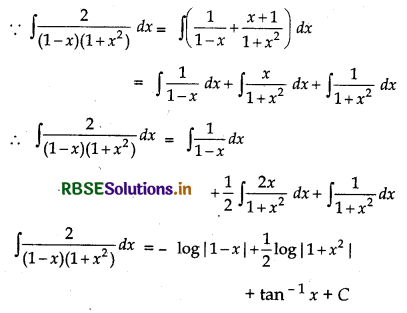

Question 14.
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}=\frac{A}{(x+2)}+\frac{B}{(x+2)^{2}}\)
⇒ 3x - 1 = A(x + 2) + B
⇒ 3x - 1 = Ax + 2A + B
Comparing the coefficient of x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A = 3, 2A + B = - 1
⇒ 2 × 3 + B = - 1
∴ B = - 1 - 6 = - 7
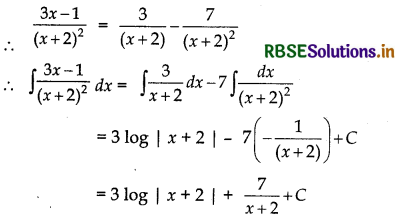
Question 15.
\(\frac{1}{x^{4}-1}\)
Answer:
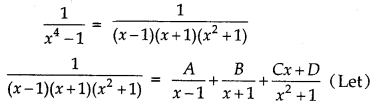
⇒ 1 = A(x + 1) (x2 + 1) + B(x2 + 1) (x - 1) + (Cx + D) (x - 1) (x + 1)
⇒ 1 = A(x3 + x2 + x + 1) + B(x3 - x2 + x - 1) + (Cx + D) (x2 - 1)
⇒ 1 = A(x3 + x2 + x + 1) + B(x3 - x2 + x - 1) + (Cx3 - Cx + Dx2 - D)
⇒ 1 = (A + B + C)x3 + (A - B + D)x2 + (A + B - C)x + A - B - D
Comparing the coefficient of x3, x2, x and constant term in both side, we get
A + B + C = 0
A - B + D = 0
A + B - C = 0
and A - B - D = 1
Now, solving these equation, we get
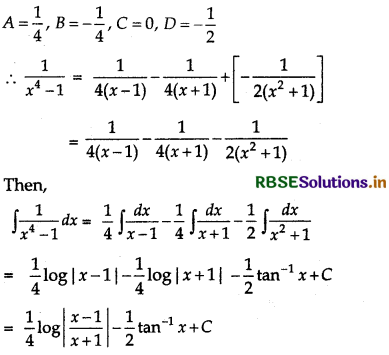

Question 16.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{n}+1\right)}\)
Answer:
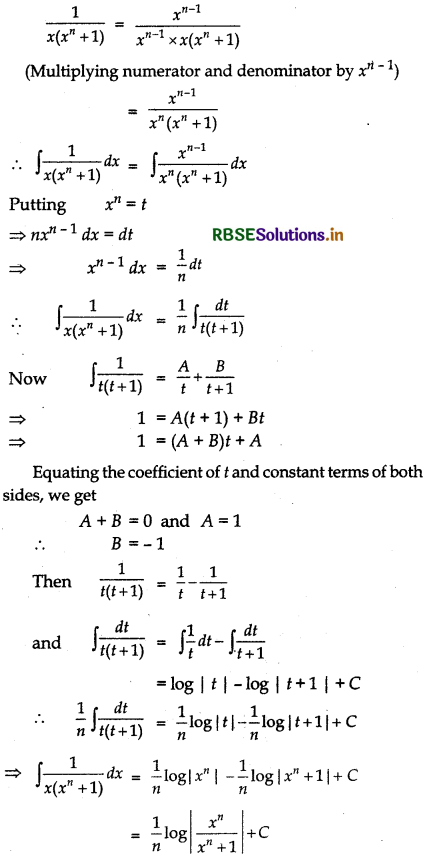
Question 17.
\(\frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}\)
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}\) dx
Putting sin x= t
⇒ cos x dx = dt
∴ \(\int \frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}=\int \frac{d t}{(1-t)(2-t)}\)
Let \(\frac{1}{(1-t)(2-t)}=\frac{A}{1-t}+\frac{B}{2-t}\)
⇒ 1 = A(2 - t) + B(1 - t)
⇒ 1 = 2A + B - (A + B)t
Equating the coefficients of f and constant terms of both sides, we get
A + B = 0 and 2A + B = 1
Now, solving these equations, we get
A = 1 and B = - 1
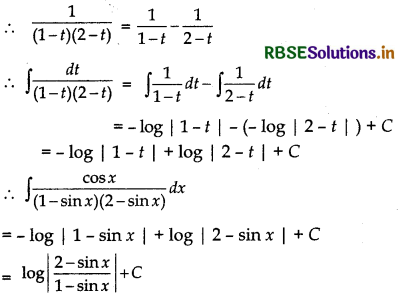

Question 18.
\(\frac{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+2\right)}{\left(x^{2}+3\right)\left(x^{2}+4\right)}\)
Answer:
Here, the given integral is improper rational function. Now putting x2 = y, we get
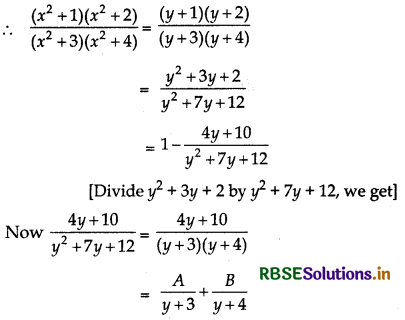
⇒ 4y + 10 = A(y + 4) + B(y + 3)
Putting y = - 3
4 × (- 3) + 10 = A(- 3 + 4)
⇒ - 12 + 10 = A
∴ A = - 2
Putting y = - 4
4(- 4) + 10 = B(- 4 + 3)
⇒ - 16 + 10 = - B
∴ B = 6


Question 19.
\(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+3\right)}\)
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+3\right)}\) dx
putting x2 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt
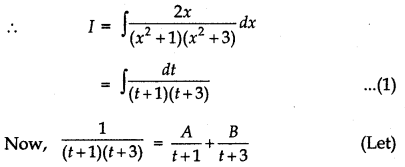
or 1 = A(t + 3) + B(t + 1)
1 = (A + B)t + 3A + B
Equating the coefficients of t and constant terms of both sides, we get
A + B = 0 and 3A + B = 1
Now, solving equations, we get
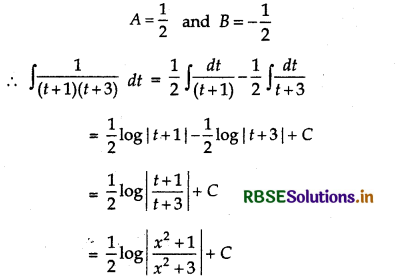
Question 20.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{4}-1\right)}\)
Answer:
Let I = \(\int \frac{1}{x\left(x^{4}-1\right)} d x=\frac{1}{4} \int \frac{4 x^{3}}{x^{4}\left(x^{4}-1\right)}\)
[Multiplying numerator and denominator by 4x3]
Putting x4 = t
⇒ 4x3 dx = dt
∴ I = \(\frac{1}{4} \int \frac{d t}{t(t-1)}\)
Now, \(\frac{1}{t(t-1)}=\frac{A}{t}+\frac{B}{t-1}\)
Equating the coefficients of t and constant terms of both sides, we get
A + B = 0, A = - 1
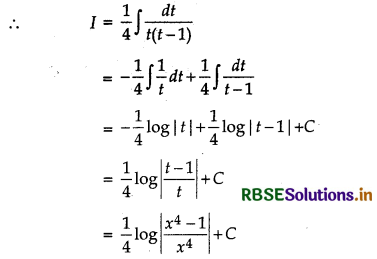

Question 21.
\(\frac{1}{\left(e^{x}-1\right)}\)
Answer:
Let I = \(\int \frac{d x}{\left(e^{x}-1\right)}=\int \frac{e^{x} d x}{e^{x}\left(e^{x}-1\right)}\)
[Multiplying numerator and denominator by ex]
Putting ex = t ⇒ ex dx = dt
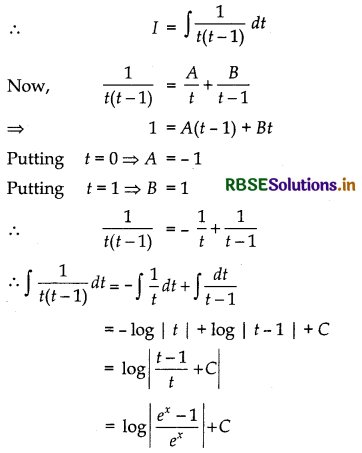
Question 22.
∫\(\frac{x d x}{(x-1)(x-2)}\) equals:
(A) log\(\left|\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{x-2}\right|\) + C
(B) log\(\left|\frac{(x-2)^{2}}{x-1}\right|\) + C
(C) log\(\left|\left(\frac{x-1}{x-2}\right)^{2}\right|\) + C
(D) log |(x - 1) (x - 2)| + C
Answer:
Let \(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)}=\frac{A}{(x-1)}+\frac{B}{(x-2)}\)
x = A(x - 2) + B(x - 1)
Putting x = 1
⇒ 1 = A(1 - 2) = - A
∴ A = - 1
Putting x = 2
⇒ 2 = B(2 - 1) = B
∴ B = 2
∴ \(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)}=\frac{-1}{x-1}+\frac{2}{x-2}\)
∴ ∫\(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)}\)
= - ∫\(\frac{d x}{x-1}\) + 2 ∫\(\frac{d x}{x-2}\)
= - log |x - 1| + 2 log |x - 2| + C
= - log |x - 1| + log | (x - 2)2 | + C
= log \(\left|\frac{(x-2)^{2}}{(x-1)}\right|\) + C
Hence, (B) is the correct answer.

Question 23.
∫\(\frac{d x}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) equals:
(A) log |x| - \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x2 + 1 | + C
(B) log |x| + \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x2 + 1| + C
(C) - log |x| + \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x2 + 1| + C
(D) \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x| + log |x2 + | + C
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{d x}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\)
= ∫\(\frac{x}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) dx
[Multiplying numerator and denominator by x]
Putting x2 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ x dx = \(\frac{1}{2}\) dt
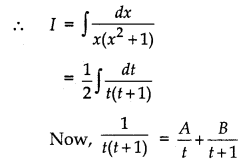
⇒ 1 = A(t + 1) + Bt
putting, t = 0
⇒ 1 = A(0 + 1) + B × 0 = A
∴ A = 1
Putting, t = - 1
⇒ 1 = B(- 1)
∴ B = - 1


- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Probability
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 12 Linear Programming
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 9 Differential Equations
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 8 Application of Integrals
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 7 Integrals
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 4 Determinants
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 3 Matrices