RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.5
Question 1.
\(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}=\frac{A}{x+1}+\frac{B}{x+2}\)
⇒ x = A(x + 2) + B(x + 1)
⇒ x = (A + B)x + 2A + B
Comparing the coefficients of x and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B = 1, 2A + B = 0
Now, solving these equations, we get
A = - 1 and B = 2
∴ \(\frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)}=\frac{-1}{x+1}+\frac{2}{x+2}\)
∴ \(\int \frac{x}{(x+1)(x+2)} d x=-\int \frac{d x}{x+1}+\int \frac{2}{x+2}\) d x
= - log |x + 1| + 2 log |x + 2| + C
= - log |x + 1| + log |x + 2|2 + C
= log\(\frac{(x+2)^{2}}{|x+1|}\) + C (∵ (x + 2)2 > 0)

Question 2.
\(\frac{1}{x^{2}-9}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{1}{x^{2}-9}=\frac{1}{(x-3)(x+3)}\)
= \(\frac{A}{x-3}+\frac{B}{x+3}\)
⇒ 1 = A(x + 3) + B(x - 3)
⇒ 1 = A(A + B)x + 3A - 3B
Comparing the coefficients of x and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B = 0 and 3A - 3B = 1
Now, solving these equations, we have
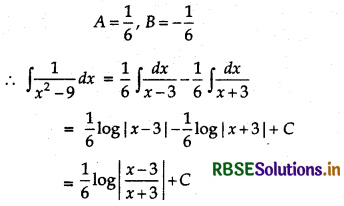
Alternative:
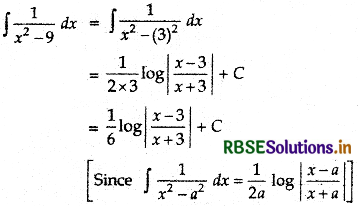
Question 3.
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{3 x-1}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
= \(\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{x-2}+\frac{C}{x-3}\)
⇒ 3x - 1 = A(x - 2) (x - 3) + B(x - 1) (x - 3) + C(x - 1) (x - 2)
⇒ 3x - 1 = A(x2 - 5x + 6) + B(x2 - 4x + 3) + C(x2 - 3x + 2)
⇒ 3x - 1 = (A + B + C)x2 + (- 5A - 4B - 3C)x + 6A + 3B + 2C
Comparing the coeffcients of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B + C = 0
- 5A - 4B - 3C = 3
and 6A + 3B + 2C = - 1
Now, solving these equations, we get
A = 1, B = -5, C = 4
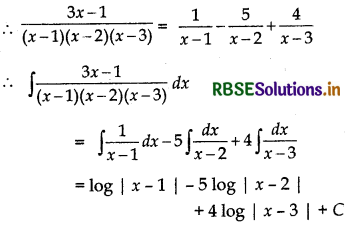
Alternative:
(3x - 1) = A(x - 2) (x - 3) + B(x - 1) (x - 3) + C(x - 1) (x - 2)
Putting x = 1
3 × 1 - 1 = A(1 - 2) (1 - 3)
⇒ 2 = A(- 1)(- 2)
⇒ 2 = 2A
⇒ A = 1
Putting x = 2
3 × 2 - 1 = B(2 - 1) (2 - 3) = B(- 1)
⇒ 6 - 1 = - B
∴ B = - 5
Putting x = 3
3 × 3 - 1 = C(3 - 1)(3 - 2)
⇒ 9 - 1 = C × 2 × 1
⇒ 8 = 2C
∴ C = 4
Values of A, B and C also obtain in this method.

Question 4.
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}\)
Answer:
Let
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{x-2}+\frac{C}{x-3}\)
⇒ x = A(x - 2) (x - 3) + B(x - 1) (x - 3) + C(x - 1) (x - 2) .... (1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
1 = A(1 - 2) (1 - 3) + 0 + 0
⇒ 1 = A( - 1) (- 2) = 2A
∴ A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Putting x = 2 in equation (1), we get
2 = B(2 - 1) (2 - 3)
⇒ 2 = B(1) (- 1)
⇒ 2 = - B
∴ B = - 2
Putting x = 3 in equation (1), we get
3 = C(3 - 1) (3 - 2) = C(2) × 1
⇒ 3 = 2C
C = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
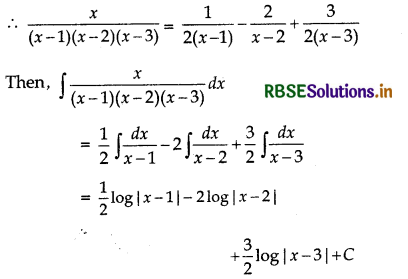
Question 5.
\(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=\frac{2 x}{(x+1)(x+2)}\)
⇒ \(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=\frac{A}{(x+1)}+\frac{B}{(x+2)}\)
⇒ 2x = A(x + 2) + B(x + 1)
Putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × (- 1) = A(- 1 + 2)A
- 2 = A
∴ A = - 2
Putting x = - 2 in equation (1). we get
2 × (- 2) = B(- 2 + 1) = - B
⇒ - 4 = - B
∴ B = 4
∴ \(\frac{2 x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=\frac{-2}{x+1}+\frac{4}{x+2}\)
∴ \(\int \frac{2 x d x}{x^{2}+3 x+2}=-2 \int \frac{d x}{x+1}+4 \int \frac{d x}{x+2}\)
= - 2 log |x + 1| + 4 log |x + 2| + C
= 4 log |x + 2| - 2 log |x + 1| + C

Question 6.
\(\frac{1-x^{2}}{x(1-2 x)}\)
Answer:
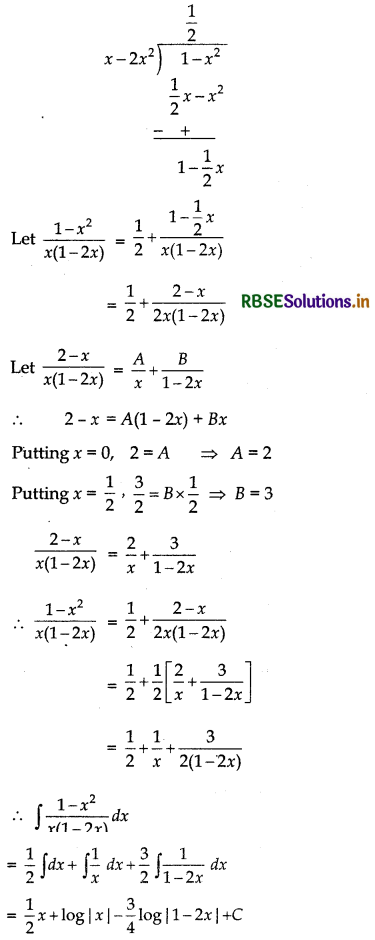
Question 7.
\(\frac{x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)}\)
Answer:
Let \(\frac{x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B x+C}{x^{2}+1}\)
⇒ x = A(x2 + 1) + (Bx + C) (x - 1)
⇒ x = A(x2 + 1) + (Bx2 + Cx - Bx - C)
⇒ x = (A + B)x2 + (C - B)x + A - C
Comparing the coefficeint of x2, and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B = 0, C - B = 1, A - C = 0
Now, solving these equation, we get
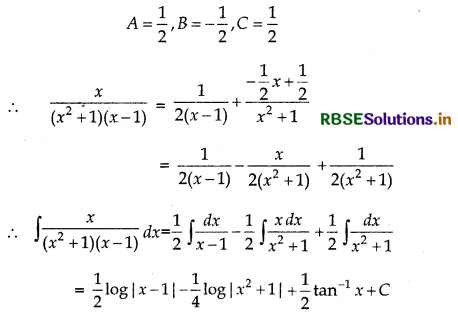
Alternative: ∫\(\frac{x d x}{x^{2}+1}\)
Putting x2 + 1 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ x dx = \(\frac{d t}{2}\)
∴ \(\int \frac{x d x}{x^{2}+1}=\frac{1}{2} \int \frac{d t}{t}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)log |t| + C1
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)log |x2 + 1| + C1

Question 8.
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x+2)}\)
Answer:
Let
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x+2)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{(x-1)^{2}}+\frac{C}{x+2}\)
⇒ x = A(x - 1) (x - 2) + B(x + 2) + C(x - 1)2 ......... (1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
1 = B(1 + 2) = 3B
∴ B = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Putting x = - 2 in equation (1), we get
- 2 = C(- 2 - 1)2
⇒ - 2 = C(- 3)2 = 9C
∴ C = - \(\frac{2}{9}\)
Again, from equation (i), we have
x = A(x2 + x - 2) + B(x + 2) + c(x2 - 2x + 1)
⇒ x = (A + C)x2 + (A + B - 2C)x - 2A + 2B + C
Comparing the coefficients of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A + C = 0
A + B - 2C = 1
and - 2A + 2B + C = 0
On solving these equations, we get
Then A = \(\frac{2}{9}\)
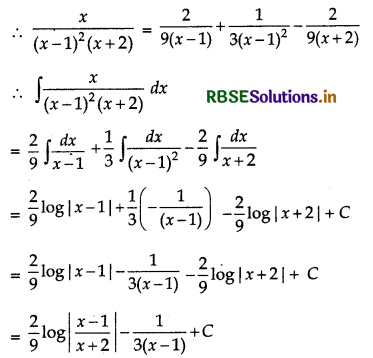
Question 9.
\(\frac{3 x+5}{x^{3}-x^{2}-x+1}\)
Answer:
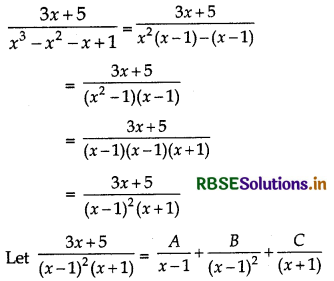
⇒ 3x + 5 = A(x - 1) (x + 1) + B(x + 1) + C(x - 1)2
⇒ 3x + 5 = A(x2 - 1) + B(x + 1) + C(x2 - 2x + 1)
⇒ 3x + 5 = (A + C)x2 + (B - 2C)x - A + B + C
Comparing the coefficeints of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A + C = 0, B - 2C = 3, - A + B + C = 5
Now, solving these equations, we get
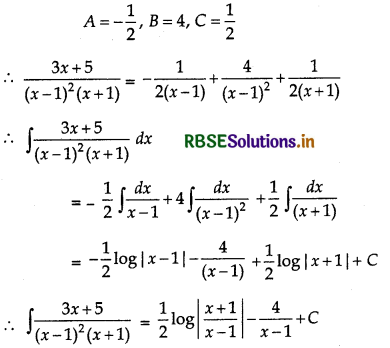

Question 10.
\(\frac{2 x-3}{\left(x^{2}-1\right)(2 x+3)}\)
Answer:
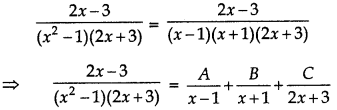
⇒ 2x - 3 = A(x + 1) (2x + 3) + B(x - 1) (2x + 3) + C(x - 1) (x + 1) ..... (1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × 1 - 3 = A(1 + 1) (2 × 1 + 3)
⇒ 2 - 3 = A × 2 × 5 = 1OA
⇒ - 1 = 10A
⇒ A = - \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × (- 1) - 3 = B( - 1 - 1) (2 × (- 1) + 3)
⇒ - 2 - 3 = B(- 2) (- 2 + 3) = - 2B
⇒ 2B = 5 ⇒ B = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Putting x = -\(\frac{3}{2}\) in equation (1), we get
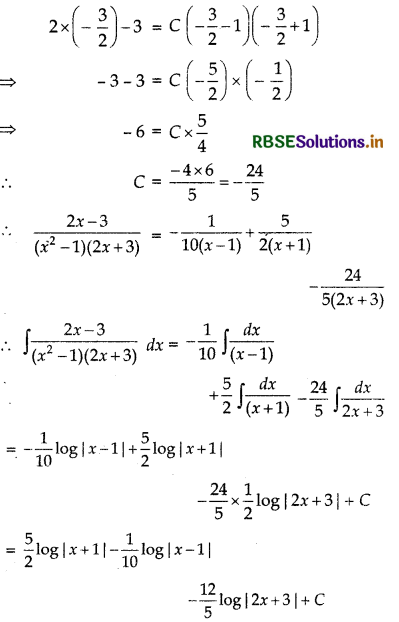
Question 11.
\(\frac{5 x}{(x+1)\left(x^{2}-4\right)}\)
Answer:
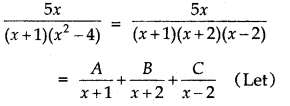
∴ 5x = A(x - 2) (x + 2) + B(x + 1) (x - 2) + C(x + 1) (x + 2) ...... (1)
Putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
5 × (- 1) = A(- 1 - 2) (- 1 + 2)
⇒ - 5 = A(- 3)(1) = - 3A
∴ A = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Putting x = -2 in equation (1), we get
5 × (- 2) = B(- 2 + 1) (- 2 - 2)
⇒ - 10 = B(- 1) (- 4) = 4B
∴ B = - \(\frac{10}{4}\) = - \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Putting x = 2 in equation (1), we get
5 × 2 = C(2 + 1) (2 + 2)
⇒ 10 = c(3) (4)
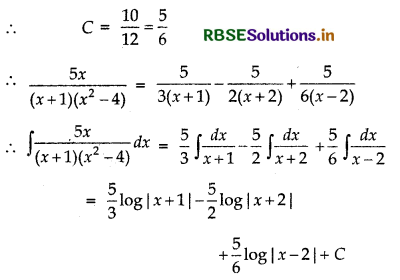

Question 12.
\(\frac{x^{3}+x+1}{x^{2}-1}\)
Answer:
Here, the given integrand is an improper rational function.
Divide x3 + x + 1 by x2 - 1, we get
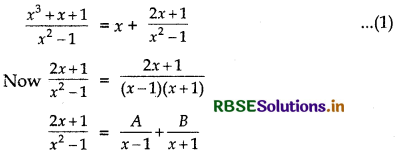
⇒ 2x + 1 = A(x + 1) + B(x - 1)
Putting x = 1 in equation (1), we get
2 × 1 + 1 = A(1 + 1) + 0
⇒ 3 = 2A
∴ A = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Again putting x = - 1 in equation (1), we get
2(- 1) + 1 = B(- 1 - 1) = - 2B
⇒ - 2 + 1 = - 2B .
⇒ - 1 = - 2B
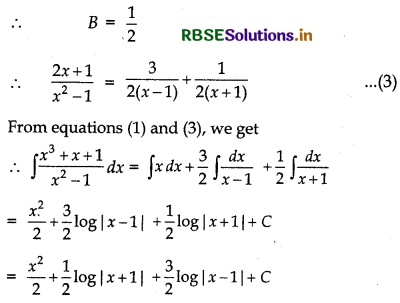
Question 13.
\(\frac{2}{(1-x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{(1-x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)}=\frac{A}{(1-x)}+\frac{B x+C}{1+x^{2}}\)
⇒ 2 = A(1 + x) + (Bx + C) (1 - x)
⇒ 2 = A + Ax2 + Bx - Bx2 + C - Cx
⇒ 2 = (A - B)x2 + (B - C)x + A + C
Comparing the coefficients of x2, x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A - B = 0, B - C = 0, A + C = 2
Now, solving these equation, we get
A = 1, B = 1, C = 1
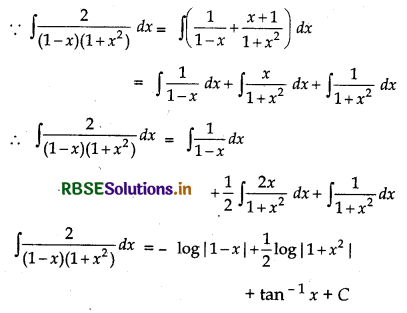

Question 14.
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3 x-1}{(x+2)^{2}}=\frac{A}{(x+2)}+\frac{B}{(x+2)^{2}}\)
⇒ 3x - 1 = A(x + 2) + B
⇒ 3x - 1 = Ax + 2A + B
Comparing the coefficient of x and constant terms in both sides, we get
A = 3, 2A + B = - 1
⇒ 2 × 3 + B = - 1
∴ B = - 1 - 6 = - 7
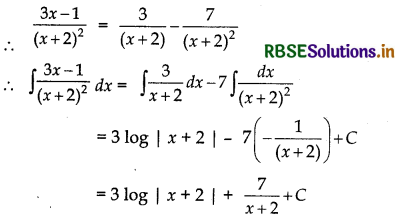
Question 15.
\(\frac{1}{x^{4}-1}\)
Answer:
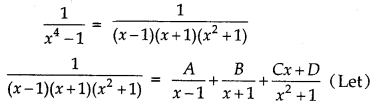
⇒ 1 = A(x + 1) (x2 + 1) + B(x2 + 1) (x - 1) + (Cx + D) (x - 1) (x + 1)
⇒ 1 = A(x3 + x2 + x + 1) + B(x3 - x2 + x - 1) + (Cx + D) (x2 - 1)
⇒ 1 = A(x3 + x2 + x + 1) + B(x3 - x2 + x - 1) + (Cx3 - Cx + Dx2 - D)
⇒ 1 = (A + B + C)x3 + (A - B + D)x2 + (A + B - C)x + A - B - D
Comparing the coefficient of x3, x2, x and constant term in both side, we get
A + B + C = 0
A - B + D = 0
A + B - C = 0
and A - B - D = 1
Now, solving these equation, we get
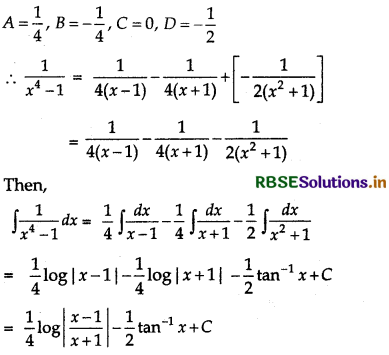

Question 16.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{n}+1\right)}\)
Answer:
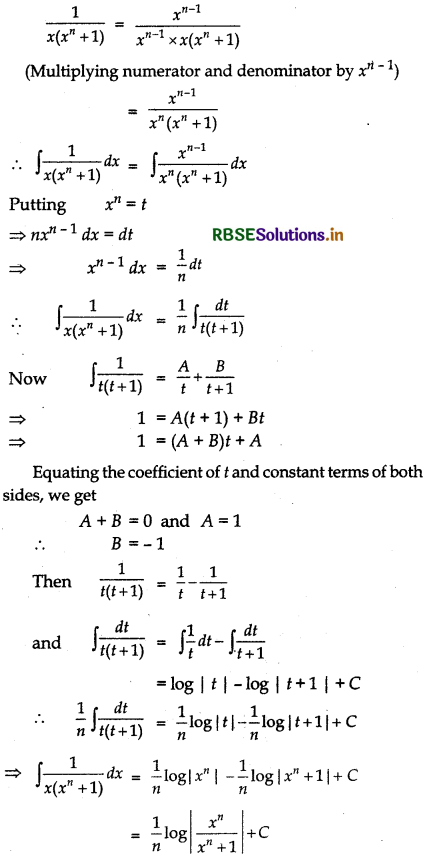
Question 17.
\(\frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}\)
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}\) dx
Putting sin x= t
⇒ cos x dx = dt
∴ \(\int \frac{\cos x}{(1-\sin x)(2-\sin x)}=\int \frac{d t}{(1-t)(2-t)}\)
Let \(\frac{1}{(1-t)(2-t)}=\frac{A}{1-t}+\frac{B}{2-t}\)
⇒ 1 = A(2 - t) + B(1 - t)
⇒ 1 = 2A + B - (A + B)t
Equating the coefficients of f and constant terms of both sides, we get
A + B = 0 and 2A + B = 1
Now, solving these equations, we get
A = 1 and B = - 1
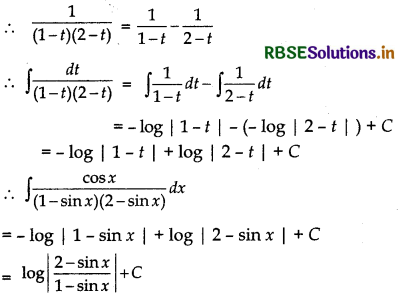

Question 18.
\(\frac{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+2\right)}{\left(x^{2}+3\right)\left(x^{2}+4\right)}\)
Answer:
Here, the given integral is improper rational function. Now putting x2 = y, we get
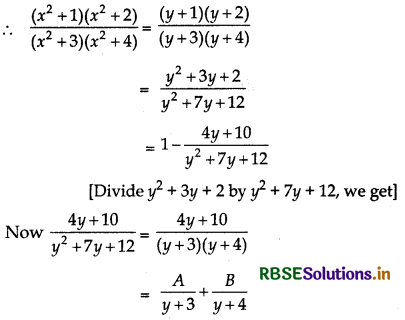
⇒ 4y + 10 = A(y + 4) + B(y + 3)
Putting y = - 3
4 × (- 3) + 10 = A(- 3 + 4)
⇒ - 12 + 10 = A
∴ A = - 2
Putting y = - 4
4(- 4) + 10 = B(- 4 + 3)
⇒ - 16 + 10 = - B
∴ B = 6


Question 19.
\(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+3\right)}\)
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)\left(x^{2}+3\right)}\) dx
putting x2 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt
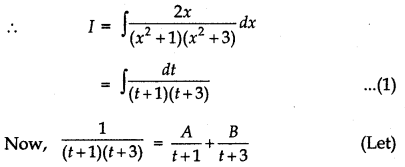
or 1 = A(t + 3) + B(t + 1)
1 = (A + B)t + 3A + B
Equating the coefficients of t and constant terms of both sides, we get
A + B = 0 and 3A + B = 1
Now, solving equations, we get
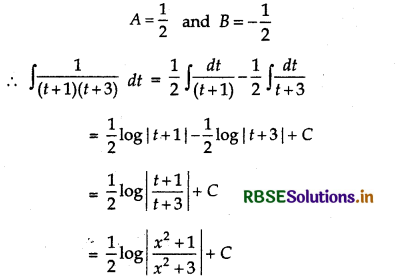
Question 20.
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x^{4}-1\right)}\)
Answer:
Let I = \(\int \frac{1}{x\left(x^{4}-1\right)} d x=\frac{1}{4} \int \frac{4 x^{3}}{x^{4}\left(x^{4}-1\right)}\)
[Multiplying numerator and denominator by 4x3]
Putting x4 = t
⇒ 4x3 dx = dt
∴ I = \(\frac{1}{4} \int \frac{d t}{t(t-1)}\)
Now, \(\frac{1}{t(t-1)}=\frac{A}{t}+\frac{B}{t-1}\)
Equating the coefficients of t and constant terms of both sides, we get
A + B = 0, A = - 1
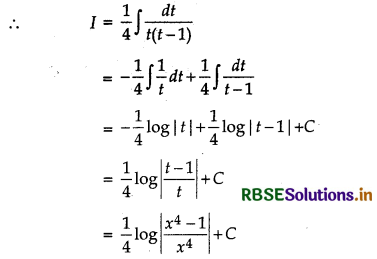

Question 21.
\(\frac{1}{\left(e^{x}-1\right)}\)
Answer:
Let I = \(\int \frac{d x}{\left(e^{x}-1\right)}=\int \frac{e^{x} d x}{e^{x}\left(e^{x}-1\right)}\)
[Multiplying numerator and denominator by ex]
Putting ex = t ⇒ ex dx = dt
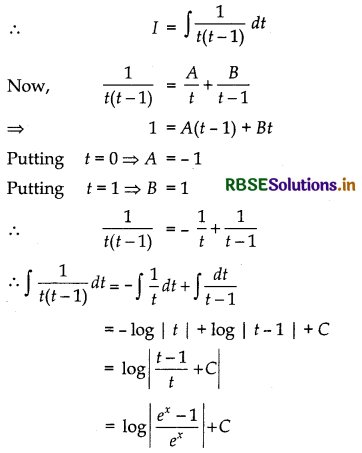
Question 22.
∫\(\frac{x d x}{(x-1)(x-2)}\) equals:
(A) log\(\left|\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{x-2}\right|\) + C
(B) log\(\left|\frac{(x-2)^{2}}{x-1}\right|\) + C
(C) log\(\left|\left(\frac{x-1}{x-2}\right)^{2}\right|\) + C
(D) log |(x - 1) (x - 2)| + C
Answer:
Let \(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)}=\frac{A}{(x-1)}+\frac{B}{(x-2)}\)
x = A(x - 2) + B(x - 1)
Putting x = 1
⇒ 1 = A(1 - 2) = - A
∴ A = - 1
Putting x = 2
⇒ 2 = B(2 - 1) = B
∴ B = 2
∴ \(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)}=\frac{-1}{x-1}+\frac{2}{x-2}\)
∴ ∫\(\frac{x}{(x-1)(x-2)}\)
= - ∫\(\frac{d x}{x-1}\) + 2 ∫\(\frac{d x}{x-2}\)
= - log |x - 1| + 2 log |x - 2| + C
= - log |x - 1| + log | (x - 2)2 | + C
= log \(\left|\frac{(x-2)^{2}}{(x-1)}\right|\) + C
Hence, (B) is the correct answer.

Question 23.
∫\(\frac{d x}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) equals:
(A) log |x| - \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x2 + 1 | + C
(B) log |x| + \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x2 + 1| + C
(C) - log |x| + \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x2 + 1| + C
(D) \(\frac{1}{2}\) log |x| + log |x2 + | + C
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{d x}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\)
= ∫\(\frac{x}{x\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) dx
[Multiplying numerator and denominator by x]
Putting x2 = t
⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ x dx = \(\frac{1}{2}\) dt
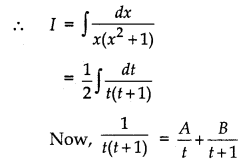
⇒ 1 = A(t + 1) + Bt
putting, t = 0
⇒ 1 = A(0 + 1) + B × 0 = A
∴ A = 1
Putting, t = - 1
⇒ 1 = B(- 1)
∴ B = - 1

