RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
RBSE Class 11 Biology Digestion and Absorption Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer among the following:
(a) Gastric juice contains :
(i) Pepsin, lipase and rennin
(ii) Trypsin, lipase and rennin.
(iii) Trypsin, pepsin and lipase
(iv) Trypsin, pepsin and rennin.
(b) Succus entericus is the name give to :
(i) a junction between ileum and large intestine
(ii) intestinal juice
(iii) swelling in the gut
(iv) Appendix
Answer:
(a) (i) Pepsin, lipase and rennin.
(b) (ii) intestinal juice.

Question 2.
Match Column-I with Column-II
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
(a) Bilirubin and biliverdin |
(i) Parotid |
|
(b) Hydrolysis of starch |
(ii) Bile |
|
(c) Digestion of fat |
(iii) Lipases |
|
(d) Salivary gland |
(iv) Amylases |
Answer:
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
(a) Bilirubin and biliverdin |
(ii) Bile |
|
(b) Hydrolysis of starch |
(iv) Amylases |
|
(c) Digestion of fat |
(iii) Lipases |
|
(d) Salivary gland |
(i) Parotid |
Question 3.
Answer briefly:
(a) Why are villi present in the intestine and not in the stomach?
(b) How does pepsinogen change into its active form?
(c) What are the basic layers of the wall of alimentary canal?
(d) How does bile help in the digestion of fats?
Answer:
(a) There are many folds and villi are found in mucosa, the internal surface of intestine. These structures are finger like. The free surface of cells of mucosa has many brush like microvilli. They increase the absorption surface 600 times. They absorb digested food. There is no complete digestion taking place in stomach, therefore, villi and microvilli are not found in stomach.
(b) Pepsinogen is converted into active pepsin by hydrochloric acid (HCl) present in gastric juice.
(c) The wall of alimentary canal has four basic layers: (i) Serosa, (ii) Muscularis, (iii) Submucosa, (iv) Mucosa.
(d) The organic salts of bile emulsify the fat in digestion of food. Emulsified fat is easily digested by lipase enzyme. Lipase converts emulsified fat into fat soluble fatty acid and glycerol.
Question 4.
State the role of pancreatic juice in digestion of proteins.
Answer:
Role of Pancreatic juice in Protein Digestion :
Pancreatic juice is watery fluid, colourless and highly alkaline. It has 96% water and its remaining part is of salt, and digestive enzymes. It is called complete digestive juice because it has protein, carbohydrate and fat digestive enzymes in alkaline medium.
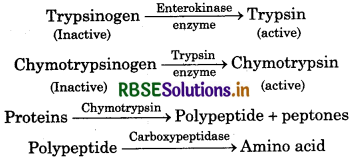
Protein digestive enzyme - Trypsin and chymotrypsin
These both enzymes combine to digest remaining protein and peptones coming from stomach as chyme and convert them into polypeptides and peptones. Initially these both enzymes secreted as inactive trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen. But in duodenum, enterokinase of intestinal juice converts inactive trypsinogen into active trypsin and trypsin converts chymotrypsinogen into active chymotrypsin.
Question 5.
Describe the process of digestion of protein in stomach.
Answer:
Digestion of Protein in Stomach : The digestive juice secreted in the gastric glands present in the stomach walls is called gastric juice. The food that enters the stomach becomes acidic on mixing with this gastric juice.
The main components of gastric juice are HCl, pepsinogen, mucous and rennin. Hydrochloric acid dissolves the bolus of food and creates an acidic medium so that pepsinogen is converted into pepsin. Pepsin is a protein digesting enzyme. It is secreted in its inactive form called pepsinogen, which then gets activated by HCl. The activated pepsin then converts proteins into proteases and peptides.
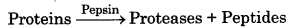
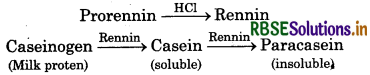
Rennin is a proteolytic enzyme, released in an infant in an inactive form called prorennin. Rennin plays an important role in the coagulation of milk.
Question 6.
Give the dental formula of human beings?
Answer:
Dental Formula of Human : The dental formula express the arrangement of teeth in each half of the upper jaw. and the lower jaw. The entire formula is multiplied by two to express the total number of teeth. The dental formula for milk teeth in children :
\(\frac{2102}{2102}\) × 2 = 20
Each half of the upper jaw and lower jaw has 2 incisors, 1 canine and 2 molars.
The dental formula for permanent teeth of human adult:
\(\frac{2123}{2123}\) × 2 = 32
Each half of the upper jaw and the lower jaw has 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars and 3 molars. An adult human has 32 permanent teeth.

Question 7.
Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. Why?
Answer:
Role of Bile juice in Digestion : Bile is a digestive juice secreted by the liver. Although it does not contain any digestive enzymes. But it plays an important role in the digestion of fat. Bile juice has bile salts such as bilirubin and biliverdin. These break down large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzymes can easily act on them. This process is known as emulsification of fats. Bile juice also makes the medium alkaline and activates lipase. Bile juice also destroys harmful bacteria.
Question 8.
Describe the digestive role of chymotrypsin. Which two other digestive enzymes of the same category are secreted by its source gland?
Answer:
Rote of chymotrypsin in Digestion : Chymotrypsin is a protein digesting enzyme, secreted from pancreas. It is secreted as its inactive form chymotrypsinogen. It is converted into active chymotrypsin in the presence of enterokinase enzyme present in intestinal juice.
It converts protein into polypeptide and peptone.
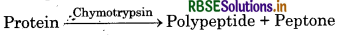
The other protein digesting enzymes secreted by pancreas are :
- Trypsinogen
- Carboxypeptidase.
Question 9.
How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested?
Answer:
Digestion of polysaccharides and disaccharides :
The digestion of carbohydrates takes place in the mouth and the small intestine region of the alimentary canal. The enzymes that act on carbohydrates are collectively known as carbohydrases.
Digestion in Mouth : As food enters the mouth, it gets mixed with saliva. Saliva, secreted by the salivary glands, contains a digestive enzyme, called salivary amylase. This enzyme partially digests the starch of food and breaks down it into maltose sugar at pH 6.8.
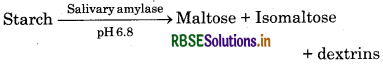
Salivary amylase continues to act in the oesophagus, but its action stops in the stomach as the contents become acidic. Hence carbohydrate digestion stops in the stomach.
Digestion in Small Intestine : Carbohydrate digestion is resumed in the small intestine. Hence, the food gets mixed with the pancreatic juice and the intestinal juice. Pancreatic juice contains the pancreatic amylase that hydrolyses the polysaccharides into disaccharides.

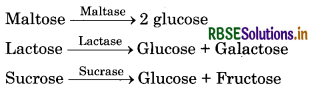
Similarly the intestinal juice contains a variety of enzymes (such as maltose, lactose, sucrose, etc.) These disaccharides helps in the digestion of disaccharides. The digestion of carbohydrates is completed in the small intestine.
Question 10.
What would happen if HCl were not secreted in the stomach?
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is secreted by oxyntic cells of gastric glands present in stomach. HCl dissolves the hard parts of the food and creates an acidic medium in stomach. The acidic medium allows pepsinogen to be converted into pepsin. Pepsin plays an important role in the digestion of proteins.
Therefore, if HCl were not secreted in the stomach, then pepsin would not be activated. This would affect protein digestion. A pH of about 1.8 is necessary for protein to be digested. This pH is achieved by HCl.

Question 11.
How does butter in your food get digested and absorbed in the body?
Answer:
Digestion of Fat: Butter is a fat product and gets digested in small intestine. The bile juice secreted by the liver contains bile salts that break down large fat globules into smaller globules, so as to increase their surface area for the action of enzyme lipase. This process is referred to as emulsification of fats.
After this, the pancreatic lipase present in the pancreatic juice and the intestinal lipase present in the intestinal juice hydrolyse the fat molecules into triglycerides, diglycerides, monoglycerides and ultimately into glycerol.

Absorption of Fats : Fat absorption is an active process. During digestion of fat, fats are hydrolysed into fatty acids and glycerol. However, since these are water insoluble, they can not be directly absorbed by the blood.
Hence, they are first incorporated into small droplets called micelles and then transported into the villi of the intestinal mucosa. They are then reformed into small microscopic particles called chylomicrons, which are small, protein-coated fat globules. These chylomicrons are transported to the lymph vessels in the villi. From the lymph vessels, the absorbed fat is finally released into the blood stream and from the blood stream, to each and every cell of the body.
Question 12.
Discuss the main steps in the digestion of proteins as the food passes through different parts of the alimentary canal.
Answer:
The digestion of protein in different parts of Alimentary Canal : The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. The enzymes that acts on proteins are called proteases.
Digestion of Proteins in Stomach : The digestive juice secreted from gastric glands present in the stomach walls is called gastric juice. The main components of gastric juice are HCl, pepsinogen and rennin. The food that enters the stomach becomes acidic on mixing with this gastric juice.
The acidic medium converts inactive pepsinogen into active pepsin. The active pepsin then converts proteins into proteoses.and peptones.

The enzyme rennin plays an important role in the coagulation of milk.
Digestion of Protein in small Intestine : The food from the stomach is acted upon by three enzymes present in the small intestine, pancreatic juice, intestinal juice (known as succus entericus) and bile juice.
Pancreatic juice contains a variety of inactive enzymes such as trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and carboxypeptidase. The enzymes are present in an inactivated state. The enzyme enterokinase secreted by the intestinal mucosa activates trypsinogen into trypsin.
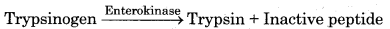
The activated trypsin then activates the other enzymes of pancreatic juice. Chymotrypsinogen is a proteolytic enzyme that breaks down proteins into peptides.

Carboxypeptidases acts on the carboxyl end of the peptide chain and help in releasing the last amino acids.

The proteases hydrolyse peptides into dipeptide and finally into amino acids.
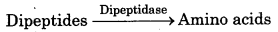
Such a way on digestion of proteins completely amino acids are formed.
Question 13.
Explain the term thecodont and diphyodont.
Answer:
Thecodont is a type of dentition in which the teeth are embedded in the deep socket of the jaw bone. Ankylosis is absent and the roots are cylindrical. Examples include living crocodilians and mammals. Diphyodont is a type of dentition in which two successive sets of teeth are developed during the life time of the organism. The first set of teeth is deciduous and the other set is permanent. The deciduous set of teeth is replaced by the permanent adult teeth. This type of dentition can be seen in humans.

Question 14.
Name different types of teeth and their number in an adult human.
Answer:
There are four different types of teeth in an adult human. They are as follows :
- Incisors : The eight teeth in the front are incisors. There are four incisors each in the upper jaw and the lower jaw. They are meant for cutting.
- Canines : The pointy teeth on either side of the incisors are canines. They are four in number, two each placed in the upper jaw and lower jaw. They are meant for tearing.
- Premolars : They are present next to the canines. They are eight in number, four each placed in the upper and the lower jaw. They are meant for grinding.
- Molars: They are present at the end of jaw, next to the premolars. There are twelve molars, six each placed in the upper jaw and the lower jaw. Hence, the dental formula in humans
\(\frac{2123}{2123}\) × 2 = 32
This means each half of the upper jaw and the lower jaw has 2 incisors, 1 canines, 2 premolars and 3 molars. Hence, an adult human has 32 permanent teeth.
Question 15.
What are the functions of liver?
Answer:
Functions of Liver:
- Deamination : Liver cells receiving surplus amino acids from blood to degrade them into pyruvic acid and ammonia. Pyruvic acid either used in energy production or glucose synthesis under gluconeogenesis.
- Synthesis of urea: Liver cells synthesise urea with the help of urease enzyme taking ammonia formed from deamination and protein metabolism and CO2. Kidney excrete it with urine taking from blood.
2NH3 + CO2 → CO(NH2)2 + H2O - Removal of excretory substances: Some excretory substances reach to duodenum with bile and then eliminated with faeces.
- Detoxification : The toxic substances produced by bacteria present in intestine reach to liver by hepatic portal vein. The liver cells destroy them into harmless substances.
- Formation and destruction of blood corpuscles : In embryonal stages RBCs are formed in liver cells. In adult stage, kupffer cells of liver eat dead RBCs and bacteria.
- Storage of inorganic substances : Liver cells store iron, copper etc., inorganic substances.
- Synthesis of blood protein : Liver cells synthesise prothrombin and fibrinogen proteins which form blood clot during injury.
- Secretion of Heparin : Liver cells secrete heparin which prevents clotting of blood in vessels.
- Phagocytosis of bacteria : Liver cells eat harmful bacteria present in blood.
- Production and storage of lymph : Lymph is formed in liver and it is stored in blood sinusoids of liver.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 The Living World
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 पुष्पी पादपों की आकारिकी