RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 9 Biomolecules
RBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are macromolecules? Give examples.
Answer:
Macromolecules are large complex molecules that occur in colloidal state in intercellular fluid. Macromolecules are formed by the polymerisation of low molecular weight micromolecules. Polysaccharides, proteins and nucleic acids are common examples of macromolecules.

Question 2.
Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phospho - diester bond.
Answer:
- Glycosidic bond: It is formed normally between carbon atoms 1 and 4 of adjacent monosaccharide units.
- Peptide bond: It is a covalent bond that joins the two apiino acids by —NH—CO—linkage.
- Phosphodiester bond: It is a strong covalent bond between phosphate and two sugar groups. Such bonds form the sugar - phosphate backbone of nucleic acids.
Question 3.
What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins?
Answer:
The helical polypeptide chain undergoes coiling and folding to form dimensional shape refered to as tertiary structure of proteins. These coils and folds are arranged to hide the non polar amino acids chains and to expose the polar side chains. The tertiary structure is held together by the weak bonds formed between various parts of the polypeptide chain.
Question 4.
Find and write down structure of 10 interesting small molecular weight biomolecules. Find if there is any industry which manufactures the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers?
Answer:
Micromolecules: They belong to monosaccharides disaccharides, fatty acids, fats, waxes, steroids, prostaglandins, amino acids and their derivatives, small peptides, nucleotides etc. (Study a book of industrial biotechnology and prepare a project report accordingly.)
Question 5.
Proteins have primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein. Can you connect this information to purity or homogeneity of a protein?
Answer:
Yes, if we are given a method to know the sequence of proteins, we can connect this information to the purity of a protein. It is known that an accurate sequence of a certain amino acid is very important for the functioning of a protein. If there is any change in the sequence, it would alter its structure, thereby altering the function. If we are provided with a method to know the sequence of an unknown protein, then using this information, we can determine its structure and compare it with any of the known correct protein sequence. Any change in the sequence can be linked to the purity or homogeneity of a protein.
For example, any one change in the sequence of haemoglobin can alter the normal haemoglobin structure to an abnormal structure that can cause sickle cell anaemia.

Question 6.
Find out and make & list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e. g., cosmetics etc.).
Answer:
Proteins used as therepeutic agents are as follows:
- Thrombin and Fibrinogen: They help in blood clotting.
- Antigen (antibody): It help in blood transfusion.
- Insulin: It helps in maintaining blood glucose level in the body.
- Renin: Renin enzyme secreted by the kidney regulates blood pressure.
Proteins are also commonly used in the manufacture of cosmetics, toxins and as biological buffers.
Question 7.
Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Answer:
Triglyceride ia a glyceride which is formed from a single molecule of glycerol, esterified with three fatty acids. It is mainly present in vegetable oils and animal fat.
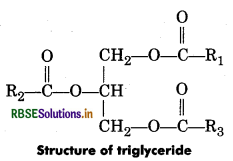
The general chemical formula of triglyceride is
R2 COO—CH2 CH(—OOCR1 )CH2 —OOCR3.
Where, R1, R2 and R3 are fatty acids. These three fatty acids can be same or different.
Question 8.
Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yoghurt from your understanding of proteins.
Answer:
Proteins are macromolecules formed by the polymerisation of amino acids. Structurally, proteins are divided into four levels:
- Primary Structure: It is linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
- Secondary Structure: The polypeptide chain is coiled to form a three dimensional structure.
- Tertiary Structure: The helical polypeptide chain is further coiled and folded to form a complex structure.
- Quaternary Structure: More than one polypeptide chains assemble to form the quaternary structure.
Milk has many globular proteins. When milk is converted into curd or yoghurt, these complex proteins get denatured. Thus converting globular proteins into fibrous proteins. Therefore, by the process of denaturation, the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins are destroyed.
Question 9.
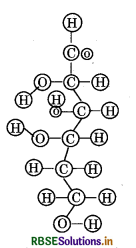
Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and stick models).
Answer:
Ball and stick models are 3 - D molecular models that can be used to describe the structure of biomolecules. In ball and stick model, the atoms are represented as balls whereas the bonds that hold the atoms are represented by the sticks. Double and triple bonds are represented by springs that form curved connections between the balls. The size and colour of various atoms are different and are depicted by the relative size of the balls. It is the most fundamental and common model of representing biomolecular structures.
Question 10.
Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Answer:
Titrating a neutral or basic amino acid against a weak base will dissociate only one functional group, whereas titration between acidic amino acid and a weak acid will dissociate two or more functional groups.

Question 11.
Draw the structure of amino acid alanine.
Answer:
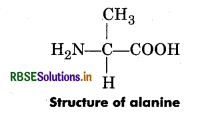
Question 12.
What are gums made of? Is fevicol different?
Answer:
Gums are heteropolysaccharides. They are made from two or more different types of monosaccharides. On the other hand, fevicol is polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) glue. It is not a polysaccharide.
Question 13.
Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine for them.
Answer:
Qualitative test for proteins, amino acids and fats:
- Biuret Test: The biuret test for protein identifies the presence of protein by producing light blue or purple colour of the solution.
- Grease test for Oil: Certain oils give a translucent stain on brown paper. This test can be used to show the presence of fat in vegetable oils.
- Ninhydrin test: If Ninhydrin reagent is added to the solution, then the colourless solution changes to pink, blue or purple colour depending on the type of amino acid.
table 1
Question 14.
Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere and compare it with how much of paper is manufactured by man and hence what is the consumption of plant material by man annually. What is a loss of vegetation?
Answer:
Approximately, 100 billion tonnes of cellulose are made per year by all the plants in the biosphere and it takes 17 full grown trees to make one ton of paper. Trees are also used to fulfil the other requirements of man such as for timber, food, medicine etc. Hence, it is difficult to calculate the annual consumption of plant material by man.
Question 15.
Describe the important properties of enzymes.
Answer:
Properties of enzymes are:
- Enzymes are complex micromolecules with high molecular weight.
- They catalyse biochemical reactions in a cell. They help in the breakdown of large molecules into smaller molecules or bring together two smaller molecules to form a large molecule.
- Enzymes do not start a reaction. However, they help in accelerating it.
- Enzymes affect the rate of biochemical reaction and not the direction.
- Most of the enzymes have high turnover number. Turnover number of an enzyme is the number of molecules of a substance that is acted upon by an enzyme per minute. High turnover number of enzyme increases the efficiency of reaction.
- Enzymes are specific in action.
- Enzymatic activity decreases with high increase in temperature.
- They show maximum activity at an optimum pH of 6 - 8.
- The velocity of enzyme increases with increase in substrate concentration and then, ultimately reaches maximum velocity.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 The Living World
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 पुष्पी पादपों की आकारिकी
- RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions Chapter 1 The Living World