RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
RBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation in Animals Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer in one word or one line.
(i) Give the common name of Periplanata americana.
(ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworm?
(iii) What is the position of ovaries in cockroach?
(iv) How many segments are present in the abdomen of cockroach?
(v) Where do you find Malpighian tubules?
Answer:
(i) American cockroach.
(ii) 4 pairs of spermathecae are found in Earthworm.
(iii) Two ovaries are found lying laterally around 2nd to 6th abdominal segments.
(iv) 10 segments.
(v) Malpighian tubules are found at the junction of midgut and the hindgut of the alimentary canals of insects.

Question 2.
Answer the following:
(i) What is the function of nephridia?
(ii) How many types of nephridia are found in earthworm based on their location?
Answer:
(i) Nephridia perform the function of excretion and osmoregulation in earthworm.
(ii) Three types of nephridia are found in the earthworm based on their location. They are:
- Septal nephridia present on both sides of inter segmental septa of segment 15 to the last that open into intestine.
- Integumentary nephridia are attached to the lining of the body wall of segment 3 to the last that opens on the body surface.
- Pharyngeal nephridia is present as three paired tufts in the 4th, 5th and 6th segment.
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of the reproductive organs of an earthworm.
Answer:
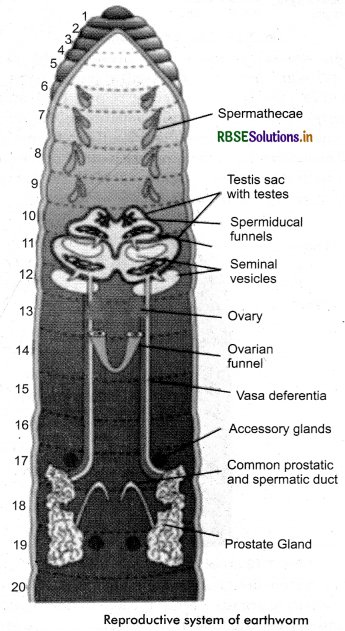
Question 4.
Draw a - labelled diagram of alimentary canal of a cockroach.
Answer:
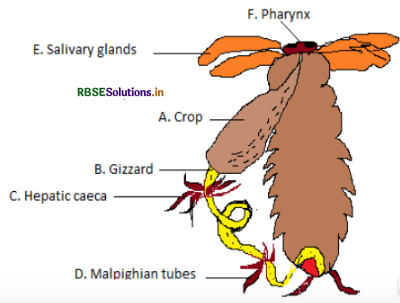
Question 5.
Distinguish between the following:
(a) Prostomium and peristomium.
(b) Septal nephridium and pharyngeal nephridium.
Answer:
(a) Differences between Prostomium and Peristomium
|
Prostomium |
Peristomium |
|
1. Small, fleshy lobe, serves as a covering for the mouth as a wedge to force open cracks in the soil wherein the earthworm crawls. |
1. It is the crescentic aperture at the anterior end of the first segment of the earthworm comprising the mouth. |
(b) Differences between septal nephridium and pharyngeal nephridium.
|
Septal Nephridium |
Pharyngeal Nephridium |
|
1. Found at the anterior and posterior surface of septa occuring after segment 15 in earthworm. |
1. Found in three pairs in the 4th, 5th and 6th segment? located on either side of alimentary canal. |
|
2. Excretory matter is discharged into the lumen of the alimentary canal. |
2. Excretory matter is discharged into the gut in the pharynx or buccal cavity. |
Question 6.
What are the cellular components of blood?
Answer:
The cellular components of blood are: Red blood corpuscles (RBCs), white blood corpuscles (WBCs) and blood platelates.

Question 7.
What are the following and where do you find them in animal body?
(a) Chondriocytes
(b) Axons
(c) Ciliated epithelium.
Answer:
(a) Chondriocytes are the cells of cartilage. Cartilage is present in the tip of nose, outer ear joints between adjacent bones of the vertebral column, limbs and hands in adults. They are rounded large and mature cells that are found occuring in clusters in the matrix of cartilage.
(b) An axon is a long slender projection of neuron or nerve cell. They are present throughout the body. They emerge from the cyton and are responsible to conduct nerve impulses away from the all body. They terminate in a group of branches known as terminal arborisations.
(c) If the columnar or cuboidal cells bear cilia on their free surface they are called ciliated epithelium. They are present in the inner surface of hollow organs like branchioles and fallopian tube. It comprises of fine vibratile cytoplasmic processes that are termed as cilia found on its free surface. The cells is functional in trapping foreign substances and dust.
Question 8.
Describe various types of epithelial tissues with the help of labelled diagrams.
Answer:
We commonly refer to an epithelial tissue as epithelium (pl.: epithelia). This tissue has a free surface, which faces either a body fluid or the outside environment and thus provides a covering or a lining for some part of the body. The cells are compactly packed with little intercellular matrix. There are two types of epithelial tissues namely-
- Simple epithelium and
- Compound epithelium.
Question 9.
Distinguish between:
(a) Simple epithelium and compound epithelium.
(b) Cardiac muscle and striated muscle.
(c) Dense regular and dense irregular connective tissues.
(d) Adipose and blood tissue.
(e) Simple gland and compound gland.
Answer:
(a)
|
Simple Epithelium |
Compound Epithelium |
|
1. Composed of one layer of cells. |
1. Consisting many layers of cells. |
|
2. They are involved in the function of absorption and secretion. |
2. They are involved in the protection. |
|
3. Present in the stomach lining and intestine. |
3. Present in the lining of the buccal cavity and pharynx. |
|
4. Cells rest on basement membrane. |
4. Cells of the lowermost layer rest on the basement membrane. |
(b)
|
Cardiac Muscle |
Striated Muscle |
|
1. They are involuntary in function, |
1. They are voluntary in function |
|
2. They are found in heart. |
2. Found in triceps, limbs and biceps. |
|
3. Branched fibres. |
3. Unbranched fibres. |
|
4. Uninucleated. |
4. Multinucleated. |
(c)
|
Dense Regular Connective Tissue |
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue |
|
1. Collagen fibres are present in rows between parallel boundless fibres. |
1. Consists of fibroblasts having several fibres that are differently oriented. |
|
2. Regular pattern of fibres observed. |
2. Irregular patterns of fibres observed. |
|
3. They are present in tendons and ligaments. |
3. They are present in skin. |
(d)
|
Adipose Tissue |
Blood Tissue |
|
1. It is made of collagen fibres, |
1. It consists of RBCs, WBCs, platelates and blood plasma. |
|
2. It is loose connective tissue. |
2. It is fluid connective tissue. |
|
3. Its function is to synthesize, store and metabolise the fats. |
3. Its function is to transport food, gases, hormones and waste. |
|
4. Present beneath the skin. |
4. Present in the blood vessels. |
(e)
|
Simple Gland |
Compound Gland |
|
1. They contain isolated glandular cells. |
1. Contains cluster of secretory cells. |
|
2. They are unicellular. |
2. They are multicellular. |
|
3. Examples: Goblet cells of the alimentary canal. |
3. Examples: Salivary glands. |
Question 10.
Mark the odd one in each series:
(a) Areolar tissue; blood; neuron; tendon.
(b) RBC; WBC; platelets; cartilage.
(c) Exocrine; endocrine; salivary gland; ligament.
(d) Maxilla; mandible; labrum; antennae
(e) Protonema; mesothorax; metathorax; coxa.
Answer:
(a) Neuron
(b) Cartilage
(c) Ligament
(d) Antennae.
Question 11.
Match the terms in column I with those in column II:
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
(a) Compound epithelium |
(i)Alimentary canal |
|
(b) Compound eye |
(ii) Cockroach |
|
(c) Septal nephridia |
(iii) Skin |
|
(d) Open circulatory system |
(iv) Mosaic vision |
|
(e) Thphlosole |
(v) Earthworm |
|
(f) Osteocytes |
(vi) Phallomere |
|
(g) Genitalia |
(vii) Bone |
Answer:
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
(a) Compound epithelium |
(iii) Skin |
|
(b) Compound eye |
(iv) Mosaic vision |
|
(c) Septal nephridia |
(v) Earthworm |
|
(d) Open circulatory system |
(ii) Cockroach |
|
(e) Thphlosole |
(i)Alimentary canal |
|
(f) Osteocytes |
(vii) Bone |
|
(g) Genitalia |
(vi) Phallomere |
Question 12.
Mention briefly about the circulatory system of earthworm.
Answer:
Another important organ system is the circulatory system. The earthworm has a closed circulatory system. An earthworm circulates blood exclusively through vessels. There are three main vessels that supply the blood to organs within the earthworm. These vessels are the aortic arches, dorsal blood vessels, and ventral blood vessels. The aortic arches function like a human heart. There are five pairs of aortic arches, which have the responsibility of pumping blood into the dorsal and ventral blood vessels. The dorsal blood vessels are responsible for carrying blood to the front of the earthworm’s body. The ventral blood vessels are responsible for carrying blood to the back of the earthworm’s body.
Question 13.
Draw a neat diagram of digestive system of frog.
Answer:
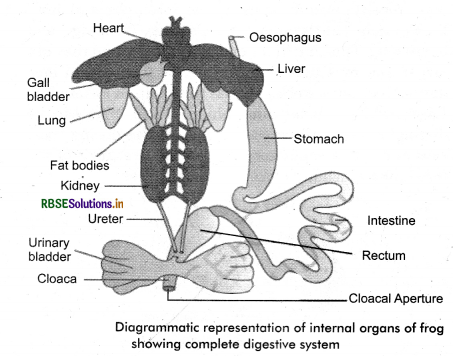
Question 14.
Mention the functions of following:
(a) Ureters in frog.
(b) malpighian tubules.
(c) Body wall in earthworm.
Answer:
(a) Ureters in frog: Acts as urinogential duct which carries urine and sperm in the male frog.
(b) Malpighian tubules: These are excretory organs in cockroaches.
(c) Bodywall in earthworm: Helps in movement and burrowing.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 The Living World
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 पुष्पी पादपों की आकारिकी
- RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions Chapter 1 The Living World