RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 7 Integrals
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 7 Integrals Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Important Questions Integrals
Question 1.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{2}{1+\cos 2 x}\) dx
Answer:
∫\(\frac{2}{1+\cos 2 x}\) dx = ∫\(\frac{2}{2 \cos ^2 x}\) dx [∵cos 2θ = 2 cos2θ - 1]
= ∫ sec2 x dx = tan x + C

Question 2.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{2 \cos x}{\sin ^2 x}\) dx
Answer:
∫\(\frac{2 \cos x}{\sin ^2 x}\) dx = 2∫\(\frac{1}{\sin x} \cdot \frac{\cos x}{\sin x}\) dx
= 2 ∫cosec x cot x dx
= 2 (- cosec x) + C
= - \(\frac{2}{\sin x}\) + C
Question 3.
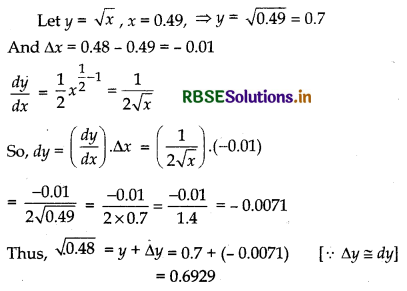
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{x^3-1}{x^2}\) dx
Answer:
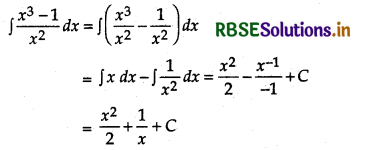
Question 4.
Evaluate: ∫2x dx
Answer:
∫2x dx = \(\frac{2^x}{\log 2}\) + C [∵ ∫ax dx = \(\frac{a^x}{\log a}\) + C]
Question 5.
Evaluate: ∫\(\sqrt{1-\sin 2 x}\) dx, \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)< x < \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
Answer:
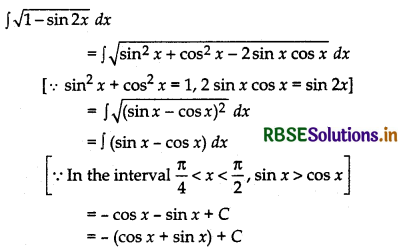

Question 6.
Find the integral of the following functions with respect to x: \(\frac{3 x^2}{1+x^3}\)
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{3 x^2}{1+x^3}\)
Putting 1 + x3 = t
Then, 3x2 dx = dt
∴ ∫\(\frac{3 x^2}{1+x^3}\) dx = ∫\(\frac{d t}{t}\)
= log |t| + C
= log |1 + x3| + C
Question 7.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{\sec x}{\log (\sec x+\tan x)}\) dx
Answer:
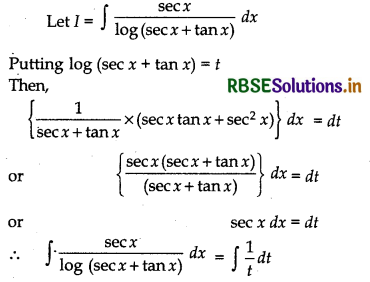
= log |t| + C
= log |log (sec x + tan x)| + C
Question 8.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{\cos x}{\cos (x-b)}\) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{\cos x}{\cos (x-b)}\) dx
Putting x - b = t
and x = t + b
Then, dx = dt
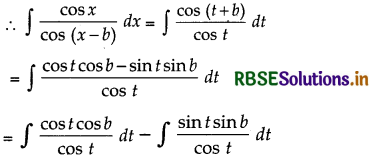
= cos b∫1 dt - sin b∫ tan t dt
= cos b × t - sin b(- log |cos t|) + C
= t cos b + sin b log |cos t| + C
= (x - b)cos b + sin b log |cos(x - b)| + C
Question 9.
Evaluate ∫\(\frac{\sin ^6 x}{\cos ^8 x}\) dx
Answer:
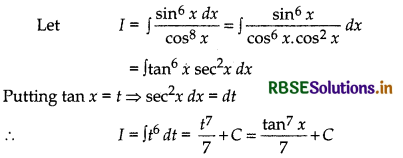

Question 10.
Evaluate: ∫\(\sqrt{1-\sin x}\) dx
Answer:
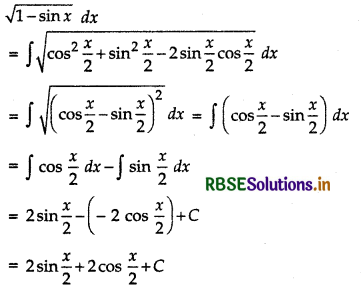
Question 11.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{d x}{\sin x+\cos x}\)
Answer:
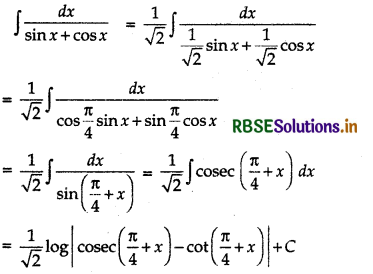
Question 12.
Evaluate:
(i) ∫\(\frac{\sin 8 x}{\cos 4 x}\) dx
Answer:
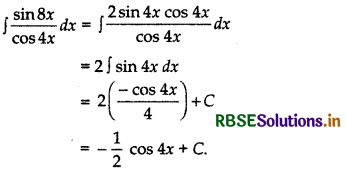
(ii) ∫\(\frac{\sin 6 x}{\sin 3 x}\)
Answer:
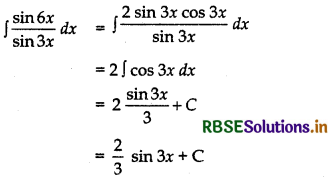
Question 13.
Evaluate: ∫cos3 x dx
Answer:
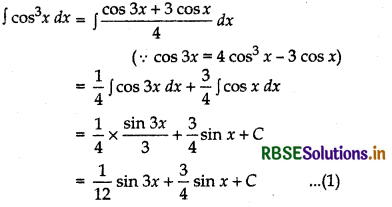

Question 14.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{x^2+4}{x^4+16}\) dx
Answer:

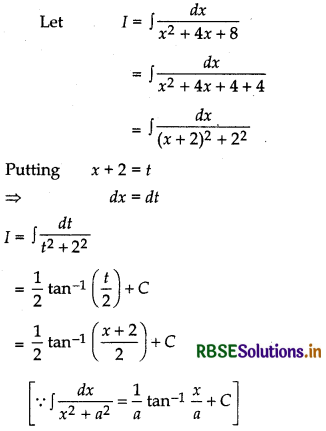
Question 15.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{d x}{x^2+4 x+8}\)
Answer:

Question 16.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{d x}{5-8 x-x^2}\)
Answer:

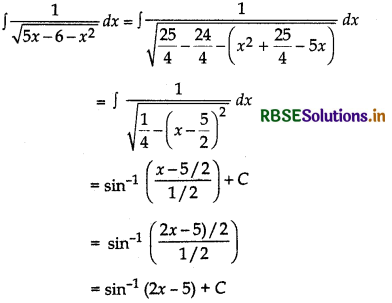
Question 17.
Find the following: ∫\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{5 x-6-x^2}}\)
Answer:
Question 18.
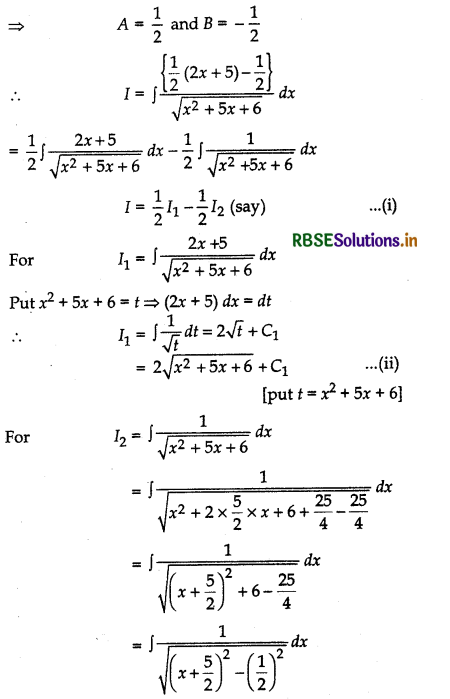
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+5 x+6}}\) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{x+2}{\sqrt{x^2+5 x+6}}\) dx
Let A and B be two numbers such that:
x + 2 = A \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x2 + 5x + 6) + B
⇒ x + 2 = A(2x + 5) + B
On equating the coefficients of x and constant terms from both sides, we get
2A = 1 and 5A + B = 2
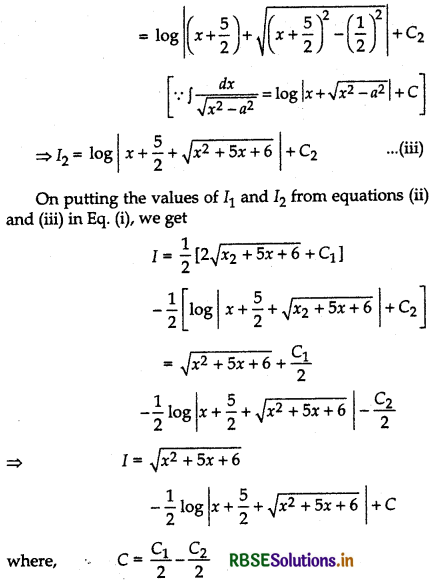

Question 19.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{5 x-2}{1+2 x+3 x^2}\) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{5 x-2}{1+2 x+3 x^2}\) dx ...... (i)
Let A and B be two numbers such that:
5x - 2 = A \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (1 + 2x + 3x2) + B
⇒ 5x - 2 = A(2 + 6x) + B
On comparing the coefficients of x and constrant terms,
we get
5 = 6A ⇒ A = \(\frac{5}{6}\)
and - 2 = 2A + B ⇒ B = - 2A - 2

Question 20.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{\cos \theta}{\left(4+\sin ^2 \theta\right)\left(5-4 \cos ^2 \theta\right)}\) dθ
Answer:


Question 21.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}{\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x^2-5\right)}\) dx
Answer:
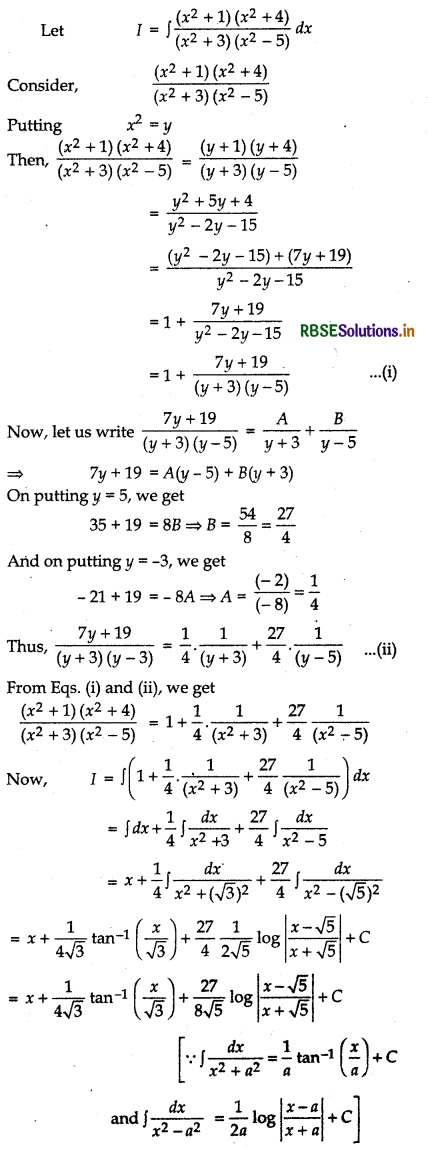
Question 22.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{d x}{\sin x+\sin 2 x}\)
Answer:
Let
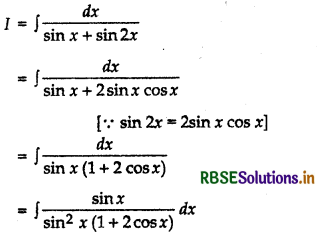
[Multiplying numerator and denominator by sin x]
= ∫\(\frac{\sin x}{\left(1-\cos ^2 x\right)(1+2 \cos x)}\) dx
Put cos x = t
⇒ - sin x dx = dt
⇒ sin x dx = - dt
∴ I = ∫\(\frac{-d t}{\left(1-t^2\right)(1+2 t)}\)
= ∫\(\frac{-d t}{(1-t)(1+t)(1+2 t)}\) ...... (i)
Now, using partial fraction,
Let \(\frac{1}{(1-t)(1+t)(1+2 t)}\) = \(\frac{A}{1-t}+\frac{B}{1+t}+\frac{C}{1+2 t}\) ...... (ii)
⇒ 1 = (1 + t) (1 + 2t)A + (1 - t) (1 + 2t)B + (1 - t) (1 + t)C .......... (iii)
On putting t = - 1 in Eq.(iii), we get
1 + (2) (- 1) B ⇒ B = - \(\frac{1}{2}\)
On putting t = 1 in Eq. (lu), we get
1 = 2. (3) A ⇒ A = - \(\frac{1}{6}\)
On putting t = - \(\frac{1}{2}\) in Eq. (iii), we get

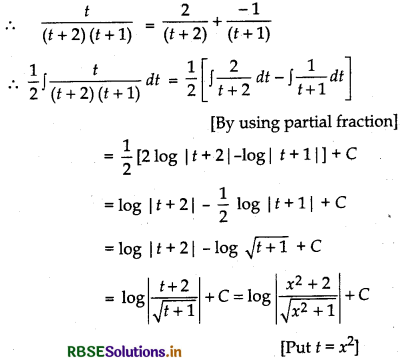
Question 23.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{x^3}{x^4+3 x^2+2}\) dx
Answer:
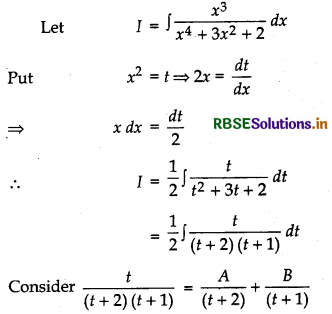
⇒ t = A(t + 1) + B(t + 2)
⇒ t = (A + B)t + A + 2B
Comparing the coefficients of t and constant terms in both sides, we have
A + B = 1
A + 2B = 0 .
Now, solving these equations, we get
A = 2 and B = - 1
Question 24.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{2 x^2+1}{x^2\left(x^2+4\right)}\) dx
Answer:
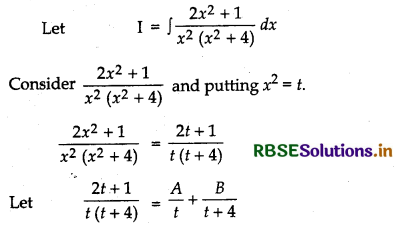
⇒ 2t + 1 = A(t + 4) + Bt
⇒ 2t + 1 = (A + B)t + 4A
On comparing the coefficients of t and constant terms, we get
A + B = 2
and 4A = 1
On solving these two equations, we get
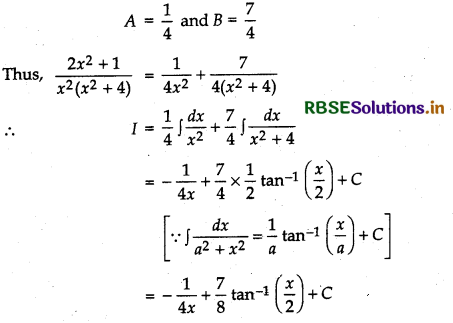

Question 25.
Find ∫\(\frac{(2 x-5) e^{2 x}}{(2 x-3)^3}\) dx
Answer:
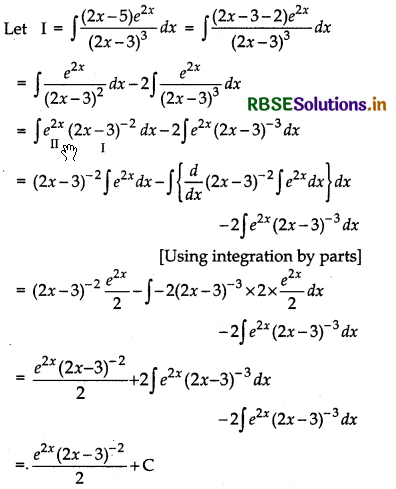
Question 26.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{x^2}{(x \sin x+\cos x)^2}\) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{x^2}{(x \sin x+\cos x)^2}\) dx
Multiplying Nr and Dr by cos x, we get
I = ∫\(\frac{x^2}{(x \sin x+\cos x)^2} \cdot \frac{\cos x}{\cos x}\) dx
⇒ I = ∫\(\frac{x \cos x}{(x \sin x+\cos x)^2}\). x sec x dx ........ (i)
Putting x sin x + cos x = t
⇒ (x cos x + sin x - sin x)dx = dt
⇒ x cos x dx = dt
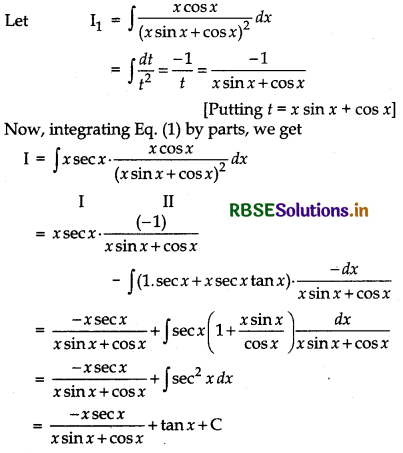

Question 27.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{\sqrt{1-\sin x}}{1+\cos x}\) e-x/2 dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫\(\frac{\sqrt{1-\sin x}}{1+\cos x}\) e-x/2 dx
Put \(\frac{-x}{2}\) = t ⇒ dx = - 2 dt

Question 28.
Evaluate: ∫\(\frac{\sqrt{x^2+1}\left[\log \left|x^2+1\right|-2 \log |x|\right]}{x^4}\)
Answer:
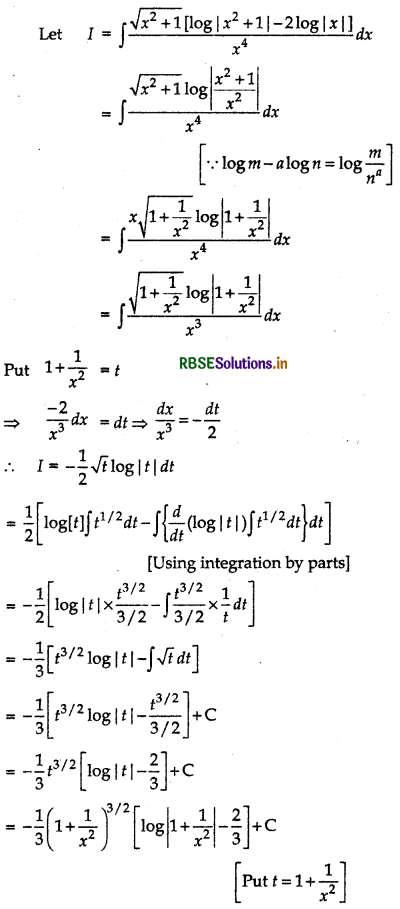

Question 29.
Evaluate: ∫\(\sqrt{x^2-x+1}\) dx
Answer:
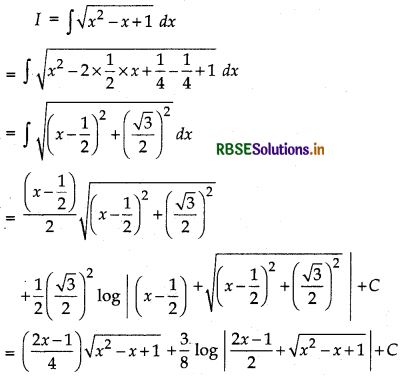
Question 30.
Evaluate: ∫(2x + 5)\(\sqrt{10-4 x-3 x^2}\) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫(2x + 5)\(\sqrt{10-4 x-3 x^2}\) dx
Now, let us write 2x + 5 = A \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (10 - 4x - 3x2) + B
where A and B are constants.
⇒ 2x + 5 = A(- 4 - 6x) + B ........ (i)
⇒ 2x + 5 = - 6Ax + (B - 4A)
On comparing the coefficient .of x and the constant term, we get
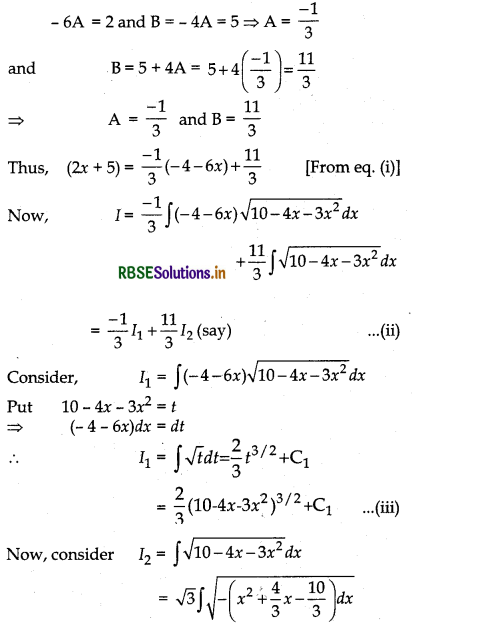
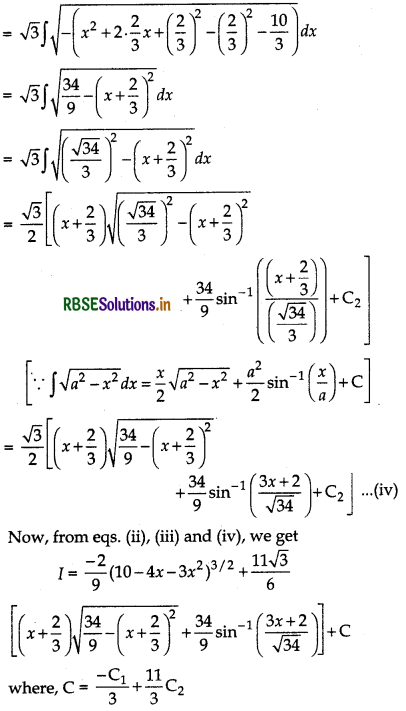

Question 31.
Evaluate: ∫(x - 3) \(\sqrt{x^2+3 x-18}\) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫(x - 3) \(\sqrt{x^2+3 x-18}\) dx
Now, let us write (x - 3) as
x - 3 = A \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x2 - 3x - 18) + B
⇒ x - 3 = A(2x + 3) + B
On equating the coefficient’s of x and constant terms from both sides, we get
2A = 1
and 3A + B = - 3
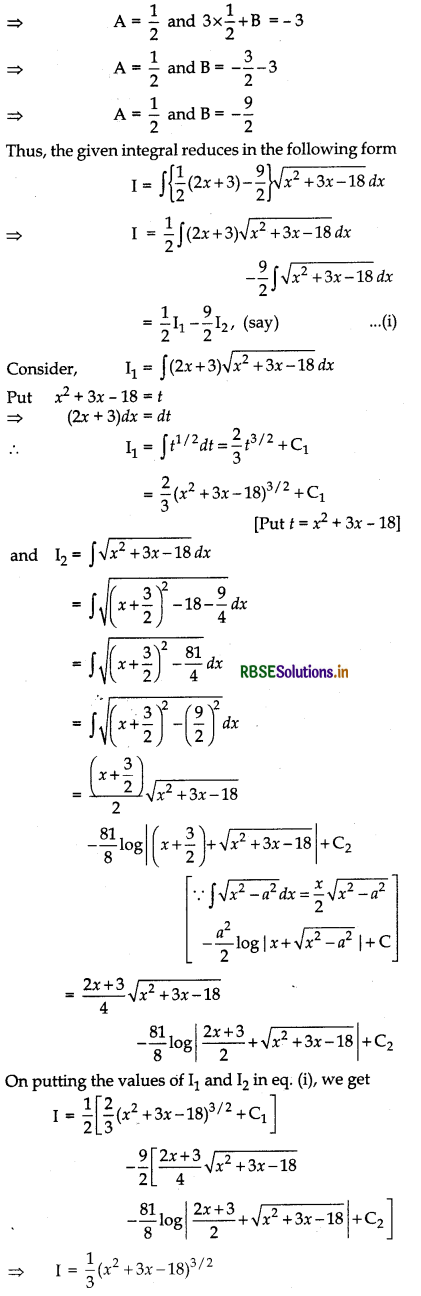
Question 32.
Evaluate \(\int_1^3\) (3x2 + 1) dx by the method of limit of sum.
Answer:
We have \(\int_1^3\) (3x2 + 1) dx
Here, a = 1, b = 3, nh = b - a = 3 - 1 = 2
and f(x) = 3x2 + 1
f(1) = 3(1)2 + 1 = 4
f(1 + h) = 3(1 + h)2 + 1 = 4 + 6h(1) + 3h2(1)2
f(1 + 2h) = 3(1 + 2h)2 + 1 = 4 + 6h(2) + 3h2(2)2
f[1 + (n - 1)h] = 3[1 + (n - 1)h]2 + 1
= 4 + 6h(n - 1) + 3h2(n - 1)2

Question 33.
Evaluate \(\int_1^3\) (2x2 + 5x) dx as a limit of sum.
Answer:
Let I = \(\int_1^3\) (2x2 + 5x) dx
Here, a = 1, b = 3, f(x) = 2x2 + 5x, and nh = b - a = 3 - 1 = 2
∴ f(1) = 2(1)2 + 5(1) = 2 + 5 = 7
f(1 + h) = 2(1 + h)2 + 5(1 + h)
= 2 + 2h2 + 4h + 5 + 5h
= 2h2 + 9h + 7
f(1+ 2h) = 2(1 + h)2 + 5(1 + 2h)
= 2 + 8h2 + 8h + 5 + 10h
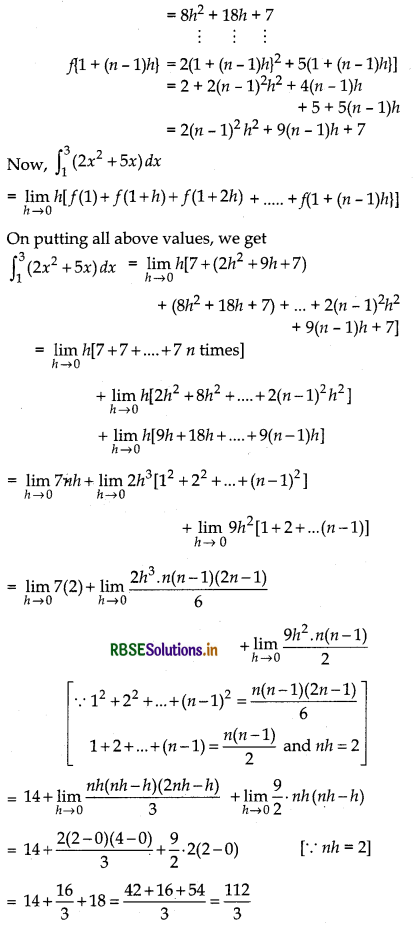

Question 34.
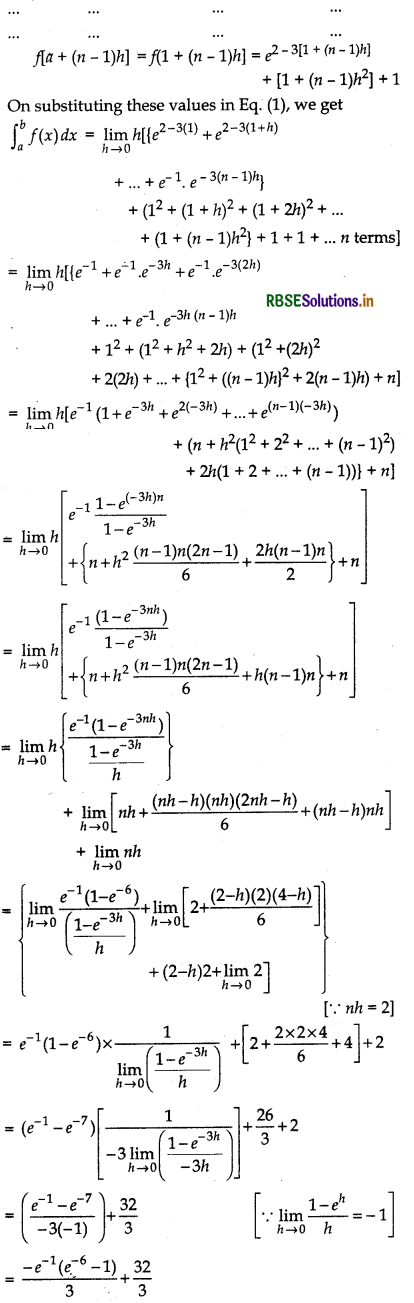
Evaluate \(\int_1^3\) (e2 - 3x + x2 dx as a limit of a sum.
Answer:
Let I = \(\int_1^3\) (e2 - 3x + x2 dx
On comparing the
\(\int_a^b\) f(x) dx, we get
a = 1, b = 3, f(x) = e2 - 3x + x2 + 1
As we know that,
\(\int_a^b\) f(x) dx = \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) h[f(a) + f(a + h) + f(a + 2h) + ...... + f[a + (n - 1)h}] ...... (1)
where, nh = b - a,
Here, nh = 3 - 1 = 2
f(a) = f(1) = e2 - 3(1) + (1)2 + 1
f(a + h) = f(1 + h) = e2 - 3(1 + h) + (1 + h)2 + 1
f(a + 2h) = f(1 + 2h) = 22 - 3(1 + 2h) + (1 + 2h)2 + 1
Question 35.
Evaluate: \(\int_1^2 \frac{x^3-1}{x^2}\) dx
Answer:
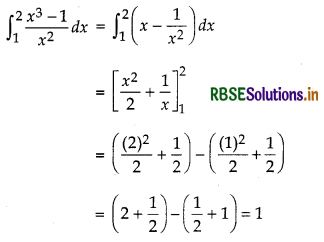
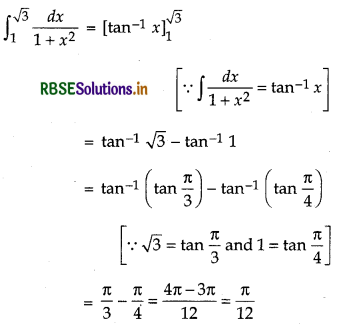
Question 36.
Evaluate \(\int_1^{\sqrt{3}} \frac{1}{1+x^2}\) dx
Answer:

Question 37.
Evaluate: \(\int_0^2 \sqrt{4-x^2}\) dx
Answer:

Question 38.
If \(\int_0^1\) (3x2 + 2x + k) dx = 0, find the value of k.
Answer:
Given \(\int_0^1\) (3x2 + 2x + k) dx = 0
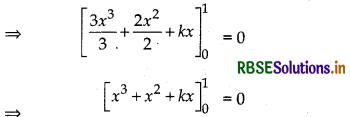
⇒ 1 + 1 + k = 0
⇒ k + 2 = 0
⇒ k = - 2
Question 39.
Evaluate: \(\int_0^{\pi / 4} \frac{\sin x+\cos x}{16+9 \sin 2 x}\) dx
Answer:
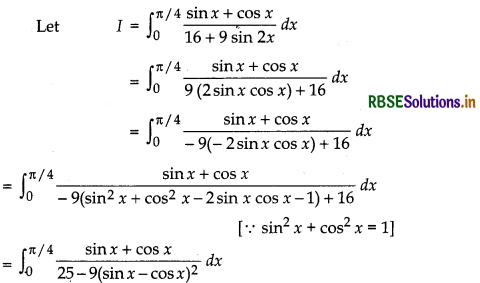
[∵ a2 + b2 - 2ab = (a - b)2]
Put sin x - cos x = t ⇒ (cos x + sin x)dx = dt
Also, when, x = 0, then t = - 1
and when, x = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) then t = 0
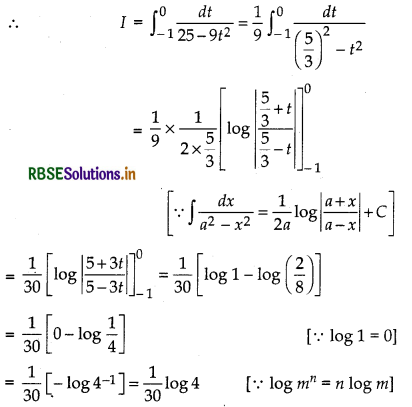

Question 40.
Prove that: \(\int_0^{\pi / 4}(\sqrt{\tan x}+\sqrt{\cot x})\) dx = \(\sqrt{2} \cdot \frac{\pi}{2}\)
Answer:

Now, put sin x - cos x = t
⇒ (cos x + sin x)dx = dt
Also, when x = 0, then t = - 1
and when x = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\), then t = 0
∴ I = √2 \(\int_{-1}^0 \frac{d t}{\sqrt{1-t^2}}=\sqrt{2}\left[\sin ^{-1} t\right]_{-1}^0\)
= √2[sin-1 (0) - sin-1 (- 1)]
= √2[sin-1 (0) + sin-1 (1)]
= √2\(\left[\frac{\pi}{2}\right]\)
Hence proved.
Question 41.
Evaluate: \(\int_0^{\pi / 4} \frac{d x}{\cos ^3 x \sqrt{2 \sin 2 x}}\)
Answer:
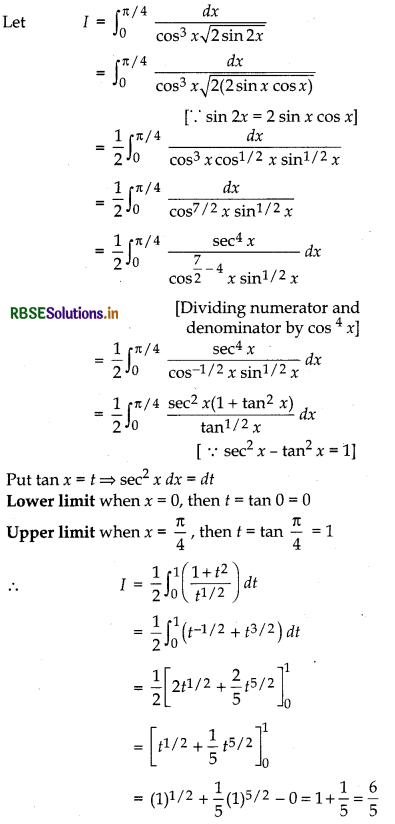

Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
∫ex(1 + tan x + tan2 x) dx =
(a) ex cos x + c
(b) ex sin x + c
(c) ex tan x + c
(d) ex sec x + c
Answer:
(c) ex tan x + c

Question 2.
∫x2 ex3 dx equals:
(a) \(\frac{1}{3}\) ex3 + C
(b) \(\frac{1}{3}\) ex4 +C
(c) \(\frac{1}{2}\) ex3 + C
(d) \(\frac{1}{2}\) ex2 + C
Answer:
(a) \(\frac{1}{3}\) ex3 + C
Question 3.
∫ \(\frac{(y-1)}{(y-3)(y-2)}\) dy =
(a) log(y - 3) - log(y - 2) + c
(b) log(y - 3)2 - log(y - 2) + c
(c) log(y - 3) + log(y - 2) + c
(d) log(y - 3)2 + log (y - 2) + c
Answer:
(b) log(y - 3)2 - log(y - 2) + c
Question 4.
The value of ∫ \(\frac{d x}{\sqrt{2 x-x^2}}\) is:
(a) sin-1 (x - 1) + c
(b) sin-1 (1 + x) + c
(c) sin-1 (1 + x) + c
(d) - \(\sqrt{2 x-x^2}\) + c
Answer:
(a) sin-1 (x - 1) + c
Question 5.
The value of ∫ y3 log y dy is:
(a) \(\frac{1}{8}\) {y4 log y - 4y4 + c}
(b) \(\frac{1}{16}\) {4y4 log y - y4 + c}
(c) \(\frac{y^4 \log y}{4}\)+c
(d) \(\frac{1}{16}\) {4y4 log y + y4 + c}
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{1}{16}\) {4y4 log y - y4 + c}

Question 6.
∫\(\frac{d x}{x^2+4 x+13}\) =
(a) log (2x + 4) + c
(b) log (x2 + 4x + 13) + c
(c) \(\frac{1}{3} \tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{x+2}{3}\right)\) + c
(d) \(\frac{1}{\left(x^2+4 x+13\right)}\) + c
Answer:
(c) \(\frac{1}{3} \tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{x+2}{3}\right)\) + c
Question 7.
∫ex {f (x) + f’(x)} dx = ex sin x, then f(x) is equal to:
(a) sin x
(b) - sin x
(c) cos x - sin x
(d) sin x + cos x
Answer:
(a) sin x
Question 8.
∫\(\frac{1}{\sin x+\cos x}\) dx is
(a) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \log \tan \left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\)+C
(b) log tan\(\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\) + C
(c) \(\frac{1}{2} logtan\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\) + C
(d) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}log tan\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\) + C
Answer:
(a) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \log \tan \left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\)+C
Question 9.
∫\(\frac{\cos 2 x+2 \sin x}{\cos ^2 x}\) dx =
(a) tan x
(b) cot x
(c) sin x
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
Question 10.
If \(\int_0^{\pi / 2} \frac{d x}{9 \sin ^2 x+4 \cos ^2 x}\) = Pπ, then P =
(a) \(\frac{1}{16}\)
(b) \(\frac{1}{12}\)
(c) \(\frac{1}{8}\)
(d) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Question 11.
The value of \(\int_{-1}^0 \frac{d x}{x^2+2 x+2}\) is:
(a) 0
(b) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
(c) - \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
(d) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)

Question 12.
\(\int_0^1\) x(1 - x)99 is equal to:
(a) \(\frac{1}{10010}\)
(b) \(\frac{1}{10100}\)
(c) \(\frac{1}{1010}\)
(d) \(\frac{1}{10100}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{1}{10100}\)
Question 13
\(\int_0^{\pi / 4} \frac{\sin \theta-\cos \theta}{\sqrt{1-\sin 2 \theta}}\) dθ is equal to:
(a) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
(b) \(\frac{-\pi}{4}\)
(c) \(\frac{\pi}{4} \text { or } \frac{-\pi}{4}\)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{-\pi}{4}\)
Question 14.
The value of the integral \(\int_0^{\pi / 2} \frac{\sqrt{\cos x}}{\sqrt{\cos x}+\sqrt{\sin x}}\) dx is:
(a) 0
(b) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
(c) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
Question 15.
\(\int_{-\pi / 2}^{\pi / 2}\) sin2 x cos2 x(sin x + cos x)dx =
(a) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
(b) \(\frac{2}{15}\)
(c) \(\frac{4}{15}\)
(d) \(\frac{8}{15}\)
Answer:
(c) \(\frac{4}{15}\)
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
The process of finding anti derivatives is called ............................... .
Answer:
integration
Question 2.
C is customarily referred to as ................................. constant.
Answer:
arbitrary

Question 3.
The process of differentiation and integration are ................................. of each other.
Answer:
inverse
Question 4.
Two indefinite integrals with the same derivative are ................................... .
Answer:
equivalent
Question 5.
Any two integrals of a function differ by a ..................................
Answer:
constant
True/False
Question 1.
When a polynomial function is differentiated, the result is a polynomial whose degree is 1 less than the degree of the function.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
When a polynomial function is integrated, the result is a polynomial whose degree is I more than that of the function.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
We make a substitution for a function whose derivative also occurs in the integrand.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
In \(\frac{P(x)}{Q(x)}\), if the degree of P(x) is greater than the degree of Q(x), then the rational function is called a proper function.
Answer:
False

Question 5.
The proper rational functions can be reduced to the proper rational functions by long division process.
Answer:
False
