RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 3 Matrices
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 3 Matrices Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Maths in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Important Questions Matrices
Question 1.
If \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} x-y & 2 x+z \\ 2 x-y & 3 z+\omega \end{array}\right]\)= \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} -1 & 5 \\ 0 & 13 \end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} -1 & 5 \\ 0 & 13 \end{array}\right]\), find x, y, z and w
Answer:
Given, matrix equation is:
\(\left[\begin{array}{cc} x-y & 2 x+z \\ 2 x-y & 3 z+w \end{array}\right]\)= \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} -1 & 5 \\ 0 & 13 \end{array}\right]\)
On equating the corresponding elements, we get
x - y = - 1 ...... (i)
2x - y = 0 ....... (ii)
2x + z = 5 ...... (iii)
3z + w = 13 .......... (iv)
Subtracting eq. (ii), from (i), we get
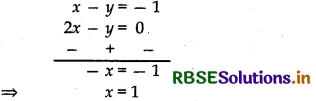
Substituting x = 1 in eq. (i), we get
1 - y = - 1
⇒ - y = - 2
⇒ y = 2
Substituting the value of x in Eq. (iii), we get
2 × 1 + z = 5
⇒ z = 5 - 2 = 3
Substituting the value of z in Eq. (iv), we get
3 × 3 + w = 13
⇒ w = 13 - 9
w = 4
Thus, x = 1, y = 2, z = 3, w = 4

Question 2.
Construct a 2 × 2 matrix A = [aij] whose elements are given by:
(i) aij = \(\frac{(i-2 j)^2}{2}\)
Answer:
Matrix of order 2 × 2 will be as follows:

(ii) aij = \(\frac{(2 i+j)^2}{2}\)
Answer:
Since, it is a 2 × 2 matrix, it has 2 rows and 2 columns.
Let the matrix be A,
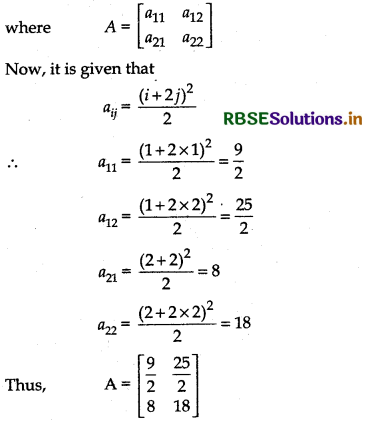
Question 3.
If \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} x-y & z \\ 2 x-y & w \end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} -1 & 4 \\ 0 & 5 \end{array}\right]\), find x, y, z and w.
Answer:
Given, matrix equation is:
\(\left[\begin{array}{cc} x-y & z \\ 2 x-y & w \end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} -1 & 4 \\ 0 & 5 \end{array}\right]\)
On equating the corresponding elements, we get
x - y = - 1 ...... (i)
2x - y = 0 ....... (ii)
z = 4 ........ (iii)
w = 5 ........ (iv)
Subtracting equation (ii), from (j), we get
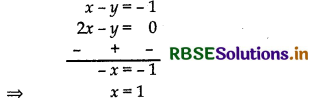
Substituting the value of x in Eq. (ii), we get
y = 2
Thus, x = 1, y = 2, z = 4 and w = 5

Question 4.
If \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} 2 x+1 & 5 x \\ 0 & y^2+1 \end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} x+3 & 10 \\ 0 & 26 \end{array}\right]\), find the value of (x + y).
Answer:
Given, matrix equation is:
\(\left[\begin{array}{cc} 2 x+1 & 5 x \\ 0 & y^2+1 \end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} x+3 & 10 \\ 0 & 26 \end{array}\right]\)
On equating the corresponding elements, we get
2x + 1 = x + 3
⇒ x = 2
And y2 + 1 = 26
⇒ y2 = 26 - 1 = 25
⇒ y = ±5
If y = + 5, then x + y = 2 + 5 = 7
and if y= - 5, then x + y = 2 - 5 = - 3
Question 5.
Construct a 2 × 2 matrix A = [aij] whose elements are given by aij = |(i)2 - j|.
Answer:
Matrix of order 2 × 2 will be as follows:
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} a_{11} & a_{12} \\ a_{22} & a_{23} \end{array}\right]\)
Now, aij = [(i)2 - j]
a11 = (1)2 - 1 = 1 - 1 = 0
a12 = (1)2 - 2 = 1 - 2 = - 1
a21 = (2)2 - 1 = 4 - 1 = 3
a22 = (2)2 - 1 = 4 - 2 = 2
Thus, the matrix of order 2 × 2 is:
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} 0 & -1 \\ 3 & 2 \end{array}\right]\)
then 3A = 3\(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 1 & -3 \\ 0 & 3 \end{array}\right]\) = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 3 \times 1 & 3 \times(-3) \\ 3 \times 0 & 3 \times 3 \end{array}\right]\)
= \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 3 & -9 \\ 0 & 9 \end{array}\right]\)
Question 6.
Find a matrix X such that 2A + B + X = 0, where A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 4 \end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 3 & -2 \\ 1 & 5 \end{array}\right]\).
Answer:
We have
2A + B + X = 0
x = - 2A - B
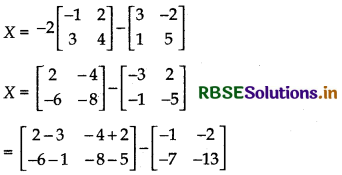
Question 7.
Find a matrix A such that 2A - 3B + 5C = 0, where B = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr} -2 & 2 & 0 \\ 3 & 1 & 4 \end{array}\right]\) and C = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr} 2 & 0 & -2 \\ 7 & 1 & 6 \end{array}\right]\).
Answer:
We have,
2A - 3B + 5C = 0
2A = 3B - 5C
A = \(\frac{3 B-5 C}{2}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)B - \(\frac{5}{2}\)C
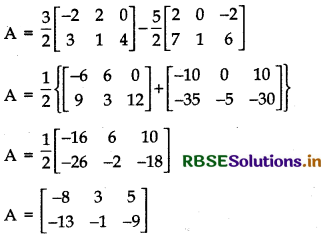

Question 8.
The monthly incomes of Aryan and Baban are in the ratio 3 :4 and their monthly expenditures are In the ratio 5 : 7. If each saves ₹ 1500 per month, find their monthly incomes using matrix method. This problem reflects which values.
Answer:
Let the incomes of Aryan and Baban be 3x and 4x respectively. Similarly, their expenditures would be 5y and 7y respectively.
Since, each saves ₹ 1500, we get
3x - 5y = 1500
4x - 7y = 1500
This can be written form as:
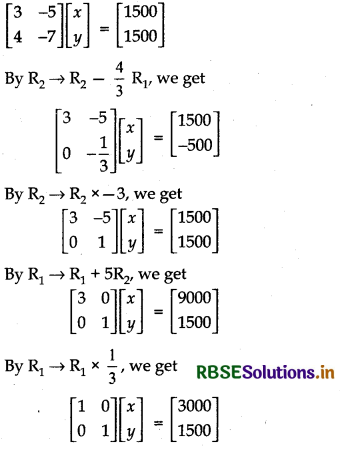
∴ x = 3000
Thus, their incomes was 3 × 3000 = ₹ 9,000 and 4 × 3000 = ₹ 12000 respectively.
Question 9.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 1 & -1 \\ 2 & -1 \end{array}\right]\), B = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} a & 1 \\ b & -1 \end{array}\right]\) and (A + B)2 = A2 + B2, find a and b.
Answer:
We have
(A + B)2 = A2 + B2
⇒ (A + B) (A + B) = A2 + B2
⇒ A2 + BA + AB + B2 + A2 + B2
⇒ BA + AB = 0
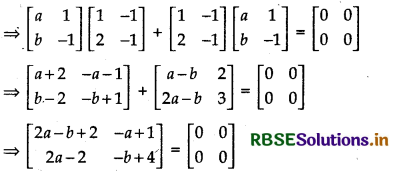
On equating the corresponding elements, we get
⇒ 2a - b + 2 = 0 ......... (i)
- a + 1 = 0 ....... (ii)
2a - 2 = 0 ........ (iii)
- b + 4 = 0 ....... (iv)
On solving these equations, we get
a = 1, b = 4

Question 10.
Find the value of x, for the following:
\(\left[\begin{array}{lll} 1 & x & 1 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 3 & 2 \\ 2 & 5 & 1 \\ 15 & 3 & 2 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} 1 \\ 2 \\ x \end{array}\right]\) = 0
Answer:
We have
⇒ \(\left[\begin{array}{lll} 1 & x & 1 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{c} 7+2 x \\ 12+x \\ 21+2 x \end{array}\right]\) = 0
⇒ 7 + 2x + 12x + x2 + 21 + 2x = 0
⇒ x2 + 16x + 28 = 0
⇒ (x + 14) (x + 2) = 0
Either x+ 14 = 0 ⇒ x = - 14
or x + 2 = 0 ⇒ x = - 2
Question 11.
If A is a square matrix such that A2 = 1, then find the simplified value of (A - I)3 + (A + I)3 - 7A.
Answer:
We have, A2 = I
∴ A3 = A2.A = IA = A
We know that
(A + B)3 = A3 + 3A2B + 3AB2 + B2
(A - B)3 = A3 - 3A2B + 3AB2 - B3
Provided that AB = BA
Since AI = IA = A
∴ (A + I)3 = A3 + 3A2I + 3AI2 + I
⇒ (A - I)3 = A3 - 3A2I + 3AI2 - I
∴ (A + I)3 + (A - I)3 = 2(A3 + 3A)
⇒ (A + I)3 × (A - I)3 = 2(A + 3A) [By (i)]
⇒ (A + I)3 + (A - I)3 = 8A
Thus, (A - I)3 + (A + I)3 - 7A
= 8A - 7A = A
Question 12.
Find the matrix A such that
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 2 & -1 \\ 1 & 0 \\ -3 & 4 \end{array}\right]\) A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} -1 & -8 \\ 1 & -2 \\ 9 & 22 \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
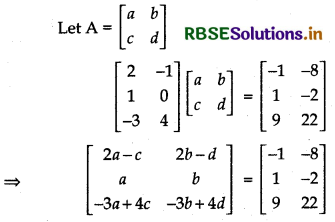
On equating the corresponding elements, we get
⇒ 2a - c = - 1 ........... (i)
2b - d = - 8 .......... (ii)
a = 1 ......... (iii)
b = - 2 ......... (iv)
- 3a + 4c = 9 .......... (v)
- 3b + 4d = 22 .......... (vi)
On solving these equations, we get
a = 1, b = - 2, c = 3, d = 4
Thus, A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} 1 & -2 \\ 3 & 4 \end{array}\right]\)
(ii) A\(\left[\begin{array}{lll} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 & 6 \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{rrr} -7 & -8 & -9 \\ 2 & 4 & 6 \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
It is given that:
\(\mathrm{A}\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 & 6 \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} -7 & -8 & -9 \\ 2 & 4 & 6 \end{array}\right]\)
The matrix given on the R.H.S. of the equation is a 2 × 3 matrix and the one given on the L.H.S. of the equation is a 2 × 3 matrix.
Therefore, A is a 2 × 2 matrix.
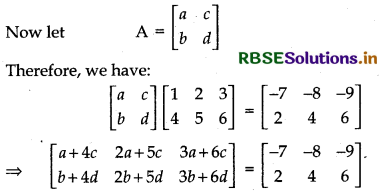
Equating the corresponding elements of the two
matrices, we get
a + 4c = - 7
2a + 5c = 8 ........ (ii)
3a + 6c = - 9 ......... (iii)
b + 4d = 2 ....... (iv)
2b + 5d = 4 ........ (v)
3b + 6d = 6 ........ (vi)
Now, from (i), we have
a + 4c = - 7
⇒ a - 7 - 4c .......... (vii)
From (ii), we have
∴ 2a + 5c = - 8 ⇒ - 14 - 8c + 5c = - 8
⇒ - 3c = 6 ⇒ c = - 2
Substituting c = - 2 in Eq. (vii), we get
∴ a = - 7 - 4(- 2)
= - 7 + 8 = 1
Now, from (iv), we get
b + 4d = 2
⇒ b = 2 - 4d ...... (viii)
From eqs. (y) and (viii), we get
⇒ 4 - 8d + 5d = 4
⇒ - 3d = 0
⇒ d = 0
Substituting d = 0 in Eq. (viii), we get
∴ b = 2 - 4(0) = 2
Thus, a = 1, b = 2, c = - 2, d = 0
Hence, the required matrix A is \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} 1 & -2 \\ 2 & 0 \end{array}\right]\).

Question 13.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} -3 & 2 \\ 1 & -1 \end{array}\right]\) and I = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]\), find scalar K so that A2 + I = KA.
Answer:
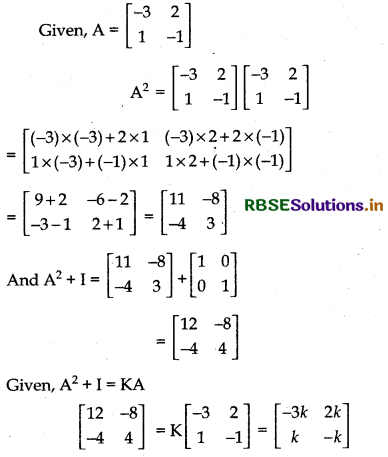
On equating the corresponding elements, we get
- 3k = 12 ⇒ k = - 4
Question 14.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{c} -1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{array}\right] \)and B = [- 2 - 1 - 4], verify that (AB)T = BTAT.
Answer:
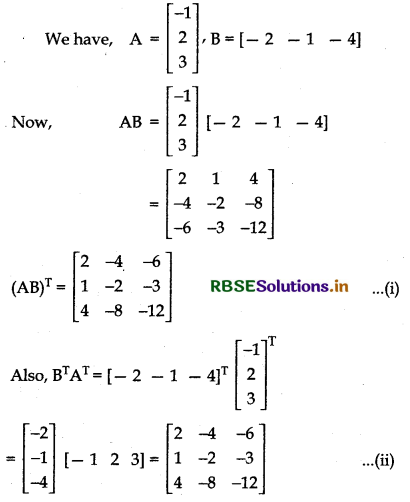
From (i) and (ii), we get
(AB)T = BTAT
Hence, proved

Question 15.
Show that the elements on the main diagonal of a skew symmetric matrix are all zero.
Answer:
Let A = [aij] be a skew-symmetric matrix.
Then aij = - aij for all i, j
Put i = j, we get
aii = - aii for all values of i
2aii = 0
= aii = 0 for all values of i
a11 = a22 = a33 = ........................ = am = 0
Thus, all the diagonals of a skew-symmetric matrix are zero.
Hence proved
Question 16.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{array}\right]\), prove that A - AT, is a skew-symmetric matrix.
Answer:
Given, A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{array}\right]\)
Let B = A - AT
B is a skew -symmetric matrix if BT = - B
Now, B = A - AT
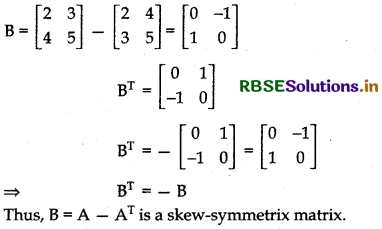
Question 17.
Express the matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 4 & 2 & -1 \\ 3 & 5 & 7 \\ 1 & -2 & 1 \end{array}\right]\) as the sum of a symmetric and skew-symmetric matrix.
Answer:
Any square matrix A can be expressed as the sum of a symmetric and skew-symmetric, i.e., A = \(\frac{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{A}^{\prime}}{2}\) + \(\frac{\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{A}^{\prime}}{2}\), where \(\frac{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{A}^{\prime}}{2}\) and \(\frac{\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{A}^{\prime}}{2}\) are symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices respectively.
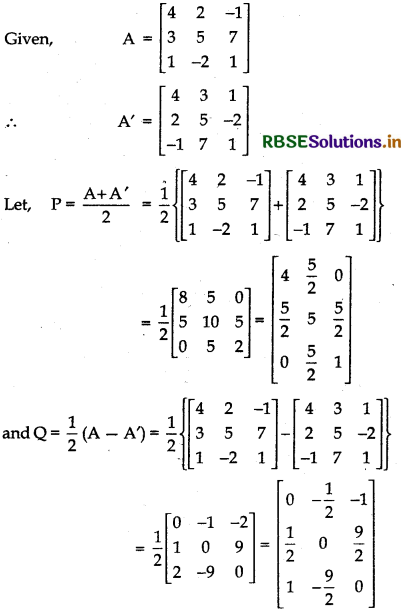
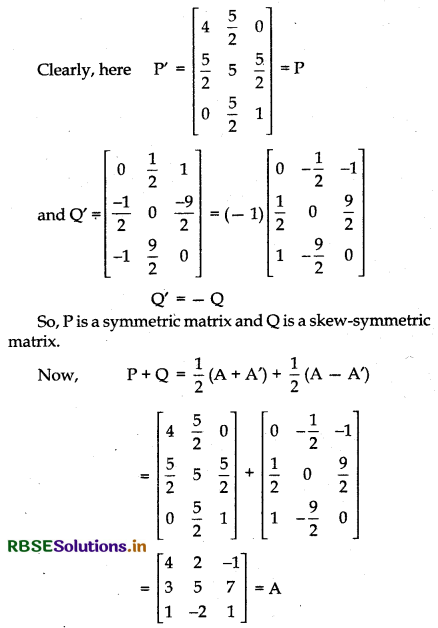
Thus, matrix A is expressed as the sum of symmetric matrix and skew-symmetric matrix.

Question 18.
Express the matrix \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 3 & -2 & -4 \\ 3 & -2 & -5 \\ -1 & 1 & 2 \end{array}\right]\) as the sum of a symmetric and skew-symmetric matrix and verify your result.
Answer:
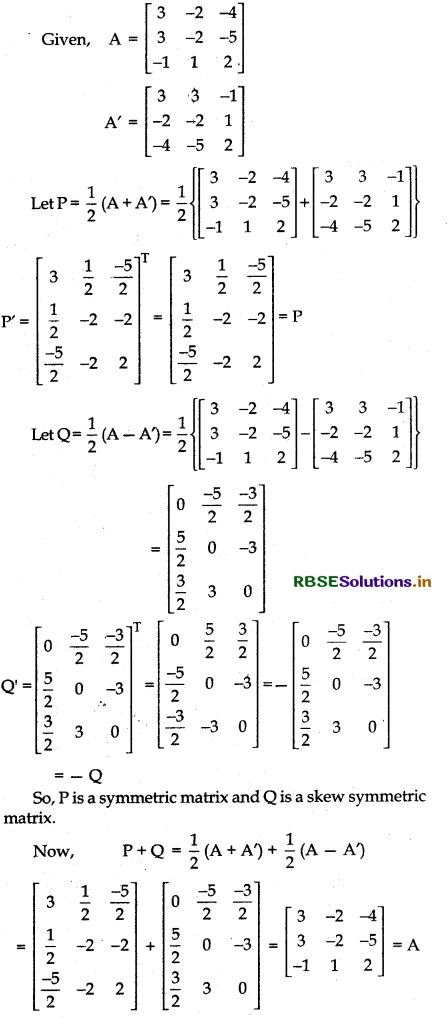
Thus, matrix A is expressed as the sum of symmetric matrix and skew-symmetric matrix.
Question 19.
Find the matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 7 \end{array}\right]\), find A + AT and verify then it is a symmetric matrix.
Answer:
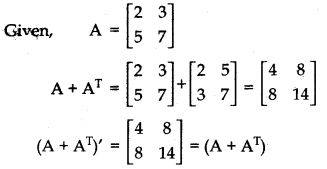
Thus, (A + A)T is a symmetric matrix.
Hence proved.
Question 20.
Given a skew-symmetric matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 0 & a & 1 \\ -1 & b & 1 \\ -1 & c & 0 \end{array}\right]\) the value of (a + b + c)2 is ................. .
Answer:
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 0 & a & 1 \\ -1 & b & 1 \\ -1 & c & 0 \end{array}\right]\) is a skew-symmetric matrix, then the value of (a + b + c)2 is 0.
Question 21.
Express A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 4 & -3 \\ 2 & -1 \end{array}\right]\) as a sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix.
Answer:
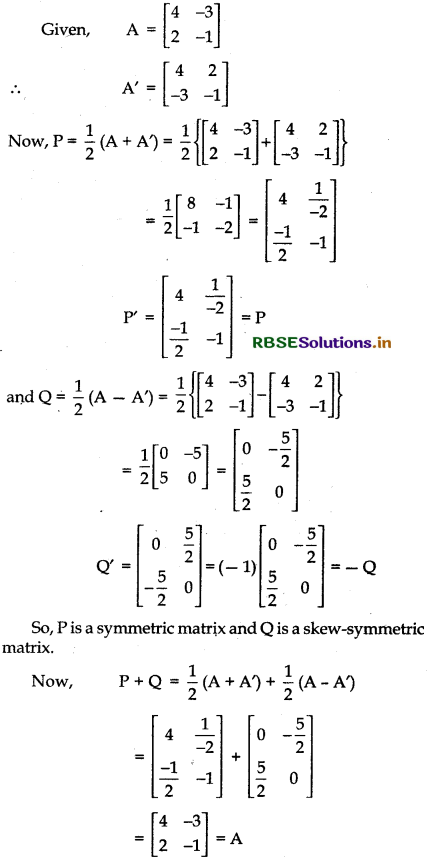
Thus, matrix A is expressed as the sum of symmetric matrix and skew-symmetric matrix.

Question 22.
Show that the matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll} 1 & 2 & 2 \\ 2 & 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 2 & 1 \end{array}\right]\) satisfies the equation A2 - 4A - 5I3 = 0 and hence find A-1.
Answer:
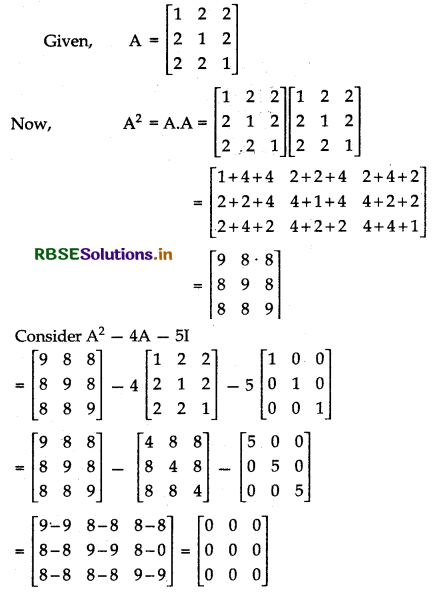
Now, A2 - 4A - 5I = 0
A2 - 4A = 5I
A2A- 1 - 4A.A-1 = 5IA-1
A - 4I = 5A-1
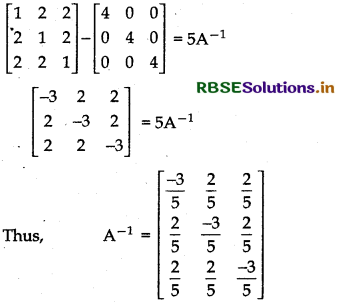
Question 23.
Find A-1, by using elementary row transformation for matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 3 & 2 \\ 7 & 5 \end{array}\right]\).
Answer:
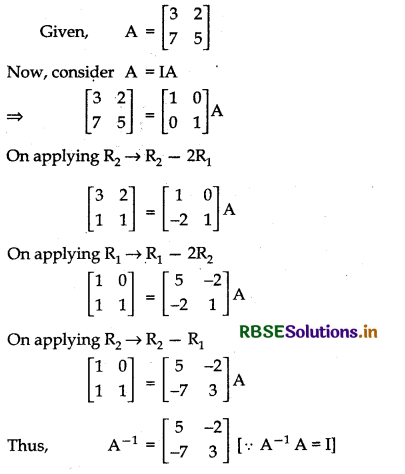

Question 24.
Find the inverse of matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 2 & -2 \\ -1 & 3 & 0 \\ 0 & -2 & 1 \end{array}\right]\) by using elementary row transformations.
Answer:
We know that
AA-1 = I

Question 25.
Find the inverse of each of the following matrices by using elementary row transformation.
(i) \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 1 & 2 \\ 2 & -1 \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
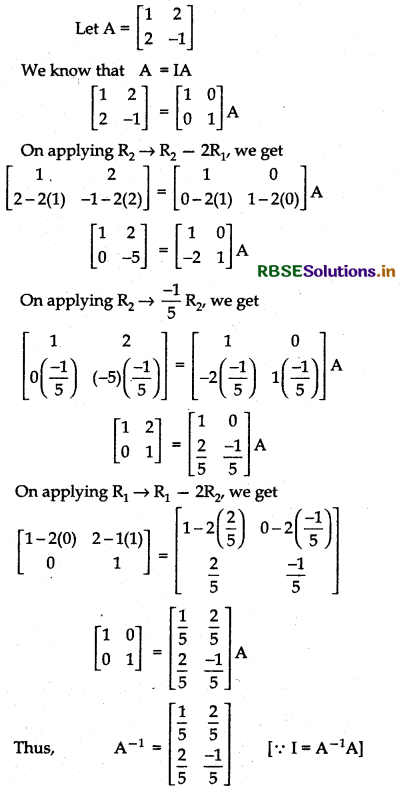
(ii)
\(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 2 & 5 \\ 1 & 3 \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
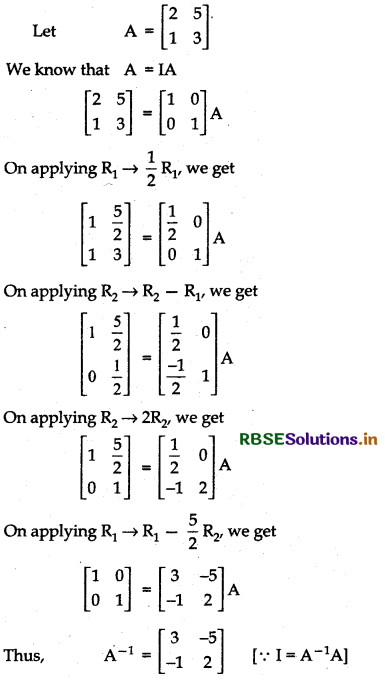

(iii)
\(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & -1 & 4 \\ 4 & 0 & 2 \\ 3 & -2 & 7 \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:


(iv) \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 3 & 0 & -1 \\ 2 & 3 & 0 \\ 0 & 4 & 1 \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:

Question 26.
Obtain the inverse of the following matrix using elementary operations:
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & 1 & -3 \\ -1 & -1 & 4 \\ 3 & 0 & 2 \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
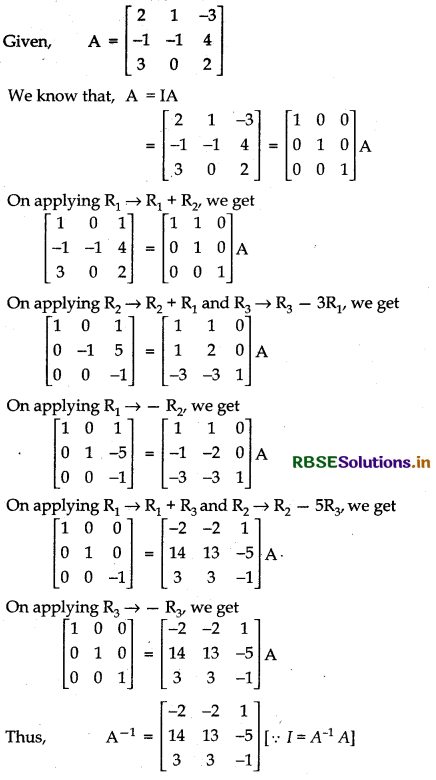

Question 27.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 3 & 2 \\ 2 & 0 & -1 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \end{array}\right]\), then show that A3 - 4A2 - 3A +111 = 0. Hence, find A-1.
Answer:
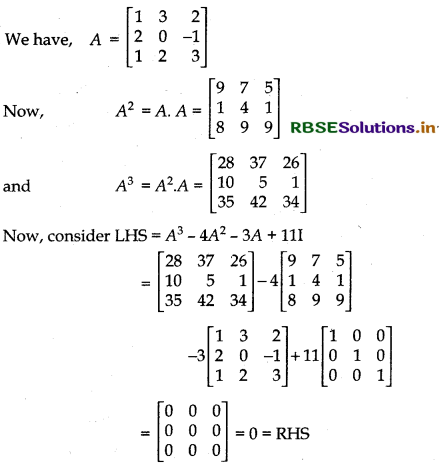
Now, A3 - 4A2 - 3A + 111 = 0
Pre-multiplied by A-1, we get
A-1A3 - 4A-1A2 - 3A-1A + 11A-1
⇒ A2 - 4A - 3I + 11A-1 = 0 [∵ A-1A = I]
⇒ 11A-1 = 3I + 4A - A2
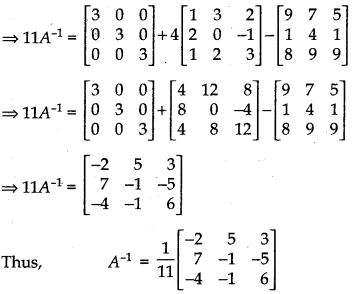
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
If A = [2, -3, 4], B = \(\left[\begin{array}{l} 3 \\ 2 \\ 2 \end{array}\right]\), X = [1, 2, 3] and Y = \(\left[\begin{array}{l} 2 \\ 3 \\ 4 \end{array}\right]\), then AB + XY equals:
(a) [28]
(b) [24]
(c) 28
(d) 24
Answer:
(a) [28]
Question 2.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll} 0 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 3 & a & 1 \end{array}\right]\), A-1 = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr} \frac{1}{2} & -\frac{1}{2} & \frac{1}{2} \\ -4 & 3 & c \\ \frac{5}{2} & -\frac{3}{2} & \frac{1}{2} \end{array}\right]\), then:
(a) a = 2, c = -\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(b) a = 1, c = -1
(c) a = -1, c = 1
(d) a = \(\frac{1}{2}\), c = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
(b) a = 1, c = -1

Question 3.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 5 & 2 & 6 \\ -2 & -1 & -3 \end{array}\right]\), then A3 = ________________
(a) I
(b) AT
(c) O
(d) A-1
Answer:
(c) O
Question 4.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 3 & -4 \\ 1 & -1 \end{array}\right]\), then An = ________________
(a) \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} 3 n & -4 n \\ n & -n \end{array}\right]\)
(b) \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 2+n & 5-n \\ n & -n \end{array}\right]\)
(c) \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 3^n & (-4)^n \\ 1^n & (-1)^n \end{array}\right]\)
(d) \(\left[\begin{array}{rc} 2 n+1 & -4^n \\ n & -1-2 n \end{array}\right]\)
Answer:
(d) \(\left[\begin{array}{rc} 2 n+1 & -4^n \\ n & -1-2 n \end{array}\right]\)
Question 5.
Suppose a matrix A satisfies A2 - 5A + 7I = O. If A5 = aA + bI then the value of 2a - 3b must be ....
(a) 4135
(b) 1435
(c) 1453
(d) 3145
Answer:
(c) 1453
Question 6.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{lll} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{array}\right]\), then A2013 = ............
(a) 32013A
(b) -32012I
(c) 32011A
(d) 31006A
Answer:
(c) 32011A
Question 7.
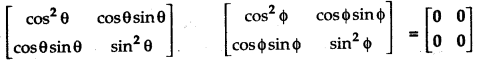
Provided θ - Φ = ......, n ∈ Z
(a) nπ
(b) \(\frac{(2 n+1) \pi}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\)
(d) 2nπ
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{(2 n+1) \pi}{2}\)
Question 8.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} \alpha & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{array}\right]\) and B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 5 & 1 \end{array}\right]\), then A2 = B for
(a) α = 4
(b) α = 1
(c) α = -1
(d) no α
Answer:
(d) no α
Question 9.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} \alpha & 0 \\ 2 & 3 \end{array}\right]\) and I = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]\), then A2 = 9I for
(a) α = 4
(b) α = 3
(c) α = -3
(d) no α =
Answer:
(c) α = -3
Question 10.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 3 & 1 \\ -9 & -3 \end{array}\right]\), then I + 2A + 3A2 + ........ + ∞ = ...........
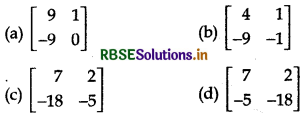
Answer:
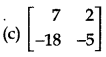

Question 11.
If A = \(\left[\begin{array}{rr} 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 7 \end{array}\right]\) and A2 = 8A + kI2, then k = ...........
(a) 1
(b) -1
(c) 7
(d) -7
Answer:
(d) -7
Question 12.
The identity element in the group M = {\(\left[\begin{array}{lll} x & x & x \\ x & x & x \\ x & x & x \end{array}\right]\)/ x ∈ R, x ≠ 0} with respect to matrix multiplication is ............
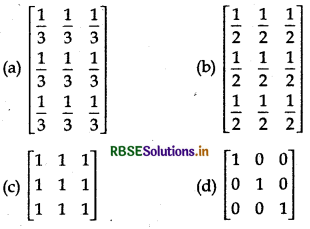
Answer:

Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
If A + B = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 \end{array}\right]\) and A - 2B =\(\left[\begin{array}{cc} -1 & 0 \\ 1 & -1 \end{array}\right]\), then A = ________________
Answer:
\(\left[\begin{array}{ll} \frac{1}{3} & \frac{1}{3} \\ \frac{2}{3} & \frac{1}{3} \end{array}\right]\)
Question 2.
If \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} x+y & 7 \\ 9 & x-y \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{cc} 2 & 7 \\ 9 & 4 \end{array}\right]\), then x,y ________________
Answer:
-3
Question 3.
If [2 1 3] \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc} -1 & 0 & -1 \\ -1 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 1 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 0 \\ -1 \end{array}\right]\) = A, then the order of matrix A is ________________
Answer:
1 × 1
Question 4.
If matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc} 1 & -1 \\ -1 & 1 \end{array}\right]\) and A2 = KA, then the value of k is ________________
Answer:
2

Question 5.
If \(\left[\begin{array}{ll} 1 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} x \\ 2 \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{l} 5 \\ 6 \end{array}\right]\), then x = ________________
Answer:
-1
True/False
Question 1.
In the matrix, the number or function is called the data of the matrix.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
A matrix having m rows and n columns is called a matrix of order n*m.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
A matrix is said to be a column matrix if it has only one column.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
A matrix is said to be diagonal matrix if all its elements are zero.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Two matrices are said to be equal if they are of the same order.
Answer:
True

- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Probability
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 12 Linear Programming
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 9 Differential Equations
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 8 Application of Integrals
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 7 Integrals
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 4 Determinants
- RBSE Class 12 Maths Notes Chapter 3 Matrices