RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Maths Important Questions Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Important Questions Vector Algebra
Question 1.
Represent graphically a displacement of 50 km, 45° west of south.
Answer:
In the figure below, the vector \(\overrightarrow{O P}\) represents the required displacement.
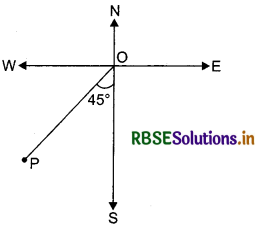

Question 2.
Classify the following measures as scalars and vectors,
(i) 10 seconds
Answer:
Time-scalar
(ii) 6000 cm3
Answer:
Volume-scalar
(iii) 8 Newton
Answer:
Force-vector
(iv) 22 km/h
Answer:
Speed-scalar
(v) 20 g/cm3
Answer:
Density-scalar
(vi) 40 m/s towards north
Answer:
Velocity-vector

Question 3.
In the given figure, which of the vectors are:
(i) equal
(ii) coinitial
(iii) collinear
Answer:
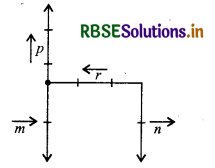
(i) Equal vectors: \(\vec{m}\) and \(\vec{n}\)
(ii) Coinitial vectors: \(\vec{p}, \vec{m}\) and \(\vec{r}\)
(iii) Collinear vectors: \(\vec{m}, \vec{n}\) and \(\vec{r}\)
Question 4.
If a unit vector \(\vec{a}\) makes angle \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) with î, \(\frac{\pi}{4} \)with ĵ and an acute angle θ with k̂ then find the value of θ.
Answer:
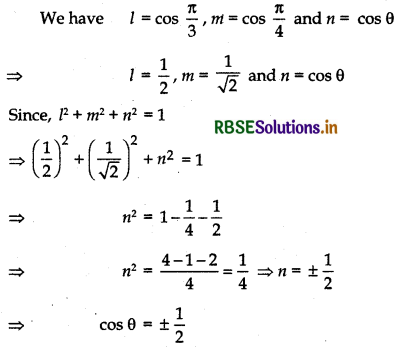
But θ is an acute angle, therefore cos θ = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
⇒ θ = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
Question 5.
For what values of \(\vec{a}\), vectors 2î - 3ĵ + 4k̂ and aî + 6ĵ - 8k̂ are collinear?
Answer:
Let \(\vec{a}\) = 2î - 3ĵ + 4k̂
and \(\vec{b}\) = aî + 6ĵ - 8k̂
Vectors \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) will be collinear, if
\(\vec{a}\) = k.\(\vec{b}\), where k is a scalar.
∴ 2î - 3ĵ + 4k̂ = k(aî + 6ĵ - 8k̂)
On comparing the coefficients of î and ĵ we get
2 = ka ........... (i)
and - 3 = 6k ⇒ k = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
From equation (i), we have
∴ 2 = - \(\frac{1}{2}\)a ⇒ a = - 4

Question 6.
Let \(\vec{a}\) = î + ĵ + k̂, \(\vec{b}\) = 4î - 2ĵ + 3k̂ and \(\vec{c}\) = î - 2ĵ + k̂. Find a vector of magnitude 6 units, which is parallel to the vector 2\(\vec{a} \)- \(\vec{b}\) + 3\(\vec{c}\).
Answer:
Given \(\vec{a}\) = î + ĵ + k̂, \(\vec{b}\) = 4î - 2ĵ + 3k̂ and \(\vec{c}\) = î - 2ĵ + k̂
∴ 2\(\vec{a}\) - \(\vec{b}\) + 3\(\vec{c}\)
= 2(î + ĵ + k̂) - (4î - 2ĵ + 3k̂) + 3(î - 2ĵ + k̂)
= 2î + 2ĵ + 2k̂ - 4î + 2ĵ - 3k̂ + 3î - 6ĵ + 3k̂
⇒ 2\(\vec{a}\) - \(\vec{b}\) + 3\(\vec{c}\) = î - 2ĵ + 2k̂
Now, a unit vector in the direction of vector
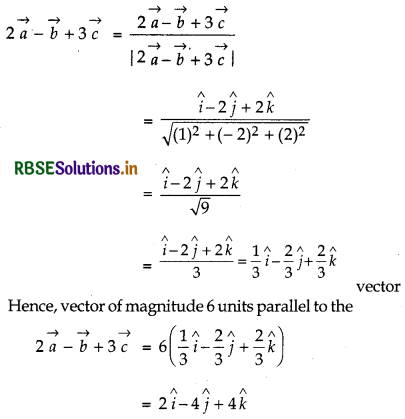
Question 7.
If \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) are perpendicular vectors, |\(\vec{a}+\vec{b}\)| = 13 and |\(\vec{a}\)| = 5, then find the value of |\(\vec{b}\)|
Answer:


Question 8.
If \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\), are two unit vectors such that \(\vec{a}\) + \(\vec{b}\) is also a unit vector, then find the angle between \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\).
Answer:
Given, |\(\vec{a}+\vec{b}\)| = 13, and |\(\vec{a}\)| = 5
Now, (\(\vec{a}+\vec{b}) \cdot(\vec{a}+\vec{b}\)) = \(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{a}+\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}+\vec{b} \cdot \vec{a}+\vec{b} \cdot \vec{b}\)
⇒ \(|\vec{a}+\vec{b}|^2 \)= \(|\vec{a}|^2\) + 0 + 0 + \(|\vec{b}|^2\)
[∵ \(\vec{x} \cdot \vec{x}=|\vec{x}|^2, \vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}=\vec{b} \cdot \vec{a}=0 \text { as } \vec{a} \perp \vec{b}\)]
⇒ (13)2 = (5)2 + \(|\vec{b}|^2\)
⇒ 169 = 25 + \(|\vec{b}|^2\)
⇒ 169 - 25 = \(|\vec{b}|^2\)
⇒ 144 = \(|\vec{b}|^2\)
⇒ \(\vec{b}\) = 12
Question 9.
Let \(\vec{a}\) = î + 4ĵ + 2k̂, \(\vec{b}\) = 3î - 2ĵ + 7 and \(\vec{c}\) = 2î - ĵ + 4k̂. Find a vector \(\vec{p}\), which is perpendicular to both \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) and \(\vec{p} \cdot \vec{c}\) = 18.
Answer:
Given \(\vec{a}\) = î + 4ĵ + 2k̂,
\(\vec{b}\) = 3î - 2ĵ + 7
and \(\vec{c}\) = 2î - ĵ + 4k̂
Let \(\vec{p}\) = xî + yĵ + zk̂
We have, \(\vec{p}\) is perpendicular to both \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\)
\(\vec{p} \cdot \vec{a}\) = 0
⇒ (xî + yĵ + zk̂).(î + 4ĵ + 2k̂) = 0
⇒ x + 4y + 2z = 0 .................. (i)
and \(\vec{p} \cdot \vec{b}\) = 0
⇒ (xî + yĵ + zk̂).(3î - 2ĵ + 7k̂) = 0
⇒ 3x - 2y + 7z = 0 .................. (ii)
Also, given \(\vec{p} \cdot \vec{c}\) = 18
⇒ (xî + yĵ + zk̂).(2î - ĵ + 4k̂) = 0
⇒ 2x - y + 4z = 18 .................. (iii)
On multiplying Eq. (i) by 3 and subtracting it from Eq. (ii), we get
- 14y + z = 0 ............ (iv)
Now, multiplying Eq. (i) by 2 and subtracting it from Eq. (iii), we get
- 9y - 18
⇒ y = - 2
On putting y = -2 in Eq. (iv), we get
- 14 (-2) + z = O
⇒ 28 + z = 0
z = - 28
On putting y = - 2 and z = - 28 in Eq. (i), we get
x + 4(- 2) + 2(- 28) = 0
⇒ x - 8 - 56 = 0
⇒ x = 64
Hence, the required vector is
\(\vec{p}\) = xî + yĵ + zk̂
i.e., \(\vec{p}\) = 64î - 2ĵ - 28k̂
Question 10.
Using vectors, find the area of the triangle ABC with vertices A(1, 2, 3), B(2, - 1, 4) and C(4, 5, - 1).
Answer:
We have, \(\vec{a}\) = î + 2ĵ + 3k̂, \(\vec{b}\) = 2î+ 4ĵ - 5k̂
So, the diagonals of the parallelogram whose adjacent sides are \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) are
\(\vec{p}\) = (î + 2ĵ + 3k̂) + (2î + 4ĵ - 5k̂)
= 3î + 6ĵ - 2k̂
and \(\vec{q}\) = (î + 2ĵ + 3k̂) - (2î + 4ĵ - 5k̂)
= - î - 2ĵ + 8k̂
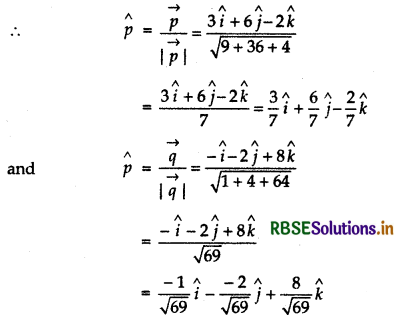

Question 11.
Find the unit vector perpendicular to each of the vertors \(\vec{a}\) = 4î + 3ĵ + k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) = 2î - ĵ + 2k̂.
Answer:
Given vectors are \(\vec{a}\) = 4î + 3ĵ + k̂
and \(\vec{b}\) = 2î - ĵ + 2k̂
Now, perpendicular vector to the given vector is
\(\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = \left|\begin{array}{ccc} \hat{i} & \hat{j} & \hat{k} \\ 4 & 3 & 1 \\ 2 & -1 & 2 \end{array}\right|\)
= î(6 + 1) - ĵ(8 - 2) + k̂(- 4 - 6)
= 7î - 6ĵ - 10k̂
|\(\vec{a} \times \vec{b}\)| = \(\sqrt{7^2+(-6)^2+(-10)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{49+36+100}\) = √185
∴ Required unit vector = ± \(\frac{\vec{a} \times \vec{b}}{|\vec{a} \times \vec{b}|}\)
= ± \(\frac{(7 \hat{i}-6 \hat{j}-10 \hat{k})}{\sqrt{185}}\)
Question 12.
Find the unit vector perpendicular to the plane ABC where the position vectors of A, B and C are 2î - ĵ + k̂, î + ĵ + 2k̂ and 2î + 3ĵ respectively.
Answer:
Let O be the origin of reference.
Then, given \(\overrightarrow{O A}\) = 2î - ĵ + k̂,
\(\overrightarrow{O B}\) = î + ĵ + 2k̂
and \(\overrightarrow{O C}\) = 2î + 3k̂
Now, \(\overrightarrow{A B} = \overrightarrow{O B} - \overrightarrow{O A}\)
= î + ĵ + 2k̂ - 2î + ĵ - k̂
= - î + 2ĵ + k̂
and \(\overrightarrow{A C} = \overrightarrow{O C} - \overrightarrow{O A}\)
= 2î + 3k̂ - 2î + ĵ - k̂ = ĵ + 2k̂
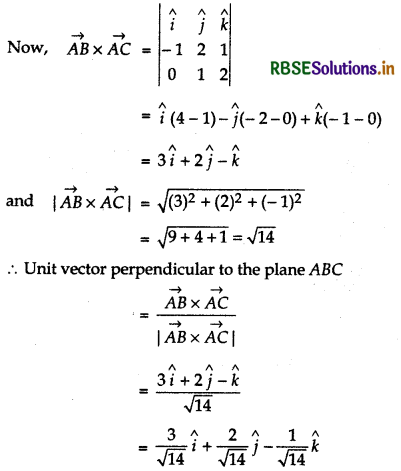

Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The figure formed by four points î + ĵ + k̂, 2î + 3ĵ, 3î + 5ĵ - 2k̂, k̂ - ĵ is a:
(a) square
(b) trapezium
(c) parallelogram
(d) rectangle
Answer:
(b) trapezium
Question 2.
If λ(3î + 2ĵ - 6k̂) is a unit vector, then the value of ?
(a) ± 7
(b) ± √43
(c) ± \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{43}}\)
(d) ± \(\frac{1}{7}\)
Answer:
(d) ± \(\frac{1}{7}\)
Question 3.
If \(\vec{a}\) = î - 2ĵ + 3k̂ and \(\vec{b}\) is a vector such that \(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}\) = \(|\vec{b}|^2\) and |\(\vec{a}-\vec{b}\)| = √7, then |\(\vec{b}\)| is equal to:
(a) 7
(b) 3
(c) √7
(d) √3
Answer:
(c) √7
Question 4.
Suppose \(\vec{a}\) = λî - 7ĵ + 3k̂, \(\vec{b}\) = λî + ĵ + 2λ k̂. If the angle between \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) is greater than 90°, then λ satisfies the inequality:
(a) λ > 1
(b) - 7 < λ < 1
(c) - 5 < λ < 1
(d) 1 < λ < 7
Answer:
(b) - 7 < λ < 1
Question 5.
The projection of \(\vec{a}\) = 3î - ĵ + 5k̂ on \(\vec{b}\) = 2î + 3ĵ + k̂ is:
(a) √14
(b) \(\frac{8}{\sqrt{14}}\)
(c) \(\frac{8}{\sqrt{39}}\)
(d) \(\frac{8}{\sqrt{35}}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{8}{\sqrt{14}}\)

Question 6.
If \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\) are two unit vectors inclined at an angle π/ 3, then the value of |\(\vec{a}+\vec{b}\)| is:
(a) greater than 1
(b) less than 1
(c) equal to 0
(d) equal to - 1
Answer:
(a) greater than 1
Question 7.
If \(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}\) = 0 and \(\vec{a}+\vec{b}\) makes an angle of 60° with a then:
(a) \(|\vec{a}|=\sqrt{3}|\vec{b}|\)
(b) \(|\vec{a}|=2|\vec{b}|\)
(c) 2\(|\vec{a}|=|\vec{b}|\)
(d) \(\sqrt{3}|\vec{a}|=|\vec{b}|\)
Answer:
(d) \(\sqrt{3}|\vec{a}|=|\vec{b}|\)
Question 8.
If \(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}\) = - \(|\vec{a} \| \vec{b}|\) then the angle between a and b is:
(a) 180°
(b) 60°
(c) 45°
(d) 90°
Answer:
(a) 180°
Question 9.
If \(\vec{x}\) and \(\vec{y}\) are unit vectors and \(\vec{x} \cdot \vec{y}\) = 0, then:
(a) \(|\vec{x}+\vec{y}|\) = √2
(b) \(|\vec{x}+\vec{y}|\) = 2
(c) \(|\vec{x}+\vec{y}|\) = 1
(d) \(|\vec{x}+\vec{y}|\) = √3
Answer:
(a) \(|\vec{x}+\vec{y}|\) = √2
Question 10.
If \(|\vec{a} \times \vec{b}|^2+|\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}|^2\) = 144 and \(|\vec{a}|\) = 4 then \(\vec{b}\) is equal
(a) 8
(b) 3
(c) 16
(d) 12
Answer:
(b) 3

Question 11.
If a and b represent the adjacent sides of a parallelogram whose area is 5 units, then the area of the parallelogram whose adjacent sides are \(3\vec{a}+2 \vec{b}\) and \(\vec{a}+3 \vec{b}\) is:
(a) 75 units
(b) 165 units
(c) 45 units
(d) 105 units
Answer:
(d) 105 units
Question 12.
If |\(\vec{a}\)| = 1, |\(\vec{b}\)| = 4, \(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}\) = 2 and \(\vec{c}\) = 2 \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b}-3 \vec{b}\), then the angle between \(|\vec{b}|\) and \(|\vec{c}|\) is:
(a) \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
(b) \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
(c) \(\frac{5 \pi}{6}\)
(d) \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
Answer:
(c) \(\frac{5 \pi}{6}\)
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
If \(\vec{a}\) is a non-zero vector, then \((\vec{a} \cdot \hat{i}) \hat{i}+(\vec{a} \cdot \hat{j}) \hat{j}+(\vec{a} \cdot \hat{k}) \hat{k}\) equals .....................
Answer:
0
Question 2.
The projection of the vector î - ĵ on the vector î + ĵ is ..................
Answer:
0

Question 3.
\(\vec{a}\) and - \(\vec{a}\) are ......................
Answer:
collinear
Question 4.
A line with two arrow heads is called a .................... line.
Answer:
directed
Question 5.
A directed line segment has ...................... as well as direction.
Answer:
magnitude
True/False
Question 1.
Resultant of two collinear vectors remains same ..........................
Answer:
False
Question 2.
A quantity bas magnitude as well as direction is called a vector ........................
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The point A from where the vector \(\overrightarrow{A B}\) starts is called its initial point .........................
Answer:
True

Question 4.
The point B where the vector \(\overrightarrow{A B}\) ends is called its terminal point ...............................
Answer:
True
Question 5.
The vector \(\overrightarrow{O P}\) having O and P as its terminal and initial points respectively, is called the position vector ........................
Answer:
False
