RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
These comprehensive RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Notes General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
→ The process of reducing a metal oxide with coke orsome other reducing agent upon heating is known as Pyrometallurgy.
→ Highly reactive metals are isolated from their ares by electrometallurgy.
→ The isolation of metal which are presents in soluble complex by the addition of more reactive metal is called hydrometallyrgy.
→ Zinc dust can be prepared by melting zinc and then atomising it with blast of air.
→ Granular Zinc canbe prepared by pouring molten zinc into cold water.
→ Pig Iron: The iron obtained from blast furnace has 4% impurities known as pig iron.
→ Cost Iron: The iron obtained by pig iron after treatment with scap of carbon and oxidising it by passing hot air through it. It has 3% impurities.

→ Wrought iron or malleable iron: It is the purest form of iron. It contains carbon and other impurities not more than 05%. It is malleable and easily weladed.
→ Steel: Iron having 05% to 15 % carbon along with small amounts of other elements like Mn, Cr, Ni etc. known as steel.
→ The bauxite having oxides of iron as main impurities are known as red bauxite.
→ The bauxite having oxides of silicon as main impurities are known as white bauxite.
→ Baeyer's process is used to purify red bauxite.
→ Serpeck's process is used to purify white Bauxite.
→ The process of extracting a metal by reduction of its oxide with carbon (inform of coke, charcoal as CO) is called smelting.
→ Iron pyrites (FeSj) is known as fool's gold.
→ The minerals from which the metal can be extracted economically and profitable is known as ores.
→ The impurities present in ores are known as gaintgae as matrix.
→ Removal of impurities to certain extent is achieved by concentration or benefication.
→ Concentrated ore is then converted into oxides by roasting known as calcination.
→ Reducing agents can reduce oxides of metals into metals.
→ During reduction process, the oxide is reduced and the reducing agent is oxidised. In these two reactions, the net Gibbs energy change is negative, which becomes more negative on raising the temperature.
→ Conversion of the physical states from solid to liquid or to gas, and formation of gaseous states favours the decrease in the Gibb's energy.
→ Ellingham diagram represents the variation of standard free energy (AG) with temperature for the formation of oxides of elements.

→ Refining process depends upon the differences in properties of the metal and the impurities.
→ Extraction of aluminium is carried out from its bauxite ore. Bauxite leached by Baeyer's process, where pure alumina is formed, which can be converted into metal by Hall-Heroult's process.
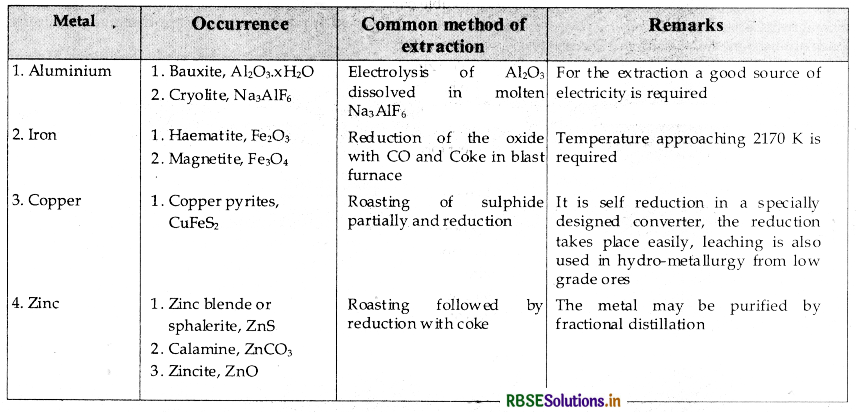
→ Summary of the occurrence and extraction of some metals is as follows:

- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 16 दैनिक जीवन में रसायन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 15 बहुलक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 जैव-अणु
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 ऐमीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12 ऐल्डिहाइड, कीटोन एवं कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 11 ऐल्कोहॉल, फीनॉल एवं ईथर
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 10 हैलोऐल्केन तथा हैलोऐरीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 उपसहसंयोजन यौगिक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 d- एवं f-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 p-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 तत्वों के निष्कर्षण के सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रम