RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry
These comprehensive RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Notes Surface Chemistry
→ Adsorption: It is the phenomenon of attracting and retaining the molecules of a substance at the surface are interface of a solid or a liquid resulting into higher concentration of the molecules on the surface than in the bulk.
→ Adsorbate: The substance which gets adsorbed at any surface is called adsorbate.
→ Adsorbent: The solid are liquid at the surface of which adsorption takes place is termed as adsorbent.
→ Desorption : The removal of adsorbate from the surface of adsorbent is termed as desorption.
→ Sorption: When adsorption and absorption occur simultaneously then the process is called sorption.

→ Interface : The surface of adsorbent, at which adsorbate is adsorbed or concentrated is known as interface.
→ Active centres of Adsorption : The surface of adsorbent has some free valencies, these free, valencies are known as active centres.
→ Positive Adsorption: When the concentration of adsorbate is higher at surface relative to the concentration in the bulk then this type of adsorption is called positive adsorption.
→ Negative Adsorption : When the concentration of adsorbate is lower at the surface relative to the concentration in the bulk then this type of adsorption is called positive adsorption.
→ Heat of Adsorption : It is the amount of heat released during the adsorption of one mole of adsorbate of adsorbate at the surface of adsorbent.
→ Physical Adsorption : When the particles are molecules of the adsorbate are held to the surface of adsorbent by some physical forces like vander Waal's forces then such type of adsorption is termed as physical adsorption are physiosorption.
→ Chemical Adsorption : When the forces of attraction existing between adsorbate and adsorbent are strong chemical bonds, then the adsorption is called chemical adsorption.
→ Critical temperature: The minimum temperature, above which a gas cannot be liiquidified even at a very high pressure, is called criitical temperature.
→ Adsorption Isotherm: The relationship between around of adsorption and pressure of gas at constant temperature is called adsorption isotherm.
→ Freundlich adsorption isotherm curve equation
log\(\frac{x}{m}\) = logk + \(\frac{1}{p}\) log p
→ Homogeneous catalysis: If the reactants products and catalyst are in same phase than this type of catalysis is known as homogeneous catalysis
2SO2(g) + O2(g) + [NO](g) → 2SO3(g) + [NO](g)
→ Heterogeneous catalysis: If the catalyst present is not in same phase as reactants and products in a chemical reaction then this type of catalysis is called heterogeneous catalysis.
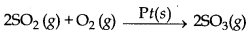
→ Positive Catalyst : The catalyst which can increase the rate of a chemical reaction is called positive catalyst.
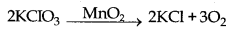
Here, MnO2 is positive catalyst
→ Negative Catalyst : The catalyst which can decrease the rate of a chemical reaction is known as negative catalyst.
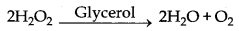
Here glycerol is negative catalyst.
→ Auto Catalysis : During a chemical reaction, when one of the products formed behaves as a catalyst and increases the rate of reaction then such catalyst is known as auto catalyst.
Example:
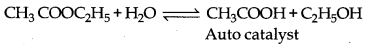

→ Catalytic Poison or Inhibitor : The substance which destroys the activity of a catalyst is called catalytic posion.
Example:
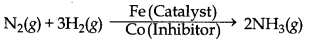
→ Catalytic Promotor : The substances which can increase the efficiency of catalyst but themselves are not catalysts are known as catalytic promoters.
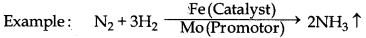
→ Colloidal Solution : It is an intermediate state between their solution and suspension. The size of their particles is in between 1 nm to 1000 nm. It has two phases :
(a) Dispersed phase
(b) Dispersion medium
→ Positive Colloids : The colloidal solutions in which the particles of dispersed phase have positive change then they are called positive colloids.
Examples: Metal hydroxides Al(OH)3, Fe (OH)3, etc.
→ Negative Colloids : The Colloidal solutions in which the particles of dispersed phase have negative charge then they are called negative colloids.
Examples: Metals like Au, Ag, Cu, Pt, Fe, Cd, Soil, etc.
→ Lyophillic Colloids: The colloidal solutions like gum, gelatin, starch, rubber, etc., with a suitable dispersion medium are called lyophilic colloids. Here the dispersed phase and dispersion medium have high affinity for each other.
→ Lyophobic Colloids : The colloidal solutions which are not easily formed, known as lyophobic calloids, here the dispersed phase and dispersion medium have very little affinity for each other.
→ Critical Micelle Concentration: The concentration below which substances behaves as electrolyte and above which behaves as colloids is known as critical micelle concentration.
→ Kraft Temperature : The formation of micells takes place only above a particular temperature which is called kraft temperature.
→ Micelle : On increasing the concentration of solution of soaps and detergents from CMC then the molecules of soaps and detergents associated and form aggregate of colloidal size. The aggregates are called micelles.
→ Peptization : The process of converting a precipitate into colloidal sol by shaking it with dispersion medium in the presence of a small amount of electrolyte is called peptization.
→ Dialysis : The process of removing excess dissolved impurities of electrolytes from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a parchment paper of animal membrane is called dialysis.

→ Electrodialysis: Dialysis is a slow process. It can be made faster by carried out this process under the influence of an electric field. Then this process is called electro dialysis.
→ Tyndall Effect : The scattering of light by the colloidal particles is known as Tyndal effect.
→ Brownion Movement : The zig-zag motion of colloidal particle is known as Brownian movement.
→ Electrophoresis : When electric field is applied on colloidal solution then colloidal particles show movement either towards cathode and anode. The movement of particle towards oppositely charged electrode is known as electrophoresis.
→ Gold Number: The number of milligrams or a hydro phylic colloid which just prevent the precipitation of 10 mL of gold sol on the addition of 1 mL of ten per cent sodium chloride solution is known as Gold number.
→ Emulsifying Agent: Emulsion of oil and water is unstable and sometimes they are distributed into two layers. So to make the system stable a third component is added to it. It is known as Emulsifying Agent or emulsifier.
