RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 Amines
These comprehensive RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 Amines will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Notes Amines
→ Aliphatic amines :
In such type of amines nitrogen atom is attach with one or more alkyl groups. Example: CH3NH2
→ Aromatic amines :
In such type of amines nitrogen atom is attaded with one or more aryl group diirectly. Example: C6H5NH2
→ Ammonolysis:
The dissociation of C-X bond wiith ammonia molecule is termed as ammonolysis.
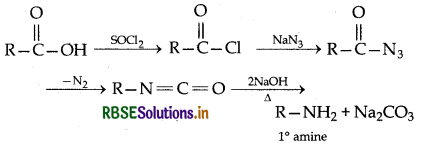
→ Curtius degradation:
The complete reaction in which acyl azide releases nitrogen and forms intermediate compound, gives primary amine on hydrolyis in acidic or basic medium which has one carbon less than carboxylic acid is known as Curtius degradation.

→ Order of basicity:
(i) 3° amine > 2° amine > 1° amine (gaseous phase)
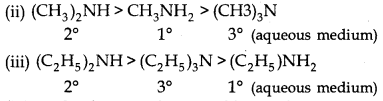
(iv) p-toluedien > aniline > p-chloroaniline > p-nitroaniline
(v) p-anisidine > m-aniline
(vi) Aniline > m-nitroaniline > p-nitroaniline > o-nitroaniline
(vii) p-mfethyl anisidine > m-methyl aniline > aniline > o-methyl aniline
→ Acylation : Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amine give nucleophilic substitution reaction with acid chlorides, anhydride and easter. This is called Acylation reaction.
→ Benzolation: Amine also reacts with benzoyl chloride (C6H5COCl) and H-atom of amine is replaced by COC6H5 group, this reaction is called Benzoylatioin.
→ Diazotisation : Primary aromatic amine reacts with nitrous acid at very low temp (0-3°C) forms aromatic diazonium salt. This is known as Diazotisation.
→ Hinsberg's reagent : Benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) is termed as Heinsberg's reagent.
→ Sulphanilic acid: p-amino benzene sulphonic acid is termed as Heinsberg's reagent.
→ Hydration effect: Stability of protonated amine by water molecule is called Hydration effect or solvation effect.
→ Coupling reaction: When benzene diazonium chloride reacts with other aromatic compound then the azo products obtained have anextended conjugate system having both the aromatic rings joined through the —N = N — bond and coloured compounds are formed. Such type of reaction are termed as Coupling Reation.
→ On dissolving alkyl halide in very less quantity of alcohol and then reaction with KCN (aqueous), alkyl cyanide are obtained whereas reaction with AgCN, alkylisocyanide are formed.
→ Alkyl Cyanides are obtained by dehydration of aldoximes in the presence of P2O5.
→ Alkyl Cyanides have pleasant odour but alkyl isocyanides of same molecular weight have very unpleasent odour.
→ Alkyl cyanides are more soluble than alkyl isocyanide because of Hydrogen bonding.
→ Alkyl isocyanides shows addition reaction with halogen, sulphur, ozone, mercuric oxide
→ Alkyl isocyanides when heated strongly for a long time is converted to more stable cyanide.
→ Urea is the first organic compound which was synthesised from inorganic compounds by Wohler.
→ Urea reacts with malonic acid to form sleeping medicine barbituric acid.
→ Nitration: Introducing nitro group in any molecule.
→ The mixture of cone. HNO3 and cone. H2SO4 is called nitrating mixture.
→ The readuction of nitroalkane in different conditions gives different product which is shown by following chart.
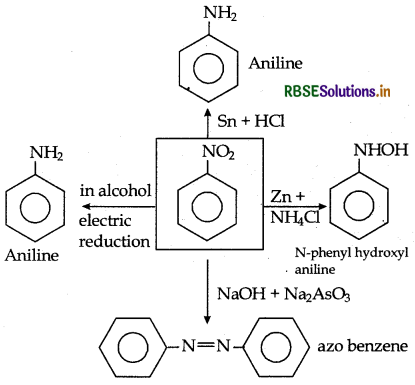
→ The differentiation among primary, secondary and tertiary nitroalkanes can be done by reaction nitro alkane forms nitrolic acid with nitrous acid which dissolving in base gives red colour solution. Secondary nitroalkane forms blue coloured pscidontrol with nitrous acid whereas tertiary nitroalkane do not react with nitrous acid.

→ Nitrozene or nitrobenzene is ortho-para (o-p) directive for nucleophilic substitution reaction.
→ Nitrozene or nitrobenzene is meta (m) directive for electrophilic substitution.
→ Gattermann Reaction:

→ Sandmeyer's Reaction:
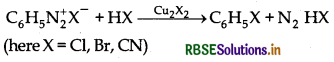
→ Baiz Schlemann Reaction:
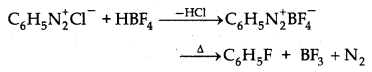
→ Diazotisation:
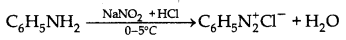
→ Hoffmann's mustard oil reaction:
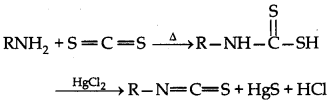
→ Libermann's nitroso reaction:
It is used differentiate between primary and secondary amine.
→ Carbylamine test:
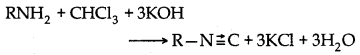
→ Sochotten Baumann reaction:
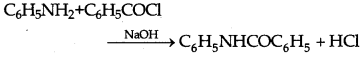
→ Schmidt reaction:
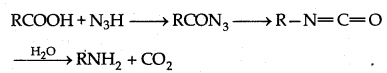

→ Curtius reaction:
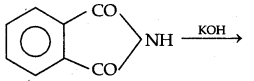
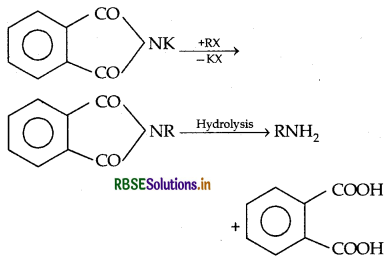
→ Hoffmann's Bromamide reaction:
RCONH2 + Br2 + 4KOH → RNH2 + K2CO3 + 2KBr + 2H2O
→ Carbyiamine test:
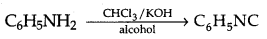
→ Mendius reduction:
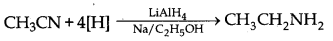
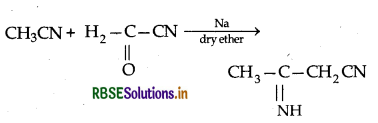
→ Thorpe reaction
→ Biuret test:
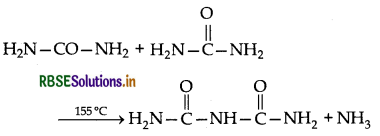

- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 16 दैनिक जीवन में रसायन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 15 बहुलक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 जैव-अणु
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 ऐमीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12 ऐल्डिहाइड, कीटोन एवं कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 11 ऐल्कोहॉल, फीनॉल एवं ईथर
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 10 हैलोऐल्केन तथा हैलोऐरीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 उपसहसंयोजन यौगिक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 d- एवं f-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 p-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 तत्वों के निष्कर्षण के सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रम