RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 Important Questions The p-Block Elements
Multi Choice Questions (MCQ):
Question 1.
Which of the following elements occur in free state:
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Arsenic
(c) Phosphorus
(d) Antimony
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen

Question 2.
PCl5 exist but NCl5 does not because:
(a) Nitrogen does not have free d-orbitals
(b) NCl5 is stable
(c) Nitrogen atom is very small
(d) Nitrogen is very inert in nature.
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen does not have free d-orbitals
Question 3.
In solid state PCl5 exist as :
(a) In the form of PCl5
(b) In the form of PCl6-
(c) In the form of PCl4+
(d) In the form of [PCl4+] [PCl-]
Answer:
(d) In the form of [PCl4+] [PCl-]
Question 4.
The mixture used in holme signals:
(a) CaC2 + CaCl2
(b) CaC2 + Ca3P2
(c) CaCl2 + Ca3P2
(d) CaC2 + CaN2
Answer:
(b) CaC2 + Ca3P2
Question 5.
Nitrogen show anomalous behaviour because of:
(a) small size and high electro negativity
(b) Absence of d-orbitals in valence shell
(c) Tendency to from multiple bonds easily
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 6.
The H-N-H bond angle in anmonia is :
(a) 109°28'
(b) 108°
(c) 105°
(d) 106°25'
Answer:
(d) 106°25'
Question 7.
Which of the following element is metalloid :
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Antimony
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Bismuth
Answer:
(b) Antimony
Question 8.
Nitrogen is inert in nature because:
(a) It is a mutiple bonded molecule
(b) Bond polarity is absence
(c) Inter nuclear distance is very less
(d) Bond energy is very high
Answer:
(d) Bond energy is very high

Question 9.
Which of the following has minimum melting point:
(a) NH3
(b) PH3
(c) AsH3
(d) SbH3
Answer:
(b) PH3
Question 10.
Which of the following is most basic:
(a) NH3
(b) PH3
(c) AsH3
(d) SbH3
Answer:
(a) NH3
Question 11.
The shape of ammonia molecule is :
(a) See-saw shape
(b) Triangular planer
(c) Octahedial
(d) Pyramidal
Answer:
(d) Pyramidal
Question 12.
When ammonia reacts with the axcess of chlorine then which fo the following compound is obtained:
(a) N2 and NCl3
(b) N2 and HCl
(c) N2 and NH4Cl
(d) HCl, and HCl
Answer:
(d) HCl, and HCl
Question 13.
What is the outer most electronic configiuation of nitrogen atom:
(a) ns2 np5
(b) ns2 np4
(c) ns2 np3
(d) ns2 np1
Answer:
(c) ns2 np3
Question 14.
Which of the following is used in drying the ammonia gas:
(a) conc. H2SO4
(b) P2O5
(c) only CaCl2
(d) CaO
Answer:
(d) CaO
Question 15.
The correct order of first ionisation potential is:
(a) C < N < O < F
(b) C > N > O > F
(c) C < N > O < F
(d) C > N < O < F
Answer:
(c) C < N > O < F
Question 16.
The basicity of H3PO3 is:
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) zero
Answer:
(b) two
Question 17.
Nitrogen is adi-atomic molecule. Which of the following is while phosphorus molecule:
(a) P2
(b) P4
(c) P6
(d) P8
Answer:
(b) P4
Question 18.
Which of the following element has the highest electro negativity:
(a) P
(b) C
(c) As
(d) N
Answer:
(d) N
Question 19.
White phosphorus is strored in which of the following liquid:
(a) Chloroform
(b) Carbon tetra chloride
(c) Benzene
(d) Water
Answer:
(d) Water

Question 20.
Nitrolim is:
(a) Ca(CN)2 + C
(b) CaC2
(c) CaCN2 + C
(d) Ca(CN)2
Answer:
(c) CaCN2 + C
Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Give reason for the following: Ozone is thermodynamically less stable than oxygen.
Answer:
Ozone is thermodynamically less stable than oxygen because its decomposition into oxygen results in the liberation of heart (∆H is negative) and increase in entropy (∆S is positive). These two effects reinforce each other that results in large negative Gibbs energy change (∆G) for its conversion into oxygen. Hence, high concentration of ozone can be dangerously explosive.
Question 2.
Give reason for the following Above 1000 K sulphur shows paramagnetism.
Answer:
Above 1000 K, sulphur show paramagnetism due to its existence in vapour state as S2 (i.e. diatomic state).
Question 3.
Complete the following reaction.
PbS(s) + O3 →
Answer:
PbS(s) + 4O3(g) → PbSO4(s) + 4O2(s)
Question 4.
Assign suitable reason for the following SF6 is inert towards hydrolysis.
Answer:
SF6 is sterically protected by six F-atoms and hence does not allow H2O molecule to attack the S-atom. Thus, SF is inert towards hydrolysis.
Question 5.
Draw the structure of H2S2O8.
Answer:
Structure of H2S2O8 is given below:
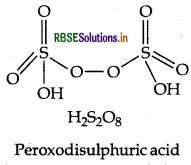
Question 6.
Sulphur in vapour state exhibits paramagnetic behaviour. Give reason.
Answer:
In vapour state, sulphur partly exists as S2 molecule which has two unpaired electron in the antibonding p-orbitals like O2 and hence, exhibits paramagnetism.

Question 7.
Complete the following chemical equation:
Fe3+ + SO2 + H2O →
Answer:
Fe3+ + SO2 + H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO4 + 4H+
Question 8.
Oxygen is a gas but sulphur is a solid at room temperature.
Answer:
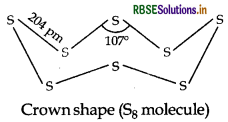
Oxygen atoms, owing to small size, form рл-рë ьоnd between atoms and exist as diatomic (O2) molecules. As a result van der Waals forces acting on these mol- ecules are very less and the molecules exist in gaseous state. On the other hand, sulphur atoms, unable to form л- bonds due to large size, form single covalent bond between atoms which results in formation of cyclic molecules comprising of 8 atoms (Sg). Hence, van der Waals' forces act on these molecules to larger extent and a result sulphur exists in solid state.
Question 9.
Write the formulae of any two oxoacids of sulphur.
Answer:
- H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid)
- H2SO3 (Sulphurous acid)
Question 10.
Which allotrope of sulphur is thermally stable at room temperature?
Answer:
Rhombic sulphur is themally stable at room temperature.
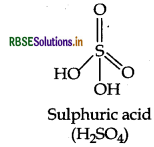
Question 11.
Draw the structure of the following H2SO4
Answer:
(i) The structure of H2SO4 is
Question 12.
Complete the following chemical equation:
Cu + H2SO4 (conc.) →
Answer:
When conc. H2SO4 is added to Cu, then CuSO4 and SO2 are formed. In this reaction, hot conc. H2SO4 acts as a moderately strong oxidising agent. Here, metal is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 and itself it is reduced to SO2.
Cu + 2H2SO4(conc) → CUSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
Question 13.
Draw the structure of the following compound:
Answer:
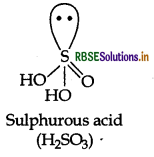
Question 14.
Give reason for the following:
Oxygen has less electrons gain enthalpy with negative sign than sulphur.
Answer:
Because of the compact nature (small size) of oxygen atom, it has less negative electron gain enthalpy than sulphur.
Question 15.
Account for the following:
Oxygen shows catenation behaviour less than sulphur.
Or
Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen. Why?
Or
Sulphur exhibits tendency for catenatio but oxygen does not do so. Give reason.
Answer:
Bond energy of S - S bond (213 kJ mol-1) is greater than O-O bond (138 kJ mol-1). Due to small size of oxygen atom, there is greater lp-bp repulsion in O - O, resulting in weakening of O - O bond more than in S - S bond. Therefore, the tendency of catenation in oxygen is lower than sulphur.
Question 16.
Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in the following case SO3 and the angle in O - S - O.
Answer:
Structure of SO3 is pyramidal as shown below:
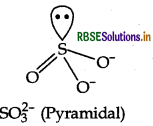
Shape: Pyramidal
Angle in O - S - O: More than 90°.
Question 17.
Of PH3 and H2S, which is more acidic and why?
Answer:
H2S is more acidic than PH3 because S is more electronegative than P. So, S-H bond is more polar than P-H bond resulting in easier removal of H+ ion from H2S.
Question 18.
All the bonds in SF4 are not equivalent. Explain, why?
Answer:
In SF4, sulphur is sp3 d-hybridised. It has trigonal bipyramidal structure in which one of the equatorial positions is occupied by a lone pair of electrons (see- saw geometry). That's why, all the bonds in SF4 are not equal.
Question 19.
Give reason : H2S is more acidic than H2O.
Answer:
Due to decrease in (E - H) bond dissociation enthalpy down the group, acidic character increases. Thus, H2S is more acidic than H2O.

Question 20.
Draw the structure of H2S2O7.
Answer:
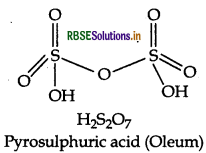
Question 21.
SF6 is kinetically inert substance. Explain.
Answer:
In SF molecule the six atoms of fluorine sterically protect the sulphur atom from attack by a reagent. Hence, SF6 is called kinetically inert substance.
Question 22.
Complete the following chemical equation:
SO3 + H2SO4(conc.) →
Answer:
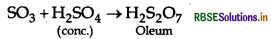
Question 23.
What happens when sulphur dioxide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a Fe(III) salt?
Answer:
Fe3+ + SO2 + H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO4 + 4H+
Question 24.
Complete the following equation:
C + H2SO4(conc.) →
Answer:
C + 2H2SO4 (conc.) → CO2 + 2SO2 + 2H2O
Question 25.
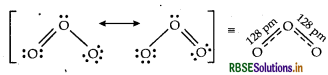
Explain : The two oxygen-oxygen bond lengths in ozone (O3) molecule are same.
Answer:
The two oxygen-oxygen bond lengths in the ozone molecule are identical (128 pm). Because it is a resonance hybrid of the following two main forms:
Question 26.
Elements of group 16 generally show lover value of first ionisation enthalpy as compared to the corresponding elements in the period of group 15. Explain why?
Answer:
Due to the presence of extra stable half-filled np - orbitals in the electronic configurations of group 15 elements (ns2np3 configuration), greater amount of energy is required to remove electrons as compared to group 16 elements (ns2 np1 configuration). Thus, ionisation energy of group 16 elements is lower than that of the corresponding elements of group 15.
Question 27.
O3 acts as a powerful oxidising agent. Give reason.
Answer:
Ozone acts as a powerful oxidising agent because it liberates nascent oxygen.
O3 → O2 + [O]
e.g. it oxidises lead sulphide to lead sulphate.
PbS(s) + 4O3(g) → PbSO4(s) + 4O2(g)
Question 28.
The value of electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for sulphur is higher than that for oxygen. Give reason.
Answer:
Because of the compact nature (small size) of oxygen atom, it has less negative electron gain enthalpy than sulphur.
Question 29.
Draw the structure of O3 molecule.
Answer:
Structure of O3 molecule is given below.
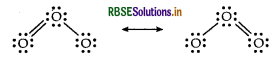
Question 30.
H2S is less acidic than H2Te. Why?
Answer:
Due to decrease in (E - H) bond dissociation enthalpy down the group, acidic character increases. Thus, H2S is less acidic than H2Te.
Question 31.
OF6 compound is not known. Why?
Answer:
Due to the absence of d-orbitals in O, it limits its covalency to four, therefore OF6 is not formed.

Question 32.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
Excess of SO2 reacts with sodium hydroxide solution.
Answer:
The asked reaction results in formation of sodium hydrogen sulphite.
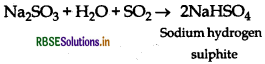
Question 33.
Sulphur hexafluoride is less reactive than sulphur tetrafluoride. Why?
Answer:
SF6 is sterically protected so, it is less reactive than SF4.
Question 34.
Why are the two S-O bonds in SO2 molecule of equal strength?
Answer:
Due to resonance, the two S-O bonds in SO2 are of equal strength.
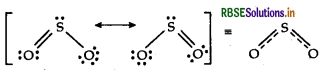
Question 35.
What happen when, chlorine gas reacts with cold and dilute solution of NaOH?
Answer:
When chlorine reacts with cold and dilute solution of NaOH, sodium hypochlorite is formed.
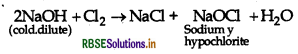
Question 36.
Draw the structure of the following HCIO3
Answer:
The structure of HCIO3 is given below
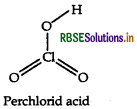
Question 37.
How can you prepare Cl2 from HCl and HCl from Cl2? Write reactions only.
Answer:

HCI can be prepared from Cl2 on treating it with water.

Question 38.
Arrange the following in increasing order of property indicated, giving reason:
Hydrides of group 17-acidic strength.
Answer:
Increasing order of acidic strength of hydrides of group- 17 follows the order
H - F < H - Br < H - C < H - I
This is because the bond dissociation enthalpy of H - X bond decrease from H - F to H - I as the size of the atom increases from F to I.
Question 39.
Despite lower value of its electron gain enthalpy with negative sign, fluorine, F2 is a stronger oxidising agent than Cl2.
Or
Although electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative than that of chlorine, yet flourine is a better oxidising agent than chlorine.
Answer:
Fluorine is the stronger oxidising agent as it is more electronegative than chlorine, it accepts electron most easily. It oxidises other halide ions in solution or even in solid phase.
F2 + 2X- → 2F + X2 (X = Cl, Br or I)
Question 40.
Give reason:
When Cl2 reacts with excess of F2, CIF3 is formed and not FCl3.
Answer:
CIF3 is formed because it is stable. FCl3 does not exist actually because
- Cl has vacant d-orbitals and hence, can show an oxidation state of +3, but F has no d-orbitals, there- fore, it cannot show positive oxidation states.
- Further, since F can show only -1 oxidation state due to its highest electronegativity. Therefore, it forms only CIF or CIF3.
Question 41.
Arrange the following in the decreasing order of their reducing character.
HF, HCl, HBr, HI
Answer:
Decreasing order of depends on the ease with which it decomposes to give H2 and X2, which in turn de- pends on bond dissociation energy. Bond dissociation energy is least for Hl, hence it has maximum reducing character.
Question 42.
Give reason, electron gain enthalpies of halogens are largely negative.
Answer:
Halogens have the smallest size in their repective periods and therefore, have high effective nuclear charge. As a result, they readily accept one electron to acquire the stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas. In other words, large amount of energy is released when a halogen atom accepts an electron to form the corresponding halide ion and thus, halogens have maximum negative electron gain enthalpies.
Question 43.
F2 is a stronger oxidising agent than Cl2. Why?
Answer:
F2 is better oxidizing agent in water than chlorine due to greater hydration energy.

Question 44.
Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas.
Answer:
Phosgene (COCl2), tear gas (CCl3NO2), mustard gas (ClCH2CH2SCH2CH2Cl) all are obtained from chlorine gas (you can write any two gases).
Question 45.
Give reason for the following:
Fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state.
Answer:
Fluorine is the most electronegative element and hence, it cannot exhibit any positive oxidation state.
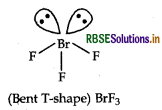
Question 46.
Draw the structure of BrF2 molecule.
Answer:
Structure of BrF3 is given below:
Question 47.
Give reason for the following:
F2 is more reactive than CIF3 but CIF3 is more reac- tive than Cl2.
Answer:
Fluorine due to its small size, high electronegativity and low bond energy is more reactive than CIF3 but bond energy of Cl - Cl bond is higher than Cl - F bond, therefore CIF3 is more reactive than Cl2.
Question 48.
Bond enthalpy of F2 is less than that of Cl2. Why?
Answer:
This is due to relatively large electronic repulsion among the lone pairs in F2 molecule where they are much closer to each other than in case of Cl2.
Question 49.
Give reason for the following:
PbCl is more covalent than PbCl2.
Answer:
If the metal exhibits more than one oxidation states, the halide in the higher oxidation state will be more covalent than the one in lower oxidation state. Therefore, PbCl is more covalent than PbCl2 due to more than one oxidation states of Pb.
Question 50.
Account for the following: HF is not stored in glass bottles but is kept in wax-coated bottles?
Answer:
HF forms fluorosilicate ion on reaction with glass. Hence, it is stored in wax-coated bottles.
Question 51.
Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in the following case:
CIF3 and the angle: F - Cl - F.
Answer:
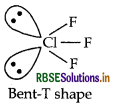
Structure of CIF3 is given below:
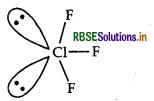
Shape Bent T-shaped
Angle F-Cl-F: Less than 90°
Question 52.
Why is ICI more reactive than I2?
Answer:
Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens (except fluorine) because X - X bond (I - Cl bond in question) in interhalogens is weaker than X-X bond (I-Ibond) in halogens, except F-F bond.

Question 53.
The halogens are coloured, why?
Answer:
All halogens are coloured due to the absorption of radiations in visible region which results in the exci- tation of outer electrons to higher energy level. By absorbing different quanta of radiation, they display different colours.
Question 54.
Draw the structure of CIF3 molecule.
Answer:
Structure of CIF3 is given below:

Shape Bent T-shaped
Angle F-Cl-F: Less than 90°
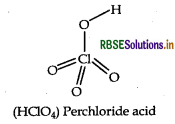
Question 55.
Draw the structure of HCIO4.
Answer:
Structure of HCIO4 is given below:
Question 56.
Complete the following reaction:
NaOH (hot and conc.) + Cl2 →
Answer:
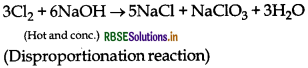
Question 57.
Despite having greater polarity, hydrogen fluoride boils at a lower temperature than water.
Answer:
Higher boiling point of H2O is due to the extensive H-bonding than HF.
Question 58.
Complete the following chemical equation:
Cl2 + F2 (excess) →
Answer:
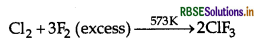
Question 59.
Account for the following:
Chlorine water losses its yellow colour on standing.
Answer:
Due to formation of HCl and HClO, chlorine water loses its yellow colour on standing.

Question 60.
F2 is most reactive of all the four common halogens. Explain.
Answer:
It is due to low bond dissociation energy and high hydration energy and high electron affinity.
Question 61.
What happens when chlorine gas is passed through a hot conc. solution of NaOH?
Answer:
When chlorine gas reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH solution, it disproportionates into Chloride (Cl-) and Chlorate (ClO3-) ions. When chlorine gas reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH solution, it disproportionates into Chloride (Cl-) and Chlorate (ClO3-) ions.
Question 62.
Why does fluorine not play the role of a central atom in interhalogen compounds?
Answer:
Fluorine does not have d-orbitals and it cannot show higher oxidation state. Therefore, it does not play the role of a central atom in interhalogen compounds.
Question 63.
How would you account for the following? The oxidising power of oxoacids of chlorine follows the order HClO, < HClO3 < HClO, < HClO.
Answer:
As the oxidation number of halogen atom in oxoacid increases, its oxidising power decreases. Therefore, HClO is least stable and gives [O] most easily, so its
oxidising power is greater than HCIO4. Thus, the oxidising power of oxoacids of chlorine is
HClO4 < HClO3 < HClO2 < HClO

Question 64.
Complete the following chemical equation:
Br2 + F2 (excess) →
Answer:
Br2 + 5F2 (excess) → 2BrF5
Question 65.
Explain in aqueous medium HCl is stronger acid than HF.
Answer:
H-Cl is a storage acid than HF in aqueous medium because with increase in H - X bond length, bond dissociation energy decreases and H+ ion is easily produced.
Question 66.
Draw the structure of HOCIO2 molecule.
Answer:
Structure of HOCIO2 is given below:
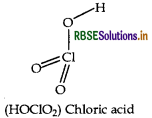
Question 67.
Complete the following reaction:
I2 + H2O + Cl2 →
Answer:
I2 + 6H2O + 5Cl2 → 2HIO3 + 10HCl
Question 68.
Electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for fluorine is less than that for chlorine.
Answer:
Due to small size of fluorine atom there are strong interelectronic repulsions in the relativity smaller 2p- orbitals of fluorine. Thus, incoming electron does not experience much attraction.
Question 69.
Arrange F2, Cl2, Br2 and I2 in the order of increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
Answer:
The order of increasing bond dissociation enthalpy is as follows:
I2 < F2 < Br2 < Cl2
Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Complete the following reaction.
XeF6 + NaF →
Answer:
XeF6 + NaF → Na + [XeF7]-
Question 2.
What happens when XeF2 undergoes hydrolysis?
Answer:
XeF2 readily hydrolysed even by traces of water.
2XeF2(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2Xe(g) + 4HF(aq) + O2(g)

Question 3.
Out of noble gases only xenon is known to form established chemical compounds.
Answer:
Only xenon is well known to form chemical com pounds because xenon is large in size and having higher atomic mass. Due to large atomic radius the force of attraction be tween the outer electron and the protons is weak hence they are easily available to form compounds.
Question 4.
Complete the following equation :
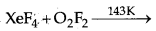
Answer:
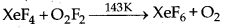
Question 5.
Draw the structure of the following:
XeF4
Answer:
Structure of XeF4 is as follow
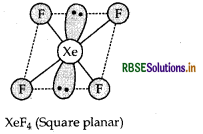
Question 6.
Complete the following reaction:
XeF4 + SbF5 →
Answer:
XeF4 + SbF5 → [XeF3] + [SbF6]-
Question 7.
Draw the structure of the following XeOF4
Answer:
Structure of XeOF4 is as follows
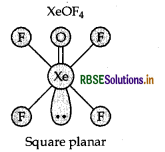
Question 8.
Complete the following reaction:
XeF6 + 2H2O →
Answer:
XeF6 + 2H2O → XeO2 F2 + 4HF
Question 9.
(i) Draw the structures of the following molecules.
(a) XeOF4
(b) H2SO4
Answer:
(i) (a) Structure of XeOF4 is as follows

(b) Helium is used as a diluent for oxygen in modern div- ing apparatus because of its very low solubility in blood.
Question 10.
Draw the structure of XeF2 molecule.
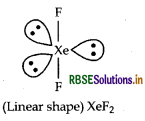
Answer:
Structure of XeF2 molecule is given below:
Question 11.
Helium is used in diving equipments. Why?
Answer:
Helium is used as a diluent for oxygen in modern div- ing apparatus because of its very low solubility in blood.
Question 12.
What inspired N Bartlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6?
Answer:
Bartlett found the first ionisation enthalpy of molecular oxygen in O2 [PtF6] to be almost similar with that of xenon. Thus, he got inspired for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6 and prepared Xe+ [PtF6]- by mixing Xe and PtF6.

Question 13.
Draw the molecular structure of XeF6.
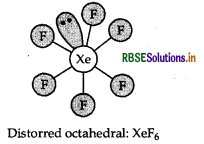
Answer:
Structure of XeF6 is given below:
Question 14.
Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in the following case:
XeF2 and the angle F-Xe-F
Answer:
Structure of XeF2 is given below:
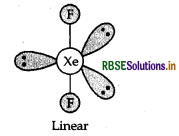
Shape: Linear
Angle: F - Xe - F: 180°
Question 15.
Answer:
According to the valence bond approach, covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals. But xenon has fully-filled electronic configuration. Hence, the structure of xenon fluorides cannot be explained by VBT.
Question 16.
Helium forms no real chemical compound. Why?
Answer:
Due to its small and high ionisation energy helium is chemically unreactive. That's why, it forms no real chemical compound.
Question 17.
Complete the following chemical equation:
XeF4 + H2O →
Answer:
6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
Question 18.
Why do noble gases have very low boiling points?
Answer:
Due to weak van der waals forces of attraction between atoms of noble gases (weak dispersion forces), these have very low boiling points.
Question 19.
Complete the following chemical equation:
XeF6 + H2O (Excess) →
Answer:
XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 +6HF
Note: Partial hydrolysis of XeF6 gives oxyfluorides,
XeOF4 and XeO2F2
XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
XeF6 + 2H2O → XeO2F2 + 4HF
Question 20.
Complete the following reaction equation:
XeF2 + PF5 →
Answer:
XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+ [PF6]-
Question 21.
XeF2 is linear molecule without a bent. Explain.
Or
XeF2 has a straight linear structure and not a bent angular structure. Explain.
Answer:
XeF2 is linear molecule. According to VSEPR theory, the three lone pairs will occupy the equatorial positions and two bond pairs will occupy axial positions to minimise lp-lp and Ip-bp repulsions.
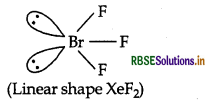
Question 22.
Noble gases are least reactive elements. Give reason.
Answer:
Least reactivity of the noble gases is due to the following reasons:
- The noble gases except helium 1s2 have completely filled ns2np electronic configuration in their valence shell.
- They have high ionisation enthalpy and more positive electron gain enthalpy.
Question 23.
What happens when XeF6 is is hydrolysed?
Answer:
The complete hydrolysis of XeF6 produces XeO3 which is xenon trioxide. This xenon trioxide is highly explosive and acts as a powerful oxidising agent in solution.

Question 24.
Write a chemical reaction to test sulphur dioxide gas. Write chemical equation involved.
Answer:
SO2 is a pungent smelling gas. Two tests are used to detect the presence of SO2 that are as follows:
(i) SO2 turns the pink-violet colour of KMnO4 solution to colourless due to the reduction of MnO-4 to Mn2+.
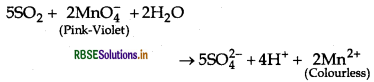
(ii) SO2 turns organge coloured acidified K2Cr2O7 solution to green due to the reduction of Cr2O2- to Cr3+ ion.
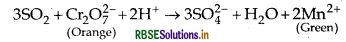
Question 25.
What happens when
(i) conc. H2SO4 is added to Cu?
(ii) SO3 is passed through water? Write the equations.
Answer:
(i) Structure of BrF3 is given below:

(ii) SO3 reacts vigorously with water, evolving a large amount of heat and forming H2SO4.
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Question 26.
Name the two most important allotropes of sulphur. Which one of the two is stable at room temperature? What happens when the stable form is heated above 370 K?
Answer:
Two most important allotropes of sulphur are
- rhombic sulphur (a-sulphur)
- monoclinic sulphur
The stable form at room temperature is rhombic sulphur which transforms to monoclinic sulphur when heated above 370K.
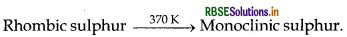
Question 27.
1. Write the conditions to maximise the yield H2SO4 by contact process.
2. Why is Ka2 << Ka1 for H2SO4 in water?
Answer:
- Low temperature (about 720 K), high pressure about 2 bar and presence of catalyst (V2O5) are the favourable conditions for the manufacture of H2SO4 by contact process.
- H2SO4 is very strong acid in water largely because of its ionisation to H3O+ and HSO4. Further, ionisation of HSO4 to SO and H3O+ is very small as losing H+ from a negatively charged HSO4 is more difficult. That's why, Ka2 << Ka1.
Question 28.
Account for the following:
(i) Decomposition of O3 molecule is a spontaneous process.
(ii) SF is inert towards hydrolysis.
Answer:
(i) For spontaneity of a reaction, AG must be negative. Decomposition of O3 is an exothermic process (∆H = - ve) and occurs with increase in entropy (∆S = +ve). These two effects reinforce each other which results in large negative Gibbs energy change. It favours its decomposition into oxygen.
(ii) In SF6,S atom is sterically protected by six F atoms and does not allow water molecules to attack the S atom. Further, F does not have d-orbitals to accept the electrons donated by H2O molecules. Due to these reasons, SF6 is kinetically an inert substance.
Question 29.
Account for the following:
1. H2S is less acidic than H2Te.
2. SO2 is an air pollutant.
Answer:
- In binary acids such as H2S and H2Se, the H - Se bonds is longer than the H - S bonds as Se is larger than S. The H - Se bond is therefore weaker than the H - S bond and H2Se is thus a stronger acid than H2S.
- SO2 is water soluble, therefore it dissolves in rain-water causing acid rain. Moreover, when released in air, it mixes with it and leads to several diseases like eyes irritation, redness, asthma, bronchitis, etc. Thus, it is considered as an air pollutant.
Question 30.
Draw the structures of O3 and S8 molecules.
Answer:
Question 31.
(i) Assign reasons for the following:
(a) H2S is more acidic than H2O.
(b) Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.
Answer:
(a) H2S is more acidic than water because OH bonds are stronger than SH bonds. Sulfur is also larger than oxygen, so that helps stabilize the SH- anion relative to OH-.
(b) Sulphur has greater catenation property than oxygen because S-S bond energy is more than O-O bond energy. This is because, oxygen atom is small in size and the lone pair of electrons in oxygen repel bond pair electrons of O-O to a greater extent than sulphur, in turn making the O-O bond weak.

Question 32.
Complete the following reactions:
1. Cl2 + H2O →
2. XeF6 + 3H2O →
Answer:
- Cl2 + H2O → HCl + HOCI
- XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
Question 33.
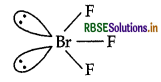
Write the structure of the following:
(i) BrF3
(ii) XeF4
Answer:
The structure of
(i) BrF3: Bent T-shaped
(ii) Structure of XeF4 is as follow

Question 34.
What happens when
(i) SO2 gas is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe3+ salt?
(ii) XeF4 reacts with SbF5?
Answer:
(i) When SO2 gas is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe3+ salt, then SO2 acts as a reducing agent and reduces Fe3+ ions present in the salt to Fe2+ ions.
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO2 ̄ + 4H+
(ii) XeF4 reacts with SbF5 to form a ionic species. XeF4 + SbF5 → [XeF3]+ [SbF6]-
Question 35.
Complete the following chemical reaction equation:
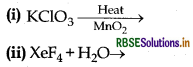
Answer:
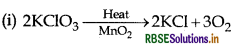
(ii) 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
Question 36.
Complete the following equations :
(i) C + H2SO4 →
(Conc.)
(ii) XeF2 + H2O→
Answer:
(i) C + 2H2SO4 → CO2 + 2SO2 + 2H2O
(ii) 2XeF2 + 2H2O → 2Xe + 4HF + O2
Question 37.
Write the formula and the structures of noble gas species (one each) which are isostructural with
(i) ICI
(ii) BrO3
Answer:
(i) XeF4 (isostructural to ICI4)
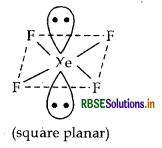
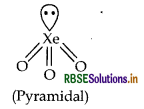
(ii) XeO3 (isostructural to BrO3)
Question 38.
(i) Account for the following:
(a) Ozone is thermodynamically unstable.
(b) Fluorine forms only one oxoacid HOF.
Answer:
(i) (a) Ozone is thermodynamically unstable because its decomposition into oxygen results in the liberation of heat (AH is negative) and increase in entropy (AS is positive). These two effects reinforce each other resulting in large negative Gibbs energy change (AG) for its conversion into oxygen.
(b) Due to high electronegativity and small size, fluorine forms only one oxoacid, HOF known as fluoric (I) acid or hypofluorous acid.
Question 39.
(i) Account for the following:
(a) H2S has lower boiling point than H2O.
(b) Reducing character decreases from SO2 to TeO2.
Answer:
(i) (a) Because of the small size and high electronegativity of oxygen molecules, water molecules are highly associated through hydrogen bonding resulting in higher boiling point of H2O than H2S.
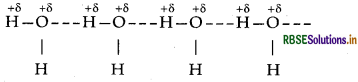
(b) Since, the stability of +6 oxidation state decrease or +4 oxidation state increases from S to Te due to inert pair effect, therefore, the reducing character of diox- ides decreases from SO, to TeO2.
Question 40.
(i) Account for the following:
Acidic character increases from HF to HI.
(ii) Draw the structure of the following:
(a) CIF3
(b) XeF4
Answer:
(i) (a) The acidic strength of hydrogen halides increases from HF to HI. This is because the stability of these halides decreases down the group due to decrease in bond dissociation enthalpy of H-X bond from HF to HI.
(b) (i) XeF4 (isostructural to ICI4)

Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
(i) Elements of group 16 generally show lower value of first ionisation enthalpy compared to the corresponding periods of group 15. Why?
(ii) What happens when
(a) concentrated H2SO4 is added to CaF2?
(b) sulphur dioxide reacts with chlorine in the presence of charcoal?
(c) ammonium chloride is treated with Ca(OH)2?
Answer:
(i) Two most important allotropes of sulphur are
- rhombic sulphur (a-sulphur)
- monoclinic sulphur
The stable form at room temperature is rhombic sulphur which transforms to monoclinic sulphur when heated above 370K.
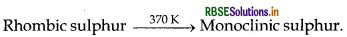
(ii) (a) It forms hydrogen fluoride (HF)
CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HE.
(b) It forms sulphuryl chloride (SO2Cl2).
SO2(g) + Cl2(g) → SO2Cl2(1)
(c) Ammonia is formed.
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → 2NH3 + 2H2O + CaCl2
Question 2.
(i) Write the formula and describe the structure of a noble gas species which is isostructural with
(a) IBr-2
(b) BrO-3
(ii) Assign reasons for the following:
(a) SF6 is kinetically inert
(b) HCl is a stronger acid than HF though flourine is more electronegative than chlorine.
Answer:
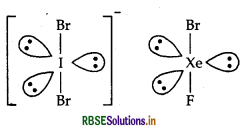
(i) (a) IBr2 Number of valence electron in this species is 7 + (2 × 7) + 1 = 22 The noble gas compound having 22 electrons is XeF2 = 8 + (2 × 7) = 22 IBr2 is linear and so, is XeF2.
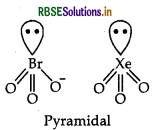
(b) BrO3 Number of valence electron in BrO3 = 7 + (3 × 6) + 1 = 26. The noble gas compound having 26 electrons is XeO3 = 8 + (6 × 3) = 26. The structure of BrO3 is pyramidal and the structure of XeO3 is also pyramidal.
(ii) (a) In SF molecule the six atoms of fluorine sterically protect the sulphur atom from attack by a reagent. Hence, SF6 is called kinetically inert substance.
(b) H-Cl is a storage acid than HF in aqueous medium because with increase in H - X bond length, bond dissociation energy decreases and H+ ion is easily produced.

Question 3.
(i) How the supersonic jet aeroplanes are responsible for the depletion of ozone layers?
(ii) F2 has lower bond dissociation enthalypy than Cl2. Why?
(iii) Which noble gas is used in filling ballons for meteorological observations?
(iv) Complete the equation:
XeF2 + PE5 →
Answer:
(i) Nirtogen oxide emitted from the exhausts of supersonic jet aeroplanes readily combine with ozone to form nitrogen dioxide and diatomic oxygen. Thereby depleting the concentration of ozone in the upper atmosphere.
NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g)
(ii) Due to smaller size, the lone pair of electrons on the F- atoms repel the bond pair of F - F bond. In constrast, due to the comparatively larger size of Cl atoms, the lone pairs, on the Cl-atoms do not repel the bond pair of Cl - Cl bond to such a extent. As a result, F - F bond energy is lower than that of Cl - Cl bond energy.
(iii) Helium, being inert, non-inflammable and light gas, is used in filling balloons for meteorological observations.
(iv) XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+ [PF6]-
COMPETITION KIT:
Question 1.
The pair of compounds showing formal (+3) oxidation state.
(a) Pyrophosphorus and hypophosphoric acid
(b) Orthophosphorus and hypophosphoric acid
(c) Pyrophosphorus and pyrophosphoric acid
(d) Orthophosphorus and pyrophosphorus acid
Answer:
(d) Orthophosphorus and pyrophosphorus acid
Question 2.
The compounds formed by the reaction of zinc with dilute and concentrate nitric acid respectively are.
(a) NO, and NO
(b) NO and H2O
(c) NO2 and N2O
(d) N2O and NO2
Answer:
(d) N2O and NO2
Question 3.
The compound formed by the reaction between CaC2 and nitrogen is
(a) CaCN2
(b) CaCN
(c) CaCN3
(d) Ca2CN
Answer:
(a) CaCN2
Question 4.
Which of the following statement is correct with respect of acid
(a) Phosphinic acid is a diprotic acid while phosphoric acid is a monoprotic acid
(b) Phosphinic acid is a monoprotic acid while phosphoric acid is diprotic acid.
(c) Both are triprotic acid.
(d) None of two acid is diprotic.
Answer:
(b) Phosphinic acid is a monoprotic acid while phosphoric acid is diprotic acid.

Question 5.
Which is correct about the nitrogen?
(a) less electronegative
(b) less ionisation enthalpy
(c) presence of d-orbitals
(d) have ability to form рл-рл bonding with itself.
Answer:
(d) have ability to form рл-рл bonding with itself.
Question 6.
Which of the following do not form nitrogen dioxide on heating.
(a) KNO3
(b) Pb(NO3)2
(c) Cu(NO3)2
(d) AgNO3
Answer:
(a) KNO3
Question 7.
Ammonium dichromate on thermal decomposition will give
(a) N2, H2O and Cr2O3
(b) N2, NH3 and CrO3
(c) (NH4)2 CrO4 and H2O
(d) N2, H2O and CrO3
(e) N2, H2O and CrO
Answer:
(a) N2, H2O and Cr2O3
Question 8.
One mole of hydrozine (N2H4) on reaction forms a new compound (X) after losing 10 mol of electron, Let all the nitrogen atom of hydrazine is obtained in the form of new compound then the oxidation number of nitrogen in (X) compound will be (NOTE: There is no change in the oxidation state of hydrogen in the reaction.)
(a) - 1
(b) -3
(c) +3
(d) +5
(e) +1
Answer:
(c) +3
Question 9.
Good reducing property of H2PO3 is due to
(a) Presence of one -OH group and two P-H bond.
(b) High electron gain enthalpy of phosphorus.
(c) High oxidation state of phosphorus.
(d) Presence of two -OH group and one P-H bond.
Answer:
(a) Presence of one -OH group and two P-H bond.
Question 10.
Aqua regia is
(a) 1 : 3 conc. HNO3 and conc. HCl
(b) 1 : 2 conc. HNO3 and conc. HCl
(c) 3 : 1 conc. HNO3 and conc. HCl
(d) 2 : 1 conc. HNO3 and conc. HCl
Answer:
(a) 1 : 3 conc. HNO3 and conc. HCl
Question 11.
Which element of the group-15 form the most stable pentavalent compound.
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Antimony
(c) Bismuth
(d) Arsenic
Answer:
(a) Phosphorus
Question 12.
What is the basicity of orthophosphoric acid
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer:
(c) three
Question 13.
Sulphuryl chloride (SO2Cl2) on reaction with white phosphorus gives
(a) PCl5, SO2
(b) OPCl3, SOCl2
(c) PCl5, SO2, S2Cl2
(d) OPCl3, SO2, S2 Cl3
Answer:
(a) PCl5, SO2
Question 14.
What is the product of following reaction
P4(s) 3NaOH(aq) + H2O(l) →
(a) PH3(g) + 3 Na2HPO4 (aq)
(b) PH2(g) + 3NaH2PO2 (aq)
(c) 2PH3(g) + 3Na2HPO2 (aq)
(d) 2PH3(g) + 3 NaH2PO4 (aq)
Answer:
(b) PH2(g) + 3NaH2PO2 (aq)

Question 15.
Which of the following gas will adsorb highly at given temperature and pressure
(a) dihydrogen
(b) dioxygen
(c) ammonia
(d) dinitrogen
Answer:
(c) ammonia
Question 16.
When white phosphorus is heated with concentrated NaOH solution an inert atmosphere of CO2 produce a gas. Which of the following statement is not correct in respect of that gas.
(a) It is highly poisonous and smell like rotten fish
(b) It is less basic than NH3
(c) Its aqueous solution decomposes in presence of light
(d) It is more basic than NH3
Answer:
(d) It is more basic than NH3
Question 17.
Which of the following show sublimation
(a) NH4Cl
(b) CaCO3
(c) BaSO4
(d) CaHPO3
Answer:
(a) NH4Cl
Question 18.
Which of the following oxide of nitrogen is colourless and neutral.
(a) N2O
(b) N2O3
(c) N2O
(d) N2O5
Answer:
(a) N2O
Question 19.
The product formed by the reaction of white phosphorus with SO2Cl2 is
(a) PCl3
(b) SO2Cl2
(c) SCl2
(d) POCl3
Answer:
(a) PCl3
Question 20.
Which is the strongest reducing agent [MP-PMT]
(a) NH3
(b) PH3
(c) AsH3
(d) SbH3
Answer:
(d) SbH3
Question 21.
After a long time conversion of concentrated nitric acid into yellow-brown colour indicates the formation of
(a) NO
(b) NO2
(c) N2O
(d) N2O4
Answer:
(b) NO2

- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 16 दैनिक जीवन में रसायन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 15 बहुलक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 जैव-अणु
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 ऐमीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12 ऐल्डिहाइड, कीटोन एवं कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 11 ऐल्कोहॉल, फीनॉल एवं ईथर
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 10 हैलोऐल्केन तथा हैलोऐरीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 उपसहसंयोजन यौगिक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 d- एवं f-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 p-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 तत्वों के निष्कर्षण के सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रम