RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Important Questions Chemistry in Everyday Life
Objective Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the following substance is an analgesic?
(1) Aspirin
(2) Penicillin
(3) Indigo
(4) Saccharin
Answer:
(1) Aspirin
Question 2.
Equanil is an example of
(1) analgesic
(2) tranquilizer
(3) antiseptic
(4) antibiotic
Answer:
(2) tranquilizer

Question 3.
Which of the following substance is not an antibiotic?
(1) Ampicillin
(2) Streptomycin
(3) Chloramphenicol
(4) Chorpheneramine
Answer:
(4) Chorpheneramine
Question 4.
Which of the following substance is an antiseptic?
(1) Paracetamol
(2) Luminal
(3) Dettol
(4) Promathazin
Answer:
(3) Dettol
Question 5.
Suipha drugs are
(1) analgesics
(2) antibiotics
(3) transquilizers
(4) antihistamins
Answer:
(2) antibiotics
Question 6.
Which of the following is an antacid?
(1) Gosypol
(2) Phenol
(3) Omeprazole
(4) Dettol
Answer:
(3) Omeprazole
Question 7.
Which of the following group is a chromophore?
(1) -CH
(2) -OH
(3) -NR
(4) -N N-
Answer:
(4) -N N-
Question 8.
Chromogens are
(1) chromophore containing compounds
(2) alkanes
(3) artificial sweeteners
(4) none of the above
Answer:
(1) chromophore containing compounds
Question 9.
Sodium benzoate is
(1) artificial sweetemer
(2) food colour
(3) preservative
(4) antioxidant
Answer:
(3) preservative
Question 10.
Saccharin is a
(1) preservative
(2) artificial Sweetener
(3) food colour
(4) antioxidant
Answer:
(2) artificial Sweetener
Question 11.
Detergents are
(1) natural substances
(2) salts of weak acid and strong base
(3) synthetic substances
(4) basic substances
Answer:
(3) synthetic substances
Question 12.
Antipyretics are used for
(1) releiving pain
(2) reduce fever
(3) malaria control
(4) distroy other infectants
Answer:
(2) reduce fever
Question 13.
Which of the following substance is not an antipyretic?
(1) Paracetamol
(2) Aspirin
(3) Chioramphenicol
(4) Phenacetin
Answer:
(3) Chioramphenicol
Question 14.
Soaps and detergents belong to
(1) surface active
(2) surface inactive
(3) water soluble
(4) water insoluble
Answer:
(1) surface active
Question 15.
How many times saccharin is sweeter than sugar?
(1) 100
(2) 200
(3) 300
(4) 600
Answer:
(4) 600

Question 16.
pH of a aqueous solution of detergent is
(1) 8-9
(2) 5-6
(3) 7
(4) 11-14
Answer:
(3) 7
Question 17.
Artificial sweetener is
(1) saccharin
(2) sodium salt of saccharin
(3) carbarnate
(4) all of the above
Answer:
(4) all of the above
Question 18.
Food preservatives are
(1) CHCOONa
(2) KSO
(3) CHCOONa
(4) (1) and (2) both
Answer:
(4) (1) and (2) both
Very Showt Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Define the following and give one example:Tranquilizers.
Answer:
Drugs which reduce anxiety and produce of feeling of well being are called tranquilizers. For example: equanil,seconal etc.
Question 2.
Name a medicine which can act as antiseptic as well as antipyretic. Give its chemical name.
Answer:
Aspirin acts both as analgesic and antipyretic. Its chemical name is 2-acetoxybenzoic acid.
Question 3.
Write the ftjrinula and IUPAC name of aspirin.
Why should it not be taken an empty stoamch?
Answer:
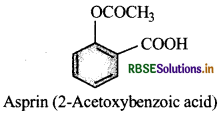
It produces sal icylic acid on hydrolysis, which causes bleeding. Therefore, it should not be talen on empty stomach.
Question 4.
Give two examples of analgesics and antipyretics.
Answer:
- Analgesics: Butazolidine, novalgin
- Antipyretics: Aspirin,. paracetamol

Question 5.
What are receptors?
Answer:
Receptor proteins help in transferring message from messengers to the cell.
Question 6.
How do omeprazole and lansoprazole act as antacids?
Answer:
They prevent the release of hydrochloric acid to stomach.
Question 7.
In what way prolonged use of antacids Is barm
Answer:
Prolonged use of antacid should he avoided sirve it may lead to constipation.
Question 8.
Why Is use of penlcillins generally discouraged?
Answer:
The use of penicillins is generally discouraged becuase these are not broad spectrum in nature and can also cause allergic reactions in many patients.
Question 9.
What is antibiotic ? Give the name of first antibiotic discovered.
Answer:
Antibiotics are the chemical substances produced by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi. etc. that inhibit the growth or even destroy other microorganisms which cause diseases Penicillin was the first antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1929.
Question 10.
What are food preservatives? Write a name of food preservative.
Answer:
Chemical substances which are used to protect food against bacteria, yeasts and moulds are called food preservatives. For example: sodium benzoate, sodium metabisulphite, etc.
Question 11.
Account for the following: Aspirin helps In the prevention of heart attack.
Answer:
One main reason for the heart attack is blood clotting. Aspirin checks the blood clotting to large extent. It therefore, recommended for heart patients.
Question 12.
Define Chemotherapy.
Answer:
The branch of chemistry which deals with the treatment of diseases using suitablechemical substances is known as Chemotherapy.

Question 13.
Give an example of a narcotic which is used as analgesic.
Answer:
Morphine.
Question 14.
What are barbiturates? To which class of drugs do they belong?
Answer:
5, 5.derìvatives of barbituric acid are called bar biturates. They belong to the class of tranquilizers. For example: luminal, seconal, veronal, etc.
Question 15.
Pick out the odd one from the following compounds on the basis of medicinal properties: luminal, secanal, phenacetin,, equaniL
Answer:
Except for phenacetin which is antipyretic, all others are tranquilizers.
Question 16.
Which type of drug is chloramphenicol?
Answer:
Broad spectrum antibiotic.
Question 17.
Name two narcotics which are used as analgesics?
Answer:
Morphine and codeine.
Question 18.
What is the use of plant Rauwolfia serpentina in Ayurveda?
Answer:
it is used for lowering blood pressure.
Question 19.
What are soaps?
Answer:
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids such as Lauric acid. palmitic acid, stearic acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid.
Question 20.
Name the chemicals responsible for the antiseptic properties of dettoL
Answer:
Chioroxylenol and terpirol.

Question 21.
Name an antacid which prevents the formatian of acid in stomach.
Answer:
Cimetidine and Ranitidine.
Question 22.
Why is glycerol added a shaving soap?
Answer:
Glycerol ïs added to shaving soaps to prevent rapid drying.
Question 23.
Name a medicine than can be used as antipyretic as well as analgesic.
Answer:
Paracetamol.
Question 24.
WrIte main uses of streptomycin.
Answer:
Fòr the treatment of tuberculosis and meningitis.
Question 25.
WrIte the name and structural formula of parent substance of sulpha drugs.
Answer:
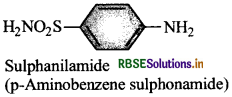
Question 26.
Define antimalarials.
Answer:
The chemical substances which are used to cure malaria are called antimalarial. For example - chloroquine.

Question 27.
Write the structure of a alkylbenzene sulpho- nate detergent.
Answer:
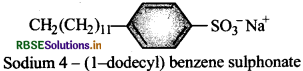
Question 28.
Soap is a weak antiseptic. What may added to soap to improve its antiseptic action ?
Answer:
Bithional is added to soap to improve its antisep¬tic properties.
Question 29.
How are antiseptics different from disinfec-tants ? Give one example of each of them.
Answer:
Antiseptics are chemicals which prevent the growth of microorganisms without affecting living tissues. For example: furacin, soframycin, 0 -2% solution of phenol, etc.
Question 30.
What is salvarsan, to which class of drugs it belong and for what disease is it used ?
Answer:
Salvarsan is an antimicrobial drug. It is used for the treatment of the syphilis.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Explain the following types of substances with one suitable example, for each case:
(i) Cationic detergents
(ii) Food preservatives
(iii) Analgesics
Answer:
(i) Cationic detergents : They are quaternary
ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides as anions and the cationic part possess a long hydrocarbon chain, and a positive charge on nitrogen atom. Therefore they are called cationic detergents.
Example: Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide
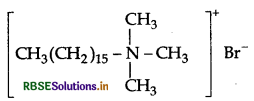
(ii) Food preservatives : They are used to prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth.
Example: Table salt, vegetable oils, sodium benzoate, etc.
(iii) Analgesics: Analgesics reduce or abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, in coordination or paralysis or some other disturbance of nervous system.
They are of two types:
(a) Non-narcotic analgesics
Example: Aspirin
(b) Narcotic analgesics
Example: Morphine

Question 2.
How do antiseptics differ from distinfectants?
Answer:
|
Antispectis |
Disinfecants |
|
1. They are chemical sub¬stances which prevent the growth of micro-organisms and may even kill them. |
They are chemical substances which kill micro organisms. |
|
2. They are safe to be applied to the living tissues. |
They are not safe to be applied to the living tissues. They are used to kill microorganisms present in the drains toilets, floors etc. |
|
3. They are generally applied on wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces. Example: Furacin, sofra-mycin, dettol and savlon, 0.2% solution of phenol. |
Example : Phenol (> 1 % solution) and chlorine (0.2 to 0.4 ppm). |
Question 3.
What are the following substances? Give one example of each type.
(i) Antacid
(ii) Non-ionic detergents
(iii) Antiseptics
Answer:
(i) Antacid: Those substances which neutralize the excess acid and raise the pH to an appropriate level in stomach are called antacids. Example: Sodium bicarbonate, Mg(OH)2.
(ii) Non7ionic detergents : These are esters of high molecular mass alcohols obtained by reaction between polyethylene glycol and steric acid.
Example:
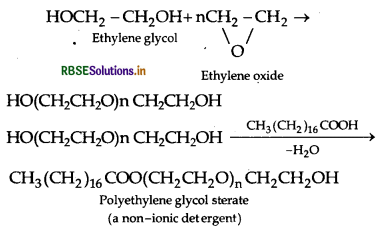
(iii) Antiseptics : These are chemical substances which prevent the growth of microorganisms and may even kill them and safe to be applied on living tissues. Example: Furacin, soframycin, etc.
Question 4.
Describe the following substances with one suitable example of each type:
(i) Non-ionic detergents
(ii) Food preservatives
(iii) Disinfectants
Answer:
(i) Non-ionic detergents: These don't contain any ion in their constitution. These are esters of high molar mass alcohols obtained by reaches between polyethylene glycol and stearic acid.
Example : lauryl alcohol ethoxylate.
(ii) Food preservatives: They are used to prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth.
Example: Table salt, vegetable oils, sodium benzoate etc.
(iii) Disinfectants : These are chemical substances that kill microorganisms but are not safe for living tissues. They are used in drains, toilets, etc.
Example : Chlorine, thymol, etc.

Question 5.
What are the following substances? Give one example of each of them.
(i) Cationic detergents
(ii) Enzymes
(iii) Sweetening agents
Answer:
(i) Cationic detergent: Cationic detergents are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with anions as acetates, chlorides or bromides.
(ii) Enzymes : Enzymes are biological catalysts which are chemically globular proteins having high molecular mass and highly specific in their actions due to presence of active sites of definite shape and size on their surfaces so that only specific substrate can fit in them. Example: Pepsin, amylase.
(iii) Sweetening agents: Those chemical substances which are sweet in taste but do not add any calories to our body are called artificial sweetening agents. These are excreted as such through urine. Example : Saccharin, aspartame, etc.'
Question 6.
What are analgesic medicines? How are they classified and when are they commonly recommended for use?
Answer:
Analgestic medicine: Drugs which reduce or abolish pain without causing reduction of consciousness, mental confusion, incoordination or paralysis or some other disorder of the nervous system are called analgesic medicines.
They are classified into the following two categories :
- Non-narcotic (non-addictive) drugs ’
- Example: Aspirin, Ibuprofen.
- Narcotic (addictive) drugs
- Example: Morphine, Heroin.
They are recommended with-proper prescription because they are habit forming drugs.
Question 7.
Explain the following terms with one suitable example in each case.
(i) Cationic detergents
(ii) Enzymes
(iii) Antifertility drugs
Answer:
(i) Cationic detergent: Cationic detergents are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with anions as acetates, chlorides or bromides.
(ii) Enzymes: Enzymes are proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our bodies.
(iii) Antifertility drugs: Chemical substances, which are used to check pregnancy in women, are called antifertility drugs or birth control pills or oral contracaptives. These control the female menstrual cycle and ovulation.
Example: Norethindrone, Ethinyl estradol, Mestranol.
Question 8.
Explain the following terms with one example in each case:
1. Food preservatives
2. Enzymes
3. Food preservatives
Answer:
- Food preservatives: They are used to prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth. Example: Table salt, vegetable oils, sodium benzoate, etc.
- Enzymes : The enzymes may be defined as bio-catalysts which catalyse the bio-chemical reactions in the living organisms. Example : Pepsin and Amylase.
- Detergents : They may be defined as ammonium, sulphonate or sulphate salts of long chain hydrocarbons containing 12-18 carbon atoms. Example : Sodium lauryl sulphate.

Question 9.
What are analgesic drugs? How are they classified and when are they usually recommended for use?
Answer:
- Analgesic drugs: These drugs are the chemical substances which are given to relieve body pains. These act on the central nervous system. These are classified as narcotics i.e. habit forming and non-narcotics i.e. non habit forming.
- Examples of Narcotics: Opium which contains alkaloids such as Codeine and Morphine. Examples of Non-Narcotics : Aspirin and Ibuprofen.
Question 10.
Describe the following giving one example for each:
1. Detergents
2. Food preservatives
3. Antacids
Answer:
- Detergents: Detergent is a chemical substance, usually in the form of a powder or liquid, which is used for washing things such as clothes or dishes.
- Food preservatives : They are used to prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth. Example: Table salt, vegetable oils, sodium benzoate etc.
- Antacids: The substances which neutralize the excess acid and raise the pH to an appropriate level in the stomach are called antacids. Example: Sodium bicarbonate, Ranitidine etc.
Question 11.
Explain the following terms with one suitable example for each:
1. A sweetening agent for diabetic patients
2. Enzymes
3. Analgesics
Answer:
- The sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient is Saccharin.
- Enzymes: Enzymes are proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our bodies.
- Analgestics: Analgesics are a class of medications designed specifically to relieve pain.
Question 12.
Answer the following questions:
1. Why do soaps not work in hard, water?
2. What are the main constituents of dettol?
3. How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants?
Answer:
- Hard water contains insoluble calcium and magnesium chlorides which forms isoluble precipitate (scum) with soap and thus cannot be rinsed off easily.
- Dettol is mixture of chloroxylenol and a-terpineol in a suitable solvent.
- Antiseptics and disinfectants are effective against micro-organisms. However, antiseptics are applied to the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers, and diseased skin surfaces, while disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments, etc.
Question 13.
What are the following substances? Give one example of each.
1. Food preservatives
2. Synthetic detergents
3. Antacids
Answer:
- Food preservatives: They are used to prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth. Example: Table salt, vegetable oils, sodium benzoate etc.
- Synthetic detergents: Synthetic detergents are cleansing agents which have all the properties of soap but which actually do not contain any soap. Example: Sodium Lauryl sulphate (or any one other).
- Antacids : Antacids: Those substances which neutralize the excess acid and raise the pH to an appropriate level in stomach are called antacids. Example: Sodium bicarbonate, Mg(OH)2.
Question 14.
(a) Differentiate between a disinfectant and an antiseptic. Give one example of each.
(b) What is tincture of iodine and what is it used for?
Answer:
(a) Antiseptics and disinfectants are effective against micro-organisms. However, antiseptics are applied to the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers, and diseased skin surfaces, while disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments, etc.
(b) Tincture of iodine is 2-3% solution of iodine in alcohol and water. Use: It is used as a powerful antiseptic and applied on wounds to kill and prevent growth of micro-organisms.

Question 15.
What are the following substances? Give one example of each one of them.
1. Tranquilizers
2. Food preservatives
3. Synthetic detergents
Answer:
- Tranquilizers : Tranquilizers are chemical compounds used for the the treatment of stress and mild or even severe mental diseases. Example: Equanil, meprobamate, veronal. (any one)
- Food preservatives : Food preservatives are the compounds which prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth. Example: Sodium benzoate, table salt vegetable oils etc.
- Synthetic detergents : Synthetic detergents are cleansing agents which have all the properties of soap but which actually do not contain any soap. Example : Sodium laurly sulphate.
Question 16.
Explain the following terms giving one example of each type:
1. Antacids
2. Disinfectants
3. Enzymes
Answer:
- Antacids: Those substances which neutralize the excess acid and raise the pH to an appropriate level in stomach are called antacids. Example: Sodium bicarbonate, Mg(OH)2
- Disinfectants : Disinfectants are chemical compounds which kill micro-organisms but are not safe when applied on living organisms. Example: Phenol, chlorine.
- Enzymes : Enzymes are biological catalysts which are chemically globular proteins having high molecular mass and highly specific in their actions due to presence of active sites of definite shape and size on their surfaces so that only specific substrate can fit in them. Example: Pepsin, amylase.
Question 17.
What are the following substances? Give one example of each.
1. Antihistamines
2. Tranquilizers
3. Broad spectrum antibiotics
Answer:
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines are amines which are used as drugs to control the allergy effects produced by histamine Example: Terfenadine.
- Tranquilizers: Tranquilizers are a class of chemical compounds used for the treatment of stress, and mild or even severe mental disease. Example: Equanil.
- Broad spectrum antibiotics : Antibiotics which kill or inhibit a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram¬negative bacteria are said to be broad specirum antibiotics. Example: Oiloroamphenicol.

Question 18.
(a) How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants? Give one example of each. (Give two differences)
(b) Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Answer:
(a) Antiseptics and disinfectants are effective against micro-organisms. However, antiseptics are applied to the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers, and diseased skin surfaces, while disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments, etc.
(b) Hard water contains Ca+2 and Mg+2 ions. These ions form insoluble calcium and magnesium salts, separate as scum which adheres to fabric, thereby making soap ineffective for cleansing action.
Question 19.
What are the following substances? Give one example of each.
1. Analgesics
2. Antibiotics
3. Tranquilizers
Answer:
- Analgesics : Analgesics reduce or abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, incoordination or paralysis or some other disturbances of nervous system. Example: Aspirin.
- Antibiotics : Antibiotics refers to a substance produced wholly or partly by chemical synthesis which in low concentration inhibits the growth or destroys micro- organisms by intervening in their metabolic processes. Example: Penicillin.
- Transquilizers: Chemical compounds used for the treatment of stress and mild or severe mental diseases.
Question 20.
What are the following substances? Give one example of each.
1. Broad Spectrum antibiotics
2. Narcotic analgesics
3. Synthetic detergents
Answer:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics can treat a wide range of bacterial infections and conditions.
- Narcotic analgesics: Narcotic analgesics are administered in medicinal doses, relieve pain and produce sleep. Example: Morphine and many of its homologues.
- Synthetic detergents are cleaning chemical agents that have all of the qualities of soap but include no soap.
Question 21.
What are food preservatives? Name two such substances.
Answer:
Food preservatives : Food preservatives are the compounds which prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth.
Examples : Sodium benzoate, vinegar.
Question 22.
Explain the cleaning action of soap. Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Answer:
Cleaning action of soap : The cleansing action of soap is due to the fact that soap molecules form micelles around the oil droplets in such a way that hydrophobic part of stearate ions is in the oil droplet and hydrophilic part projects out of the grease droplet like the bristles. Since the polar groups can interact with water, the oil droplet surrounded by stearate ions is now pulled in water and removed from the dirty surface. Thus soap helps in emulsification and washing away of oils and fats.
Reason : Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ion : These ions form insoluble Ca and Mg salts. These salts act as scum. The insoluble scum stick on the clothes, so the cleaning capacity of soap is reduced when Na or K soaps are dissolved in hard water.

Question 23.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples :
(a) Cationic detergents
(b) Anionic detergents
Answer:
(a) Cationic detergents : They are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides as anions and the cationic part possess a long hydrocarbon chain, and a positive charge on nitrogen atom. Therefore they are called cationic detergents.
example:
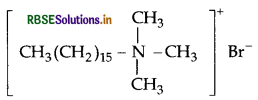
Question 24.
(a) Which one of the following is a food preservative?
Equanil, Morphine, Sodium benzoate
(b) Why is bithional added to soap?
(c) Which class of drugs is used in sleeping pills?
Answer:
(a) Sodium Benzoate: It is a food preservative.
(b) Bithional acts as deodorant in soaps, hence it works as an antiseptic agent and reduces the odours produced by bacterial decomposition of organic matter on the skin.
(c) Tranquilizers like barbiturates are used in sleeping pills.
Question 25.
1. What class of drug is Ranitidine?
2. If water contains dissolved Ca2+ ions, out of soaps and synthetic detergents, which will you use for cleaning clothes?
3. Which of the following is an antiseptic? 0.2% phenol, 1% phenol
Answer:
- Ranitidine is an antacid.
- We will use synthetic detergents because they can produce lather with the hard water containing Ca2+ ions.
- 0.2% phenol acts as an antiseptic.
Question 26.
(a) How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants? Give one example of each.
(b) What are tranquilizers? Give one example.
Answer:
(a) Antiseptics are the chemicals which either kill or prevent growth of microbes on living tissues, e.g., Penicillin.
(b) Tranquilizers : Drugs which are used for the treatment of stress, fatigues mild and severe mental diseases are called tranquilizers. Example: Iproniazid, Phenelzine, etc.
Question 27.
Explain the following and give one example for each:
1. Broad spectrum antibiotics
2. Antipyretics
3. Anti-oxidants
Answer:
- Broad spectrum antibiotics : Antibiotics which kill or inhibit a wide range of Gram-positive and Cram-negative bacteria and called broad spectrum antibiotics. Example: Chloroamphicol.
- Antipyretics: Chemicals, which are used to bring down the body temperature during high fever, are called antipyretics. Example: Paracetamol, Aspirin, etc.
- Anti-oxidants : Those molecules, which inhibit the oxidation of other molecules, are called anti-oxidants. Example: Thiols, Ascorbic acid, etc.

Question 28.
1. Give two examples of macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
2. What are antiseptics? Give an example.
3. Why is use of aspartame limited to cold foods and soft drinks?
Answer:
- Carbohydrates and proteins.
- Antiseptics are the chemicals which either kill or prevent growth of microbes on living tissues, e.g., Penicillin.
- Because it decomposes at baking or cooking temperature.
Question 29.
1. Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
2. What are antibiotics? Give an example.
3. Give two examples of macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
Answer:
- Saccharin is used for a diabetic patient for preparation of sweets.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are chemical substances produced by a living organism that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing micro-organisms such as fungi and bacteria.
- Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acid etc.
Question 30.
1. What are disinfectants? Give an example.
2. Give two examples of macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
3. What are anionic detergents? Give an example.
Answer:
- Disinfectants : These are the chemical substances which are used for killing or preventing the growth of micro-organisms but they are not safe for living tissues.
- Macromolecules used as drug targets are carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acid and lipids.
- Anionic detergents. Anionic Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons.
Question 31.
Explain the following terms with a suitable example for each :
1. Disinfectants
2. Antacids
3. Food preservatives.
Answer:
- Disinfectants: These are the chemical substances which are used for killing or preventing the growth of micro-organisms but they are not safe for living tissues.
- Antacid: Those substances which neutralize the excess acid and raise the pH to an appropriate level in stomach are called antacids. Example: Sodium bicarbonate, Mg(OH)2.
- Food preservatives : They are used to prevent spoilage of food due to microbial growth. ExampleTable salt, vegetable oils, sodium benzoate, etc.
Question 32.
What are the following? Give our example of each.
1. Sweetening agents
2. Food preservatives
3. Antibiotics
Answer:
- Sweetening agents : Those chemical substances which are sweet in taste but do not add any calories to our body are called artificial sweetening agents. These are excreted as such through urine. Example : Saccharin, aspartame, etc.
- Preservatives are chemical substances that are added to food to help: prevent spoiling. improve appearance and/or. maintain the food's nutritional quality.
- Antibiotics : Those chemical substances which are produced completely or partially by chemical synthesis in low concentration and either kill or inhibit the growth of micro-organisms by intervening in their metabolic processes, are known as antibiotics. Example: Tetracycline, Vancomycin.

Question 33.
What are biodegradable and non-biodegradable detergens? Give one example of each.
Answer:
Biodegradable detergents: Detergents, having straight hydrocarbon chains are easily degraded or decomposed by micro-organism, are known as biodegradable detergents.
Example : Sodium lauryl sulphate.
Non-biodegradable detergents: Detergents containing branched hydrocarbon chains and are not easily decomposed by the micro-organisms, are known as non- biodegradable detergents.
Example: Sodium 4 - (1, 3, 5, 7 tetramethyloctyl) benzene sulphonate.
Question 34.
What is meant by the following terms? Explain with an example for each.
1. Target molecules as used in medicinal chemistry
2. Food preservative
3. Non-ionic detergents
Answer:
- Drugs interact with macromolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids etc. and are called as target molecules.
- Preservatives are chemical substances that are added to food to help: prevent spoiling. improve appearance and/or. maintain the food's nutritional quality.
- Nonionic detergents contain uncharged hydrophilic head groups that consist of either polyoxyethylene moieties as in BRIJ, PEG-sorbitan units as in TWEEN, or glycosidic groups as in octyl-ß-D-glucoside, dodecyl-ß-D-maltoside or digitonin.
Question 35.
Answer the following questions:
1. Why should medicines not be taken without consulting a doctor?
2. What is meant by 'broad spectrum antibiotics'?
3. What are the main constituents of Dettol?
Answer:
- Because medicines can cause harm to human body. If a person does not know its physiological function on body.
- Antibiotics which kill or inhibit a wide range of gram positive and gram negative bacteria, are called broad spectrum antibiotics.
- Dettol is mixture of chloroxylenol and a-terpineol in a suitable solvent.
Question 36.
Answer the following:
1. Why is the use of aspartame limited to cold foods and drinks?
2. How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants?
3. Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Answer:
- Use of aspartame is limited to cold foods and soft drinks because it is unstable at cooking temperature.
- Antiseptics and disinfectants are both widely used to control infections. They kill microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi using chemicals called biocides. Disinfectants are used to kill germs on nonliving surfaces. Antiseptics kill microorganisms on your skin.
- Hard water contains insoluble calcium and magnesium chlorides which forms insoluble ppt (scum) with soap and thus cannot be rinsed off easily.
Question 37.
Define the following:
1. Anionic detergents
2. Broad spectrum antibiotics
3. Antiseptic
Answer:
- Anionic Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons.
- The term "broad spectrum antibiotics" was originally used to designate antibiotics that were effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- An antiseptic is a substance that stops or slows down the growth of microorganisms.
Question 38.
Define the following:
(i) Cationic detergents
(ii) Narrow spectrum antibiotics
(iii) Disinfectants
Answer:
(i) Cationic detergents : They are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides as anions and the cationic part possess a long hydrocarbon chain, and a positive charge on nitrogen atom. Therefore they are called cationic detergents.
example:

(ii) Narrow spectrum antibiotics : Narrow spectrum antibiotics are those antibiotics which are mainly effective against gram positive or gram negative bacteria.
(iii) Disinfectants : Disinfeciants kill or prevent growth of microbes and are applied on inanimate/non living objects. Example: Phenol.

Question 39.
Define the following:
1. Anionic detergents
2. Limited spectrum antibiotics
3. Tranquilizers.
Answer:
- Those detergents in which large part of their molecules are anions and used in cleansing action, are called anionic detergents. Example : Sodium alkyl sulphates.
- Limited spectrum antibiotics are those which are effective against a single organism or disease.
- Tranquilizers are class of chemicals used for treatment of stress or mild or severe mental diseases.
Question 40.
Define the following:
(a) Anionic detergents
(b) Limited spectrum antibiotics
(c) Antiseptics
Answer:
(a) Anionic Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons.
(b) Limited spectrum antibiotics are effective against a single organism or disease, e.g., Streptomycin.
(c) Antiseptics are the chemicals which either kill or prevent growth of microbes on living tissues, e.g., Penicillin.
Question 41.
Define the following:
(a) Anionic detergents
(b) Narrow spectrum antibiotics
(c) Antacids
Answer:
(a) Anionic Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons.
(b) Narrow spectrum antibiotics are those which are negative against either gram positive or gram negative bacteria.
(c) Antacids are chemical compounds which are used for the treatments of excess acid produced in the stomach.
Question 42.
Define the following:
(a) Cationic detergents
(b) Broad spectrum antibioitcs
(c) Tranquilizers
Answer:
(a) Cationic detergents are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with anions as acetates, chlorides or bromides.
(b) Broad spectrum antibiotics : Antibiotics which kill or inhibit a wide range of gram-positive and gram negative bacteria.
(c) Transquilizers: Chemical compounds used for the treatment of stress and mild or severe mental diseases.
Question 43.
Write the therapeutic action of following on human body and mention the class of drugs to which each of these belong:
1. Ranitidine
2. Morphine
3. Aspirin
Answer:
- Ranitidine belongs to antacids and it neutralizes the excess acid and raises the pH to an appropriate level in stomach.
- Morphine belongs to narcotic analgesics and relieves pain and produces sleep even when taken in small dose.
- Aspirin belongs to non-narcotic analgesic and it inhibits the synthesis of compounds such stimulate inflammation in the tissues cause pain. Aspirin relieves pain and fever.
Question 44.
Write the therapeutic action of following on human body and mention the class of drugs to which each of the these belong:
1. Equanil
2. Aspirin
3. Chloramphenicol
Answer:
- Equanil belongs to the class of tranquilizers and it is used in controlling depression and hypertension.
- Aspirin belongs to non-narcotic analgesies and it inhibits the synthesis of compounds which stimulate inflammation in the tissues and cause pain. Aspirin reduces pain and fever.
- Chloramphenicol belongs to antibiotics and it is used for treatment of typhoid. It kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms.

Question 45.
1. Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well as disinfectant.
2. Name an artificial sweetener whose use is limited to cold foods apd drinks.
3. What are cationic detergents?
Answer:
- Phenol
- Aspartame
- Cationic detergents are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with anions as acetates, chlorides or bromides
COMPETITION CORNER:
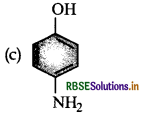
Question 1.
Which of the following gives paracetamol on acetylation?
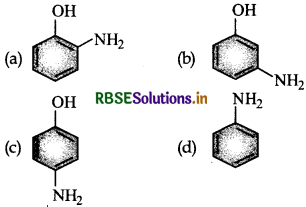
Answer:
Question 2.
Which anong the following is not an antibiotic?
(a) Penicillin
(b) Oxytocin
(c) Erythromycin
(d) Tetracycline
Answer:
(b) Oxytocin
Question 3.
The oxidant which is used asan antiseptic is:
(a) KBzO3
(b) KMnO4
(c) CrO3
(d) KNO3
Answer:
(b) KMnO4
Question 4.
Whichofthefoliowingisemployedasatranquilizer?
(a) Naproxen
(b) Tetracycline
(c) Chi orpheniramine
(d) Equanil
Answer:
(a) Naproxen

Question 5.
The drug Ç 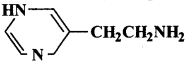 is used as:
is used as:
(a) antacid
(b) analgesic
(c) antimicrobial
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these
Question 6.
The role of phosphate in detergent powder is to:
(a) control pH level to the detergent water mixture
(b) remove Ca2+ and Mg2 ions from the water that cause the hardness of water
(c) provide whiteness of the fabrics
(d) form solid detergent as phosphateless detergents are riquid in nature
Answer:
(b) remove Ca2+ and Mg2 ions from the water that cause the hardness of water
Question 7.
Which of the following molecules is most suitable to disr,erse benzene in water:
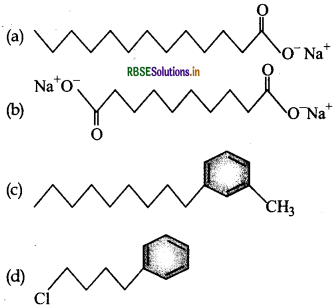
Answer:
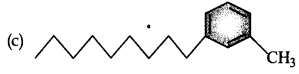
Question 8.
Parkinson’s disease is linked to abnormalities in the levels of dopamine in the body. The structure of dopamine is:
Answer:
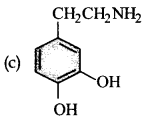
Question 9.
The class of drug used for the treatment of stress is:
(a) analgesics
(b) antiseptic
(c) antihistamine
(d) tranquilizers
Answer:
(d) tranquilizers

Question 10.
Which of the following is employed as a tranquilizer drug?
(a) Mifepristone
(b) Promethazcne
(c) Valium
(d) Naproxen
Answer:
(c) Valium
Question 11.
Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide is a popular:
(a) anionic detergent
(b) cationic detergent
(c) non-ionic detergent
(d) sweetener
Answer:
(b) cationic detergent
Question 12.
Terfenadine is commonly used as i/an:
(a) tranquilizer
(b) antihistamine
(c) antimicrobial
(d) antibiotic
Answer:
(b) antihistamine
Question 13.
Which of the following is employed as antihistamine?
(a) Omeprazole
(b) Œloramphenicol
(c) Diphenyihydramine
(d) Norethindrone
Answer:
(c) Diphenyihydramine
Question 14.
The artificial sweetener containing chlorine that has the appearance and taste as that of sugar and is stable at cooking temperature is:
(a) Aspartame
(b) Saccharin
(c) Sucralose
(d) Alitame
Answer:
(c) Sucralose

Question 15.
Salts of sorbic acid and propionic acid are used as:
(a) antioxidants
(b) flavouring agents
(c) food preservatives
(d) detergents
Answer:
(c) food preservatives

- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 16 दैनिक जीवन में रसायन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 15 बहुलक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 जैव-अणु
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 ऐमीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12 ऐल्डिहाइड, कीटोन एवं कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 11 ऐल्कोहॉल, फीनॉल एवं ईथर
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 10 हैलोऐल्केन तथा हैलोऐरीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 उपसहसंयोजन यौगिक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 d- एवं f-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 p-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 तत्वों के निष्कर्षण के सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रम