RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Polymers
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Polymers Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Important Questions Polymers
Objective Questions:
Question 1.
Which one among the following is a thermosetting plastic?
(a) PVC
(b) PVA
(c) Bakelite
(d) Polypropene
Answer:
(c) Bakelite
Question 2.
On the basis of mode of can be classified mation, the polymers
(a) As addition polymers only
(b) As condensation polymers only
(c) As copolymers
(d) Both as addition and condensation polymers
Answer:
(d) Both as addition and condensation polymers

Question 3.
Thermoplastics are:
(a) Linear polymers
(b) Highly cross-linked
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Crystalline
Answer:
(a) Linear polymers
Question 4.
'Cis-1, 4-polymers :
(a) Thermoplastic
(b) Thermosetting plastic
(c) Elastic (rubber)
(d) Resin
Answer:
(c) Elastic (rubber)
Question 5.
'Shellac' secreted by lac insects is :
(a) Natural plastic
(b) Natural resin
(c) Natural elastic
(d) Any of these
Answer:
(b) Natural resin
Question 6.
Which of the following is a natural polymer:
(a) Polyster
(b) Glyptal
(c) Starch
(d) Nylon-6
Answer:
(a) Polyster
Question 7.
Which is a naturally occuring polymer?
(a) Polythene
(b) PVC
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Protein
Answer:
(d) Protein
Question 8.
Which of the following is a branched polymer?
(a) Low density polymer
(b) Polyester
(c) High density polymer
(d) Nylon
Answer:
(d) Nylon

Question 9.
Which is the monomer of polypeptide?
(a) Propene
(b) Butadiene
(c) Adipic acid
(d) Amino acid
Answer:
(d) Amino acid
Question 10.
Which of the following is an addition polymer?
(a) Glucose
(b) Polyethylene
(c) Ethylene
(d) Terylene
Answer:
(b) Polyethylene
Question 11.
Which one of the following is a linear polymer?
(a) Amylopectin
(b) Glycogen
(c) Starch
(d) Amylose
Answer:
(d) Amylose
Question 12.
Which of the following polymer is an example of fibre?
(a) Silk
(b) Dacron
(c) Starch
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 13.
Natural rubber is which type of polymer?
(a) Condensation polymer
(b) Addition polymer
(c) Co-ordination polymer
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Addition polymer
Question 14.
Polyethylene is:
(a) Random copolymer
(b) Hompolymer
(c) Alternate polymer
(d) Cross linked polymer
Answer:
(b) Hompolymer

Question 15.
Which of the following is an example of condensation polymer?
(a) Polythene
(b) PVC
(c) Orlon
(d) Terylene
Answer:
(d) Terylene
Very Short Questions:
Question 1.
Give an example of elastomers.
Answer:
Buna-S, Buna-N.
Question 2.
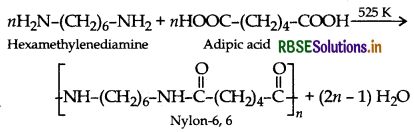
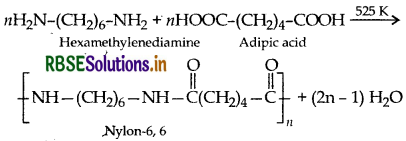
What does the part ‘6, 6′ mean in the name nylon-6, 6?
Answer:
Nylon 6, 6' implies that it is a condensation poly- ner of two types of monomer molecules each containing six carbon atoms i.e. adipic acid (HOOC (CH), COOH) and examethylenediamine (H2NCH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH2)
Question 3.
What is the primary structural feature necessary or a molecule to make it useful in a condensation polynerization reaction?
Answer:
The presence of two bifunctional monomer mol- ecules undergo condensation with the loss of simple molecule of water, alcohol to form dimer.
Question 4.
What does the designation '6, 6′ mean in the name nylon-6, 6?
Answer:
Since both adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine contain six carbon atoms each.
Question 5.
What is meant by 'copolymerisation'?
Answer:
When two or more different monomers are allowed o polymerize together, the product formed is called a co-polymer and the process is called copolymerisation.
Question 6.
What are biodegradable polymers?
Answer:
Biodegradable polymers: All those biopolymers which disintegrate by themselves in biological systems during certain period of time by enzymatic hydrolysis are called biodegradable polymers.
Example: Poly-β-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-ß-Hydro- kyvalerate (PHBV)
Uses: These are used
- in packaging
- in orthopaedic devices
- in controlled drug release
- in bacterial degradation
Question 7.
In nylon 6, 6, what does the designation ‘6, 6 mean?
Answer:
Since both adipic acid and hexamethylenediamin contain six carbon atoms each.

Question 8.
Define the term, 'homopolymerisation' givin an example.
Answer:
The polymer formed by the polymerization of single/same monomeric species is known a homopolymerization.
Example: Polythene/PVC/Polypropene.
Question 9.
Is 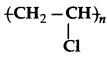 a homopolymer or a copoly
a homopolymer or a copoly
Answer:
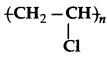 is a homopolymer as it is made u of same monomer units.
is a homopolymer as it is made u of same monomer units.
Question 10.
Give one example of a condensation polymer
Answer:
Example: Nylon 6, 6.
Question 11.
Which of the following is a natural polymer? Buna-S, Proteins, PVC
Answer:
Protein is a natural polymer.
Question 12.
Based on molecular forces what type of polymer is neoprene?
Answer:
Elastomers
Question 13.
Which of the following is a fibre?
Nylon, Neoprene, PVC
Answer:
Nylon is a fibre.
Question 14.
How does a homopolymer differ from a copolymer?
Answer:
Homopolymers: Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from only one type of monomer units are called homopolymers. Example: Polyethene, PVC, teflon.
Copolymers: Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomer molecules are copolymers. Example: Buna-S, Nylon 6, 6
Short Answer Type Question:
Question 1.
Draw the structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Teflon
(ii) Polyethene
Answer:
(i) Teflon
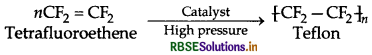
(ii) Polyethene
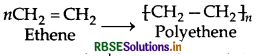
Question 2.
What is the repeating unit in the condensation polymer obtained by combining HO2CCH2CH2CO2H (succinic acid) and H2NCH2CH2NH2 (ethylene diamine)?
Answer:
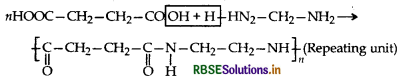

Question 3.
Answer:
|
Thermoplastic polymer |
Thermosetting polymer |
|
(i) These polymers have intermolecular forces of attraction between those of elastomers and fibres. |
(i) These are semifluid substances with low molecular masses which when heated in a mould, undergo change in chemical composition to give a hard, infusible and insoluble mass. |
|
(ii) These are linear or slightly branched chain polymers which are hard at room temperature and become soft and viscous on heating and again rigid on cooling. |
(ii) These have extensive cross-linking between different polymers chain to give a three dimensional network solid on heating. |
|
(iii) These can be melted again and again without any change. Example: PVC, polyethene |
(iii) These can be heated only once when these are permanently set into a solid which cannot be remelted and reworked. Example: Bakelite, melamine |
Question 4.
Differentiate between condensation and addition polymerisations. Give one example each of the resulting polymers.
Answer:
Condensation polymerisation: In this, two or more bifunctional molecules andergo a series of independent con- densation reactions with the elimination of simple molecules like H2O, alcohol, NH3, CO2, HCl etc. to form a macromolecule.
Example: Formation of nylon 6,6
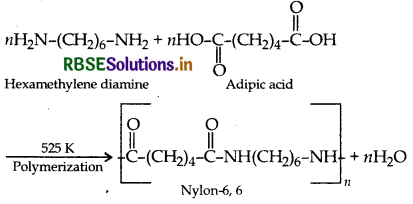
Addition polymerisation: In this, the molecules of the same or different monomers simply add on one another to form macromolecule. These molecules occur among molecules containing double and triple bonds.
Example: Formation of polyethene

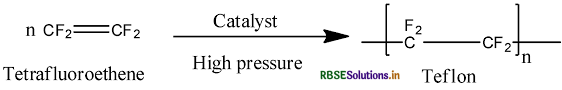
Question 5.
Draw the molecular structures of the monomers of
(i) PVC
(ii) Teflon
Answer:
(i) PVC: (Polyvinyl chloride)
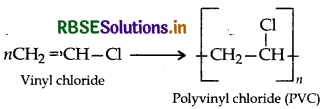
(ii) Teflon:
Question 6.
Draw the structures of the monomers of the following poiymers :
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Nylon-6
Answer:
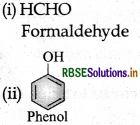
(i) Bakelite: Phenol and formaldehyde → Condensation polymer.
(ii) Nylon-6: The monomeric repeating unit of Nylon-6
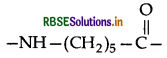
which is derived from caprolactum.
Question 7.
Mention two important uses of each of the following:
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Nylon 6
Answer:
(i) Bakelite:
- It is used in making handles of utencils.
- Also used in production of billiard balls, dominoes and pieces for games like chess.
(ii) Nylon 6:
- Nylon is used in making stockings.
- It is also used for making parachutes.

Question 8.
Name the sub-groups into which polymers are classified on the basis of magnitude of intermolecular forces.
Answer:
- Elastomers
- Fibres
- Thermoplastic polymers
- Thermosetting polymers.
Question 9.
Draw the structure of the monomer for each of the following polymers:
(i) Nylon-6
(ii) Polypropene
Answer:
(i) Nylon-6:
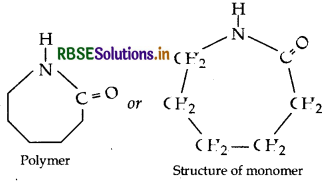
(ii) Polypropene: (-CH3 – CH = CH2)- Propene
Question 10.
Define thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give ene example of each.
Answer:
Thermoplastic polymer:
A thermoplastic is a plastic material that softens when melted and gets solidified when undergoes cooling. These types of plastics can be reshaped or remolded numerous times. Thermoplastic substances can be recycled or reused. Examples are: Polyester, Polypropylene, Polystyrene, Teflon, Acrylic, etc.
Thermosetting polymer:
Thermosetting plastics are a type of plastic that exists in its permanent solid state after being molded once and doesn't undergo melting even when exposed to extreme temperatures. Examples are: PVC (polyvinyl chloride), Polystyrene, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, etc.
Question 11.
What is a bio-degardable polymer? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester.
Answer:
Bio-degardable polymer: All those biopolymers which disintegrate by themselves in biological systems during certain period of time by enzymatic hydrolysis are called biodegradable polymers.
Example: Poly-β-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-β-Hydroxyvalerate (PHBV).
Uses: These are used
- in packaging
- in orthopaedic devices
- in controlled drug release
- in bacterial degradation
Question 12.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
1. Bakelite
2. Neoprene
Answer:
- Bakelite: Phenol and Formaldehyde
- Neoprene: Chloroprene.

Question 13.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
1. Terylene
2. Nylon-6, 6
Answer:
- Monomers of terylene are: Ethylene glycol and Terephthalic acid.
- Monomers of nylon-6, 6 are: Adipic acid and Hexamethylene diamine.
Question 14.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
1. Teflon
2. Buna-N
Answer:
- Tefion: Tetrafluoroethylene.
- Buna-N: Monemers of Buna-N are 1, 3 Butadiene and acrylonitrile.
Question 15.
Write the names and structures of monomers used for getting the following polymers.
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Nylon-6, 6
Answer:
(i) Buna-S:
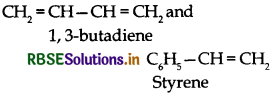
(ii) Nylon-6, 6: It has two repeating monomers
(a) Hexa methylene diamine
(b) Adipic acid
Question 16.
Give one example each of
(i) addition polymers
(ii) condensation polymers
(iii) copolymers.
Answer:
(i) Addition polymers
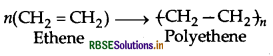
(ii) Condensation polymers
(iii) Copolymers
Question 17.
Write the name and structure of the monomer of each of the following polymers:
(i) Neoprene
(ii) Buna-S
(iii) Teflon
Answer:
(i) Neoprene:
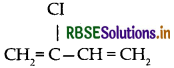
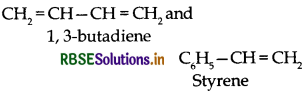
(ii) Buna-S:
(iii) Teflon:

Question 18.
Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each.
Answer:
Thermoplastic polymers: Linear polymers in which the intermolecular forces of attraction are in between those of elastomers and fibres and can be melted again and again on heating followed by moulding to give desired shape.
Example: Polyethene, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) etc.
Thermosetting polymers: These are semifluid substances with low molecular masses which when heated in a mould underoes change in chemical composition to give a hard, infusible and insoluble mass. These cannot be remelted.
Example: Bakelite, Melamine etc.

Question 19.
Draw the structures of the monomers of the following polymers :
(i) Polythene
(ii) PVC
(iii) Teflon
Answer:
(i) Polythene : nCH2 = CH2 Ethene
(ii) PVC:

(iii) Teflon:

Question 20.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S
(iii) Neoprene
Answer:
(i) Buna-S:
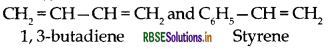
(ii) Dacron: Monoters of dacron are:
- Ethylene glycol HO-CH2-CH2-OH
- Terephthalic acid HOOC-(CH2)4 -COOH
(iii) Neoprene:
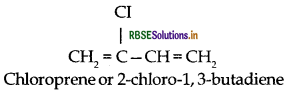
Question 21.
Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each.
Answer:
Thermoplastic polymers: Linear polymers in which the intermolecular forces of attraction are in between those of elastomers and fibres and can be melted again and again on heating followed by moulding to give desired shape.
Example: Polyethene, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) etc.
Thermosetting polymers: These are semifluid substances with low molecular masses which when heated in a mould underoes change in chemical composition to give a hard, infusible and insoluble mass. These cannot be remelted.
Example: Bakelite, Melamine etc.

Question 22.
Explain the following terms giving a suitable example for each:
(i) Elastomers
(ii) Condensation polymers
(iii) Addition polymers
Answer:
(i) Elastomers: These are rubber-like solids with elastic properties. The polymer chains are held together by the weakest intermolecular forces so that they can be stretched.
Example: Buna-S, Buna-N etc.
(ii) Condensation polymers:
Example: Nylon 6, 6.
Addition polymers:

Example: Formation of polyethene from ethene.
Question 23.
(a) What are the differences between thermo- setting and thermoplastic polymers ? Give one example of each.
(b) Write down the structure of monomer and one use of the polymer polystyrene.
Answer:
(a) Thermoplastic polymers: Linear polymers in which the intermolecular forces of attraction are in between those of elastomers and fibres and can be melted again and again on heating followed by moulding to give desired shape.
Example: Polyethene, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) etc.
Thermosetting polymers: These are semifluid substances with low molecular masses which when heated in a mould underoes change in chemical composition to give a hard, infusible and insoluble mass. These cannot be remelted.
Example: Bakelite, Melamine etc.
(b) Polymer polystyrene : The monomer of polystyrene is styrene and its structure is
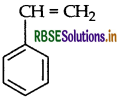
Use: It is used in the manufacture of food containers, cosmetic bottles etc.
Question 24.
How are polymers classified on the basis of mode of polymerization? Explain with suitable examples.
Answer: Polymers can be classified on the basis of mode of polymerisation into two groups:
(i) Addition polymers : The addition polymers are formed by the repeated addition of monomer molecules pos- sessing double or triple bonds.
Example:
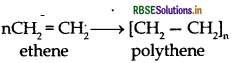
(ii) Condensation polymers: They are formed by repeated condensation reaction between two different bi-functional or tri-functional monomeric units.
Example: Nylon-6, 6
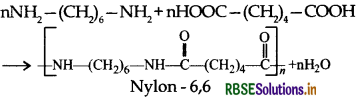
Question 25.
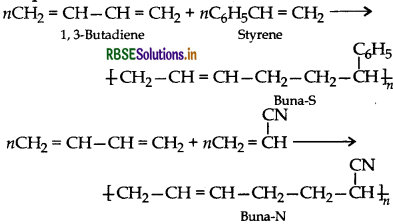
Explain the term co-polymerization and give two examples of copolymers and the reactions for their preparations.
Answer:
Co-polymerization : Co-polymerization is a polymerization reaction in which a mixture of more than one monomeric species is allowed to polymerise and form a co- polymer.
Example: Buna-S, Buna-N.
Equations:

Question 26.
Write the names and structures of the 26 monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Neoprene
(iii) Nylon-6, 6
Answer:
(i) Buna S:
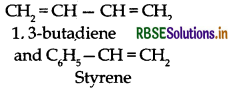
(ii) Neoprene:
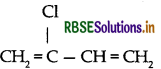
(iii) Nylon-6, 6: Monomers of Nylon-6, 6 ar hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid.
Question 27.
Write the names and structures of the mono mers of the following polymers:
(i) Polystyrene
(ii) Dacron
(iii) Teflon
Answer:
(i) Polystyrene: Monomer is styrene
Structure: C6H5CH = CH2
(ii) Dacron : Monomers are ethylene glycol and tereph thalic acid
Structure:
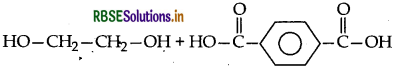
(iii) Teflon : Monomer is tetrafluoroethylene
Structure:
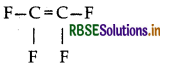
Question 28.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Nylon-6
(iii) Polythene
Answer:
(i) Bakelite: Monomers are
(a) Phenol Structure: (C6H5OH) and
(b) formaldehyde Structure: (HCHO).
(ii) Nylon-6: Monomer unit, which is derived from Ca prolactam.
Structure: 
(iii) Polyethene : Monomer is Ethene
Structure: CH2 = CH2
Question 29.
(a) Differentiate between copolymerization anc homopolymerization. Give one example of each.
(b) What is the role of Benzoyl peroxide in prepara tion of Polythene?
Answer:
(a) Homopolymers: Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from only one type of monome units are called homopolymers. Example: Polyethene, PVC, teflon.
Copolymers: Polymers whose repeating structural unit are derived from two or more types of monomer molecule are copolymers. Example: Buna-S, Nylon 6, 6
(b) Benzoyl peroxide acts as radical initiator which de composes on mild heating to form initiator free radical:
which add to double bond of ethene to form a new and larger free radical.

Question 30.
(a) How are thermosetting polymers different from thermoplastic polymers?
(b) Name the polymer which is used for making non- stick cooking utensils.
Answer:
(a) (a) Thermoplastic polymers: Linear polymers in which the intermolecular forces of attraction are in between those of elastomers and fibres and can be melted again and again on heating followed by moulding to give desired shape.
Example: Polyethene, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) etc.
Thermosetting polymers: These are semifluid substances with low molecular masses which when heated in a mould underoes change in chemical composition to give a hard, infusible and insoluble mass. These cannot be remelted.
Example: Bakelite, Melamine etc.
(b) Teflon is used for making non-stick cooking utensils.
Question 31.
(a) Differentiate between chain growth and step growth polymerization.
(b) What is the function of sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber?
Answer:
(a) Chain growth polymerization involves successive addition of monomer units to the growing chain carrying a reactive intermediate such as a free radical, a carbocation or a carbanion. Example: Polyethene, Teflon, PAN etc.
In step growth or condensation polymerization, the polymer is formed in a stepwise manner with the loss of simple molecules like H2O, alcohol etc. Example: Polyamides like Nylon 6, 6 Polyesters etc.
(b) Sulphur introduces sulphur bridges or crosslinks between polymer chains thereby impartins more tensile strength, elasticity and resistance to abrasion.
Question 32.
Write the monomers of the following polymers and classify them as addition or condensation polymers:
Teflon, Bakelite and Natural Rubber.
Answer:
Teflon
- Monomer → Tetrafluoroethylene
- Type →Addition polymer
Bakelite
- Monomer → Phenol and Formaldehyde
- Type → Condensation polymer
Natural Rubber
- Monomer → isoprene
- Type → Addition polymer
Question 33.
(a) Distinguish between homopolynes and copolymers. Give one example of each.
(b) What are biodegradable polymers? Give one example.
Answer:
(a) Homopolymers: Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from only one type of monome units are called homopolymers. Example: Polyethene, PVC, teflon.
Copolymers: Polymers whose repeating structural unit are derived from two or more types of monomer molecule are copolymers. Example: Buna-S, Nylon 6, 6
(b) Biodegradable polymers are defined as materials whose chemical and physical characteristics undergo deterioration and completely degrade when exposed to microorganisms, aerobic, and anaerobic processes. Poly β-hydroxybutyrate - co-β-hydroxy valerate (PHBV).
Question 34.
(a) What are biodegradable polymers? Give one example.
(b) Is polythene a condensation or an addition polymer?
Answer:
(a) Those polymers which can be decomposed by microorganisms are called biodegradable polymers.
Example: Nylon-2-Nylon-6
(b) Polythene is an addition polymer.

Question 35.
Write the names of the nomomers of the following polymers:
(i) Polythene
(ii) Polyvinyl chloride
(iii) Bakelite
Answer:
(i) Polyethene
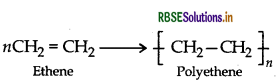
(ii) PVC (Polyvinyl chloride)
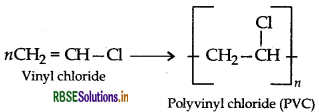
(iii) Bakelite → Phenol and formaldehyde → Condensation polymer
Question 36.
Give names of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Neoprene
(ii) Polystyrene
(iii) Polypropene
Answer:
(i) Neoprene: Monomer is 2-chloro-1, 3-butadiene
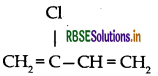
(ii) Polystyrene: Monomer is Styrene.
C6H5CH = CH2
(iii) Polypropene: Monomer is Propene.
(-CH3CH = CH2-)
Question 37.
Write the names of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Teflon
(ii) Bakelite
(iii) Neoprene
Answer:
(i) Teflon (Tetrafluoroethylene)
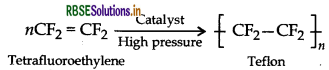
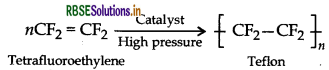
(ii) Bakelite → Phenol and formaldehyde → Condensation polymer
(iii) Neoprene: Monomer is 2-chloro-1, 3-butadiene
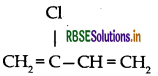
Question 38.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Nylon-6, 6
(ii) PHBV
(iii) Neoprene
Answer:
(i) Nylon-6, 6: It has two repeating monomers
(a) Hexa methylene diamine
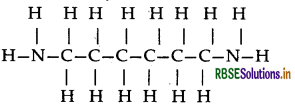
(b) Adipic acid
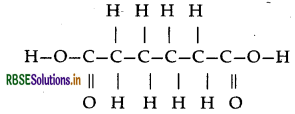
(ii) CH3CH-CH COOH
(iii) Neoprene: Monomer is 2-chloro-1, 3-butadiene
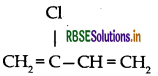

Question 39.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Terylene
(ii) Buna-S
(iii) Neoprene
Answer:
(i) Terylene:
Terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol
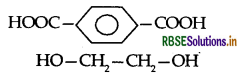
(ii) Buna-S:
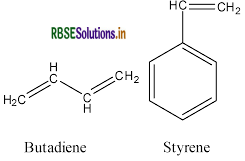
(iii) Neoprene: Monomer is 2-chloro-1, 3-butadiene
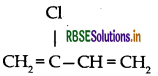
Question 40.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers.
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Neoprene
(iii) Teflon
Answer:
(i) Buna-S:

(ii) Neoprene: Monomer is 2-chloro-1, 3-butadiene
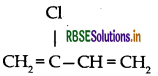
(iii) Teflon (Tetrafluoroethylene)


Question 41.
Explain the term 'copolymerization' and give two examples of copolymerization.
Answer:
When two or more different monomers are allowed to polymerize together, the product formed is called a co-polymer and the process is called copolymerization.
Co-polymerization is a polymerization reaction in which a mixture of more than one monomeric species is allowed to polymerize and form a copolymer. e.g. Buna-S, Buna-N.
Equations:
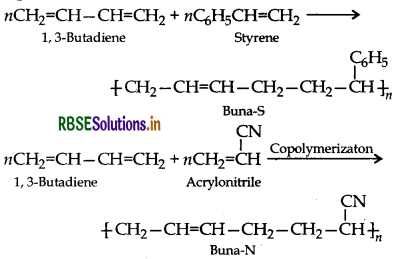
Question 42.
(i) What is the role of t-butyl peroxide in th polymerization of ethene?
(ii) Identify the monomers in the following polymer
[-NH2 - (CH2)6 - NH - CO - (CH2)4 -CO-]n
(iii) Arrange the following polymers in the increasir order of their intermolecular forces:
Polystyrene, Terylene, Buna-S
Answer:
(i) t-butyl peroxide acts as a radical initiator chain initiator in the polymerization of ethene. This initi tor readily decomposes on mild heating to form initiate free radicals which adds to double bond of ethene molecu to form a new and larger free radical.
(ii) Adipic acid HOOC(CH2)4 -COOH an Hexamethylene diamine NH2(CH2)6 NH2.
(iii) The increasing order of polymers on the basis their intermolecular forces:
Buna-S < Polystyrene < Terylene

Question 43.
Write the mechanism of free radical polyme ization of ethene.
Answer:
Free radical polymerization of ethene: This cess normally occurs at high temperature and under hig pressure in presence of small amounts of benzoyl peroxic as the initiator in three steps:
(i) Chain initiation step: Benzoyl peroxide undergo homolysis and works as chain initiator.
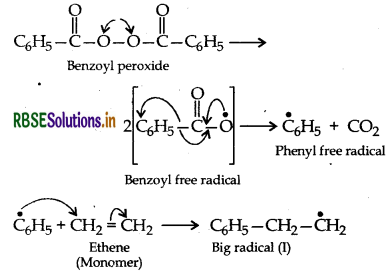
(ii) Chain Propagating step:
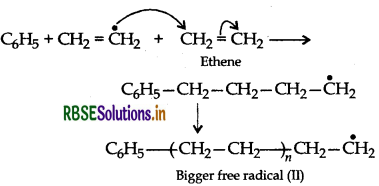
(iii) Chain Terminating step:
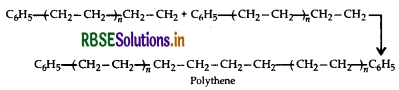
Question 44.
(i) What is the role of Sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber?
(ii) Identify the monomers in the following polymer.
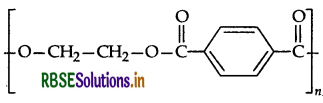
(iii) Arrange the following polymers in the increasing order of their intermolecular forces:
Terylene, Polythene, Neoprene
Answer:
(i) On vulcanisation, sulphur forms cross-links at the reactive sites of the double bond and thus rubber gets stiffened.
(ii) The monomers in the given polymer are: Ethylene glycol HO-CH2CH2-OH
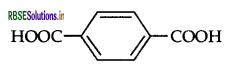
(iii) Neoprene < Polyethene < Terylene
Question 45.
Write two uses of each of the following polymers.
1. Polypropylene
2. PVC
3. Nylon-6, 6
Answer:
- Poiypropylene: Manufacture of ropes, toys, pipes etc.
- PVC: Manufacture of raincoats, handbags, vinyl flooring, water pipes etc.
- Nyion-6, 6: Manufacture of sheets, bristles of brushes, textiles etc.
Question 46.
Write two uses of each of the following polymers.
1. Polyproplene
2. PVC
3. Nylon-6, 6
Answer:
- Polypropylene : Manufacture of ropes, toys, pipes etc.
- PVC: Manufacture of raincoats, handbags, vinyl flooring, water pipes etc.
- Nylon-6, 6: Manufacture of sheets, bristles of brushes, textiles etc.
Question 47.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Dacron
(ii) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(iii) Buna-N
Answer:

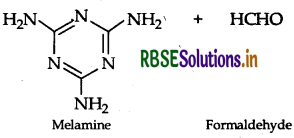
(ii) Monomers of melamine-formaldehyde polymer are melamine and formaldehyde.
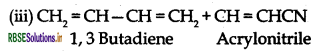

Question 48.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Neoprene
(ii) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(iii) Buna-S
Answer:
(i) Neoprene: Monomer is 2-chloro-1, 3-butadiene
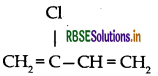
(ii) Monomers of melamine-formaldehyde polymer are melamine and formaldehyde.

(iii) Buna-S:

Question 49.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Nylon-6
(ii) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(iii) Teflon
Answer:
(i) Monomer: Caprolactam
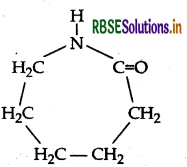
(ii) Monomers of melamine-formaldehyde polymer are melamine and formaldehyde.

(iii) Monomer: Tetrafluoroethene - CF2 = CF2
Question 50.
Write the structures of the monomers used for or getting the following polymers:
(a) Nylon-6, 6
(b) Melamine - formaldehyde polymer
(c) Buna-S
Answer:
Nylon-6, 6: It has two repeating monomers
(a) Hexa methylene diamine
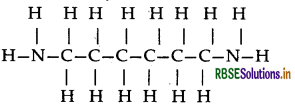
(b) Adipic acid
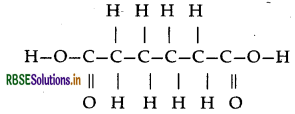
(b) Monomers of melamine-formaldehyde polymer are melamine and formaldehyde.

(c) Buna-S:

Question 51.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(a) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
(b) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(c) Buna-N
Answer:
(a) CH2 = CH - CI
(b) Monomers of melamine-formaldehyde polymer are melamine and formaldehyde.

Question 52.
Write the structures of the monomers used for etting the following polymers:
(a) Teflon
(b) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(c) Neoprene
Answer:
(a) Monomer: Tetrafluoroethene - CF2 = CF2
(b) Monomers of melamine-formaldehyde polymer are melamine and formaldehyde.

(c) Neoprene: Monomer is 2-chloro-1, 3-butadiene
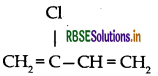
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What are polymers? How are they classified on e basis of:
(i) Structure
(ii) Synthesis
(iii) Molecular involved between polymeric chains? Give one example of each kind.
Answer:
(i) A polymer is composed of many simple molecules that are repeating structural units called monomers. A single polymer molecule may consist of hundreds to a million monomers and may have a linear, branched, or network structure.
The four basic polymer structures are linear, branched, crosslinked, and networked.
(ii) Synthesis:
- Natural polymers: Polymers which are found in nature i.e., in plants and animals are called natural polymers. For example: proteins, cellulose, starch, some resins, rubber etc.
- Semi-synthetic polymers: Polymers which are mostly derived from naturally occurring polymers by chemical modifications are called semi-synthetic polymers. For example, in cellulose on acetylation with acetic anhydride presence of concentrated sulphuric acid yields cellulose diacetate which is used for making theards of acetate rayon and other substances like films, glasses etc.
- Synthetic polymers: A variety of synthetic polymers as plastics (polythene, polypropene), synthetic fibres (nylon, polyester) and synthetic rubbers (neoprene, polystyrene) are examples of man made polymers extensively used in daily life as well as in industry.
(iii) A polymer is composed of many simple molecules that are repeating structural units called monomers. A single polymer molecule may consist of hundreds to a million monomers and may have a linear, branched, or network structure.

Question 2.
What is polymerization? Define and explain e terms: addition polymerization, condensation olymerization and copolymerization. Give one example each type.
Answer:
Polymers can also be classified on the basis of mode of polymerization into two sub groups:
(1) Addition polymers and
(2) Condensation polymers.
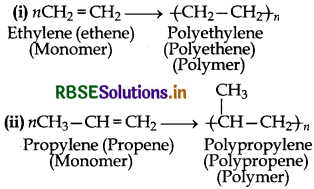
(1) Addition Polymers: The addition polymers are formed by the repeated addition of monomer molecules possessing double or triple bonds and the process by which addition polymers are formed is called addition polymerization.
for example:
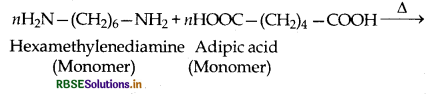
(2) Condensation polymers: The condensation polymers are formed by repeated condensation reactions between two different bifunctional or trifunctional monomeric units and process by which the condensation polymers are formed is called condensation polymerization. In these polymerization reactions, the elimination of small molecules such as water, alcohol, hydrogen chloride etc. take place. For example, nylon 6,6 is obtained by condensation polymerization of two monomers i.e., hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid, each containing two functional groups with the loss of water molcule.
example:
Question 3.
Give a brief description of natural and synthetic rubber. What is vulcanization? How does it improve the properties of natural and synthetic rubbers.
Answer:
Natural Rubber:
Rubber is a natural polymer and possesses elastic properties. It is also termed as elastomer and has a variety of uses. It is manufactured from rubber latex which is a colloidal dispersion of rubber in water. This latex is obtained from the bark of rubber tree and is found in India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Malaysia and South America.
Chemically natural rubber is a hydrocarbon polymer. It is a linear 1, 4-addition polymer of isoprene i.e., 2-methyl- 1,3-butadiene.
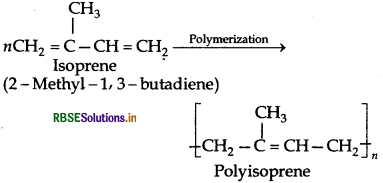
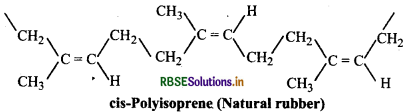
Since each repeating unit in polyisoprene contains a double bond, it may have either a cis- or trans-orientation. Actually a natural rubber is cis-polyisoprene.
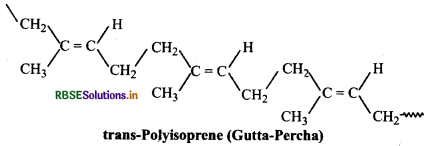
On the other hand, synthetic rubber (gutta percha) obtained by free radical polymerisation of isoprene is trans-
polyisoprene.
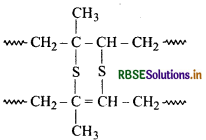
Vulcanization of Rubber:
Vulcanization is a chemical process in which the rubber is heated with sulphur, accelerator and activator at 140 -160°C. The process involves the formation of cross-links between long rubber molecules so as to achieve improved elasticity, resilience, tensile strength, viscosity, hardness and weather resistance.
synthetic rubber:
Majority of these rubbers are derived from butadiene derivatives and contain C = Cbonds so that they can also be vulcanized. Thus, synthetic rubbers are either homopolymers of 1,3-butadiene and its derivatives or are copolymers of 1,3-butadiene or its derivatives with another unsaturated monomer.
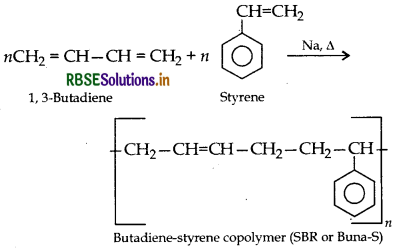
Some important synthetic rubbers are: cis-polybuta-1, 3-diene, Neoprene, Buna-S, Buna-N and thiokol.
(1) Cis-polybuta-1, 3-diene: Buta-1, 3-diene on polymerization in presence of Ziegler-Natta catalyst (a mixture of triethylaluminium and titanium tetra chloride) gives cis-polybuta-1, 3-diene in which 1, 4-addition takes place in each butadiene molecule and the remaining double bonds are in cis-orientation.
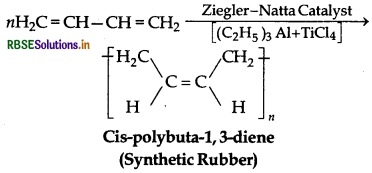
(2) Neoprene: It was the first synthetic rubber manufactured on large scale. It is a polymer of chloroprene (2-chloro-1,3-butadiene) and is also called polychloroprene. Its monomer chloroprene is prepared from acetylene as follows:

Question 4.
Distinguish between additon polymers and ondensation polymers. Classify the following into Addition and condensation polymers:
(i) Polythene
(ii) PTFE
(iii) Polybutadiene
(iv) Bakelite
Answer:
|
(i) Polythene |
CH2=CH2 |
Houseware, containers, bottles toys, films, packing material etc. |
|
(ii) PTFE |
CF2 =CF2 |
Non-stick utensils, gaskets, pump packings, valves, seals and non-lubricated bearings. |
|
(iii) Polybutadiene |
CH2 = CH - CH = CH2 |
Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production. |
|
(iv) Bakelite |
|
For making gears, protective coating and electrical fittings. |
Question 5.
What are biodegradable polymers? Give examples of such polymers with their uses.
Answer:
A polymer that can be decomposed by bacteria is called a biodegradable polymer. These polymers contain functional groups similar to groups present in biopolymers.
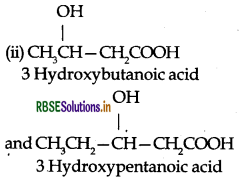
(1) Polyhydroxy butyrate (PHB): It is prepared by the condensation polymerization of hydroxy butyric acid (3hydroxy butanoic acid).
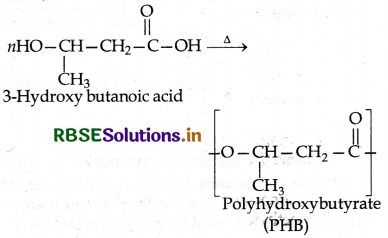
(2) Poly-β-hydroxy butyrate-Co-β-hydroxyvalerate
(PHBV): It is a copolymer (co-polyester) of 3-hyroxy butanoic acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid in which the monomer units are joined by ester linkages.
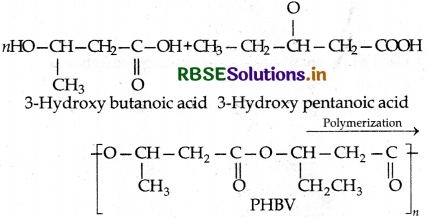
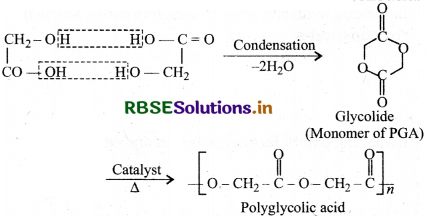
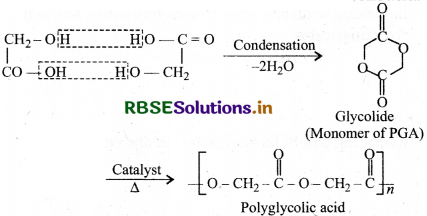
(3) Polyglycolic acid (PGA): It is obtained by dimerisation of glycolic acid to form glycolide which further undergoes ring opening addition to form polyglycolic acid.

Question 6.
Why does styrene undergo anionic polyme sation easily?
Answer:
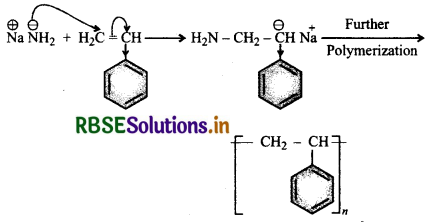
In styrene, an electron withdrawing phenyl gro is present. As a result, the nucleophile or anionic attack c easily take place leading to anionic polymerization.
Question 7.
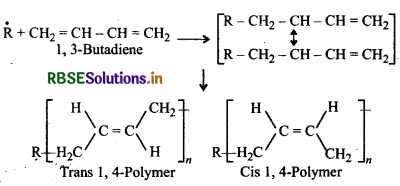
Explain how does 1, 3-butadiene polymerize different routes.
Answer:
Butadiene is a conjugated diene and its free radi polymerization can occur in following two ways:
(i) When the polymerisation takes place at C1 and of butadiene, an unbranched polymer is formed. It can ex either as a mixture of both polymers.
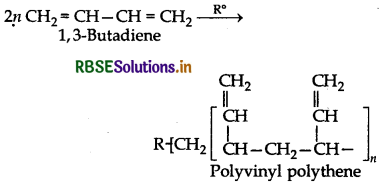
(ii) 1,3-Butadiene can also undergo polymerizatior: C1 and C2 to give polyvinyl polythene as the product.
Question 8.
Will you prefer polymerize acrylonitrile under anionic or cationic polymerization conditions? Explain your choice.
Answer:
Acrylonitrile (CH2 = CH - CN) has an electron withdrawing -CN group which prefers to form anion under anionic conditions. This anion further participaties in the polymeristion.
Question 9.
Arrange the following alkenes towards order of increasing reactivity in cationic polymerization H2C = CHCH3, H2C = CHCl, H2Ċ = CHC6H5, H2C = CHCO2CH3.
Answer:
Reactivity towards cationic polymerization increases as the stability of the intermediate carbocation increases. Since the stability of intermediate carbocations increases in the following order:
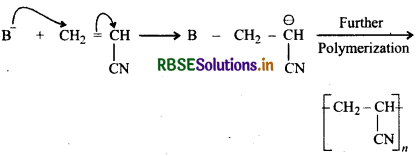
Therefore, reactivity of corresponding alkenes towards cationic polymerization increases in the following order:
H2C = CHCO2CH3 < H2C = CHCI < H2C = CHCH3 < CH2 = CHC6H5.
Question 10.
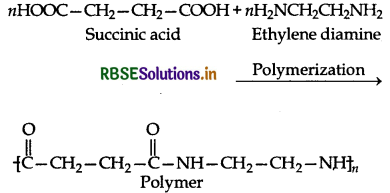
What is the repeating unit of condensation polymer obtained by combining HO2CH2CH2CO2H (succinic acid) and H2NCH2CH2NH2 (ethylene diamine)?
Answer:
(i) Remove 2n molecules of H2O from these monomers.
(ii) Now add three monomers to get condensation polymer.
COMPETITION CORNER:
Question 1.
Which one of the following statements is not true?
(a) Buna-S is a copolymer fo butadiene and styrene
(b) Natural rubber is a 1, 4 polymer of isoprene
(c) In vulcanization the formation of sulphur bridges between different chain makes rubber harder and stronger.
(d) Natural rubber has the trans-configuration at every double bond.
Answer:
(d) Natural rubber has the trans-configuration at every double bond.
Question 2.
Which of the following polymer contains nitrogen?
(a) Polyvinyl chloride
(b) Bakelite
(c) Nylon
(d) Terylene
Answer:
(c) Nylon

Question 3.
Bakelite is obtained from phenol by reaction with :
(a) HCHO
(b) (CH2OH)2
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3COCH3
Answer:
(a) HCHO
Question 4.
Which polymers occur naturally?
(a) Starch and nylon
(b) Starch and cellulose
(c) Proteins and nylon
(d) Proteins and PVC
Answer:
(b) Starch and cellulose
Question 5.
The monomer used to produce orlon is:
(a) CH2 = CHF
(b) CH2 = CCl2
(c) CH2 = CHCl
(d) CH2 = CH-CN
Answer:
(d) CH2 = CH-CN
Question 6.
Among cellulose, polyvinyl chloride, nylon and natural rubber, the polymer in which the inter-molecular force of attraction is weakest, is:
(a) Nylon
(b) Polyvinyl chloride
(c) Cellulose
(d) Natural rubber
Answer:
(d) Natural rubber
Question 7.
Structures of some common polymers are given. Which one is correctly represented?
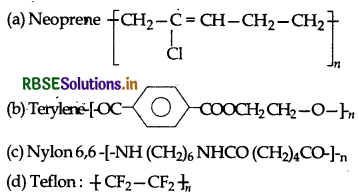
Answer:
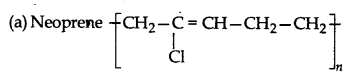
Question 8.
Buna-N, synthetic rubber is a copolymer of:
(a) H2C = CH-CH = CH2 and C6H5CH = CH2
(b) H2C = CH-CN and H2C = CH-CH = CH2
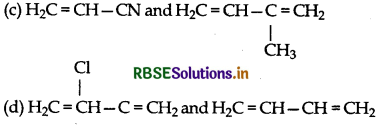
Answer:
(b) H2C = CH-CN and H2C = CH-CH = CH2

Question 9.
The catalyst used for olefin polymerization is:
(a) Ziegler-Natta catalyst
(b) Wilkinson Catalyst
(c) Raney Nickel Catalyst
(c) Merrified resin
Answer:
(a) Ziegler-Natta catalyst
Question 10.
The polymer used in the manufacture of orlon is:
(a) PTFE
(b) PAN
(c) PMMA
(d) PVC
Answer:
(b) PAN
Question 11.
Which of the following polymer is prepared from caprolactam ?
(a) Nylon-6,6
(b) Nylon-6,10
(c) Nylon-6
(d) Nylon-11
Answer:
(c) Nylon-6
Question 12.
The monomers of buna-S rubber are:
(a) Vinyl chloride and sulphur
(b) butadiene
(c) Styrene and butadiene
(d) Isoprene and butadiene
Answer:
(c) Styrene and butadiene
Question 13.
Which of following structures represents Neoprene polymer?
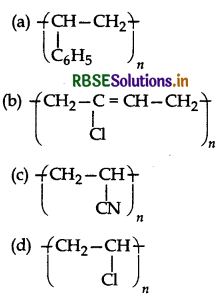
Answer:
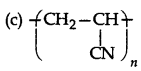

Question 14.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Caprolactam is a monomer of nylon-6.
(b) Terylene is a polyester polymer.
(c) Phenol-formaldehyde resin is known as bakelite.
(d) The monomer of natural rubber is butadiene.
Answer:
(d) The monomer of natural rubber is butadiene.
Question 15.
Which of the following is a copolymer formed by condensation polymerization?
(a) Terylene
(b) Buna-S
(c) Buna-N
(d) Neoprene
Answer:
(a) Terylene
Question 16.
Of the following which one is classified as polyester polymer?
(a) Nylon-6,6
(b) Terylene
(c) Bakelite
(d) Melamine
Answer:
(b) Terylene
Question 17.
Which of the following is a biodegradable polyme
(a) Polythene
(b) Bakelite
(c) PHBV
(d) PVC
Answer:
(c) PHBV
Question 18.
Which of the following is false statement?
(a) Artificial silk is derived from cellulose.
(b) Nylon-6,6 is an example of elastomer.
(c) The repeating unit in natural rubber is isopren
(d) Both starch and cellulose are polymers of gluco
Answer:
(b) Nylon-6,6 is an example of elastomer.
Question 19.
The species which can best serve as an initiator the cationic polymerization is :
(a) HNO3
(b) AlCl3
(c) BuLi
(d) LiAlH4
Answer:
(b) AlCl3

Question 20.
Which of the following is not a condensati polymer?
(a) Melamine
(b) Glyptal
(c) Dacron
(d) Neoprene
Answer:
(d) Neoprene
Question 21.
Which one of the following sets forms biodegradable polymer?
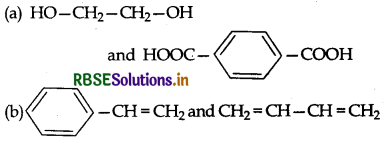
(c) CH2 = CH - CN and CH2 = CH - CH = CH2
(d) H2N - CH2 - COOH and H2N - (CH2)S - COOH
Answer:
(d) H2N - CH2 - COOH and H2N - (CH2)S - COOH
Question 22.
A polymer of prop-2-enenitrile is called:
(a) Saran
(b) Orlon
(c) Dacron
(d) Teflon
Answer:
(b) Orlon
Question 23.
Which is a monomer of neoprene in the followin
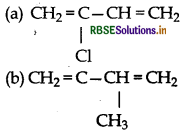
(c) CH2=CH-C – CH
(d) CH2=CH-CH=CH2
Answer:
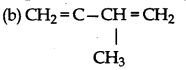
Question 24.
Nylon is an example of
(a) Polyamide
(b) Polythene
(c) Polyester
(d) Polysaccharide
Answer:
(a) Polyamide
Question 25.
Which of the following organic compounds polymerize to form polyester dacron?
(a) Benzoic acid and ethanol
(b) Terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol
(c) Benzoic acid and para OH-(C6H4)-OH
(d) Propylene and para HO-(C6H4)-OH
Answer:
(b) Terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol

Question 26.
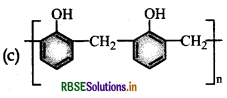
Which one of the following is an example of a thermosetting polymer?
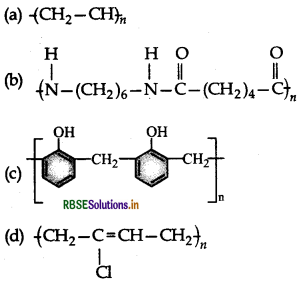
Answer:

- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 16 दैनिक जीवन में रसायन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 15 बहुलक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 जैव-अणु
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 ऐमीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12 ऐल्डिहाइड, कीटोन एवं कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 11 ऐल्कोहॉल, फीनॉल एवं ईथर
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 10 हैलोऐल्केन तथा हैलोऐरीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 उपसहसंयोजन यौगिक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 d- एवं f-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 p-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 तत्वों के निष्कर्षण के सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रम