RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 14 Biomolecules
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 14 Biomolecules Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Important Questions Biomolecules
Objective Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the following carbohydrate is not a sugar.
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Starch
(d) Sucrose
Answer:
(c) Starch
Question 2.
Which solution will give blue colour with iodine solution?
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Fructose
(d) Starch
Answer:
(d) Starch

Question 3.
Which of the following solution on heating with Benedict solution will give red precipitate?
(a) Starch
(b) Fructose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Cellulose
Answer:
(b) Fructose
Question 4.
Which of the following is a aldohexose?
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Starch
(d) Sucrose
Answer:
(a) Glucose
Question 5.
Which of the following is a monosaccharide pentose?
(a) Glucose
(b) Orbinose
(c) Fructose
(d) Galactose
Answer:
(b) Orbinose
Question 6.
Molecular formula of simple disaccharide is:
(a) C10O18O9
(b) C10H20O11
(c) C18H32O16
(d) C12H22O11
Answer:
(d) C12H22O11
Question 7.
The end product of hydrolysis of starch is:
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Glucose and Fructose
(d) Sucrose
Answer:
(a) Glucose
Question 8.
Which of the following is laevorotatory?
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Fructose
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Fructose
Question 9.
In which glucose does not classified?
(a) Hexose
(b) Carbohydrate
(c) Oligosaccharide
(d) Aldose
Answer:
(c) Oligosaccharide
Question 10.
On treatment with methyl alcohol glucose gives:
(a) a-methyl glucoside
(b) B-methyl glucoside
(c) Bothe (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Bothe (a) and (b)
Question 11.
Sucrose is a :
(a) Monosaccharide
(b) Disaccharide
(c) Polysaccharide
(d) Steroid
Answer:
(b) Disaccharide
Question 12.
On heating glucose with Fehling's solution a precipitate is obtained. The colour of precipitate is:
(a) Yellow
(b) Black
(c) White
(d) Red
Answer:
(d) Red
Question 13.
Which of the following is a disaccahride?
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Xylose
Answer:
(c) Sucrose

Question 14.
Disaccharide present in milk is:
(a) Sucrose
(b) Lactose
(c) Maklose
(d) Sorbose
Answer:
(b) Lactose
Question 15.
Starch converts into disaccharide in the present of:
(a) Diastase
(b) Maltase
(c) Lactase
(d) Zymase
Answer:
(a) Diastase
Question 16.
Which of the following is a sweetest sugar?
(a) Sucrose
(b) Glucose
(c) Fructose
(d) Maltose
Answer:
(c) Fructose
Question 17.
Which gives iodine test?
(a) Polypeptide
(b) Glucose
(c) Starch
(d) Glycogen
Answer:
(c) Starch
Question 18.
Which compound is obtained during the complete hydrolysis of cellulose?
(a) D-glucose
(b) L-glucose
(c) D-fructose
(d) D-ribose
Answer:
(a) D-glucose
Question 19.
Biodegradable polymer is:
(a) Cellulose
(b) Polythene
(c) Polyvinyl chloride
(d) Nylon-6
Answer:
(a) Cellulose
Question 20.
Which disease is caused due to the deficiency of vitamin D ?
(a) Nightblindness
(b) Beri-beri
(c) Xerophthalmia
(d) Rickets
Answer:
(d) Rickets
Very Short Answer Type Question:
Question 1.
What is meant by 'reducing sugars'?
Answer:
Reducing sugar contains aldehydic or ketonic group in the hemiacetal and hemiketal forms and can reduce Tollen's reagent or Fehling's solution.
Question 2.
What are monosaccharides?
Answer:
These are the simplest carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed to smaller molecules. Their general formula is (CH2O)n where n = 3 −7
Example: glucose, fructose etc.

Question 3.
Write the structure of the product obtained when glucose is oxidised with nitric acid.
Answer:
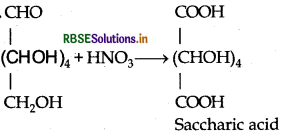
Question 4.
Write a reaction which shows that all the carbon atoms in glucose are linked in a straight chain.
Answer:
On prolonged heating with HI, it forms n-hexane, shows that all the six carbon atoms are linked in a straight chain :
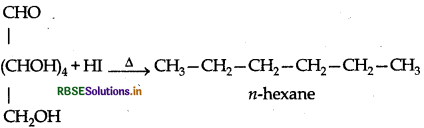
Question 5.
What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose?
Answer:
On hydrolysis, lactose gives B-D-galactose and B-D-glucose.
Question 6.
Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg?
Answer:
Because the egg comes in contact with a solution of higher osmotic pressure, the egg will shrink due to going out of water. This shrinking of egg is called plasmolysis.
Question 7.
Name a water soluble vitamin which is a powerful antioxidant. Give its one natural source.
Answer:
- Water soluble vitamin: Vitamin C
- Natural source: Amla
Question 8.
What are three types of RNA molecules which perform different functions.
Answer:
m-RNA, t-RNA, r-RNA
Question 9.
What is a glycosidic linkage?
Answer:
The two monosaccharide units are joined together through an etheral or oxide linkage formed by loss of a molecule of water. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.
Question 10.
What are the products of hydrolysis of sucrose?
Answer:
Invert sugar: An equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose is obtained by hydrolysis of sucrose in presence of an acid such as dil. HCI or the enzyme invertase or sucrase and is called invert sugar.

Question 11.
Write the name of linkage joining two amino acids.
Answer:
Peptide linkage joins two amino acids.
Question 12.
Name the deficiency diseases resulting from lack of Vitamins À and E in the diet.
Answer:
Deficie-ncy of Vitamin A causes Xerophthalmia and deficiency of Vitamin E causes Sterility.
Question 13.
Name one water soluble vitamin which is a powerful antioxidant. Give its one natural source.
Answer:
- Water soluble vitamin: Vitamin C
- Natural source: Amla
Question 14.
Name one oil soluble vitamin which is a powerful antioxidant and give its one natural source.
Answer:
Oil soluble Vitamin: Vitamin D Natural source: Fish liver oil, butter, milk, eggs etc.
Question 15.
Name the products of hydrolysis of lactose.
Answer:
Lactose on hydrolysis with dilute acids gives an equimolar mixture of D-glucose and D-galactose.
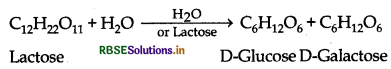
Question 16.
Name the only vitamin which can be synthesized in our body. Name the disease caused due to the deficiency of this vitamin.
Answer:
Vitamin which can be synthesized in our body: Vitamin A Its deficiency causes xerophthalmia.
Question 17.
Mention one important function of nucleic acids in our body.
Answer:
Function of nucleic acid: Nucleic acids control the transmission of hereditary characters from one generation to another.
Question 18.
Which of the two components of starch is water soluble?
Answer:
Amylose is water soluble component of starch.

Question 19.
Name the products of hydrolysis of sucrose.
Answer:
Glucose and fructose are the products of hydrolysis of sucrose.
Question 20.
Which component of starch is a branched polymer of a-glucose and insoluble in water?
Answer:
Amylopectin.
Question 21.
What are the products of hydrolysis of sucrose?
Answer:
Glucose and fructose.
Question 22.
What are the products of hydrolysis of maltose?
Answer:
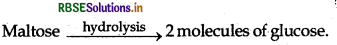
Question 23.
Write the products of hydrolysis of lactose.
Answer:
Lactose on hydrolysis with dilute acids given an equimolar mixture of D-glucose and D-galactose.
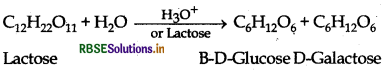
Question 24.
Define a 'Peptide linkage'.
Answer:
Peptide Tinkage: It is an amide linkage formed between -COOH group of one a-amino acid and NH2 group of the other a-amino acid by loss of a molecule of water. CO-NH-bond is called Peptide linkage.
Question 25.
What are enzymes ?
Answer:
Enzymes are protein molecuies which act as catalyst in biochemical reaction.
Short Answer type Question:
Question 1.
Explain what is meant by
(i) a peptide linkage
(ii) a glycosidic linkage.
Answer:
(i) Peptide linkage: A peptide linkage is an amide linkage formed between -COOH group of one a-amino acid and NH2 group of the other a-amino acid by loss of a molecule of water.
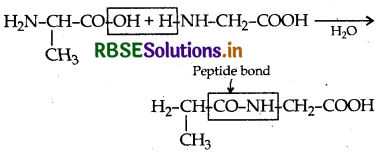
(ii) Glycosidic linkage: The two monosaccharide units are joined together through an etheral or oxide linkage formed by loss of a molecule of water. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.

Question 2.
Name two water solubie vitamins, their sources and the diseases caused due to their deficiency in diet.
Answer:
|
Vitamins |
Sources |
Deficime disease |
|
1. Vitamic B2 (Riboflavin or Lactoflavin) |
Milk, yeast, green vegetables, meat, liver, kidney, egg white etc. Daily dosage is 2-3 mg. |
Relards growth causes inflamation of tonguie (glossitis), dermatitis and (chellosis (cracking or flssuring at corners of mouth and lips.) |
|
2. Vitamic C (Ascorbic acid) |
Citrus fruits, green leafy vegetablos, chilles, Sprouted Pulses and terminated grains Daily dosage is 75 mg. |
Scervy (pieeding) of gums), pyorrhea (loose ing and bleeding of teeth). |
Question 3.
Name the four bases present in DNA. Which one of these is not present in RNA?
Answer:
The four bases present in DNA are:
- Adenine (A)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
- Thymine (T)
In RNA, Thymine (T) is absent. It has Uracil (U) in place of Thymine.
Question 4.
Name two fat soluble vitamins, their sources and the diseases caused due to their deficiency in diet.
Answer:
|
Vitamins |
Sources |
Deficime disease |
|
1. Vitamin A |
Milk, butter, eggs, fish, liver oil, rice, kidney, green vegetables etc. |
Xerophthalmia (hardening of cornea), night blindness and xerosis (drying of skin) |
|
2. Vitamin D |
Fish liver oil, butter, milk, eggs, liver and meat. |
Rickets, osteomalacia (soft bones and ioint pain). |
Question 5.
Explain the following terms:
(i) Invert sugar
(ii) Polypeptides
Answer:
(i) Invert sugar: An equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose obtained by hydrolysis of sucrose in presence of an acid such as dil. HCl or the enzyme invertase or sucrase is called invert sugar.
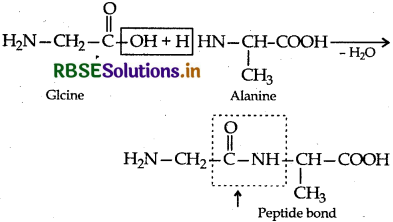
(ii) Polypeptides: They are formed when several molecules of a-amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds.
Question 6.
Name the products of hydrolysis of sucrose. Why is sucrose not a reducing sugar?
Answer:
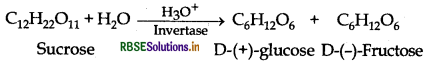
Sucrose is not a reducing sugar because it is unable to reduce Tollen's reagent and Fehling solution.

Question 7.
What are essential and non-essential amino acids in human food? Give one example of each type.
Answer:
- Essential amino acids: Amino acids which the body cannot synthesize are called essential amino acids.
- Example: Valine, leucine etc. Therefore they must be supplied in diet.
- Non-essential amino acids: Amino acids which the body can synthesize are called non-essential amino acids. Therefore, they may or may not be present in diet.
- Example: Glycine, alanine etc.
Question 8.
State clearly what are known as nucleosides and nucleotides.
Answer:
Nucleoside: A nucleoside contains only two basic components of nucleic acids i.e. a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. During their formation 1-position of the pyrimidine or 9-position of the purine moitey is linked to C1 of the sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) by a β-linkage.
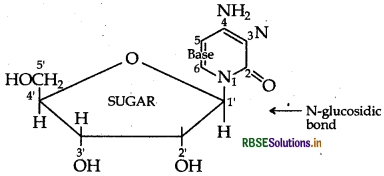
Nucleotides: A nucleotide contains all the three basic components of nucleic acids, i.e. a phosphoric acid group, a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. These are formed by esterification of C5'-OH of the sugar of the nucleoside with phosphoric acid.
Question 9.
What is essentially the difference between a- orm of glucose and ß-form of glucose? Explain.
Answer:
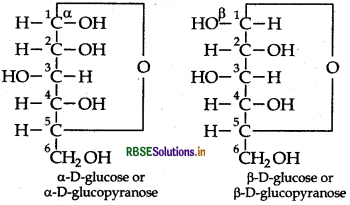
In a-glucose, the OH group at C1 is towards right vhile in β-D-glucose, the OH group at C1 is towards left.
Question 10.
Describe what you understand by primary structure and secondary structure of proteins.
Answer:
- Primary structure of proteins: Proteins may have ne or more polypeptide chains. Each polypeptide in a rotein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific equence which is known as primary structure of protein.
- Secondary structure of proteins: The conformation which the polypeptide chains assume as a result of hydrogen onding is called the secondary structure of the protein.
Depending upon the size of the R groups, the two ifferent secondary structures are possible which are:
- a-Helix structure: Intramolecular H-bonds present between the C = O of one amino acid and N-H of four amino acid.
- B-Pleated sheet structure: The two neighbouri polypeptide chains are held together by intermolecular bonds.
Question 11.
Explain what is meant by
1. a peptide linkag
2. a glycosidic linkage.
Answer:
- “Peptide linkage is an amide formed between group and group.” “Proteins are the polymers of α amino acids and they are connected to each other by a peptide bond or peptide linkage.
- A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Question 12.
Name the bases present in RNA. Which one these is not present in DNA?
Answer:
The four bases present in RNA are: Purines: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) Pyrimidines: Uracil (U) and Cytosine (C) Uracil is not present in DNA.

Question 13.
Explain what is meant by the following:
(i) peptide linkage
(ii) pyranose structure of gluco
Answer:
(i) Peptide linkage: A peptide linkage is an ami linkage formed between -COOH group of one a-amino ac and NH2 group of the other a-amino acid by loss of molecule of water.
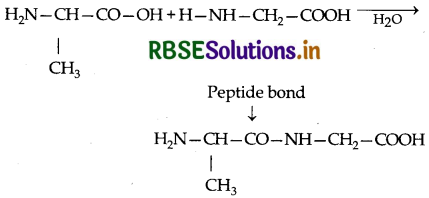
(i) Pyranose structure of glucose: The six member ring containing 5 carbon atoms and one oxygen atom becau of its resemblance with pyran is called the pyranose forn
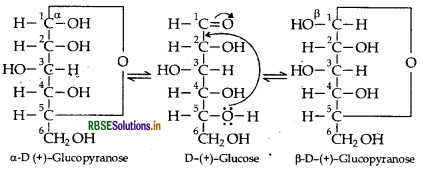
Question 14.
Write the main structural difference between DNA and RNA. Of the four bases, name those which a common to both DNA and RNA.
Answer:
|
DNA |
RNA |
|
1. The sugar present in DNA is 2-deoxy-(-) ribose. |
The sugar present in RNA is D-(-) ribose. |
|
2. DNA contains cytosine and thymine as pyrimidine bases. |
RNA contains cytosine and uracil as pyrimidine bases. |
|
3. DNA has double stranded α-helix structure. |
RNA has single stranded α-helix structure. |
|
4. DNA molecules are very large. Their molecular mass may vary from 6 x 106-16 x 106u i.e., from six to sixteen million. |
RNA molecules are much smaller with molecular mass ranging from 20,000 to 40,000u |
Question 15.
Write such reactions and facts about glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
Answer:
Limitations of the open chain structure of glucose:
- Glucose does not form NaHSO3 addition product. Despite having aldehyde-group, it does not respond to 2,4-DNP test and does not respond to Schiff's reagent test.
- Glucose penta acetate does not react with NH2OH due to absence of aldehydic group.
Question 16.
Write any two reactions of glucose which cannot be explained by the open chain structure of glucose molecule.
Answer:
- Despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give 2, 4-DNP test or Schiff's test.
- It does not form the hydrogen sulphite addition product with NaHSO3.
- The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine indicating the absence of free -CHO group.

Question 17.
Write the main structural difference between DNA and RNA. Of the two bases, thymine and uracil, which one is present in DNA?
Answer:
|
DNA |
RNA |
|
1. DNA has a double helix structure |
1. RNA has a single helix structure. |
|
2. The nitrogenous bases present in DNA are Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine. |
2. The nitrogenous bases present in RNA are Adenine, Guanine, Uracil, and Cytosine. |
|
3. Thymine is present in DNA. |
3. RNA is generally single-stranded and not double-stranded , and (3) RNA contain uracil in place of thymine. |
Question 18.
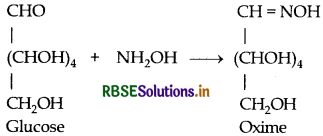
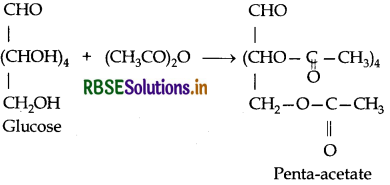
Write down the structures and names of the products formed when D-glucose is treated with (i) Hydroxylamine (ii) Acetic anhydride.
Answer:
(i) D-glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form oxime.
(ii) D-glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to give penta-acetate.
Question 19.
(a) Name the only vitamin which can be synthesized in our body. Name one disease that is caused due to the deficiency of this vitamin.
(b) State two functions of carbohydrates.
Answer:
(a) Vitamin that can be synthesized Vitamin B12 Disease due to the doficiency of Vitamin B12 Pernicious anaemia.
(b) Two functions of glucose:
- Carbohydrates such as glucose, starch, glycogen etc. provide energy for functioning of living organisms.
- Carbohydrates, especially cellulose in the form of wood is used for making furniture, houses etc. by us.
Question 20.
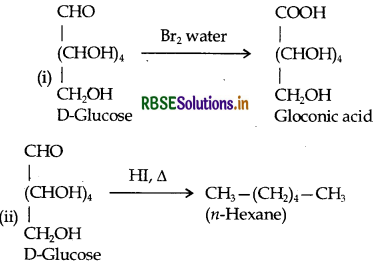
Write down the structures and names of the of the products formed when D-glucose is treated with (i) Bromine water (ii) Hydrogen Iodide (Prolonged heating).
Answer:
Question 21.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Why are vitamin A and vitamin C essential for us?
(ii) What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
Answer:
(i) Because denciency of vitamin A and vitamin C causes night blindness and scurvy respectively.
(ii)
|
Nucleotide |
Nucleoside |
|
1. The chemical composition of nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar and a nitrogenous base. |
1. A nucleoside has a chemical composition that consists of a sugar and a base without the phosphate group. |
|
2. They are one of the major causes of cancer-causing agents to this very day. |
2. They are used as agents in medicine that are primarily used against viruses and cancer-causing agents |
|
3. Some of the major examples of nucleotides are adenosine, guanosine etc. |
3. Some of the key examples of nucleosides are the same as nucleotides only with the addition of phosphate groups. |

Question 22.
Enumerate the reactions of glucose which annot be explained by its open chain structures.
Answer:
Limitations of the open chain structure of lucose:
- Glucose does not form NaHSO3 addition product. Despite having aldehyde-group, it does not give 2, 4-DNP est and does not respond to Schiff's reagent test.
- Glucose penta acetate does not react with NH2OH ue to absence of aldehydic group.
Question 23.
Write the ambident nucleophiles? Give an xample.
Answer:
A group containing two nucleophilic centres. xample: -CN (Cyanide) and -NC (Isocyanide).
Short Answer Type Questions-II:
Question 1.
Amino acids may be acidic, alkaline or neutral. low does this happen? What are essential and non- ssential amino acids? Name one of each type.
Answer:
1. Amino acids can be broadly classified into three lasses i.e. acidic, alkaline and neutral amino acids epending on the number of -NH2 group and -COOH group.
2. Acidic amino acids: Those a-amino acids such as spartic acid, asparagine and glutamic acid which contain NO-COOH groups and one -NH2 group are called acidic mino acids.
3. Alkaline or Basic amino acids: Those a-amino acids uch as lysine, arginine and histidine which contain two H2 groups and one -COOH group, are called basic amino cids.
4. Neutral amino acids: Those a-amino acids such as lycine, alanine, valine etc. which contain one -NH2 and ne -COOH group, are called neutral amino acids.
5. Essential and non-essential amino acids : Refer to Question 2, Page 315.
Question 2.
Differentiate between fibrous proteins and lobular proteins. What is meant by the denaturation of a protein?
Answer:
|
Globular Proteins |
Fibrous Proteins |
|
1. Globular proteins have almost spheroidal shape due to folding of the polypeptide chain. |
Polypeptide chains of fibrous proteins consist of thread like molecules which tend to lie side by side to form fibres. |
|
2. Globular proteins are soluble in water. |
Fibrous proteins are insoluble in water. |
|
3. Globular proteins are sensitive to small changes of temperature and pH. Therefore they undergo denaturation on heating or on treatment with acids /bases. |
Fibrous proteins are stable to moderate changes of temperature and pH. |
|
4. They possess biological activity that's why they act as enzymes. |
They do not have any biological activity but serve as chief structural material of animal tissues. |
|
Example: Maltase, invertase etc., hormones (insulin) antibodies, transport agents (haemoglobin) etc. |
Example : Keratin in skin, hair, nails and wool, collagen in tendons, fibroin in silk etc. |
Denaturation of protein: Due to coagulation globular protein under the influence of change temperature, change in pH etc., the native shape of protein is destroyed and biological activity is lost and formed protein is called denaturated proteins and phenomenon is denaturation.
Question 3.
What is essentially the difference between glucose and β-glucose? What is meant by pyran structure 3 of glucose?
Answer:
The two cyclic hemiacetal forms of glucose dif only in the configuration of the hydroxyl group on the fi carbon atom called anomeric carbon. Such isomers i.e. form and β-form are called anomers. a-glucose is monomer unit of starch and B-glucose is the monomer u of cellulose. The six membered cyclic structure of glucos called pyranose structure.
Pyranose structure of glucose: Refer to Question 38 (ii). Also study the following:
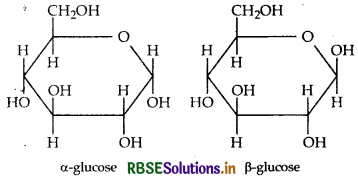
Question 4.
Define the following as related to proteins:
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation
Answer:
(i) Peptide linkage: A peptide linkage is an am linkage formed between -COOH group of one a-amino a and NH2 group of the other a-amino acid by loss o molecule of water. The-CO-NH-bond formed is cal petide linkage.
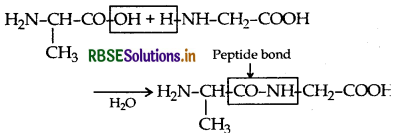
(ii) Primary structure: Proteins may have one or more polypeptide chains. Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence and it is this sequence of amino acids that is called the primary structure of that protein.
(iii) Denaturation : Due to coagulation of globular protein under the influence of change in temperature, change in pH etc., the native shape of the protein is destroyed and biological activity is lost and the formed protein is called denaturated proteins and the phenomenon is denaturation.

Question 5.
What are the different types of RNA found in cells of organisms? State the functions of each type.
Answer:
Different types of RNA found in the cell are:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): carries the message of DNA for specific protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) : provides the site for protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (t-RNA) : transfers amino acids to the site of protein synthesis.
Question 6.
(a) What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type.
(b) What are the hydrolysis products of sucrose?
Answer:
(a) Non-essential amino acids: The amino acids which can be synthesised in the body, are known as non-essential amino acids. Example: Glycine, Alanine etc.
Essential amino acids: The amino acids which cannot be synthesised in the body and must be obtained through diet are known as essential amino acids.
Example: Valine, Leucine etc.
(b) Sucrose on hydrolysis gives equimolar mixture of D(+)-glucose and D(-) fructose
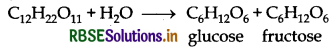
Question 7.
(a) Write the structural and functional differences between DNA and RNA
(b) Name two components of starch.
Answer:
(a) Structural difference DNA:
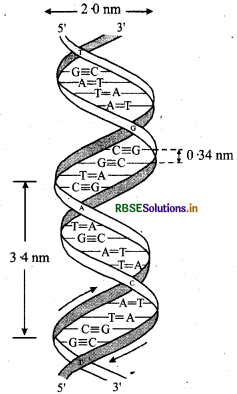
Structural difference RNA:
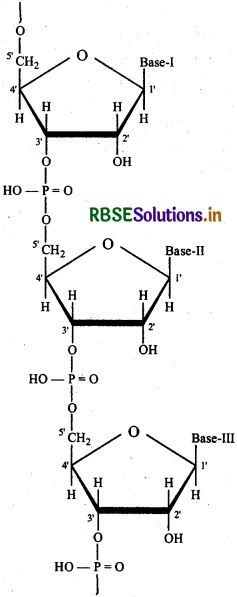
Functional difference: DNA's main function is to control cell activities like telling each organ what to make and what to do. RNA's main function is to make protein.
(b) Components of starch: mylose and amylopectin.
Question 8.
(a) Give two differences between globular and fibrous proteins.
(b) What change Occurs in the nature of egg protein on boiling?
Answer:
(a)
|
Globular Proteins |
Fibrous Proteins |
|
1. Globular proteins have almost spheroidal shape due to folding of the polypeptide chain. |
Polypeptide chains of fibrous proteins consist of thread like molecules which tend to lie side by side to form fibres. |
|
2. Globular proteins are soluble in water. |
Fibrous proteins are insoluble in water. |
|
3. Globular proteins are sensitive to small changes of temperature and pH. Therefore they undergo denaturation on heating or on treatment with acids /bases. |
Fibrous proteins are stable to moderate changes of temperature and pH. |
|
4. They possess biological activity that's why they act as enzymes. |
They do not have any biological activity but serve as chief structural material of animal tissues. |
|
Example: Maltase, invertase etc., hormones (insulin) antibodies, transport agents (haemoglobin) etc. |
Example : Keratin in skin, hair, nails and wool, collagen in tendons, fibroin in silk etc. |
(b) Because the egg comes in contact with a solution of higher osmotic pressure, the egg will shrink due to going of out of water. This shrinking of egg is called plasmolysis.
Question 9.
(a) How are hormones and vitamins different in respect of their source and functions?
(b) Give one example each of
(i) Globular protein
(ii) Fibrous protein
Answer:
(a) Hormones are synthesized in our body and help in regulation of our body systems while vitamins are synthesized artificially in the laboratory or obtained from the food which helps in controlling many diseases.
(b) (i) Globular protein: All enzymes and hormones like insulin.
(ii) Fibrous protein: Keratin in skin, nails etc.

Question 10.
(a) What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each.
(b) How are nucleosides different from nucleotides?
Answer:
(a)
- Essential amino acids: Amino acids which the body cannot synthesize are called essential amino acids.
- Example: Valine, leucine etc. Therefore they must be supplied in diet.
- Non-essential amino acids: Amino acids which the body can synthesize are called non-essential amino acids. Therefore, they may or may not be present in diet.
- Example: Glycine, alanine etc.
(b)
|
Nucleotide |
Nucleoside |
|
1. The chemical composition of nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar and a nitrogenous base. |
1. A nucleoside has a chemical composition that consists of a sugar and a base without the phosphate group. |
|
2. They are one of the major causes of cancer-causing agents to this very day. |
2. They are used as agents in medicine that are primarily used against viruses and cancer-causing agents |
|
3. Some of the major examples of nucleotides are adenosine, guanosine etc. |
3. Some of the key examples of nucleosides are the same as nucleotides only with the addition of phosphate groups. |
Question 11.
1. Deficiency of which vitamin causes night-blindness?
2. Name the base that is found in nucleotide of RNA only.
3. Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Answer:
- Vitamin A causes night blindness.
- Uracil is found in nucleotide of RNA only.
- It suggests the open structure of glucose.
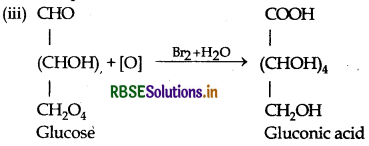
Question 12.
(i) Deficiency of which vitamin causes rickets?
(ii) Give an example for each of fibrous protein and globular protein.
(iii) Write the product formed on reaction of D-glucose with Br2 water.
Answer:
(i) Deficiency of Vitamin D causes rickets.
(ii) Fibrous protein → a-keratin
Globular protein → Insulin
Question 13.
(i) Deficiency of which vitamin causes scurvy?
(ii) What type of linkage is responsible for the mation of proteins?
(iii) Write the product formed when glucose is treated th HI
Answer:
(i) Vitamin C causes scurvy.
(ii) Peptide linkages are responsible for the formation proteins.
(iii) Glucose is treated with HI:
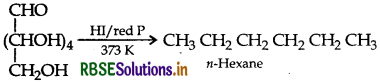
Question 14.
Define the following terms as related to proteins:
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation
Answer:
(I) Peptide linkage is the peptide bond formed between the amino acids. It is a covalent bond formed between amino group of one molecule and carboxylic acid group of another molecule.
(II)The primary structure of a peptide or protein is the linear sequence of its amino acid structural units. The primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end.
(III) The process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary structure, tertiary structure and secondary structure which is present in their native state known as denaturation. by application of some external stress or compound such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic sol.

Question 15.
Define the following terms:
1. Glycosidic linkage
2. Invert sugar
3. Oligosaccharides
Answer:
- Glycosidic linkage: The two monosaccharide its are joined together through an etheral or oxide linkage med by loss of a molecule of water. Such a linkage between o monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called cosidic linkage.
- Invert sugar: An equimolar mixture of glucose and ictose obtained by hydrolysis of sucrose in presence of an d such as dil. HCl or the enzyme invertase or sucrase is led invert sugar.
- Oligosaccharides: Those carbohydrates which on drolysis give 2-10 molecules of monosaccharides are led oligosaccharides. Example: sucrose, maltose.
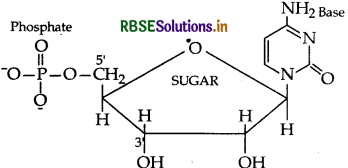
Question 16.
Define the following terms:
(i) Nucleotide
(ii) Anomers
(ii) Essential amino acids
Answer:
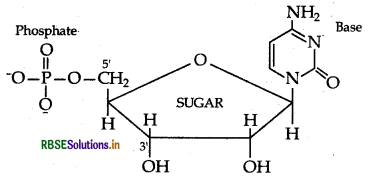
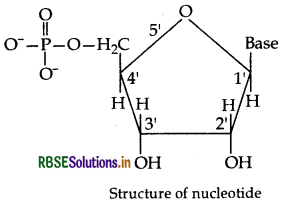
(i) Nucleotide : A nucleotide contains all the three sic components of nucleic acids, i.e. a phosphoric acid up, a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. These are med by esterification of C5'-OH of the sugar of the cleoside with phosphoric acid.
Structure of Nucleotide:
(ii) Anomers: A pair of stereoisomers which differ i configuration only around C, are called anomers. Tw isomers are said to be anomers if the isomerisation in th molecule is at first carbon.
(iii) These are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Although your body can make nonessential amino acids, it cannot make essential amino acids, so you have to get them from your diet.
Question 17.
What are essential and non-essential amin acids? Give two examples of each.
Answer:
- Essential amino acids: Amino acids which th body cannot synthesize are called essential amino acids. Example: Valine, leucine etc. Therefore they must b supplied in diet.
- Non-essential amino acids: Amino acids which th body can synthesize are called non-essential amino acid Therefore, they may or may not be present in diet. Example: Glycine, alanine etc.
Question 18.
(i) Which one of the following is a disaccharide Starch, Maltose, Fructose, Glucose?
(ii) What is the difference between fibrous protei and globular protein?
(iii) Write the name of vitamin whose deficienc causes bones deformities in children.
Answer:
(i) Maltose is a disaccharide.
(ii)
|
Globular Proteins |
Fibrous Proteins |
|
1. Globular proteins have almost spheroidal shape due to folding of the polypeptide chain. |
Polypeptide chains of fibrous proteins consist of thread like molecules which tend to lie side by side to form fibres. |
|
2. Globular proteins are soluble in water. |
Fibrous proteins are insoluble in water. |
|
3. Globular proteins are sensitive to small changes of temperature and pH. Therefore they undergo denaturation on heating or on treatment with acids /bases. |
Fibrous proteins are stable to moderate changes of temperature and pH. |
|
4. They possess biological activity that's why they act as enzymes. |
They do not have any biological activity but serve as chief structural material of animal tissues. |
|
Example: Maltase, invertase etc., hormones (insulin) antibodies, transport agents (haemoglobin) etc. |
Example : Keratin in skin, hair, nails and wool, collagen in tendons, fibroin in silk etc. |
(iii) Vitamin D

Question 19.
1. Which one of the following is polysaccharide:
Starch, Maltose, Fructose, Glucose?
2. What one difference between a-helix and ‹ pleated sheet structure of protein.
3. Write the name of the disease caused by th deficiency of Vitamin B12.
Answer:
- Starch is a polysaccharide.
- a-Helix structure: The polypeptide chains are he together (stabilized) by intramolecular H-bonding. B-Pleated sheet structure: The two neighbourir polypeptide chains are held together by intermolecular F bonding.
- Disease caused by the deficiency of Vitamin B12 Pernicious anaemia.
Question 20.
How are vitamins classified? Name the vitami responsible for the coagulation of blood.
Answer:
Vitamins are classified into two types:
- Water insoluble vitamins: These are fat solub substances E.g. Vitamin A, D, E and K.
- Water soluble vitamins: These include Vitamin] Complex and Vitamin C (except B12).
- Vitamin K or phylloquinone is responsible for th coagulation of blood.
Question 21.
Define the following as related to proteins:
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation
Answer:
(I) Peptide linkage is the peptide bond formed between the amino acids. It is a covalent bond formed between amino group of one molecule and carboxylic acid group of another molecule.
(II)The primary structure of a peptide or protein is the linear sequence of its amino acid structural units. The primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end.
(III) The process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary structure, tertiary structure and secondary structure which is present in their native state known as denaturation. by application of some external stress or compound such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic sol.
Question 22.
(i) Write the name of two monosaccharides le obtained on hydrolysis of lactose sugar.
(ii) Why Vitamin C cannot be stored in our body?
(iii) What is the difference between a nucleoside and nucleotide?
Answer:
(i) On hydrolysis, lactose gives β-D-galactose and β-D-glucose.
(ii) Vitamin C is mainly ascorbic acid which is water soluble and is readily excreted through urine and thus cannot be stored in the body.
(iii) Nucleoside: A nucleoside contains only two basic components of nucleic acids, i.e., a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. It is formed by the attachment of a base to l' position of sugar.
Nucleoside = Sugar + Base
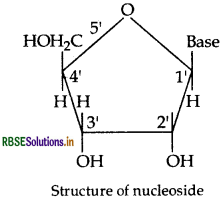
Nucleotides: A nucleotide contains all the three basic components of nucleic acids, i.e., a phosphoric acid group, a pentose sugar and nitrogenous base. These are formed by the esterification of C5-OH of the sugar of the nucleoside with phosphoric acid.
Nucleotide = Sugar + Base + Phosphoric acid
Nucleotide = Sugar + Base + Phosphoric acid
Question 23.
1. Write the structural difference between starch and cellulose.
2. What type of linkage is present in Nucleic acids?
3. Give one example each for fibrous protein and globular protein.
Answer:
- Starch contains the a-D-glucose as its monomer units while cellulose contains β-D glucose as its monomer units. Acids
- Phosphodiester linkages are present in Nucleic
- Globular protein: All enzymes and hormones like insulin. Fibrous protein: Keratin in skin.

Question 24.
Define the following as related to proteins:
1. Peptide linkage
2. Primary structure
3. Denaturation
Answer:
- Peptide linkage: Two amino acids of same type or different types combine together by. the elimination of H2O molecule to form -CO-NH-linkage.
- Primary structure: It refers to the sequence in which amino acids are joined.
- Denaturation: When a native protein is subjected to change in temperature or pH, hydrogen bonds get disturbed and globules get uncoiled and proteins lose their biological activity.
Question 25.
What are enzymes? Describe their functions. Name two diseases which are caused due to deficiency of enzymes.
Answer:
- Enzymes are protein molecules which acts catalyst in Biochemical Reactions (biocatalyst). They increase the rate of biochemical reactions,
- For exampie: Zymase, Invertase etc.
- Two diseases due to deficiency of enzymes are: Anemia, Gauchea's disease.
Question 26
(a) What type of linkage is present in disaccha- ides?
(b) Write one source and deficiency disease of iiamin B12.
(c) Write the difference between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
(a) Glycosidic linkage is present in disaccharides.
(b) Eggs are the source of Vitamin B12 and its deficiency auses pernicious anaemia.
(c) DNA is a double strand while RNA is a single trand molecule.
Question 27.
(a) What type of linkage is present in proteins?
(b) Give one example each of water soluble and fat oluble vitamins.
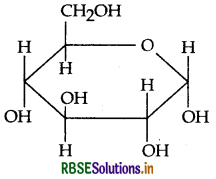
(c) Draw pyranose structure of glucose.
Answer:
(a) Peptide linkage is present in proteins.
(b) Vitamin C is water soluble and Vitamin D is fat oluble vitamin.
(c) Pyranose structure of glucose
COMPETITION CORNER:
Question 1.
Which set of terms correctly identifies the carbohydrates shown?
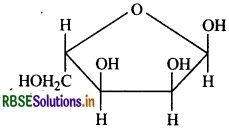
1. Pentose
2. Hexose
3. Aldose
4. Ketose
5. Pyranose
6. Furanose
(a) 1,2 and 6
(b) 1,3 and 5
(c) 2,3 and 5
(d) 2,3 and 6
(e) 1,4 and 6
Answer:
(a) 1,2 and 6

Question 2.
The a-and B-glucose have different specific rotation. When either is dissolved in water, their rotation changes until the same fixed value results. This called:
(a) epimerization
(b) racemisation
(c) anomerisation
(d) mutarotation
Answer:
(d) mutarotation
Question 3.
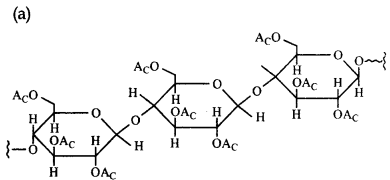
Cellulose upon acetylation with excess acetic anhydride/H2SO4 (catalytic) gives cellulose triacetate whose structure is:
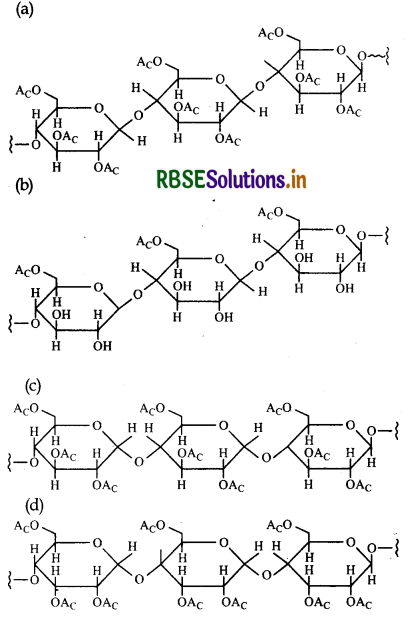
Answer:
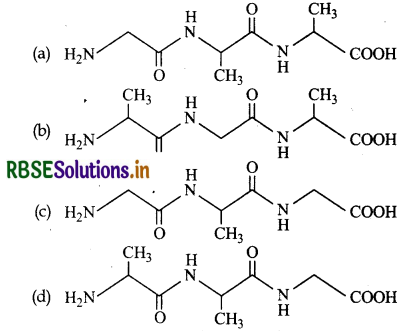
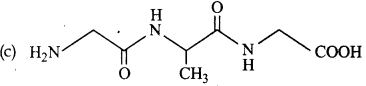
Question 4.
The tripeptide is written as Glycine-Alanine-cine. The correct structure of tripeptide is
Answer:
Question 5.
In DNA, the complimentary bases are:
(a) Adenine and guanine; thymine and cytosine
(b) Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
(c) Adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
(d) Adenine and thymine; guanine and uracil
Answer:
(c) Adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
Question 6.
Glucose does not react with:
(a) NH2OH
(b) NaHSO4
(c) C6H5NHNH2
(d) HCN
Answer:
(b) NaHSO4
Question 7.
In the following structure:
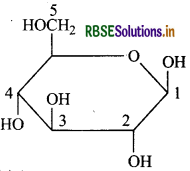
anomeric carbon is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(a) 1

Question 8.
Which of the following has maximum laevorotat
(a) D-Glucose
(b) D-Fructose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Invert sugar
Answer:
(b) D-Fructose
Question 9.
Select the incorrect statement, among the follow
(a) Haemoglobin is soluble in water
(b) a-keratin is soluble in water
(c) Cellulose is a polymer of glucose
(d) Chlorophyll is responsible for the synthesis of carbohydrates in plants.
Answer:
(b) a-keratin is soluble in water
Question 10.
The hormone which controls the processes of buring of fats, proteins and carbohydrates and liberates energy in the body is:
(a) Thyroxine
(b) Adrenaline
(c) Insulin
(d) Cortisone
Answer:
(c) Insulin
Question 11.
Which of the following contain cobalt?
(a) Haemoglobin
(b) Chlorophyll
(c) Vitamin-B12
(d) Vitamin C
Answer:
(c) Vitamin-B12
Question 12.
Fructose reduces Tollen's reagent due to:
(a) Asymmetric carbons
(b) Primary alcoholic group
(c) Seconadry alcoholic group
(d) Enolisation of fructose following by conversion to aldehyde by base.
Answer:
(d) Enolisation of fructose following by conversion to aldehyde by base.
Question 13.
Which one of the following does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation?
(a) (-) Fructose
(b) (+) Sucrose
(c) (+) Lactose
(d) (+) Maltose
Answer:
(b) (+) Sucrose
Question 14.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:
(a) inversion
(b) esterfication
(c) hydration
(d) saponification
Answer:
(a) inversion
Question 15.
The correct statement about the following disaccharide is:
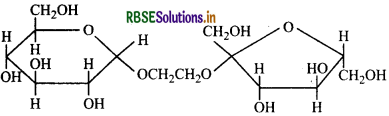
(a) Ring (A) is pyranose with a-glycosidic link.
(b) Ring (A) is furanose with a-glycosidic link.
(c) Ring (B) is furanose with a-glycosidic link.
(d) Ring (B) is pyranose with a-glycosidic link.
Answer:
(a) Ring (A) is pyranose with a-glycosidic link.
Question 16.
Cellulose is not digestible by human being due to the absence of cellulose hydrolysing enzyme called:
(a) Cellulose
(b) Zymase
(c) Invertase
(d) Urease
Answer:
(a) Cellulose
Question 17.
Secondary structure of proteins refers to:
(a) mainly denatured proteins and the structure of the prosthetic group.
(b) three dimensional structure, especially between amino acid residue that are distant from each other in the polypeptide chain.
(c) Linear structure of amino acid residues in the polypeptide chain.
(d) regular folding patterns of continuous portion of the polypeptide chain.
Answer:
(d) regular folding patterns of continuous portion of the polypeptide chain.

Question 18.
Biuret test is not given by:
(a) Urea
(b) Proteins
(c) Carbohydrates
(d) Polypeptides
Answer:
(c) Carbohydrates
