RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Important Questions Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Objective Type Questions:
Question 1.
Chloroethane (C2H5Cl) reacts with A to form diethylether. The compound A may be:
(a) NaOH
(b) H2SO4
(c) C2H5ONa
(d) Na2S2O3
Answer:
(c) C2H5ONa
Question 2.
Primary alcohol on catalytic hydrogenation gives a/an:
(a) aldehyde
(b) Ketone
(c) alkane
(d) ester
Answer:
(a) aldehyde

Question 3.
An organic compound X having C, H and O possesses a pleasant odour with boiling point of 78°C.
(a) C2H5C
(b) C2H5OH
(c) CH3COOC2H5
(d) C2H6
Answer:
(b) C2H5OH
Question 4.
An organic compound having molecular formula C4H9Cl on reaction with Na in the presence of di-ethyl ether gives a hydrocabon which on monochlorination gives only one chloroderivative, the organic compound is:
(a) n-butyl chloride
(b) iso-butylchloride
(c) tert-butyl chloride
(d) sec. butylchloride
Answer:
(c) tert-butyl chloride
Question 5.
An oxygen containing organic compound forms a carboxylic acid as the main product upon oxidation with its molecular mass higher by 14 units. The organic compound is:
(a) an aldephyde
(b) a ketone
(c) a primary alcohol
(d) a secondary alcohol
Answer:
(c) a primary alcohol
Question 6.
An alcohol is less volatile than ether having same molecular formula. It is due to:
(a) inter-molecular H-bonding in alcohol
(b) inter-molecular H-bonding in ethers
(c) dipolar nature of ethers
(d) resonance in alcohol
Answer:
(a) inter-molecular H-bonding in alcohol
Question 7.
Which one of the following in least acidic?
(a) Phenol
(b) p-nitrophenol
(c) p-chlorophenol
(d) o-cresol
Answer:
(d) o-cresol
Question 8.
Which of the following alkenes produces tertbutyl alcohol on acid hyration?
(a) CH3-CH=CH2
(b) CH3-CH-CH-CH3
(c) CH3-CH2-CH=CH2
(d) (CH3)2C=CH2
Answer:
(d) (CH3)2C=CH2
Question 9.
Acid catalysed hydration of alkenes except ether leads to the formation of:
(a) Primary alcohol
(b) Secondary or tertiary alcohol
(c) Mixture of secondary and tertiary alcohol
(d) Mixture of primary and secondary alcohol
Answer:
(b) Secondary or tertiary alcohol

Question 10.
Which of the following cannot be formed as a prod- uct in the reaction given below under any condition?
(a) C2H4
(b) C2H5HSO4
(c) C2H5OC2H5
(d) C2H2
Answer:
(d) C2H2
Question 11.
Denatured alcohol is:
(a) Ethanol + Methanol
(b) Rectified spirit
(c) Ethanol
(d) Rectified spirit + methanol + naphtha
Answer:
(d) Rectified spirit + methanol + naphtha
Question 12.
Which of the following reactions converts ethylchloride in to diethyl ether?
(a) Wurtz reactions
(b) Williamson's synthesis
(c) Grignard reagent
(d) Perkin's reaction
Answer:
(b) Williamson's synthesis
Question 13.
............reaction forms diethyl ether from ethanol.
(a) Hydrogenation
(b) Dehydration
(c) Dehydrogenation
(d) Heterolytic fission
Answer:
(b) Dehydration
Question 14.
Which of the following alcohols would react fastest with Lucas reagent?
(a) 2-Butanol
(b) 1-Butanol
(c) 2-Methyl propanol
(d) 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
Answer:
(d) 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
Question 15.
Which factor is more effective in the preparation of alkene from alcohol by using Al2O3?
(a) Temperature
(b) Concentration
(c) Surface area of Al2O3
(d) Porosity of Al2O3
Answer:
(a) Temperature
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
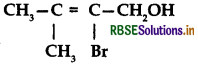
Answer:
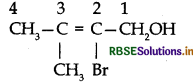
IUPAC name: 2-bromo-3-methyl-but-2-en-1-ol
Question 2.
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:

Answer:
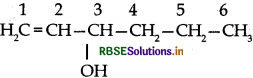
IUPAC Name: Hex-1-en-3-ol or 3-Hexenol

Question 3.
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 1-phenylpropan-2-ol.
Answer:
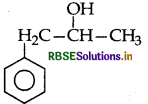
Question 4.
How would you convert ethanol to ethene ?
Answer:
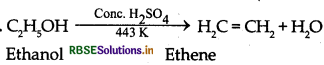
Question 5.
Draw the structure of 2,6-Dimethylphenol.
Answer:
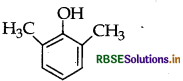
Question 6.
Draw the structural formula of 2-methylpropan- 2-ol molecule.
Answer:
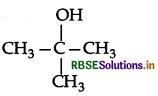
Question 7.
Draw the structure of hex-1-en-3-ol compound.
Answer:
CH2 = CH - CH(OH) - CH2 -CH2 - CH3
Question 8.
Ortho nitrophenol has lower boiling point than p-nitrophenol. Why?
Answer:
Ortho-nitrophenol has lower boiling point due to formation of intramolecular H-bonding whereas p- nitrophenol forms intermolecular H-bonding.
Question 9.
Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol. Why?
Answer:
NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group while methoxy group is electron donating in nature. The release of H+ is easier from o-nitrophenol while it is difficult from o-methoxyphenol.
Question 10.
The C-O bond is much shorter in phenol than in ethanol. Give reason.
Answer:
Carbon of C-Obond of phenol is sp2 hybridised, So it acquires a partial double bond character but in ethanol, it is sp3 hybridised and a single bond. Double bond is shorter than a single bond.

Question 11.
Write the IUPAC name of the following:
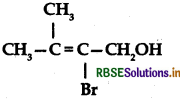
Answer:
IUPAC name: 2-Bromo-3-methyl but-2-en-1-ol.
Question 12.
Of the two hydroxy organic compounds ROH and R'OH the first one is basic and other is acidic in behavior. How is R different from R'?
Answer:
When R = alkyl ROH behaves as a Bronsted base and when R'-aryl, ROH behaves as a Bronsted acid.
Question 13.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between 2- Pentanol and 3-Pentanol.
Answer:
2-pentanol gives lodoform test with yellow ppt of lodo form while 3-pentanol does not give this test.
Question 14.
Write the chemical reaction to explain Kolbe's reaction.
Answer:
The Kolbe reaction can be classified as a carboxylation chemical reaction. The reaction occurs when sodium phenoxide is allowed to absorb carbon dioxide and the resulting product is heated at a temperature of a 125-degree celsius and a pressure of over a hundred atmospheres. An unstable intermediate is now formed.
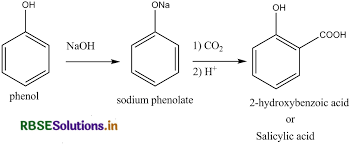
Question 15.
How would you obtain ethane-1,2-diol from Ethanol ?
Answer:
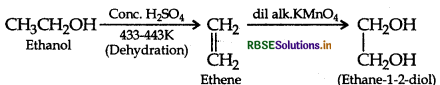
Question 16.
How would you obtain acetophenone from phenol?
Answer:
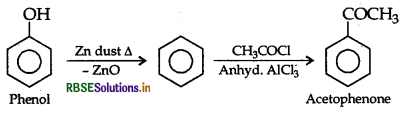
Question 17.
How would you obtain phenol from benzene?
Answer:
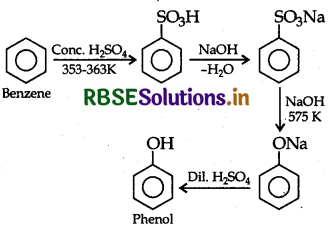
Question 18.
Write IUPAC name of the following:
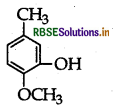
Answer:
IUPAC name: 2-Methoxy-5-methyl phenol
Question 19.
Which of the following isomers is more volatile: o-nitrophenol or p-nitrophenol?
Answer:
o-nitrophenol is more volatile than p-nitrophenol due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding.

Question 20.
Name the alcohol that is used to make the following ester:
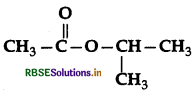
Answer:
Alcohol used: Propan-2-ol
Question 21.
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.
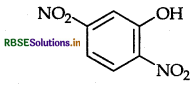
Answer:
2,5-dinitrophenol.
Question 22.
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound:

Answer:
IUPAC name: 1-Ethoxy-2-methylpropane
Question 23.
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound:
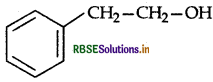
Answer:
2-Phenylethanol.
Question 24.
Write equation of the nitration of anisole.
Answer:
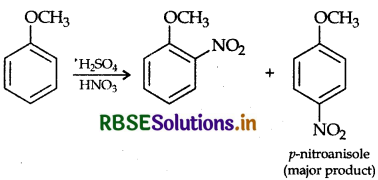
Question 25.
Out of CH3OH and 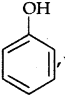 which one is more acidic?
which one is more acidic?
Answer:
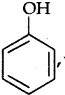 is more acidic, as Phenoxide formed is more stabilized by Resonance.
is more acidic, as Phenoxide formed is more stabilized by Resonance.
Question 26.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
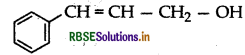
Answer:
3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ol
Question 27.
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
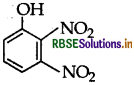
Answer:
2,3-Dinitrophenol.

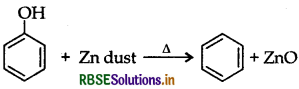
Question 28.
What happens when phenol is heated with zinc dust?
Answer:
Benzene is formed when phenol is heated with zinc dust.
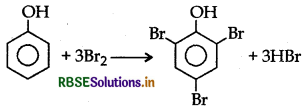
Question 29.
What happens when phenol is treated with bromine water?
Answer:
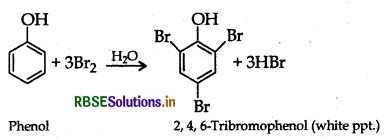
2, 4, 6-tribromophenol is formed when phenol is treated with bromine water.
Question 30.
Give simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Benzoic acid and Phenol
Answer:
Ferric chloride test: Add neutral FeCl3 in both the solutions, phenol reacts with neutral FeCl3 to form an iron-phenol complex giving violet colour but benzoic acid does not.
Short Answer type Questions:
Question 1.
Complete the following reaction equations:
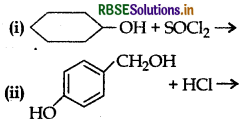
Answer:
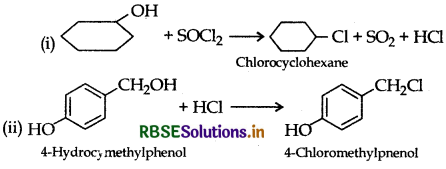
Question 2.
Illustrate the following reactions giving a chemical equation for each:
(i) Kolbe's reaction
(ii) Williamson synthesis of an ether.
Answer:
(i) Kolbe's reaction: Phenol reacts with CO2 in presence of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at 4-7 atm and 390 - 410 K giving salicylic acid.
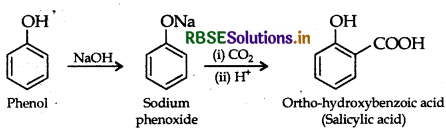
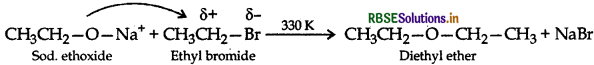
(ii) Williamson synthesis of an ether: The reaction involves the nucleophilic substitution of the halide ion from the alkyl halide by the alkoxide ion by S2 mechanism.
Example:
Question 3.
Explain the following reactions with an example for each:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(ii) Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Answer:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction: Treatment of phenol with CHCl3, in presence of aqueous NaOH at 340K followed by hydrolysis gives salicylaldehyde.
Example:
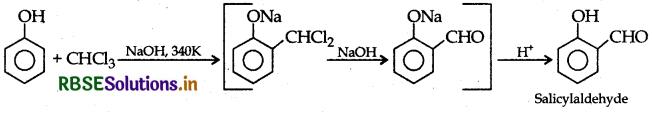
(ii) Friedel-Crafts reaction: This reaction is used for introducing an alkyl or an acyl group into an aromatic compond in presence of Lewis acid catalyst (AICl3)
Example:
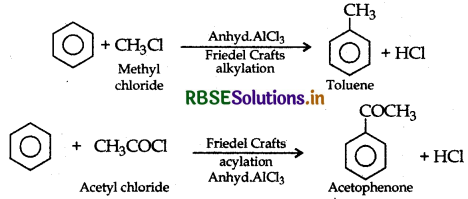
Question 4.
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-2-ol
(ii) Ethylmagnesium chloride to propan-1-ol.
Answer:
(i) Propene to propan-2-ol
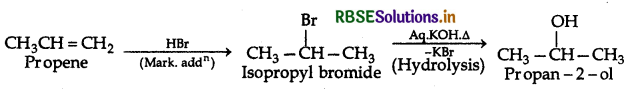
(ii) Ethylmagnesium chloride to propan-1-ol
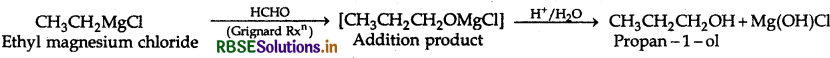
Question 5.
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol,
(ii) Methyl magnesium bromide to 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
Answer:
(i) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol

(ii) Methyl magnesium bromide to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
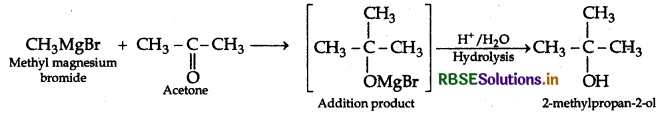

Question 6.
Explain the following giving one example for each:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(ii) Friedel-Craft's acetylation of anisole.
Answer:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction: Treatment of phenol with CHCl3, in presence of aqueous NaOH at 340K followed by hydrolysis gives salicylaldehyde.
Example:

(ii) Friedel-Craft's acetylation of anisole:
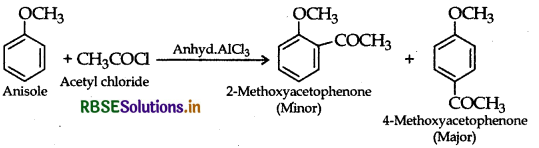
Question 7.
How would you obtain?
(i) Picric acid (2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol) from phenol,
(ii) 2-Methylpropene from 2-methylpropanol?
Answer:
(i) Picric acid from phenol:
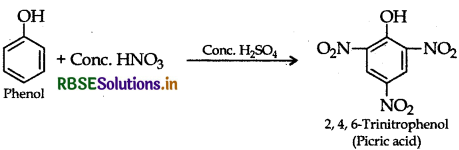
(ii) 2-Methylpropene from 2-methylpropanol:

Question 8.
Explain the mechanism of acid catalysed hydration of an alkene to form corresponding alcohol.
Answer:
Acid catalyed hydration : Alkenes react with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form alcohols.
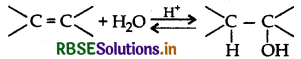
Mechanism: It involves three steps:
(i) Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by electrophilic attack of H3O+
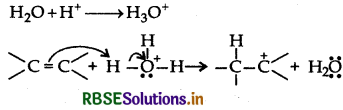
(ii) Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation

(iii) Deprotonation to form an alcohol
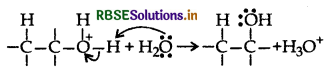
Question 9.
Explain the following behaviours:
(i) Alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
(ii) Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol.
Answer:
(i) Alcohols can form H-bonds with water and break the H-bonds already existing between water molecules. So they are soluble in water.
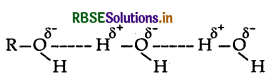
On the other hand, hydrocarbons cannot form H-bonds with water and hence they are insoluble in water.
(ii) Due to strong -R and -I effect of the - NO, electron density in the -OH bond decreases and hence the loss of a proton becomes easier. Moreover o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilized by resonance, there by making o-nitrophenol a stronger acid. In o-methoxyphenol, due to + Reffect of the - OCH, group the electron density in the O-H bond increases thereby making the loss of proton difficult. Further more, the o-methoxy phenoxide ion left after the loss of a proton is destabilized by resonance because the two negative charges repel each other. So o-methoxyphenol is a weaker acid.

Question 10.
Explain the mechanism of the following reaction:
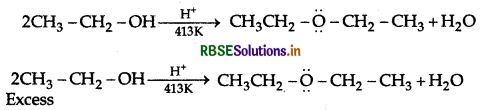
Answer:
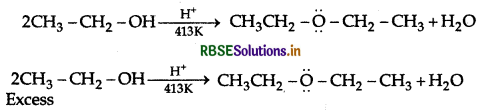
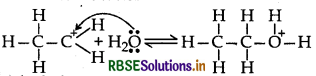
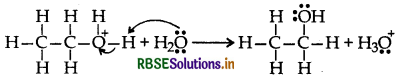
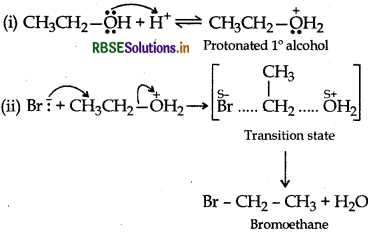
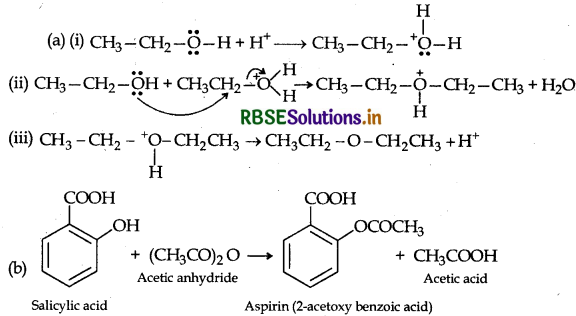
Mechanism: Step 1: Protonation of alcohol
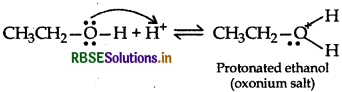
Step 2: Nucleophillic attack by unprotonated alcohol molecule an protonated alcohol molecule
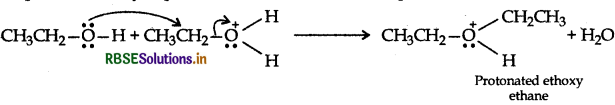
Step 3: Loss of a porton to form ethoxy ethane
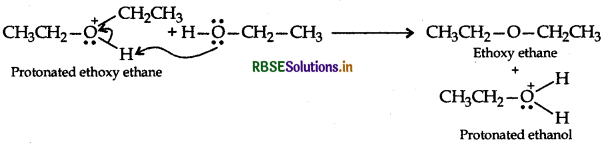
Question 11.
How will you convert?
(i) Propene to propan-2-ol?
(ii) Phenol to 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol
Answer:
(i) Propene to propan-2-ol
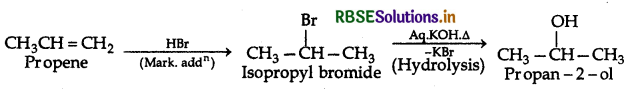
(ii) Phenol to 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol
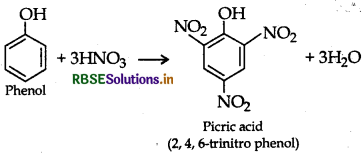
Question 12.
How will you convert the following?
(i) Propan 2-ol to propanone
(ii) Phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
Answer:
(i) Propan-2-ol to propanone
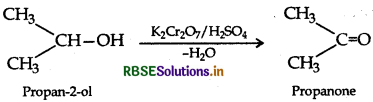
(ii) Phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol : Phenol reacts with bromine in presence of polar solvent H2O to form 2, 4, 6- tribromophenol (white ppt.)
Question 13.
How will you convert?
(i) Propene to Propan-1-ol
(ii) Ethanal to Propan-2-ol?
Answer:
(i) Propene to Propan-1-ol
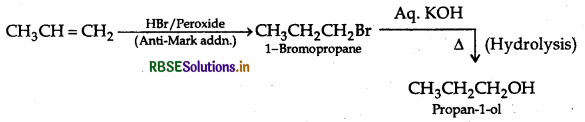
(ii) Ethanal to Propan-2-ol
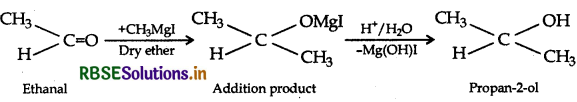
Question 14.
How are the following conversion carried out?
(i) Propene to Propan-2-ol
(ii) Ethyl chloride to Ethanal
Answer:
(i)Propene to Propan-2-ol
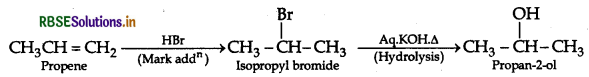
(ii) Ethyl chloride to Ethanal
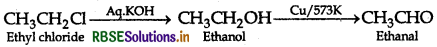
Question 15.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Answer:
The mechianism of dehydration of ethanol involves the following steps:
Step 1: Formation of protonated alcohol
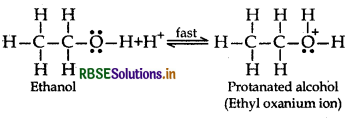
Step 2: Formation of Carbocation: It is the slowest and rate determining step.

Step 3: Formation of ethene by elimination of a proton
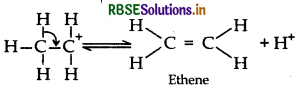
Question 16.
Write the mechanism of the following reaction.
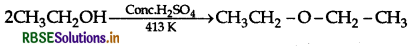
Answer:
Mechanism:
Step 1:
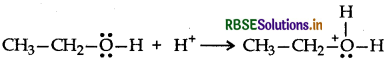
Step 2:
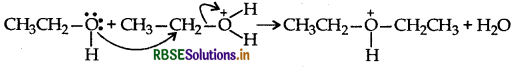
Step 3:

Question 17.
(a) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their acid strength :
p-cresol, p-nitrophenol, phenol
(b) Write the mechanism (using curved arrow notation) of the following reaction:
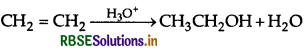
Answer:
(i) Order of acidic strength:
p-cresol <phenol <p-nitrophenol
(b) Mechanism of acid catalysed hydration of alkene:
Step 1: Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by electrophilic attack of H2O+.
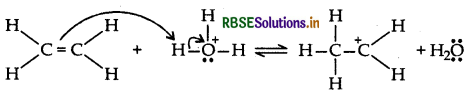
Step 2: Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation
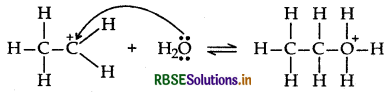
Step 3: Deprotonation to form an alcohol
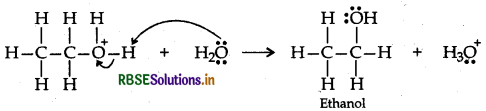
Question 18.
Write the structures of the product when Butan 2-ol reacts with the following:
(a) CrO3
(b) SOCl2
Answer:
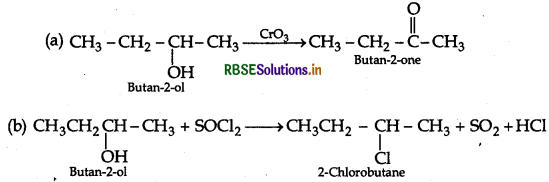
Question 19.
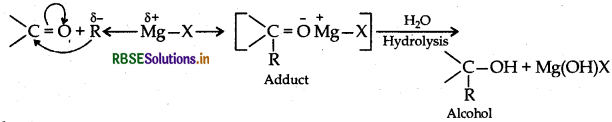
Explain the mechanism of the following reactions :
(i) Addition of Grignard's reagent to the carbonyl group of a compound forming an adduct followed by hydrolysis.
(ii) Acid catalysed dehydration of an alcohol forming an alkene.
(iii) Acid catalysed hydration of an alkene forming an alcohol.
Answer:
(i) Carbonyl group undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction with Grignard reagent to form an adduct which undergoes hydrolysis to give alcohol in the following manner:
(ii) The mechanism of dehydration of ethanol involves the following steps:
Mechanism: It involves the following three step:
Step 1: Formation of protonated alcohol
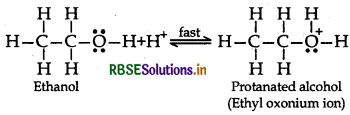
Step 2: Formation of Carbocation: It is the slowest and rate determining step.
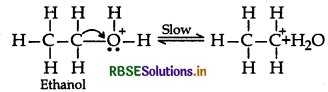
Step 3: Formation of ethene by elimination of a proton
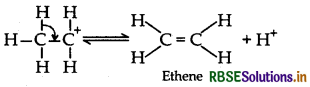
(iii) Acid catalysed hydration : Alkenes react with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form alcohols. Mechanism: It involves the following three steps:
Step 1: Protonation of alkene to from carbocation by electrophilic attack of H3O+
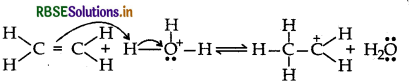
Step 2: Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation
Step 3: Deprotonation to from an alcohol
Question 20.
Explain the following observations:
(i) The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methoxymethane.
(ii) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
(iii) o- and p-nitrophenol are more acidic than phenol.
Answer:
(i) Due to presence of intermolecular H-bonding, associated molecules are formed, hence ethanol has high boiling point while methoxymethane does not have intermolecular H-bonding.
(ii) Phenol on losing H+ ion forms phenoxide ion, and ethanol on losing H+ ion forms ethoxide ion. Phenoxide ion is more stable than ethoxide ion as phenoxide ion exists in resonance structure. Due to this, phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
(iii) Both o- and p-nitrophenol contain the NO2 group which is an electron withdrawing group. Due to -R and -I effect of the -NO2 group, electron density in the OH bond of substituted phenol decreases and hence the loss of proton becomes any and therefore more acidic.

Question 21.
How would you convert the following?
(i) Phenol to benzoquinone
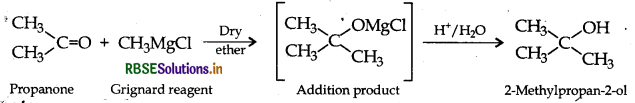
(ii) Propanone to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Propene to propan-2-ol
Answer:
(i) Phenol to benzoquinone
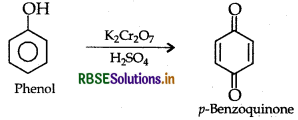
(ii) Propanone to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Propene to propan-2-ol
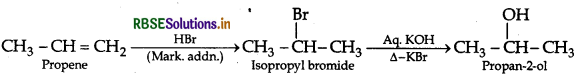
Question 22.
How would you obtain the following
(i) Benzoquinone from phenol
(ii) 2-Methylpropan-2-ol from ethylmagnesium chloride
(iii) Propan-2-ol from propene
Answer:
(i) Benzoquinone form phenol
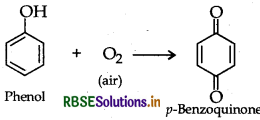
(ii) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol

(iii) Propene to propan-2-ol
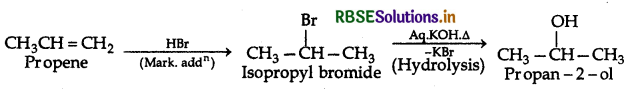
Question 23.
Draw the structure and name the product formed if the following alcohols are oxidized. Assume that an excess of the oxidizing agent is used:
(i) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
(iii) 2-methyl-1-propanol
Answer:
|
Structure of Product |
Name of Product |
|
(i) CH3CH2CH2COOH |
Butanoic acid |
|
(ii) CH3-CH=CH-COOH |
But-2-en-1-oic acid or 2-butenoic acid |
|
(iii) CH3-CH(CH3)-COOH |
2-methylpropanoic acid |
Question 24.
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
(ii) Williamson Synthenis.
(b) Give a chemical test to distinguish between 2-propanol and 2-methy1-2-propanol.
Answer:
(a) (i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction: Treatment of phenol with CHCl3, in presence of aqueous NaOH at 340K followed by hydrolysis gives salicylaldehyde.
Example:

(ii) Williamson synthesis of an ether: The reaction involves the nucleophilic substitution of the halide ion from the alkyl halide by the alkoxide ion by S2 mechanism.
Example:

(b) 2-Propanol is a secondary alcohol. When it reacts with I, in NaOH, it forms a yellow ppt of iodoform but 2 methyl- 2 propanol does not respond to this test.
Question 25.
(a) Give a separate chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Ethanol and Phenol
(ii) 2-Pentanol and 3-Pentanol
(b) Explain Kolbe's reaction with the help of suitable example.
Answer:
(a) (i) Ethanol on reacting with I2 in NaOH gives yellow ppt of iodoform whereas phenol does not respond to this test.
(ii) 2-Pentanol on reacting with I2 in NaOH gives yellow ppt of iodoform whereas 3-pentanol does not respond to this test.
(b) Kolbe's reaction: Phenol reacts with NaOH to give sodium phenoxide which on reaction with CO2 in acid gives salicylic acid.
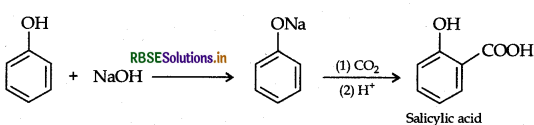
Question 26.
(a) How would you obtain the following
(i) 2-methylpentan-2-ol from 2-methyl-1-pentene
(ii) Acetophenone from phenol
(b) Write IUPAC name of the following:
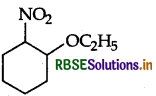
Answer:
(a) (i) 2-Methylpentan-2-ol from 2-methyl-1-pentene
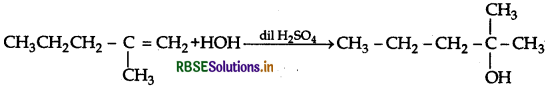
(ii) Acetophenone from phenol

(b) IUPAC name: 1-ethoxy-2-nitrocyclohexane.
Question 27.
(a) Give mechanism of preparation of ethoxy ethane from ethanol.
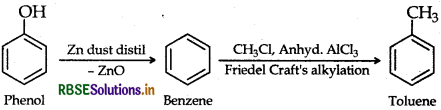
(b) How is toluene obtained from phenol?
Answer:
(a) Mechanism of formation of ethoxy ethane
Step 1: Protonation of ethanol
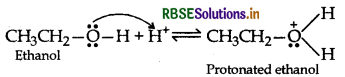
Step 2: Nucleophillic attack by unprotonated alcohol molecule on protonated alcohol molecule
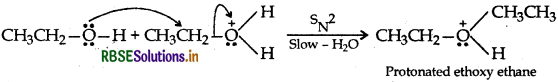
Step 3: Loss of proton to form ethoxy ethane
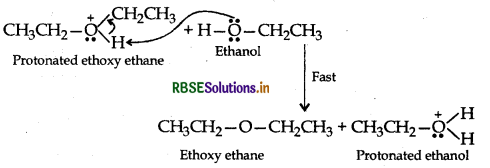
(b) Toluene from Phenol
Question 28.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Pentan-2-ol and Pentan-3-ol
(ii) Methanol and Phenol
(b) o-nitro phenol is more acidic than o-methoxy phenol. Explain why.
Answer:
(a) (i) 2-pentanol gives iodoform test with yellow ppt of iodoform while 3-pentanol does not give this test.
(ii) Distinction between Methanol and Phenol:
By FeCl3 test: Phenol gives violet coloured solution with FeCl3 while methanol dose not.
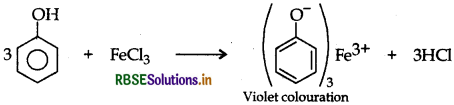
(b) o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxy phenol due to presence of NO2 group which has-I effect. It weakens the O-H bond of phenol by withdrawing their electrons and thus releases H+ ion easily while due to +I, + R effect of OCH3, o-methoxy phenol is less acidic.
Question 29.
(a) Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
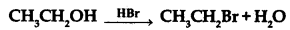
(b) Write the equation involved in Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Answer:
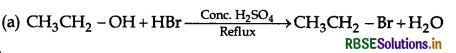
Mechanism: SN2 mechanism
(b) (i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction: Treatment of phenol with CHCl3, in presence of aqueous NaOH at 340K followed by hydrolysis gives salicylaldehyde.
Example:

Question 30.
How do you convert the following:
(i) Phenol to anisole
(ii) Propan-2-ol to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(iii) Aniline to phenol.
Answer:
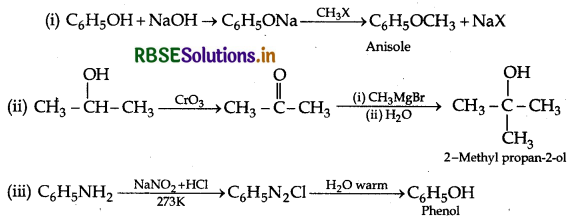

Question 31.
(a) Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
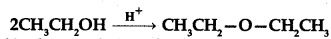
(b) Write the equation involved in the acetylation of Salicylic acid.
Answer:
Question 32.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Phenol is more acidic than methanol.
(ii) The C-Q-H bond angle in alcoholsin slightly less than the tetrahedral angle (190°28′).
(iii) (CH3)3C-O-CH3 on reaction with HI gives (CH3)3CI and CH3 - OH as the main products and not (CH3)3C - OH and CH3 - I.
Answer:
(i) Phenol is more acidic than methanol because in phenol, phenoxide ion formed is more stabilized by resonance than phenol. There is no resonance in methanol.
(ii) The C-O-H bond angle in alcohol is slightly less than tetrahedral angle due to repulsion between the ion pairs of electrons of oxygen.
(iii) (CH3)3C* is 3° carbocation which is more stable than CH3+ for SN1 reaction.
Question 33.
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-2-ol
(ii) Benzly chloride to Benzyl alcohol
(iii) Anisole to p-Bromoanisole.
Answer:
(i) Propene to propan-2-ol
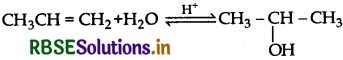
(ii) Benzyl chloride to Benzyl alcohol
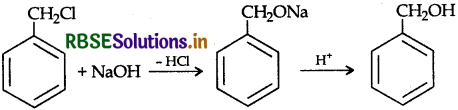
(iii) Anisole to p-Bromoanisole.
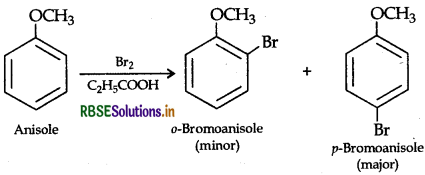
Question 34.
Write the major product in the following equations:
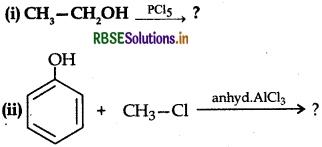
(iii) CH3 - Cl + CH3CH2 -ONa → ?
Answer:
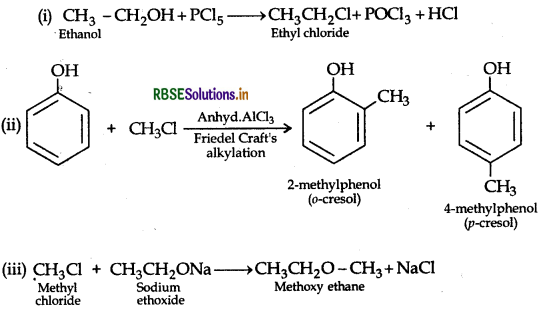
Question 35.
Write the main product(s) in each of the following reaction.
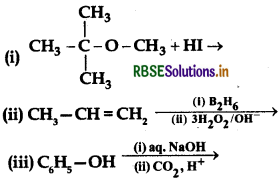
Answer:
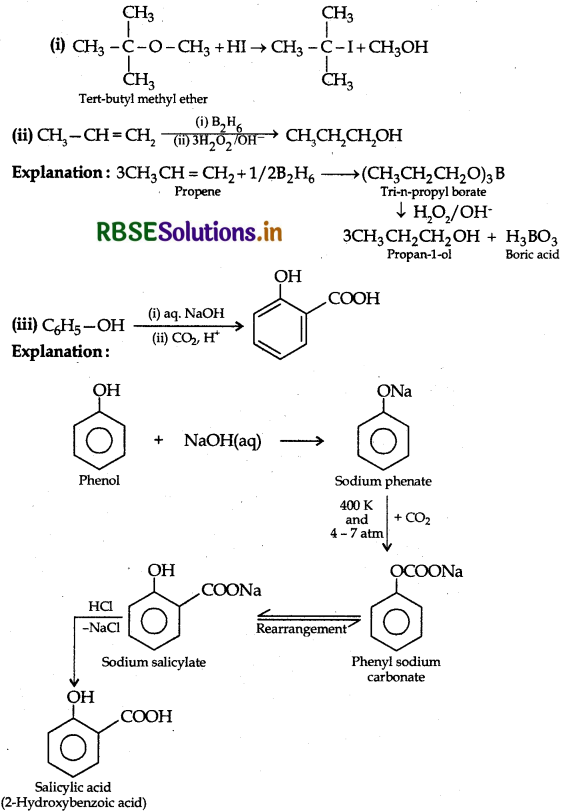
Question 36.
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reaction:
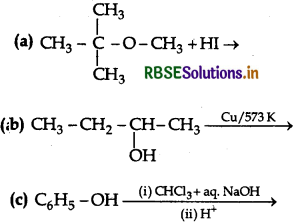
Answer:
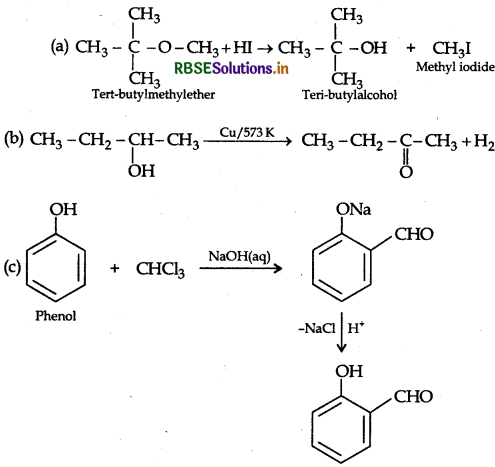
Question 37.
(a) What happens when CH3-O-CH3 is heated with HI?
(b) Explain mechanism for hydration of acid catalyzed ethane:
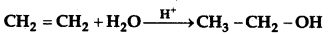
Answer:
(a) Methly iodide (CH3I) and Methonal (CH3OH) are formed when CH3-O-CH3 is heated with HI.

(b) Acid catalyzed hydration: Alkenes react with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form alcohols. Mechanism: It involves the following three steps:
Step 1: Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by electrophilic attack of H3O+.
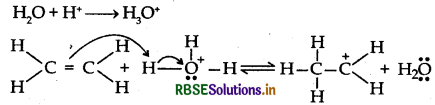
Step 2: Nucleophilic attack of water on carbonation
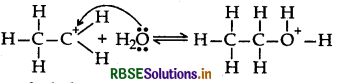
Step 3: Deprotonation to form an alcohol
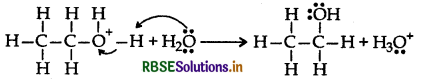
Question 38.
(a) Why phenol is more acidic than ethanol?
(b) Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ether:
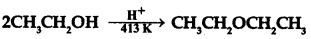
Answer:
(a) Phenol on losing H+ ion forms phenoxide ion, and ethanol on losing H+ ion forms ethoxide ion. Phenoxide ion is more stable than ethoxide ion as phenoxide ion exists in resonance structure. Due to this phenol is more acidic than ethanol.
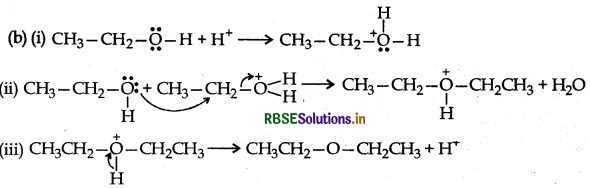
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
(a) Write the product(s) in the following reactions :
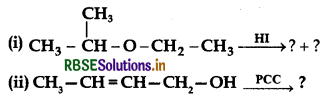
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Ethanol and Phenol
(ii) Propanol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
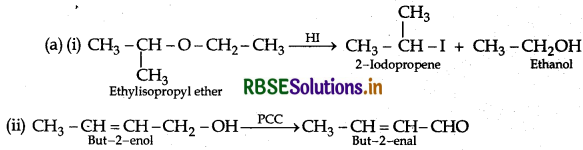
Answer:
(b) (i) Ethanol gives a positive lodoform test.
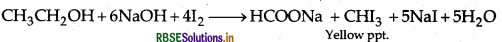
Phenol gives a negative lodoform test.
(ii) Distinction between propanol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol:

Question 2.
(a) Write the formula of reagents used in the following reactions:
(i) Bromination of phenol to 2,4,6-tribromophenol
(ii) Hydroboration of propene and then oxidation to propanol.
(b) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their property indicated
(i) p-nitrophenol, ethanol, phenol (acidic character)
(ii) Propanol, Propane, Propanal (boiling point)
(c) Write the mechanism (using curved arrow notation) of the following reaction:
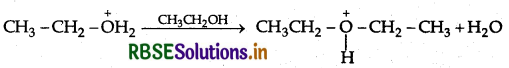
Answer:
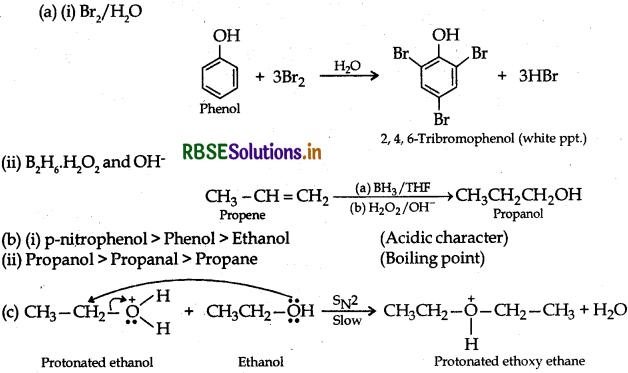
Competition Corner:
Question 1.
The major organic product in the reaction. imm product is:
(a) ICH2OCH(CH3)2
(b) CH3OC(CH3)2
(c) CH3I + (CH3)2 CHOH
(d) CH3OH + (CH3)2 CHI
Answer:
(c) CH3I + (CH3)2 CHOH
Question 2.
In the reaction:

product is:
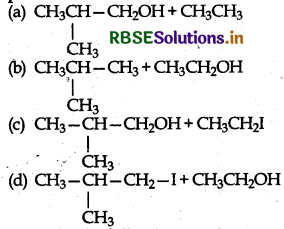
Answer:
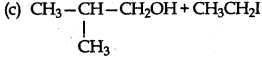
Question 3.
Consider the following reaction:

The product Z is:
(a) CH3CH2OCH2CH3
(b) CH3CH2O-SO3H
(c) CH3CH2OH
(d) CH2 = CH2
Answer:
(c) CH3CH2OH

Question 4.
Consider the following reaction:

The product Z is:
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) Benzene
(d) Toluene
Answer:
(b) Benzoic acid
Question 5.
Which one of the following compounds has the most acidic nature?
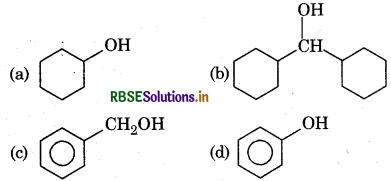
Answer:
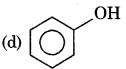
Question 6.
Given are cyclohexanol (I), acetic acid (II), 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol (III) and phenol (IV). In these compounds, the decreasing acidic character will be:
(a) II > III > IV > I
(b) III > IV > II > I
(c) III > II > IV > I
(d) III > II > I > IV
Answer:
(d) III > II > I > IV
Question 7.
In the following reactions:
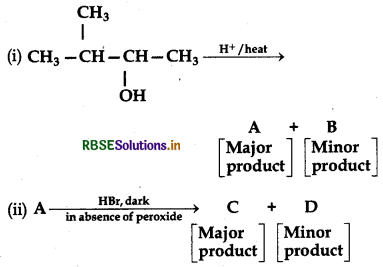
The major product (A) and (C) are respectively:
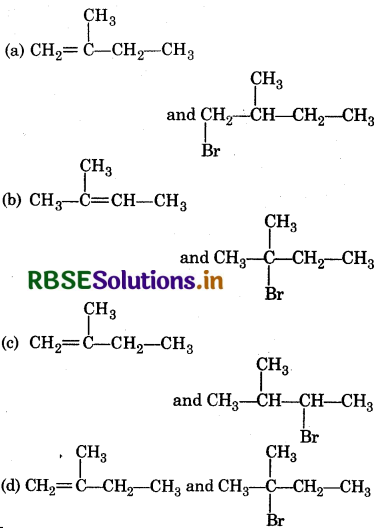
Answer:
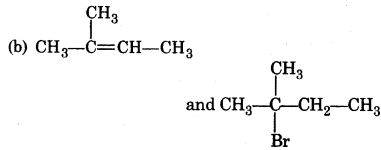
Question 8.
Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic reagent?
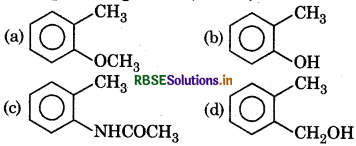
Answer:
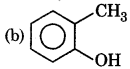
Question 9.
Among the following ethers, which one will produce methyl alcohol on treatment with hot concentrated HI?
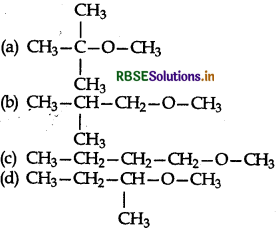
Answer:
Question 10.
Among the following sets of reactants which one produces anisole?
(a) CH3CHO; RMgX
(b) C6H5OH; NaOH; CH2I
(c) C6H5OH; neutral FeCl3
(d) C6H5CH3; CH3COCI; AlCl3
Answer:
(b) C6H5OH; NaOH; CH2I

Question 11.
Identify Z in the sequence of reactions

(a) CH3-(CH2)3-O-CH2CH3
(b) (CH3)2CH-O-CH2CH3
(c) CH3(CH2)4-O-CH3
(d) CH3CH2-CH(CH3)-O-CH2CH3
Answer:
(a) CH3-(CH2)3-O-CH2CH3
Question 12.
The major product formed when 3, 3-dimethyl- butan-2-ol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid is:
(a) 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
(b) 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene
(c) 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene
(d) cis- and trans-isomers of 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene
(e) cis- and trans-isomers of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butene
Answer:
(a) 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
Question 13.
Which among the following compounds will give a secondary alcohol on reacting with Grignard reagent followed by acid hydrolysis?
I. HCHO
III. CH3COCH3
II.CH,CHO
IV. HCOOC2H5
Select the correct answer giving the order given be-low:
(a) II only
(b) III only
(c) I and V
(d) II and III
(e) II and IV
Answer:
(e) II and IV
Question 14.
Which of the following is an appropriate set of reac- tants for preparation of 1-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene?
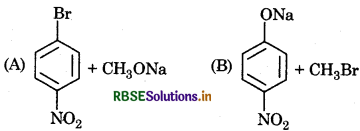
(a) (A)
(b) (B)
(c) Both (A) and (B)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) (B)
Question 15.
Which of the following alcohols gives the best yield of dialkyl ether on being heated with a trace of sulphuric acid?
(a) 2-Pentanol
(b) Cyclopentanol
(c) 2-Methyl-2-butanol
(d) 2-Propanol
(e) 1-Pentanol
Answer:
(e) 1-Pentanol

- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 16 दैनिक जीवन में रसायन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 15 बहुलक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 जैव-अणु
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 ऐमीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12 ऐल्डिहाइड, कीटोन एवं कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 11 ऐल्कोहॉल, फीनॉल एवं ईथर
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 10 हैलोऐल्केन तथा हैलोऐरीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 उपसहसंयोजन यौगिक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 d- एवं f-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 p-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 तत्वों के निष्कर्षण के सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रम