RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 8 Index Numbers
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 8 Index Numbers Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Economics Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 8 Index Numbers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is index number
Answer:
Index number is a statistical tool for measuring change in variable or a group of related variables over two different situations.
Question 2.
State any one feature of index numbers.
Answer:
Index numbers are expressed in terms of percentage.

Question 3.
Define base period.
Answer:
Base period is the period with which the comparison is to be made.
Question 4.
What does an Index number of ISO reflect
Answer:
An index number of 150 the value is one and half times that of the base period.
Question 5.
What does quantity index numbers
Answer:
Quantity index numbers measure the changes in the physical volume of production, construction or employment.
Question 6.
What does a production index indicate?
Answer:
A production index indicates the level of output in the economy.

Question 7.
What is the simple aggregate method?
Answer:
In this method, aggregate of the prices of commodities in the current year are divided by the aggregate of their prices in the base year and multiplied by 100.
Question 8.
Give the formula for calculating index number using average price relatives method.
Answer:
It is calculated by using the formula:
\(P_{01}=\frac{1}{N} \Sigma \frac{P_1}{P_0} \times 100\)
Question 9.
Give one point of difference between Laspeyres and Paasche price index.
Answer:
Laspeyres price index uses base period quantities as base while Paasche price index uses current period quantities as weights.
Question 10.
Why is the base period weight is preferred to the current period weight?
Answer:
The base period weight is preferred to the current period weight because it is inconvenient to calculate weight every year.
Question 11.
Define consumer price index.
Or
What do you mean by cost of living index number’
Answer:
Consumer Price Index (CPI) or cost of living index number measures the average change in prices paid by the specific class of consumers for goods and services consumed by them in the current year in comparison with base year.
Question 12.
Name the methods used for constructing consumer’s price index.
Answer:
The methods used for constructing consumers price index are:
(i) Aggregative expenditure method
(ii) Family budget method

Question 13.
What does wholesale price index indicate
Answer:
Wholesale Price index (WPI) indicates the change in the general price level.
Question 14.
Define index number of industrial production.
Answer:
Index number of Industrial Production (lIP) measures the relative increase or decrease in the level of industrial output in a country in comparison to the level of production in the base year.
Question 15.
State the formula of constructing index number of industrial production.
Answer:
The formula of constructing index number of industrial production is:
\(\| P_{01}=\frac{\sum W\left(\frac{q_i}{q_0} \times 100\right)}{\sum W}\)
Question 16.
Define inflation.
Answer:
Inflation refers to a situation of rise in the general price leave in a country over a fairly long period of time
Question 17.
State the formula to calculate rate of inflation.
Answer:
The formula to calculate rate of inflation is:
Real of Inflation(ROl) \(=\frac{X_t-X_{t-1}}{X_{t-1}} \times 100\)
Question 18.
How is reI wage
Answer:
RaI wage is calculated by dividing the money wage by cost of living index and multiplying the result by 100. That is,
\(\text { Real Wage }=\frac{\text { Money Wage }}{\text { Cost of Living Index }} \times 100\)
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the uses of index number.
Answer:
The important uses of index number are:
(i) Makes Complex Facts Simple: Index numbers enable the measure of the facts whose measure is not possible by any other method. For example, simple measure of trade processes is not possible.
(ii) Studies Changes in General Value: Index number helps measuring the changes in general price level or changes in the purchasing power of money.
(iii) Determines Salary and Dearness Allowance: Consumer price index helps to know about the changes in the expenditure on living standards of different classes of society. This is helpful in determining wages for labourers and dearness allowances for the servants.
(iv) Estimates Change in National Income: A production index indicates the level of output and national income in the economy.

Question 2.
Mention the limitations of index number.
Answer:
The main limitations of index numbers are:
(i) The choice of basket goods may lead to misleading conclusions as they are based on samples.
(ii) The comparisons of changes in variables are not reliable over long periods.
(iii) They are only approximate indications of relative changes.
(iv) There may be errors in the choosing base periods or weights.
(v) They are specialised types of averages and hence, are subject to all the limitations which an average suffers.
Question 3.
What are the steps for the construction of weighted index number?
Answer:
The steps for the construction of weighted index number are:
(i) For each item, find the ratio of current period price to the base period price and multiply it by 100 as \(R=\frac{P_1}{P_0} \times 100 .\)
(ii) Multiply each price ratio with the assigned weight to obtain RW.
(iii) Find the sum, i.e. ∑RW.
(iv) Find the sum of weights, i.e. ∑W.
(v) Find index number using the formula:
\(P_{01}=\frac{\Sigma W R}{\Sigma W}\)
Question 4.
Differentiate between simple index number and weighted index number.
Answer:
In simple index numbers, all the items are given equal importance. The index is calculated only on the basis of the price of each item.
In weighted index number, on the other hand, weights assigned to the various items according to their relative importance.

Question 5.
Describe the methods of constructing simple index number.
Answer:
There are two methods of constructing simple index number:
(i) Simple Aggregative Method: It is the simplest method of constructing index number. In this method, the sum of prices of current year (∑P1) is divided by the sum of base year prices (∑P0) and the result is multiplied by 100.
\(P_{01}=\frac{\sum P_1}{\sum P_0} \times 100\)
(ii) Simple Price Relative Average Method: In this method, the price ratio of various commodities or items is calculated and the average index is calculated by using the following formula:
\(P_{01}=\frac{1}{N} \sum \frac{P_1}{P_0} \times 100\)
Question 6.
What is weighted index? Explain the methods of constructing index number.
Answer:
In weighted index, weights assigned to the various items according to their relative importance. Different methods of calculating a weighted aggregative index use different baskets with respect to time. To important methods of constructing weighted index number are:
(i) Laspeyres Method: In this method, base year quantities are used as weights. The formula used is:
\(P_{01}=\frac{\sum P_1 q_0}{\Sigma P_0 q_0} \times 100\)
(ii) Paasche Method: In this method, current year quantities are used as weights. The formula used is:
\(P_{01}=\frac{\sum P_{q_1}}{\sum P_0 q_1} \times 100\)
Question 7.
Write the steps of construction of CPI
Answer:
The steps of construction of CPI are as below
(i) Class determination - Select the section of people for whom the index is to be constructed
(ii) Budget research - Collect the data related to the average expenditure of the family belonging to the selected class
For convenience, all the commodities have been classified into six categories:
Food, Clothes, Fuel and Electricity
House, rent, Expenditure on education Miscellaneous Expenditure
(iii) Price determination - Collect the wholesale prices of the selected commodities from a reliable source
(iv) Weightage - Assign weights to the commodities as per their importance
(v) Use the formula (family budget method)
\(C P I=\frac{\sum W R}{\sum W} ; \text { where } R=\frac{P_1}{P_0} \times 100\)

Question 8.
State the importance of Consumer Price Index.
Answer:
Consumer Price Index is important due to the following reasons:
(i) It helps to determine the change in the living expenditure of a particular class of society.
(ii) It helps to estimate the payments of various kinds to the workers.
(iii) It acts as a measure of general inflation.
(iv) it helps in formulating policies to control the price of the commodities.
Question 9.
How are the commodity weights are determined in the WPP
Answer:
Commodities are broadly classified into three categories - primary articles, fuel, power, light and lubricants and manufactured products. The commodity weights in the WPI are determined by the weekly estimates of the commodity value of domestic production and imports (inclusive of import duty) during the base year.
Question 10.
What are the uses WPI:
Answer:
The uses of WPI are:
(i) It helps to eliminate the effect of price change on national level are gates such as national income, capital formation, etc.
(ii) It measures the rate of inflation in the economy.
(iii) It determines the situation of demand and supply in the economy. Increase in WPI indicates a situation of excess demand while decrease in WPI indicates a situation of deficíerït demand
Question 11.
State the difference between CPI and WPI.
Answer:
CPI aims to determine the cost of living of a specified group of consumers in the society. WPI, on the other hand, tries to assess the situations of aggregate demand and supply in the economy.
Question 12.
State the steps of constructing industrial production index numbers.
Answer:
The steps of constructing industrial production index numbers are:
(i) Classify the industries into the following categories:
- Mining and quarrying
- Manufacturing
- Electricity
(ii) Collect monthly or quarterly or annual data related to these industries.
(iii) Assign weights to these industries on the basis of their pure production and contribution to the national income.
(iv) For each category. find the ratio of current period quantity to the base period quantity and multiply it by 100.
(vi) Multiply each quantity ratio with the assigned weight to obtain \(\mathrm{W}\left(\frac{q_1}{q_0} \times 100\right)\)
(vii) Find the sum, i.e. \(\Sigma W\left(\frac{q_1}{q_0} \times 100\right)\)
(viii) Find the sum of weights, i.e.∑W
(ix) Find industrial production index numbers using the formula
\(\| \mathrm{P}_{01}=\frac{\sum \mathrm{W}\left(\frac{q_1}{q_0} \times 100\right)}{\sum W}\)
Question 13.
What is the use of index number in Sensex
Answer:
Sensex is the index showing changes in the Indian stock market Sensex is a useful guide for investors in the stock market If the Sensex is rising, it indicates that the market is doing well and investors can expect better earnings from companies.

Question 14.
State the various uses of index numbers in economics.
Answer:
The various uses of index numbers in economics are:
(i) Consumer Price Index (CPI) helps to formulate policies related to income, price, rent control, taxation and other general economic issues.
(ii) Wholesale Price Index (WPI) helps in eliminating the effect of price change on national level aggregates such as national income, capital formation, etc. it also measures the rate of inflation in the economy.
(iii) Index of industrial and agricultural production gives a quantitative figure about the change in production and performance in the respective sectors.
(iv) Sensex is a usefuI guide for investors in the stock market.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the problems faced during the construction of Index number.
Answer:
There may come many difficulties in the formation of index numbers. If ideas are not right, conclusion will be wrong. Certain points must be kept in mind while forming index numbers.
(i) Objective of Index: Objective of the index should be clear as many decisions such as selection of base year and types of items depends on the objective of the index.

(ii) Selection of Base Year: Base year should be selected very carefully. Two things should be kept in mind while deciding base year.
- Base year should be a normal year free of war, earthquake, flood and unavoidable accident.
- Base year should be close to the running year.
(iii) Selection of Items or Values: Large number of items can make the calculation process very difficult. Since it is neither possible nor necessary to include all the items for the construction of index number, items should be selected such that they represent the whole business.
(iv) Selection of Price of Items: The wholesale values should be considered while selecting the prices of items prices as they are generally free from market fluctuations. Also, the source of such values should be authentic.
(v) Selection of weighing Method: When values are to be given weight on their basis of importance, suitable method of weighing should be selected.
(vi) Selection of Suitable Formula: The choice of the formula depends on the nature of question under study. The only difference between the Laspeyres index and the Paasche index is the weights used in these formulae.
Numerical Questions
Question 1.
Construct an index number for the year 2013. from the data given below taking 2012 as the base year:
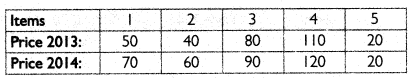
Answer:
Construction of Index number
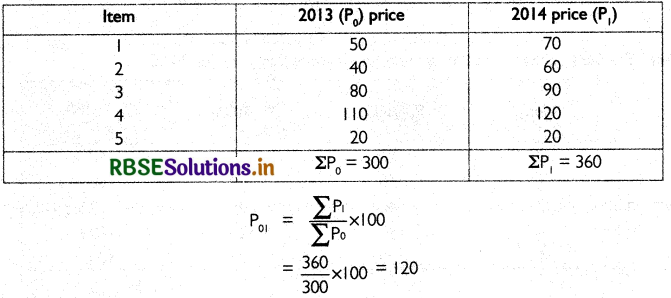
Thus, the price base has increased by 20% in the year 2013 in comparision to 2012.
Question 2.
Find index number for 2013 taking 2012 as base year using weighted index of price relatives method
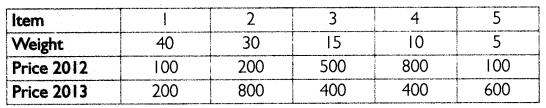
Answer:
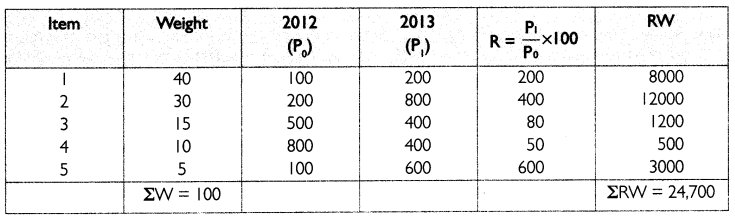
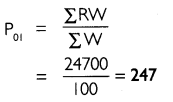

Question 3.
From the following data construct an index for 2006 taking 2005 as base. Use average of relative method.
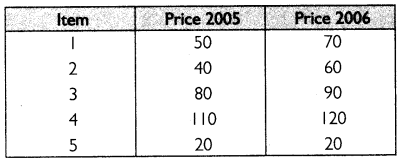
Answer:
The table below shows the calculation to construct an index for 2006:
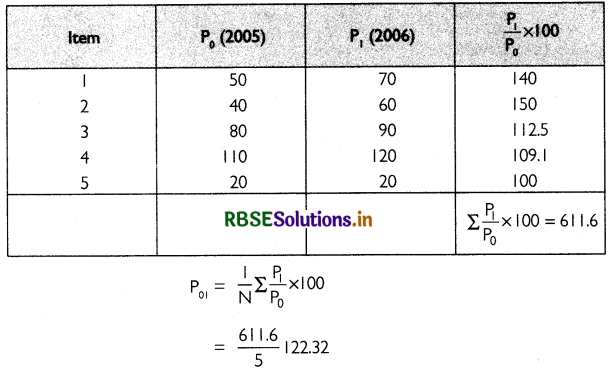
The index number for 2006 with 2005 as the base is 122.32.
Question 4.
Construct price index using (i) Laspeyre (ii) Paasche’s method for the following data.
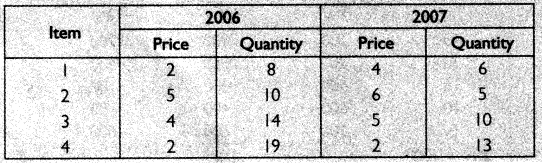
Answer:
The table below the calculations required to find index number
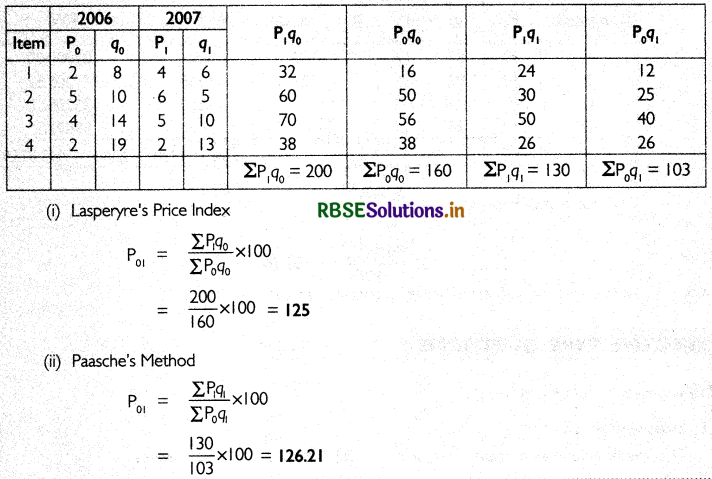

Question 5.
Find out the consumer price index using aggregate expenditure and family budget method.
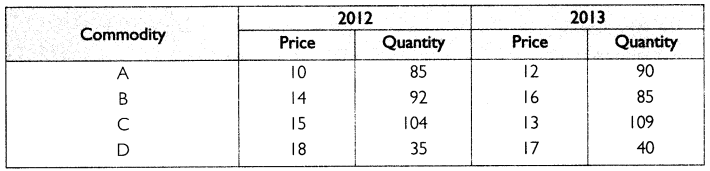
Answer:
Construction of index number with aggregate expenditure method:
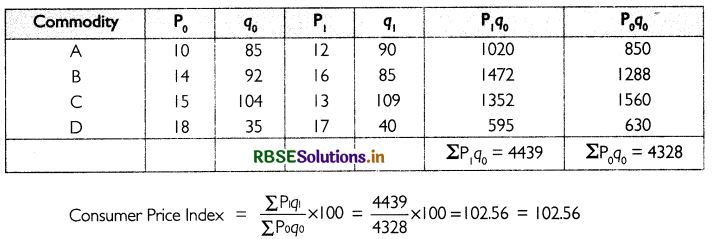
(ii) Construction of Index number with family Budget method.
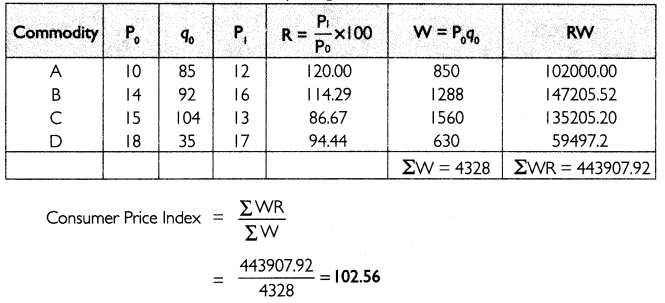
Higher Order thinking Skills
Question 1.
How do we calculate price relative?
Answer:
Price relative is calculated by taking the ratio of current year price to the base yar price. That is,
\(\text { Price Relative }=\frac{P_1}{P_0} \times 100\)
Question 2.
Differentiate between consumer price index number and wholesale price index on the basis of purpose.
Answer:
The purpose of computing Consumer Price Index is to know the cost of living of a specified group of consumers in the society. On the other hand, the basic purpose of computing Wholesale Price Index is to assess the situations of overall demand and supply in the economy.

Multiple Choose Question
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
lndex number is a .................
(A) special type of an average
(B) measure of relative changes
(C) a percentage relative
(D) all the above
Answer:
(D) all the above
Question 2.
What is the ratio of a new price to the base year price called?
(A) Price increase
(B) Price relative
(C) Price decrease
(D) Price absolute
Answer:
(B) Price relative
Question 3.
A simple aggregate quantity index is used to measure the:
(A) change in quantity of a good
(B) change in price of a good
(C) overall change in price of a group of goods
(D) overall change in the quantity of a group of goods
Answer:
(C) overall change in price of a group of goods

Question 4.
What is the percentage increase if index for a year is 130 to the base?
(A) 130 percent
(B) 150 percent
(C) 30 percent
(D) 20 percent
Answer:
(C) 30 percent
Question 5.
The price relative for refrigerators was 86.8 n 2010 calculated with a base period of 2000. What does this imply?
(A) The price of refrigerator5 was 13.2% lower in 2010 than 2000.
(B) The real price of refrigerators has fallen ₹ 13.20 between 2000 and 2010 because of quality change.
(C) The price of refrigerators was 86.8% higher in 2010 than in 2000.
(D) The price of refrigerators was 86.80 higher than 2000.
Answer:
(C) The price of refrigerators was 86.8% higher in 2010 than in 2000.
Question 6.
The Laspees and Paasche index are the examples of
(A) Weighted quantity index only
(B) Weighted price index only
(C) Aggregate index numbers
(D) Weighted dex numbers
Answer:
(D) Weighted dex numbers
Question 7.
Which of the following weights are used in the Paasche price index?
(A) Base year
(B) Current year
(C) Average of (A) and (B)
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B) Current year
Question 8.
What is fixed in the Laspeyres price index?
(A) Base year prices
(B) Base year quantities
(C) Current year prices
(D) Current year quantities
Answer:
(B) Base year quantities

Question 9.
Rate of inflation is calculated by using
(A) Wholesale Price Index
(B) Consumer Price Index
(C) Industrial Price Index
(D) Agricultural Price Index
Answer:
(A) Wholesale Price Index
Question 10.
Which of the following years is taken as the base while calculating Index number of Industrial Production in India?
(A) 1973 - 74
(B) 1983 - 84
(C) 1993 - 94
(D) 2003 - 04
Answer:
(C) 1993 - 94
I. Fill in the blanks with correct answer.
I. In family budget method, cost of Iiving index number is calculated as __________
2. _______ index numbers measure and facilitate comparison of the prices of certain
3. A production index is an important indicator of the ________ level in the economy.
4, An index number of 200 reflect that the value is that of the base period.
5. All items are given ______ weights in simple index method.
6. Paasche price index uses _____ year quantities as weights.
7. ______ measures the average change in prices.
8. WPI is widely used to measure the rate of _______
9. _______ is a useful guide for investors in the stock market
10. Index numbers help in framing economic _______
Answers:
1. \(\frac{\sum W\left(\frac{P_1}{P_0} \times 100\right)}{\sum W}\)
2. Price
3. output
4. twice
5. equal
6. current
7. CPI
8. inflation
9. Sensex
10. policies

II. State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Index numbers are expressed in terms of percentage.
2. Index numbers are the exact indications of relative changes.
3. Construction of simple index numbers requires weight
4. Current period is the period with which the comparison is to be made.
5. Change in any price is not reflected in a price index number.
6. We obtain the same index number whether we use simple index method or weighted index method.
7. A poor family spends proportionately more on food than a rich family.
8. Laspeyres price index uses current year quantities as weights.
9. Consumer Price Index (CPI) indicates the change in the general price level.
I O. Inflation refers to a situation of rise in the general price level in a country over a fairly long period of time.
Answers:
I. True
2. False
3. False
4. False
5. True
6. False
7. True
8. False
9. False
10. True

Ill. Match the following.
|
Column -I |
Column -I |
|
1. Index number |
(A) \(\frac{\sum P_1}{\sum P_0} \times 100\) |
Answer:
1. (C) 2. (D) 3. (A) 4. (B) 5. (F) 6. (E) 7. (H) 8. (G) 9. (j) 10. (I)
IV. Read the following statement- Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): Fisher’s index number is an ideal index number.
Reason (R): Fisher index number correctly predicts the expenditure index and it satisfies both time reversal test as well as factor reversal test.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are Üie and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).

V. Read the following hypothetical case study carefully and answer the following questions on the base of the same:
An index number is a statistical device for measuring changes in the magnitude of a group of related variables. In other words. it is a measure of the average change in a group of related variables two different situations. It represents the general trend of diverging ratios from which it is calculated The comparison may be between categories such as persons, schools, hospitals, etc. An index number also measures changes in the value of the variables such as prices of specified list of commodities. volume of production in different sectors of an industry, production of various agicuhuraI crops, cost of long, etc.
1. index numbers are expressed in terms of. . (percentage/natural numbers)
2. period is the period with which the comparison ¡sto be made. (Base/Current)
3. A.consumer price index measures changes in_________ price. (retail/wholesale)
4. Baseyearisdenotedby _________.(O/l)
Answer:
1. percentage
2. Base
3. retail
4. 0

- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 9 पर्यावरण और धारणीय विकास
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 3 Organisation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 2 Collection of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics for Economics
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 6 Measures of Dispersion
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 7 Correlation
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Economics Important Questions Chapter 5 Measures of Central Tendency
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 7 Correlation