RBSE Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
These comprehensive RBSE Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants will give a brief overview of all the concepts.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 Notes Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
→ All green plants synthesize their own food and they are called producers.
→ Photosynthesis is a process in which all green parts of the plant prepare carbohydrates with the help of CO2 and water in the presence of sun light. Oxygen is released as by product.
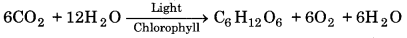
→ Von Helmont was explain first to that plants obtain their food only from water.
→ Joseph Priestley demonstrated that plants purify the foul air.
→ Jean Senebier proved that plants absorb carbon dioxide from air and release O2.
→ Julius Robert Mayer in 1845 discovered that green plants store light energy in the form of chemical energy.

→ The oxygen released from photosynthesis comes from water not from CO2.
→ According to modern concept, the photosynthesis is a oxidation-reduction process in which water oxidises to form O2 and CO2 reduces to form sugar.
→ In higher plant, there are two phases of photosynthesis:
- Light dependent reaction or Hill reaction.
- Dark reaction or Blackman reaction.
→ Photochemical reaction takes place in grana of chloroplast in the presence of sunlight, here photolysis of water takes place and ATP and NADPH2 are formed. In this process O2 is released.
→ Photosynthetic plants have pigments to absorb light energy. These pigments are found in chloroplasts. The pigments which are present outside do not take part in photosynthesis. Photosynthetic pigments are mainly of three types:
- Chlorophyll,
- Carotenoids and
- Phycobillins.
→ In light reaction of photosynthesis, two photo acts are worked photo act-I which has pigment system-I and photo act-II which has pigment system-II.
→ The process of ATP formation from ADP and inorganic phosphate in the presence of sunlight is called photophosphorylation. It is of two types: cyclic photophosphorylation and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
→ The dark reaction of photosynthesis does not require light, i.e., it takes place both in presence and absence of light. In this process ATP and NADPH2 obtained from light reaction are used in the synthesis of carbohydrates after reducing CO2.

→ Three forms of dark reaction are known, they are:
- Calyin cycle
- Hatch and Slack cycle and
- CAM cycle.
→ Calvin-Benson cycle is also called C3 cycle. The plants in which this cycle is found are called C3 plant because in these plants first stable compound of CO2 fixation is phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) a three carbon compound.
→ Hatch and Slack cycle is also called C4 cycle. The plants in which it found are called C4 plants because in these plant the first stable compound of CO2 fixation is formed 4-C compound oxaloacetic acid (OAA).
→ The leaves of C4 plants such as sugarcane, maize etc., possess special anatomy called Kranz anatomy.
→ The CAM cycle of photosynthesis is found in various types of succulent plants such as Kalanchoe, Sedum etc. In these plants stomata open at night and close during the day. These plants accumulate CO2 in sufficient amount as carbonic acid at night and during day time they reduce CO2 to carbohydrates.
→ The process of photosynthesis is affected by various external (environmental) and internal factors.
→ Photosynthesis: An anabolic process in which solar energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of food.
→ Chloroplast: A cell organelle of green plants. Plastid with chlorophyll.

→ Grana: Structure found in chloroplast made of lamellae. The site of photosynthesis.
→ Stroma: Extra lamellar space of chloroplast. The site of dark reaction of photosynthesis.
→ Carbon assimilation: Use of CO2 to form carbohydrates.
→ Photolysis: The spliting of water molecule into H+ and OH- by sunlight.
→ Quantasome: The unit of absorbed light by chlorophyll molecules.
→ Spectrometer: Light measurement device.
→ Kranz Anatomy: Internal structure of leaves of C4 plants.
→ Photorespiration: The process of releasing CO2 under high concentration of O2.
→ RUBISCO: An enzyme which acts as carboxylase and oxygenase.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 The Living World
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 पुष्पी पादपों की आकारिकी