RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Which one of the following type of resources is a biotic resource?
(a) Rocks
(b) Metals
(c) Playing ground
(d) Animal resource
Answer:
(d) Animal resource
Question 2.
Renewable resource is :
(a) Wind energy
(b) Forest
(c) Water
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 3.
What is the main cause of land degradation in Gujarat and Rajasthan ?
(a) Over grazing
(b) Mining
(c) Over irrigation
(d) Deforestation
Answer:
(a) Over grazing
Question 4.
In which state red and yellow soils are found ?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Gujarat
(c) Madhva Pradesh
(d) Orissa
Answer:
(d) Orissa

Question 5.
Which of the following type of soil is found in northern plain region?
(a) Black soil
(b) Red and yellow soil
(c) Alluvial soil
(d) Laterite soil
Answer:
(c) Alluvial soil
Question 6.
The result of indiscriminate exploitation of resources is
(a) global warming
(b) land degradation
(c) ozone layer depletion
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 7.
When did the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit take place ?
(a) In June, 1986
(b) In June, 1992
(c) In May, 1996
(d) In January, 2002
Answer:
(b) In June, 1992
Question 8.
What is the main reason for land degradation in Jharkhand ?
(a) over grazing
(b) mining
(c) over irrigation
(d) intensive farming
Answer:
(b) mining
Question 9.
Who is the author of the book "Small is Beautiful" ?
(a) Schumacher
(b) Brundtland
(c) Morarji Desai
(d) Mahatma Gandhi
Answer:
(a) Schumacher
Question 10.
Which soil is mostly deep and acidic (ph<6.0) ?
(a) Black soil
(b) Alluvial soil
(c) Arid soil
(d) Laterite soil
Answer:
(d) Laterite soil

Fill in the blanks
1. Resources are a function of ................. activities.
2. ................. is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources.
3. At the international level, the ................ advocated resource conservation for the first time in a more systematic way in 1968.
4. ................. includes rocky, arid and desert areas and land.
5. The black soils are also known as ................
Answer:
1. human
2. Planning
3. club of Rome
4. Waste land
5. regur soils.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
On the basis of origin, state the classification of natural resources with example.
Answer:
- Biotic- Human being
- Abiotic- Metals.
Question 2.
Write any two differences between khadar and bangar.
Answer:
- Khadar soil is finer in texture and bangar is coarser in texture.
- Khadar soil is more fertile and bangar soil is less fertile.

Question 3.
What is agenda-21?
Answer:
It is the declaration signed by world leaders in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development.
Question 4.
Why is there a need to conserve resources ?
Answer:
Resources are vital for any developmental activity. Most of the resources have limited supplies as compared to their demand.
E.g., Supply of fossil fuel is limited.
Question 5.
Classify the resources on the basis of exhaustibility.
Answer:
- Renewable resource-e.g., Solar energy.
- Non-renewable resource-e.g., Coal.
Question 6.
Where was the first International Earth Summit held?
Answer:
Rio de Janeiro (Brazil).
Question 7.
Which are the main physical factors of land use pattern?
Answer:
Topography, climate and soil types.

Question 8.
According to National Forest Policy (1952) of India, how much area of total geographical area should be covered under forests ?
Answer:
33% of geographical area.
Question 9.
Which areas does waste land include?
Answer:
Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas.
Question 10.
How much of the Indian land is considered as degraded ?
Answer:
Approximate 13 crore hectares of land.
Question 11.
Which type of soil is very useful for cotton cultivation ?
Answer:
Black soil.
Question 12.
What do you mean by Resource ?
Answer:
Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs is called Resource.

Question 13.
What are renewable resources ?
Answer:
Renewable resources are the resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, mechanical or chemical processes (e.g., solar energy).
Question 14.
What are potential resources ?
Answer:
Resources which are found in a region but have not been utilized due to lack of capital or other reasons.
Question 15.
What is sustainable development ?
Answer:
Sustainable development is that process of development which meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of the future generation to meet their own needs.
Question 16.
Name the three states in India where coal is found ?
Answer:
Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.

Question 17.
What is the total geographical area of India ?
Answer:
3.28 million square kilometers.
Question 18.
Name the states of India which have below 10% nét sown area of the total area.
Answer:
Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Question 19.
What is the main cause of degradation of land resource in Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh ?
Answer:
Over irrigation degrades land due to water logging which leads to the increase in salinity and alkalinity of the soil.
Question 20.
State two causes of soil erosion.
Answer:
- Flooding of rivers
- Deforestation.
Question 21.
Write two methods to prevent soil erosion.
Answer:
- Terrace cultivation
- Afforestation.

Question 22.
Write the factors responsible for soil formation.
Answer:
Relief, bed rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil.
Question 23.
Why is the population higher in the alluvial soil region ?
Answer:
Alluvial soil is very fertile soil which is useful for cultivation of crops.
Question 24.
Write two characteristics of black soil.
Answer:
- Black soil is black in colour.
- The soil is well known for its capacity to hold moisture.
Question 25.
In which areas is laterite soil developed ?
Answer:
This soil develops in areas is of high temperature and heavy rainfall.
Question 26.
Where is the lesser quantity of humus found less in laterite soil. Explain.
Answer:
The quantity of humus is found less in laterite soil under sparse vegetation and in semiarid environment regions.

Question 27.
Where are the laterite soils found in India ?
Answer:
Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and hilly areas of Assam.
Question 28.
Explain the term erosion.
Answer:
Removal of the soil by forces of nature particularly by wind and water, is called erosion.
Question 29.
Write any two human factors responsible for soil erosion.
Answer:
- Urbanisation
- Industrialisation.
Question 30.
What is terrace farming ?
Answer:
Hill slope is cut into a number of terraces having horizontal top and steep slopes on the back and front. It is very effective for controlling the speed of flowing water.
Question 31.
Where are alluvial soils found other than in the northern region ?
Answer:
Rajasthan, Gujarat and eastern coastal plains.

Short Answer Type Questions (Type-I)
Question 1.
Clarify the meaning of international resources ?
Answer:
International resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions. These are called international resources.
Question 2.
Classify the resources.
Answer:
Resources can be classified as follows-
- On the basis of origin-(i) Biotic, (ii) Abiotic.
- On the basis of exhaustibility-(i) Renewable, (ii) Non-renewable.
- On the basis of ownership-(i) Individual, (ii) Community, (iii) National, (iv) International.
- On the basis of status of development(i) Potential, (ii) Developed, (iii) Stock, (iv) Reserves.
Question 3.
Write any two features of Arid soil ?
Answer:
- Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
- They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.

Question 4.
Suggest two measures to conserve soil.
Answer:
- Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. Soil can be conservated through it.
- Planting lines of trees to create shelter also works in a similar way.
Question 5.
Explain two problems caused due to the indiscriminate use of resources by humans.
Or
Write two problems created by over exploitation of resources.
Answer:
- Depletion of resources-Over utilization has led to depletion of resources for meeting the greed of few individuals.
- Global ecological crisis-Over utilization of resources has led to the global ecological crisis such as global warming, depletion of ozone layer, pollution and land degradation.
Question 6.
Write any two differences between renewable and non-renewable resources.
Answer:
- Renewable resources can be renewed in a short time (solar energy) and nonrenewable resources cannot be renewed in a short time.
- Renewable resources are the free gifts of nature. Non-renewable resources are not the free gifts of nature.
Question 7.
Mention two measures for conservation of land degradation.
Answer:
- Afforestation
- Controlling animal grazing
- Afforesting thorny plants in the desert area
- Controlling mining.

Question 8.
What do you mean by resource planning ? Mention any one step of resource planning.
Answer:
Resource Planning Resource planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources.
Step of resource planning (anyone)- Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
Question 9.
What is the main concept of resource planning ?
Answer:
Resource planning is a complex process which involves :
- Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country.
- Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional setup for implementing resource development plans.
- Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Question 10.
Why is there a need for resource planning ?
Answer:
- Most of the resources are limited in supply.
- Most of the resources are unevenly distributed over the country.
- Over utilization of resources may lead to the pollution of the environment.
Question 11.
Write two characteristics of black soil.
Answer:
- Black soil is formed due to weathering of lava which is made up of fine materials.
- This soil is rich with soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, potash and lime.
- This soil is well known for its capacity to hold moisture.

Question 12.
Why is there a need for conservation of resources ?
Answer:
Resources are vital for any developmental activity. But irrational consumption and over utilization of resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important.
Question 13.
What do you mean by Agenda21 ? Explain it.
Answer:
It is the declaration signed by world leaders in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) which took place at Rio de Janerio, Brazil. Its aim is to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease through global cooperation on common interests.
Question 14.
What is the role of humans in resource development ?
Answer:
- Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development.
- Human beings transfer material available in our environment into resource and use them.
Question 15.
“It is important to use the available land for various purposes with careful planning”. Give reasons.
Answer:
Land is an asset of finite magnitude. It supports natural vegetation, wild life, human life, economic activities, transport and communication systems. So it is important to use the available land for various purposes with careful planning.

Question 16.
Why is it required to distribute resources effectively in the society?
Answer:
An equitable distribution of resources has become essential for sustainable quality of life and global peace. If the present trend of resource depletion by a few individuals and countries continues, the future of our planet will be in danger.
Question 17.
Explain the relation between nature, technology and institutions.
Answer:
Nature contains resources. These resources are converted into usable forms with the help of technology. Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development.
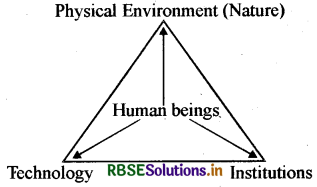
Question 18.
What was Gandhiji's opinion regarding the conservation of resources ?
Answer:
Gandhiji was very apt in voicing his concern about resource conservation. He said, “There is enough for everybody's need, and not for anybody's greed”.
According to him, there were the greedy and selfish individuals who were responsible for depleting of resources. He was in favour of producing for the masses than mass production.
Short Answer Type Questions (Type II)
Question 1.
Write the differences between individual resources and community owned resources.
Answer:
Individual resources: Resources which are owned privately by individuals are called individual resources. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue. In the villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, Pasteur lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals.
Community owned resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds etc.), public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there.

Question 2.
What is the aim of the conference of Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit 1992 ?
Answer:
In June 1992 more than 100 heads of states met in Rio de Jeneiro in Brazil for the first International Earth Summit. The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
The assembled leaders signed the declaration on global climatic change and biological diversity. This convention adopted Agenda 21 for achieving sustainable development.
Question 3.
What are the steps taken by the Indian government for resource planning ?
Answer:
Resource planning is a complex process which involves:
(a) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country.
(b) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional setup for implementing resource development plans.
(c) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
India has made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning right from the first five year plan launched after independence.
Question 4.
“Resource planning is very important for a country like India". Justify by giving reasons.
Answer:
(i) There are regions in India which are rich in certain types of resources but are deficient in some other resources. There are some regions which can be considered selfsufficient in terms of the availability of resources and there are some regions which have acute shortage of some vital resources.
(ii) The states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits but lack in infrastructural development.
(iii) The states like Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh are rich in soil but lack in minerals.
So resource planning is very important for a country like India.
Question 5.
Write the characteristics of alluvial soil.
Answer:
- This soil extends in Rajasthan and Gujarat through a narrow corridor. It is also found in the eastern coastal plains particularly in deltas of Mahanadi, Godavari, Kaveri and Krishna rivers. Alluvial soil is found mostly in the Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra river and valley basins.
- This soil consists of varying proportions of sand, silt and clay.
- According to the age of the alluvial soil, it is divided into two groups, old alluvium-bangar and new alluvium-khadar.
- This soil is very much fertile due to presence of potash, phosphorus and lime.
- This soil is very fertile and hence good for agriculture.
- Alluvial soil in the dry areas is more alkaline and can be productive after proper treatment and irrigation.

Question 6.
Distinguish between khadar and bangar.
Answer:
(i) The khadar soil is found in the low areas of the valley which is flooded every year.
The Bangar soil is found in the higher areas. It reaches about 30 mt above the flood level.
(ii) Khadar- This soil is finer in texture.
Bangar soil has higher concentration of kanker nodules.
(iii) The khadar soil is more fertile. Bangar soil is less fertile.
Question 7.
Write the relief features of India.
Answer:
India has land under a variety of relief features, namely, mountains, plateaus, plains and islands. About 43% of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry. Mountains account for 30% of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects. About 27% of the area of the country is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
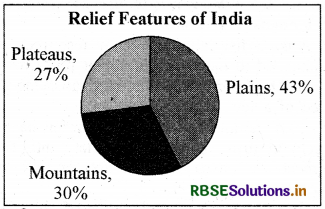
Question 8.
What is soil erosion ? Explain the reasons responsible for soil erosion.
Answer:
Soil Erosion: The removal of soil by the forces of nature particularly by wind and water is called soil erosion.
Factors responsible for soil erosion:
- Nature and human being are both responsible for soil erosion.
- Powerful natural agent wind can lift the valuable top soil from one area and deposit it in another area.
- Over grazing-during the long dry period grass is grazed from the ground and torn out with the root by animals.
- Over irrigation - excessive water logging leads to increase of salinity and alkalinity of the soil.
- Continuous cutting of trees is the most important factor for soil erosion.
Question 9.
How can we check soil erosion ?
Answer:
- Terracing and contour bunding- Soil erosion can be reduced by contour and terrace bunding. Ploughing along the contour lines can be decelerate the flow of water down the slopes.
- Strip cropping- Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks the force of the wind
- Shelter belt- Planting lines of trees to create shelter works in a similar way.

Question 10.
Make a classification of resources by making a chart.
Answer:
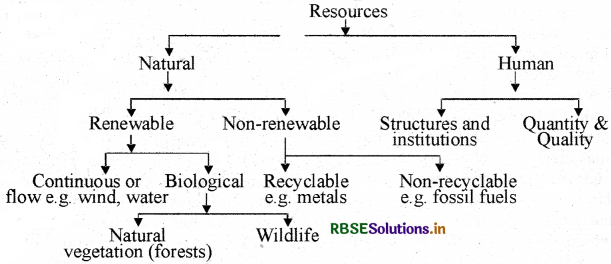
Question 11.
Classify resources on the basis ..of exhaustibility.
Answer:
On the basis of exhaustibility resources are of 2 types
(1) Renewable Resources: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources.
For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. The renewable resource may further be divided into continous or flow.
(2) Non-Renewable Resources: These occur over a very long geological time. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take million of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use.
Question 12.
What are national resources ? Explain.
Answer:
National resources : Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on the fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities are empowered by the government to acquire land. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area upto 12 nautical miles (19.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation.

Question 13.
“There is enormous diversity in the availability of resources in India”. Explain.
Answer:
There are regions in India which are rich in certain types of resources but are deficient in some other resources. There are some regions which can be considered selfsufficient in terms of the availability of resources and there are some regions which have acute shortage of some vital resources. e.g, the states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits. Arunachal Pradesh has abundance of water resources but lacks in infrastructural development. The state of Rajasthan is very well in solar and wind energy but lacks water resources. Thus, there is enormous diversity in the availability of resources in India.
Question 14.
Write a short note on the planning at the international level for conservation of resources.
Answer:
- At the international level the club of Rome advocated resource conservation for the first time in a more systematic way in 1968.
- Subsequently, in 1974, Gandhian philosophy was again presented by Schumacher in his book Small is beautiful.
- The seminal contribution with respect to resource conservation at the global level was made by Brundtland Commission Report 1987. This report introduced the concept of sustainable development.
- Another significant contribution was made at the Earth Summit at Rio de Jeneiro, Brazil in 1992.
Question 15.
What are the problems that arise due to the indiscriminate use of resources by humans ? Explain.
Answer:
Indiscriminate use of resources by humans led to the following major problems-
- Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of a few individuals.
- Accumulation of resources in few hands, which, in turn, divided the society into two segments i.e. haves and have nots or rich and poor.
- Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to gobal ecological crises such as, global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.

Question 16.
Write a short note on Rio de Jeneiro Earth Summit, 1992.
Answer:
In June 1992 more than 100 heads of sistes met in Rio de Jeneiro in Brazil for the fiu t international Earth Summit. The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
The assembled leaders signed the declaration on global climatic change and biological diversity. This convention adopted Agenda-21 for achieving sustainable development.
Question 17.
“Soil as a resource". Explain.
Answer:
Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. It is the medium of plant growth and it supports different types of living organisms on the earth. The soil is a living system.
Relief, parent rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil. Various processes of nature (temperature, water, wind, glacier) contribute to the formation of soil.
Chemical and organic changes which take place in the soil are equally important.
On the basis of factors responsible for soil formation, colour, thickness, texture, edge, chemical and physical properties, the soil in India can be classified in different types- alluvial soil, black soil, red and yellow soil, laterite soil, arid soil, mountain soil.
Question 18.
Write the characteristics of black soil. Where is this type of soil found in India ?
Answer:
Characteristics of Black Soil-
- Black soil is formed due to weathering of lava which is made of fine materials.
- This soil has rich soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, potash and lime.
- The soil is well known for its capacity to hold moisture.
- The black soil is made of extremely fine materials - clayey materials.
- These soil is generally poor in phosphoric content.
- This type of soil is very much useful for cotton cultivation.
- This type of soil is called regur soil due to its black colour.
Founding areas:
- It is typical of the Deccan trap region spread over north west deccan plateau.
- It covers the plateau of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
- It is also found in Godavari and Krishna valleys.

Question 19.
Write the characteristics of arid soil.
Answer:
Arid soil is generally found in western deserts.
Features :
- Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
- They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
- The soil lacks humus and moisture.
- The lower horizons of the soil are occupied by kankar because of the increasing calcium content downwards. The kankar layer formations in the bottom horizons restrict the infiltration of water.
- After proper irrigation these soils become cultivable.
Question 20.
Write a short note on forest soil.
Answer:
- Forest soil is generally found in mountainous area where abundant rainfall occurs throughout the year.
- This soil is formed due to mechanical weathering caused by snow, rain and temperature variation etc.
- This soil is heterogeneous in nature.
- The soil is very rich in humus but is deficient in potash, phosphorus and lime.
- This soil is specially suitable for plantation of tea, coffee, spices and tropical fruits.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are resources ? Classify the resources on the basis of ownership.
Answer:
Meaning of Resources: Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable, can be termed as resource.
Classification of resources on the basis of ownership:
(1) Individual resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue. In the villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasteur lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources owned by individuals. .
(2) Community owned resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds etc.), public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there.
(3) National resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on the fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area upto 12 nautical miles (19.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation.
(4) International resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the exclusive economic zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilize these without concurrence of international institutions.

Question 2.
Along with the availability of resources for the development of any region, technological development and institutional change is also necessary. Explain.
Answer:
It can be explained in the following ways-
(1) The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of any region but mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development.
(2) There are many regions in our country that are rich in resources but these are included in economically backward regions because there is lack of technology and corresponding institutions. On the contrary there are some regions which have a poor resource base but they are economically developed due to advanced technology development.
The history of colonisation reveals that it was primarily the higher level of technological development of the colonising countries that helped them to exploit resources of other regions and establish their supremacy over the colonies.
Therefore, resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes. India has also experienced all this in different phases of colonisation. Therefore, development, in general, and resource development in particular does not only involve the availability of resources, but also the technology, quality of human resources and the historical experiences of the people.
Question 3.
Write about the resource planning in detail. What are the steps for conservation of resources ?
Answer:
Resource planning is a complex process which involves:
- Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country.
- Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional setup for implementing resource development plans.
- Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Steps for conservation of resources:
- Controlling over-population which will further reduce frequent utilization of resources.
- Using resources judiciously and properly for future generations.
- Controlling environmental pollution.
- Spreading awareness among people about the value of resources.
- Spreading awareness and knowledge about environment and resource.

Question 4.
Write different types of soils in India. Explain in detail.
Answer:
Types of Soils in India India has varied relief features, landforms, climatic realms and vegetation types. These have contributed in the development of various types of soils :
(1) Alluvial soil :
- This soil extends in Rajasthan and Gujarat through a narrow corridor. It is also found in the eastern coastal plain particularly in deltas of Mahanadi, Godavari, Kaveri and Krishna rivers. Alluvial soil is found mostly in the Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra river valley basins.
- This soil consists of varying proportions of sand, silt and clay.
- According to the age of the alluvial soil, it is divided into two groups, old alluviumbangar and new alluvium-khadar.
- This soil is very much fertile due to presence of potash, phosphorus and lime.
- This soil is very fertile and hence is good for agriculture.
- (Alluvial soil in the dry areas is more alkaline and can be productive after proper treatment and irrigation.
(2) Black soil:
- Black soil is formed due to weathering of lava which is made of fine materials.
- This soil has rich soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, potash and lime.
- The soil is well known for its capacity to hold moisture.
- The black soil is made of extremely fine materials- clayey materials.
- This soil is generally poor in phosphoric content.
- This type of soil is very much useful for cotton cultivation.
- This type of soil is called regur soil due to its black colour.
Finding areas:
- It is typical of the Deccan trap region spread over north west deccan plateau.
- It cover the plateau of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chattisgarh.
- It is also found in Godavari and Krishna valleys.
(3) Laterite soil: Laterite soil develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall. This is the result of intense heavy rainfall. Humus content of the soil is low. The laterite soils are suitable for cultivation with adequate doses of manures and fertilizers.
Finding areas: This soil is mainly found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh and the hilly areas of Odisha and Assam.
(4) Forest soil:
- Forest soil is found generally in mountainous areas where abundant rainfall occurs throughout the year.
- This soil is formed due to mechanical weathering caused by snow, rain, temperature variation etc.
- This soil is heterogeneous in nature.
- This soil is very rich in humus but is deficient in potash, phosphorus and lime.
- This soil is specially suitable for plantation of tea, coffee, spices and tropical fruits.
(5) Arid soil: Arid soil is generally found in western deserts.
Features:
- Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
- They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature.
- In some areas the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
- The soil lacks humus and moisture.
(6) Red and yellow soils: Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the deccan plateau.
This soil develops a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks. It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form.

Question 5.
In which areas is the laterite soil found ? explain their main features.
Answer:
Areas of Laterite soil: Laterite soil is found mostly in southern states, western ghats region of Maharashtra, Odisha, some part of West Bengal and North-east regions.
Features of Laterite soil:
- The laterite soil develops under tropical and subtropical climate with alternate wet and dry season.
- This soil is the result of intense leaching due to heavey rain.
- Lateritic soils are mostly deep to very. deep, acidic (pH < 6.0).
- Generally it is deficient in plant nutrients.
- Where these soils support decidous and evergreen forests, It is humus rich, but under sparse vegetation and in semi-arid environment, it is generally humus poor.
- They are prone to erosion and degradation due to their position on the landscape.
- After adopting appropriate soil conservation techniques particularly in the hilly areas of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, this soil is very useful for growing tea and coffee. Red laterite soils in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Kerala are more suitable for crops like cashew nut.
Question 6.
Discuss land degradation and suggest the steps to be taken to control it to some extent.
Answer:
Land Degradation: Rendering a land unfit for cultivation is called degradation of land. Human beings due to personal greed have degraded the natural environment to a great extent. The human activities also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to land.
Main causes of land degradation :
- Mining Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over-burdening.
- Overgrazing- It is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
- Over irrigation- In the states of Punjab and Haryana, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation.
- Mineral processing- The mineral processing like grinding of lime stones for cement industry generates huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land.
Steps which can be taken to control land degradation :
- Afforestation- The best way to conserve soil is to increase the area under forest. Cutting trees should be stopped and growing more and more trees in new areas should be encouraged.
- Restricting grazing of animals- Animals should be removed from different pastures so as to avoid erosion of soil.
- Constructing dam- This checks the speed of water and saves soil erosion.
- Proper farming techniques- Crop rotation, checking and reducing shifting agriculture, terracing and contour bunding etc. are proper farming techniques.

Question 7.
Explain soil erosion in detail and write the steps to be taken in controlling soil erosion?
Answer:
Soil Erosion: The removal of the soil by forces of nature particularly by wind and water is called soil erosion.
Generally, there is a balance between soil forming process and the erosional process. The balance can be disturbed by natural and human factors.
Causes of soil erosion:
- Human activities like deforestation, overgrazing, construction and mining etc. and natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil. erosion.
- The running water cuts through the clay soils and makes deep channels as gullies. The land becomes unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land. In the Chambal basin such lands are called ravines.
- Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. In such cases the top soil is washed away. This is known as sheet erosion.
- Wind blows loose soil off flat or sloping land known as wind erosion.
- Soil erosion is also caused due to defective methods of farming. Ploughing in a wrong way i.e., up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion.
Steps to be taken to control soil erosion :
(a) Terracing and contour bunding- Terracing and contour bunding across the hill slopes is a very effective method of soil conservation. Hill slopes are cut into number of terraces having horizontal tops and steep slopes on back and front. Contour bunding involves the construction of bank along the contour.
(b) Strip cropping- Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks the force of the wind.
(c) Shelter belt- Planting lines of trees to crcate shelter works in a similar way.
Question 8.
Classify the resources on the basis of status of development.
Answer:
(a) Potential resources- These are found in a region, but are not utilized. e.g., Rajasthan and Gujarat have lot of potential for development of wind and solar energy but so far have not been developed properly.
(b) Developed resources- Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation.
(c) Stock- These are the materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy the human needs but can not be used as the human beings do not have the appropriate technology.
(d) Reserve- Reserves are the subset of the stock which can be put into use with the help of existing technical “knowhow”, but their uşe has not been started.

Question 9.
For what purposes are land résources used in India ? Explain.
Answer:
In India land resources are used for the following purposes:
(1) Forests
(2) Land not available for cultivation
- Barren and waste land.
- Land put to non-agricultural uses, e.g., buildings, roads, factories, etc.
(3) Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land)-
- Permanent pastures and grazing land,
- Land under miscellaneous tree crops groves (not included in net sown area),
- Cultruable waste land (left uncultivated for more than 5 agricultural years.)
(4) Fallow lands-
- Current fallow (left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year),
- Other than current fallow left uncultivated for the past 1 to 5 agricultural years)
(5) Net sown area- Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as gross cropped area.
