RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Psychology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Psychology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Solutions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Accounts from Incomplete Records Textbook Questions and Answers
Test Your Understanding I
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Incomplete record mechanism of book keeping is:
(a) Scientific
(b) Unscientific
(c) Unsystematic
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(b) Unscientific
Question 2.
Opening capital is ascertained by preparing:
(a) Total debtors account
(b) Total creditors account
(c) Cash account
(d) Opening statement of affairs
Answer:
(d) Opening statement of affairs
Question 3.
Credit purchase, during the year is ascertained by preparing:
(a) Total creditors account
(b) Total debtors account
(c) Cash account
(d) Opening statement of affairs
Answer:
(a) Total creditors account

Question 4.
If opening capital is ₹ 60,000, drawings ₹ 5,000, capital introduced during the period ₹ 10,000, closing capital ₹ 90,000. The value of profit earned during the period will be:
(a) 7 20,000
(b) 7 25,000
(c) 7 30,000
(d) 7 40,000
Answer:
(b) 7 25,000
Test Your Understanding II
Fill in the correct word.
1. Credit sales can be ascertained as the balancing figure in the ............... account.
2. Excess of ............... over ............... represents loss sustained during the period.
3. To ascertain the profit, closing capital is to be adjusted by deducting ............... and ............... adding
4. Incomplete records are generally used by ...............
Answers:
1. Total debtors
2. Opening capital, closing capital
3. Fresh capital introduced, drawings
4. Small traders
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the meaning of incomplete records?
Answer:
It is an incomplete system of accounting wherein no proper system of accounting is followed, for some transactions, proper debit and credit are followed, for some either side is followed or sometimes no entry is passed.
Question 2.
What are die possible reasons for keeping incomplete records?
Answer:
Many businessmen keep incomplete records because of the following reasons:
(a) It is adopted by those people who don’t have proper knowledge of accounting principles.
(b) It is an inexpensive mode of maintaining records as specialized accountants are not required.
(c) Less time is consumed due to maintenance of few books.
(d) It is a convenient mode of maintaining records as the owner maintains the accounts of his choice.
Question 3.
Distinguish between statement of affairs and balance sheet.
Answer:
Difference between Statement of Affairs and Balance Sheet.
|
Basis |
Statement of affairs |
Balance sheet |
|
Base |
It is prepared from incomplete records |
It is prepared from complete records |
|
Preparation |
It is prepared from the estimated balances of assets and liabilities |
It is prepared from the closing balances of accounts |
|
Trial balance |
Trial balance is not prepared |
Trial balance is prepared |
|
Objective |
To find financial position |
To find balance of capital |
Question 4.
What practical difficulties are encountered by a trader due to incompleteness of accounting records?
Answer:
Difficulties a trader faces under single entry system:
1. Comparison of profits and losses cannot be mad.
2. It makes difficult to trace the errors.
3. It increases the chances of committing frauds because checks and counter checks are not possible under it.
4. We cannot prepare Trial Balance due to lack of arithmetical accuracy of the Ledger Accounts.

Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by a ‘statement of affairs’? How can the profit or loss of a trader be ascertained with the help of a statement of affairs?
Answer:
Meaning of statement of affairs: Statement of Affairs is a statement which is prepared to find out capital by placing assets and liabilities in it. It resembles balance sheet but it is not called balance sheet as the data is not wholly based on ledger balances.
Calculation of Profit or Loss under Single Entry System:
|
Particulars |
₹ |
|
Capital at the end |
Xxx |
|
(-) Capital in the beginning |
Xxx |
|
(+) Drawings during the year |
Xxx |
|
(+) Capital withdrawn |
Xxx |
|
(-) Capital further introduced |
Xxx |
|
Profit / Loss |
Xxx/(xxx) |
Note: Positive figure will represent profit and negative figure will represent loss.
Question 2.
‘Is it possible to prepare the profit and loss account and the balance sheet from the incomplete book of accounts kept by a trader’? Do you agree? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, it is possible to prepare profit and loss account and balance sheet from the incomplete book of accounts by following procedure:
1. Preparation of statement of affairs in the beginning to find capital in the beginning.
2. Analysis of cashbook to find out either cash sales, cash purchases, cash incomes, cash expenses, drawings, closing balance of cash etc.
3. Preparation of creditors’ account to find out either of credit purchases, purchase returns, discount received, bills payable issued, closing balance etc.
4. Preparation of debtors’ account to find out either of credit sales, sales returns, discount allowed, bills receivable received, closing balance etc.
5. Bills receivable book to prepare to find out bills receivable received, honoured, dishonoured, closing balance etc.
6. Bills payable account is normally prepared to find out bills payable issued, bills paid, closing balance etc.
7. Other transactions such as profit or loss on sale of assets, purchase or sale of assets on credit, outstanding expenses, accrued incomes, incomes received in advance, prepaid expenses etc. are also recorded.
8. Trial balance may be prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of accounts
9. Now, Trading Account, Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet can be prepared.

Question 3.
Explain how the following may be ascertained from incomplete records:
(a) Opening capital and closing capital
(b) Credit sales and credit purchases
(c) Payments to creditors and collection from debtors
(d) Closing balance of cash.
Answer:
(a) Opening capital and closing capital may be obtained by preparing opening statement of affairs and closing statement of affairs.
(b) Credit sales can be obtained by preparing debtors account and credit purchases can be obtained by preparing creditors account.
(c) Payment to creditors can be found out either from the debit side of creditors account or from the credit side of cash book. Collection from debtors can be found out from the credit side of debtors account or from the debit side of debtors account.
(d) Closing balance of cash book can be obtained by posting all cash receipts and cash payments in the cash account.
Numerical Questions
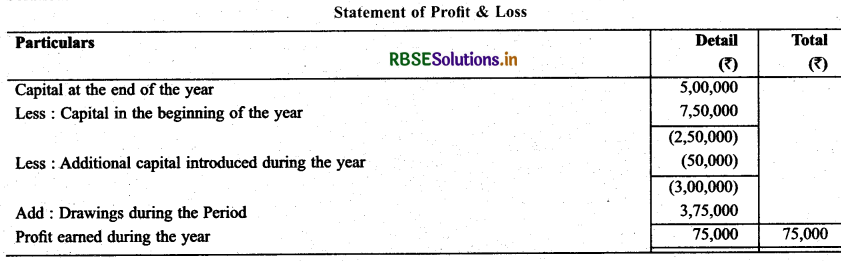
Question 1.
Prepare Profit & Loss statement with the help of undermention informations).
Capital at the end of year Capital at the beginning of year Drawing during the Period Additional Capital Introduced
Capital at the end of year : ₹ 5,00,000
Capital at the beginning of year : ₹ 7, 50,000
Drawing during the Period : ₹ 3,75,000
Additional Capital Introduced : ₹ 50,000
Solution:
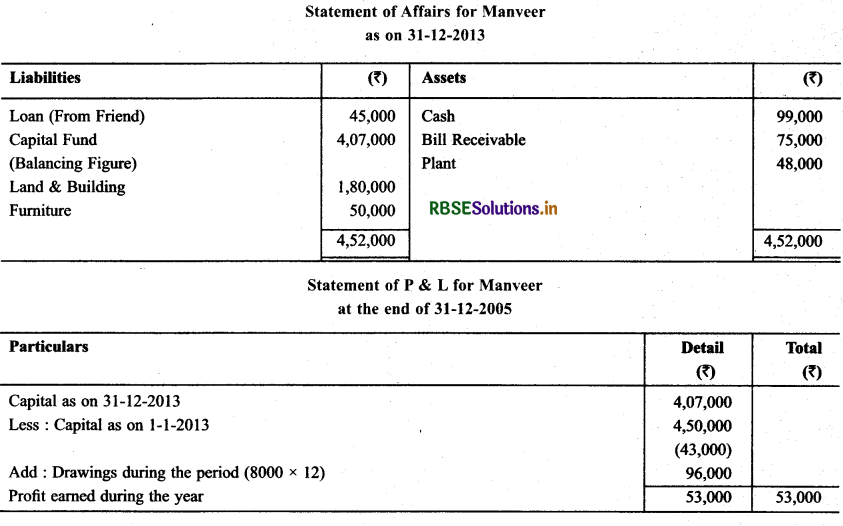
Question 2.
Shri Manveer commence business w.e.f January 1, 2013 with a capital of ₹ 4,50,000. His Position on December
31, 2013 were as under:
Cash : ₹ 99,0O0
BIR : ₹ 75,000
Plant : ₹ 48,000
Land & Building : ₹ 1,80,000
Furniture : ₹ 50,000
On this day Manveer borrowed 45,000 from his friend & withdraw 8,000 p.m. for his household expenses. Calculate P & L for the year ending as on December 31, 2013.
Solution:

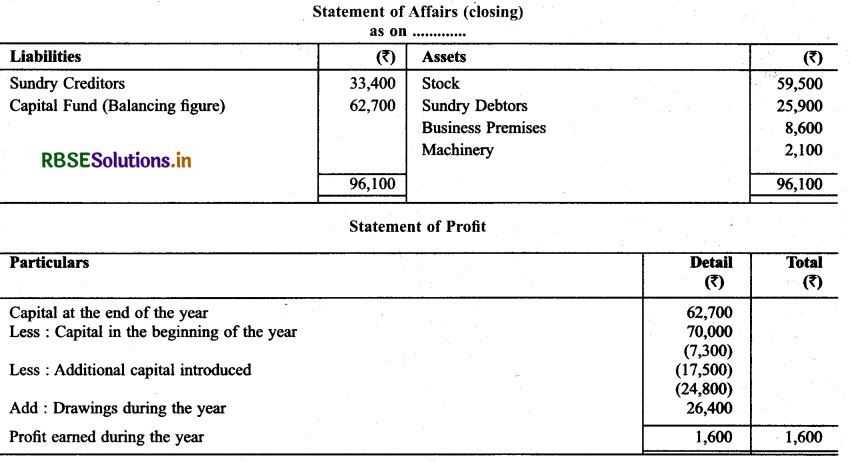
Question 3.
Ascertain the amount of Profit for the year on the basis of under mentioned informations:

Solution:
Question 4.
Calculate opening capital with the help of following informations:

Solution:

Question 5.
Calculate Opening & Closing capital with the help of following informations:
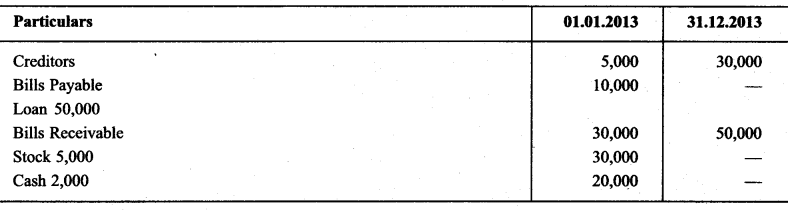
Solution:
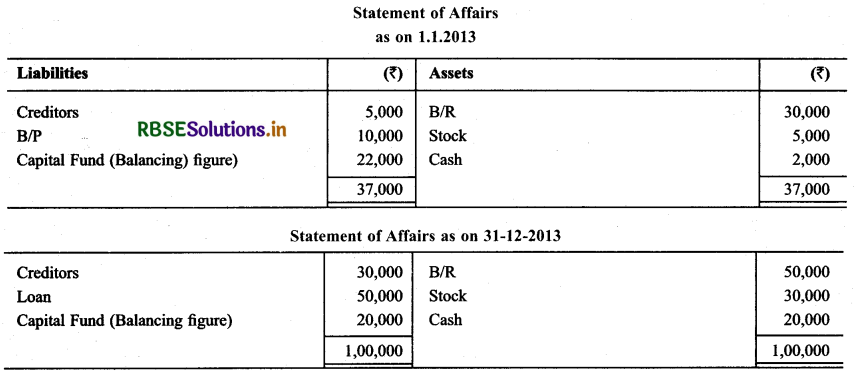

Question 6.
Smt. Annu commence business w.e.f. July, 2013 with a capital of ₹ 4,00,000. She borrowed ₹ 1,00,000 @ 10% p.a. from her friend for business and introduced additional capital ₹ 75,000. Her position as on December 31, 2013 were as under:
Cash : ₹ 30,000
Stock : ₹ 4,70,000
Debtors : ₹ 3,50,000
Creditors : ₹ 3,00,000
She withdraw ₹ 8,000 per month. Calculate Profit or Loss for the year & show your calculations.
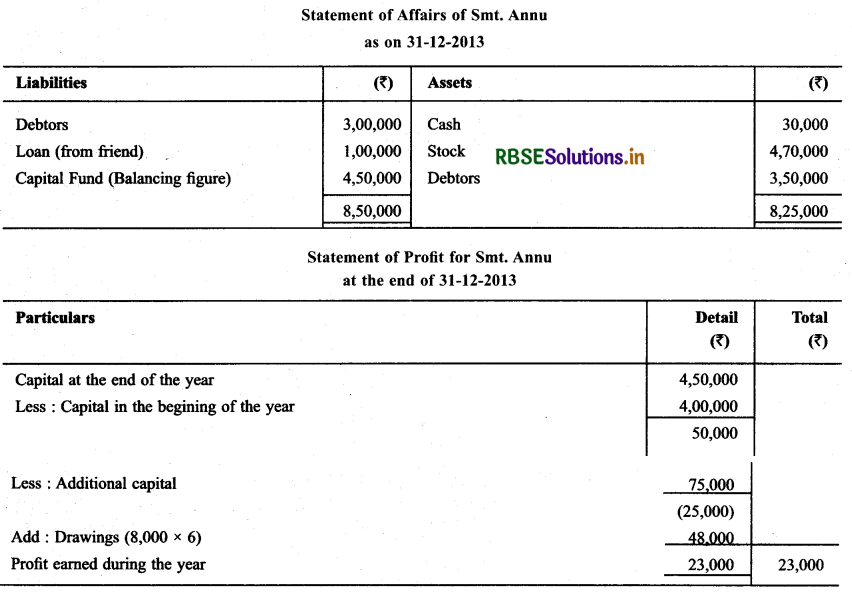
Question 7.
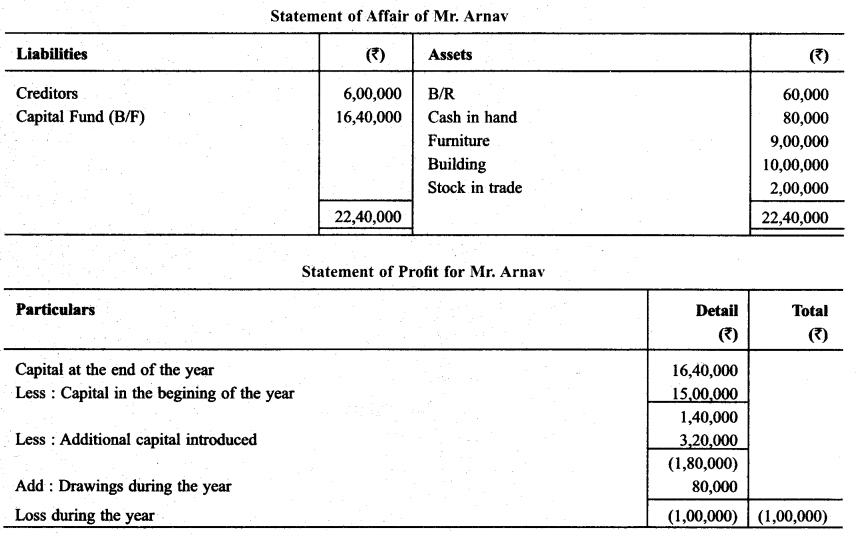
Proper documents record was not maintained by Sh. Amav. Prepare Statement of P & L with the help of below mentioned informations :

Solution:
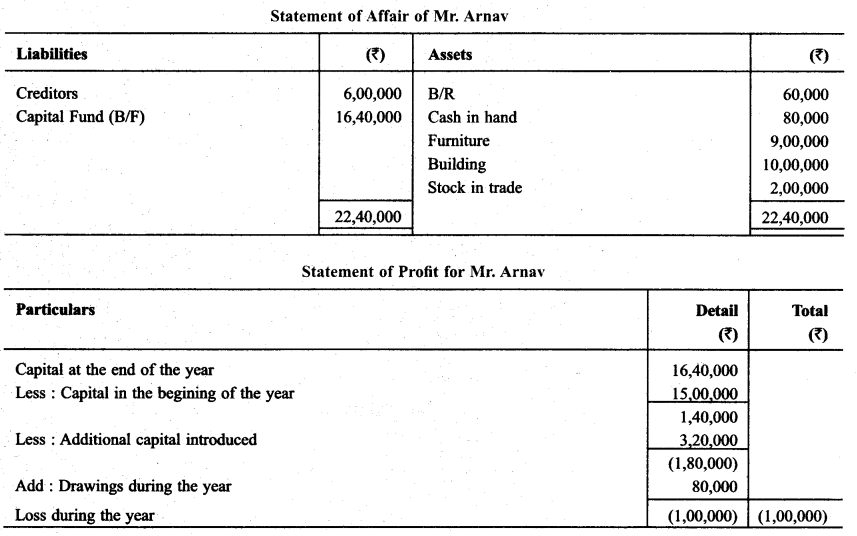
Question 8.
Following informations are related to Sh. Akshat, who keeps his books according to single entry

He withdraw 45,000 during the year and produced further capita 25,000. Calculate Profit and Loss of the year.
Solution:
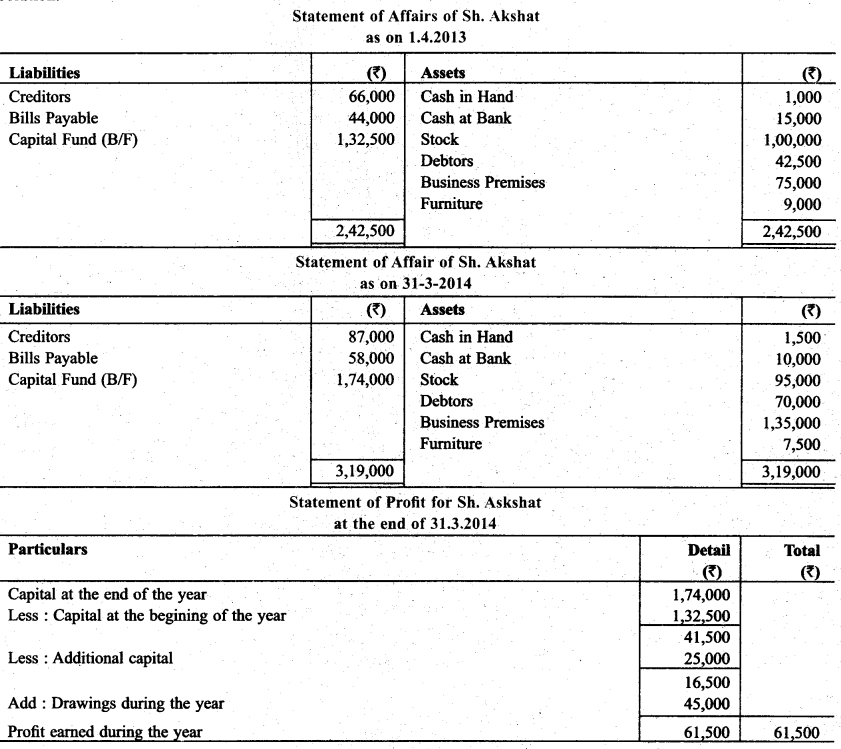

Question 9.
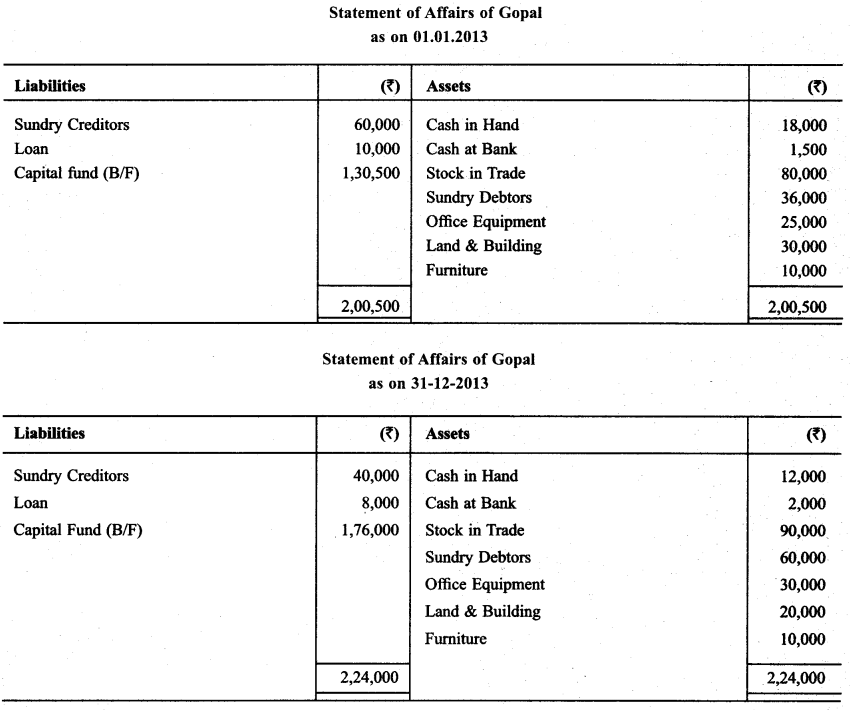
Gopal does not maintain records properly. Following informations are given:

During the year ₹ 20,000 were withdrawn & ₹ 12,000 were introduced as additional capital. Prepare Profit & Loss statement based on given informations.
Solution:

Question 10.
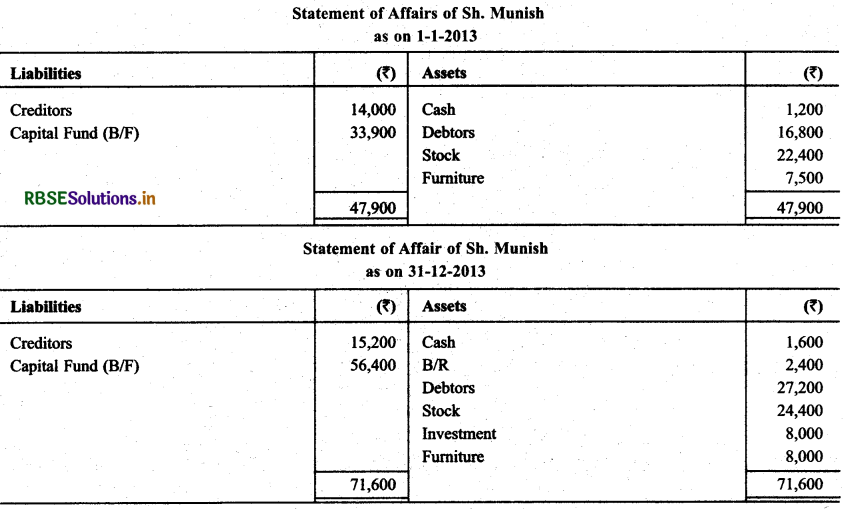
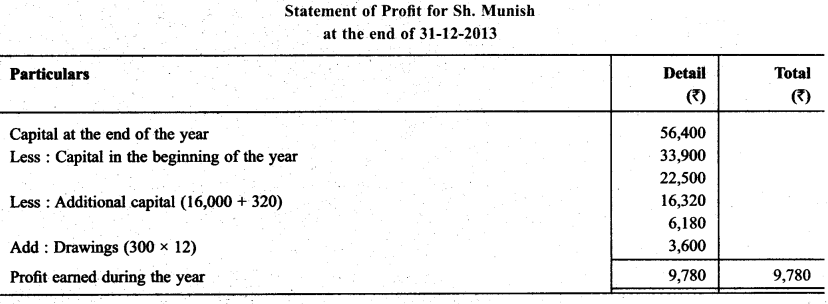
Sh. Munish maintain his books according to incomplete records. His books provide following informations:

He withdraw ₹ 300 per month. He sells his investment of ₹ 16,000 at 2% Super Profit & Introduce this amount of business. Prepare statement of profit for them.
Solution.
Question 11.
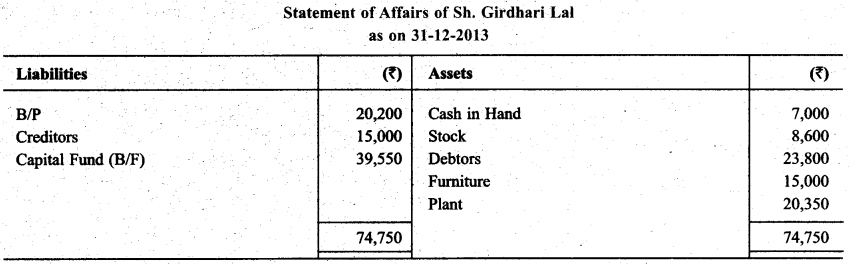
Sh. Girdhari Lai does not addoped the complete record system. There Balances in January 2013 are as follow:
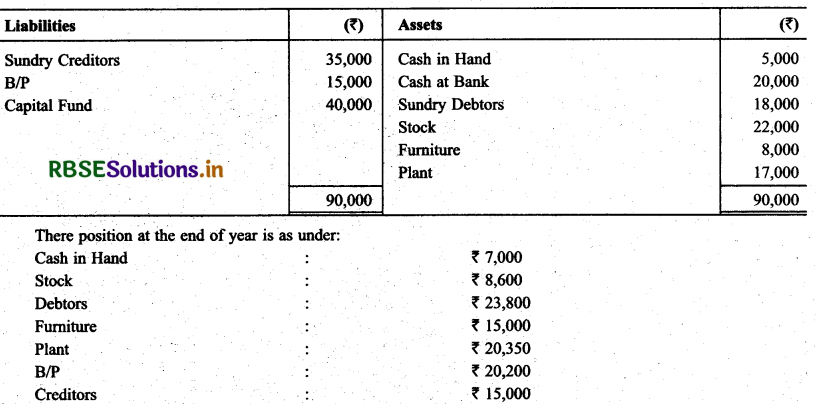
Question 12.
He withdraw @ ₹ 500 per month. Out of this he expand ₹ 1,500 for business. Prepare Statement of Profit & Loss
Solution:

Question 13.
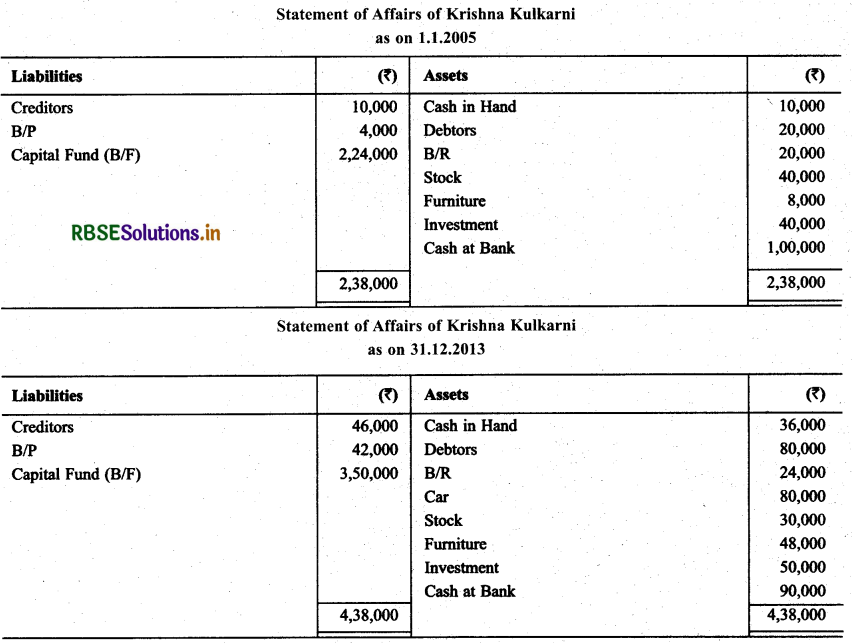
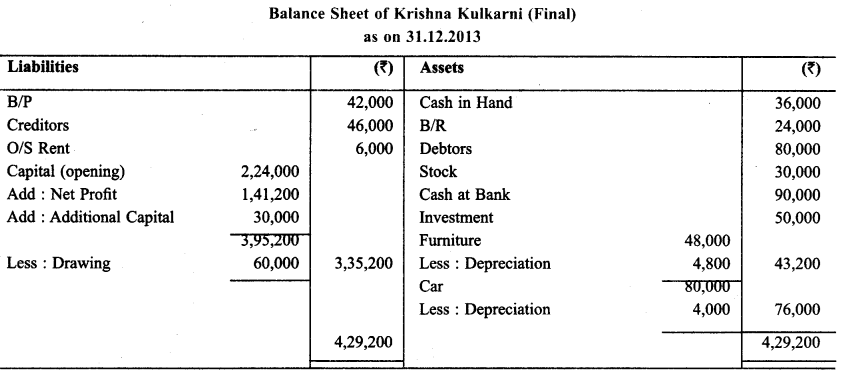
Krishna Kulkami does not keeps his books properly. Prepare P & L Statement as on December 31,2013 on the basis of following informations:

Make following adjustments:
Krishna withdraw ₹ 5,000 per month for personal use. Depriciate car by 5% & furniture by 10%
Rent outstanding is ₹ 6,000.
Fresh Capital ₹ 30,000 introduced during the year.
Solution:

Question 14.
M/s Sanya Sports Equipment does not keep proper documcnts/Records. Prepare statement of P & L and balance sheet as on December 31, 2013 with the help of following informations:

During the year ₹ 10,000 per month were withdrawn for personalise. Capital of ₹ 2,00,000 were introduced during the year. Bad debts ₹ 2,000 & make a provision for doubtful debts @5%, outstanding salary ₹ 2,400, Prepaid insurance ₹ 700, Depreciate Furniture & Machinery @ 10% p.a.
Solution:
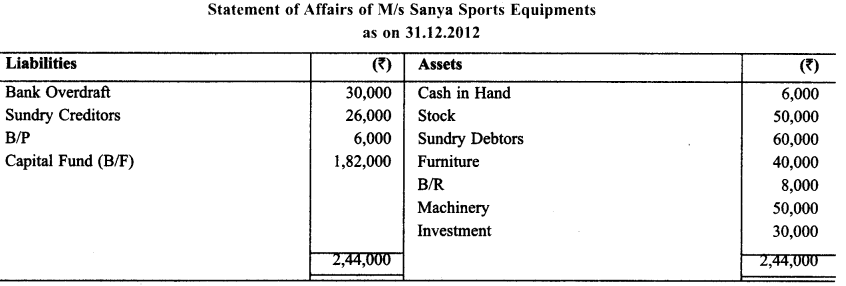
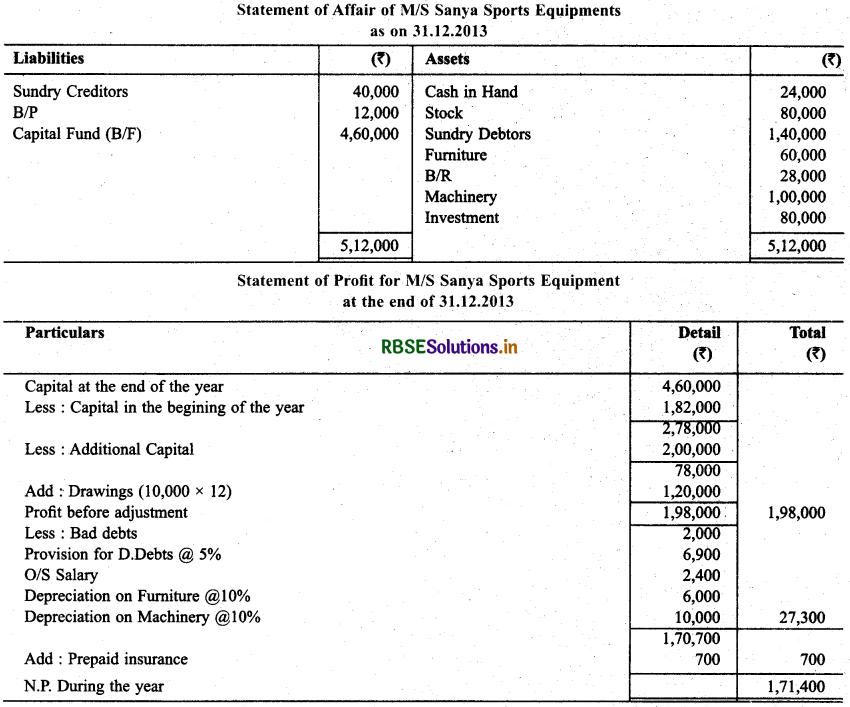
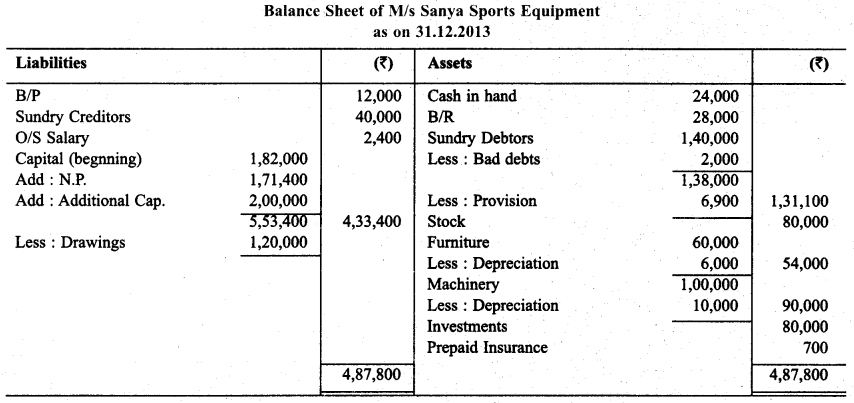

Question 15.
Calculate amount paid to creditors with the help of following :

Solution:
We have to prepare total creditors accounts to find out the payment to creditors.
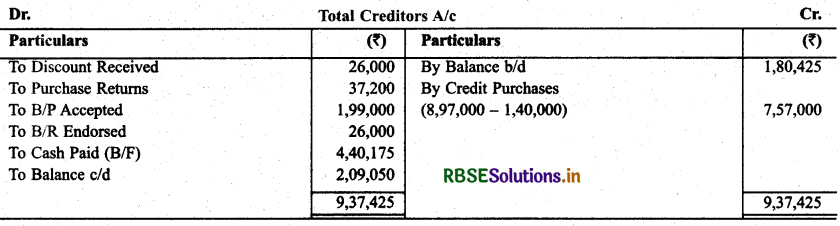
Question 16.
Calculate credit purchase with the help of following informations:

Solution:
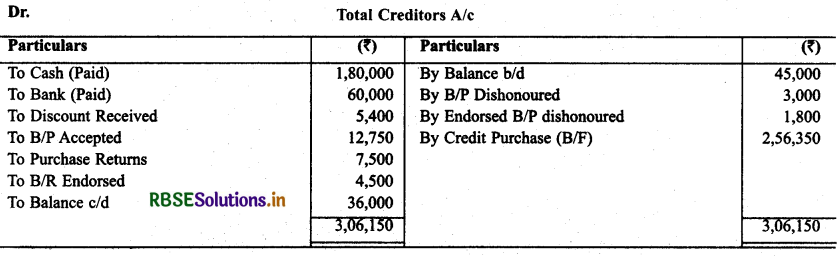
Question 17.
Calculate total purcahses with the help of following informations

Solution:
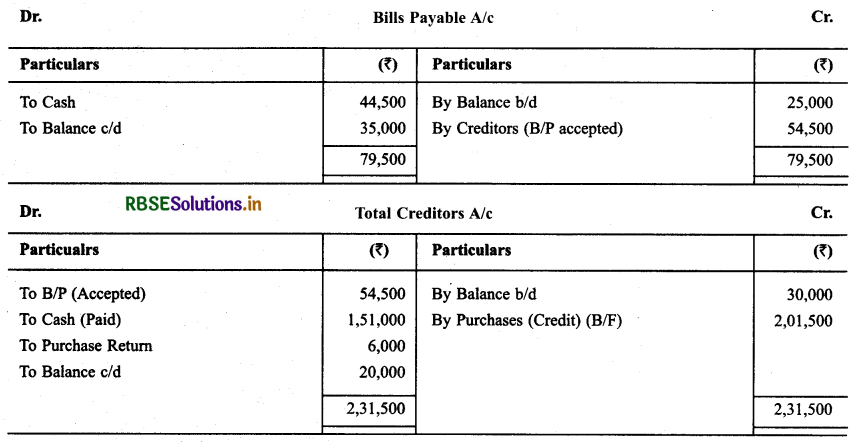
Cash Purchases = 1,29,000
Credit Purchases = 2,01,500
Total Purchases = 3,30,500
Question 18.
Following informations are given:

Solution:
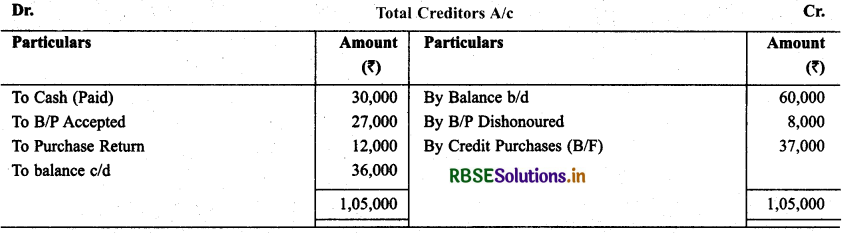

Question 19.
With the help of following information calculate B/P accepted during the year:
B/P as on 1.4.2013 : ₹ 1,80,000
B/P as on 31.3.2014 : ₹ 2,20,000
B/P Dishonoured during the year : ₹ 28,000
B/P Matured during the year : ₹ 50,000
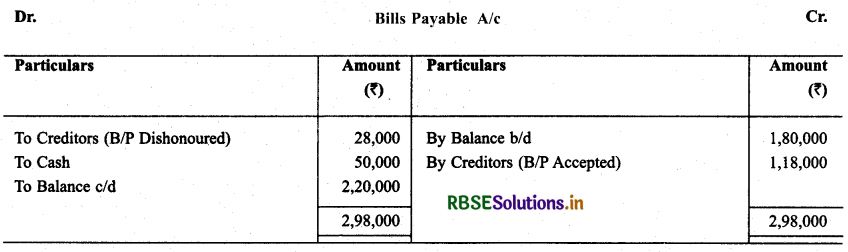
Question 20.
Calculate amount of bills matured during the year, with the help of given informations:

Solution:
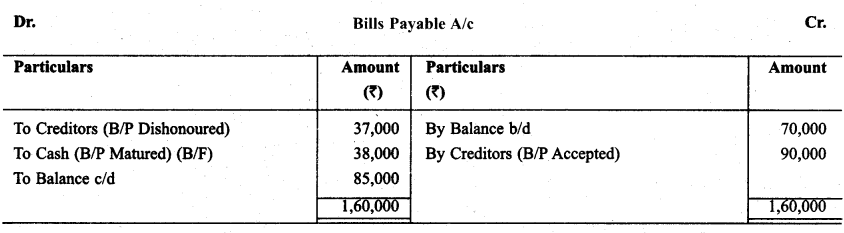
Question 21.
With the help of following informations prepare payable accounts & find out unknown figures:

Solution:
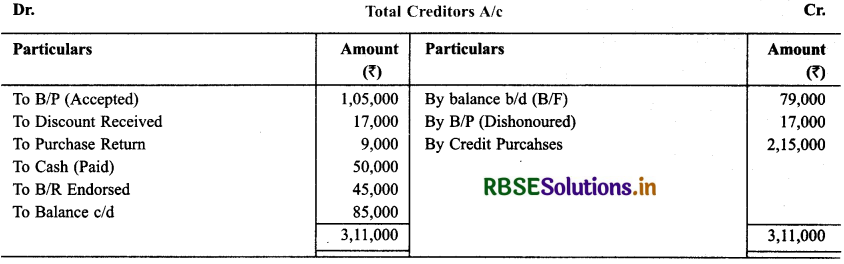
Question 22.
Calculate the amount of Bills Receivable, Received during the year :
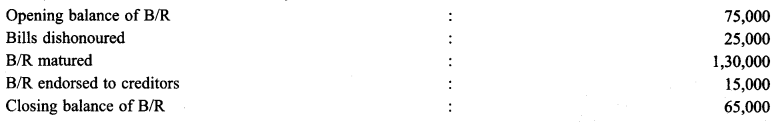
Solution:
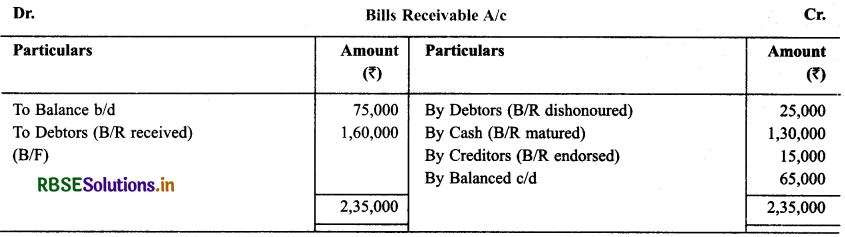
Question 23.
With the help of following informations calculate amount of B/R dishonoured:

Solution:
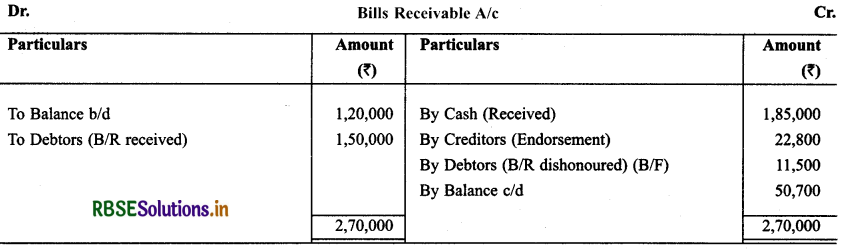
Question 24.
With the help of under mentioned particulars calculate Credit Sales & Total Sales:

Solution:
Cash Sale = 80,000
Credit Sale = 2,82,300
Total Sale = 3,62,300
Question 25.
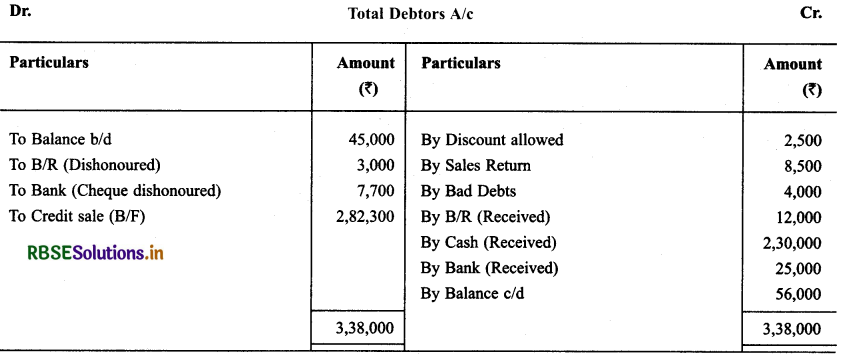
With the help of following informations prepare B/R A/c & Total Debtors A/c for the year ending on December 31,2013.

Solution:
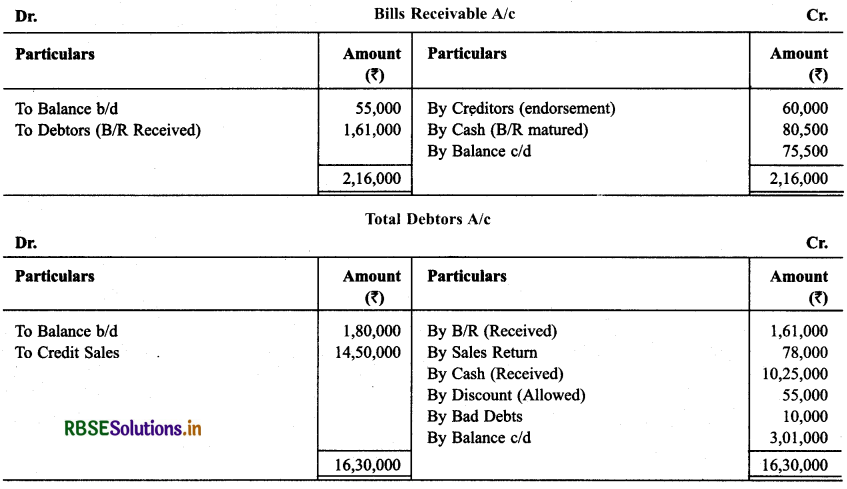

Question 26.
Find out missing items after preparing concerned accounts:

Solution:
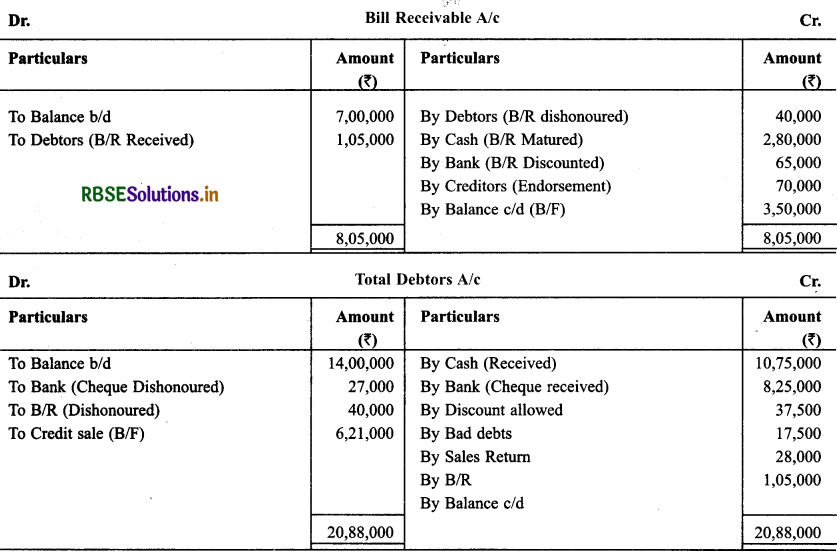
Question 27.
With the help of following informations calculate opening balance of debtors & closing balance of creditors :

Rate of Gross Profit is 25% on Selling Price & ₹ 85,000 is Cash Sale out of Total Sale.
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Purchases - Closing stock
= 30,000 + 2,95,000 - 25,000 = 3,00,000
∴ Gross profit = 25% of selling price
Suppose, Sale price = ₹ 100
Gross profit \(=\frac{100 \times 25}{100}\)= ₹ 25
Cost of goods sold = 100 - 25 - ₹ 75
If the cost of goods sold is ₹ 75 then selling price ₹ 100
If the cost of goods sold is ₹ 1 then selling price = \(\frac{100}{75}\)
If the cost of goods sold is 3,00,000 then selling price = \(\frac{100}{75}\) x 300,00 = ₹ 4,00,000
Credit sale = Total sale - cash sale 4,00,000 - 85,000 = ₹ 3,15,000
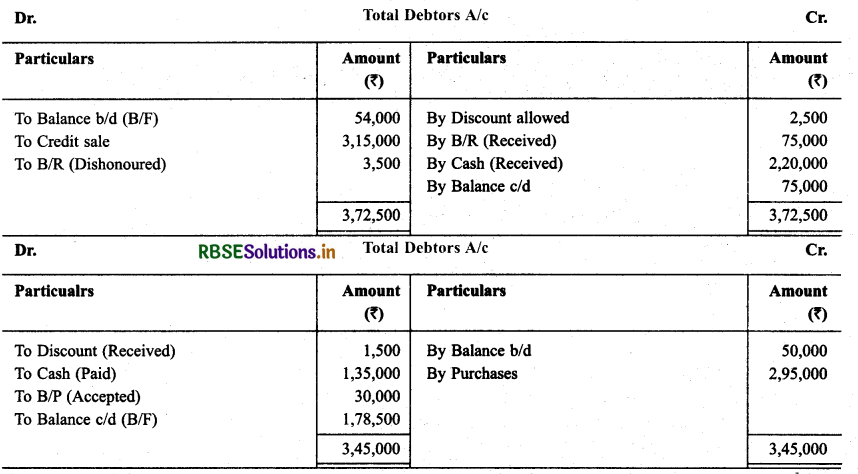
Question 28.
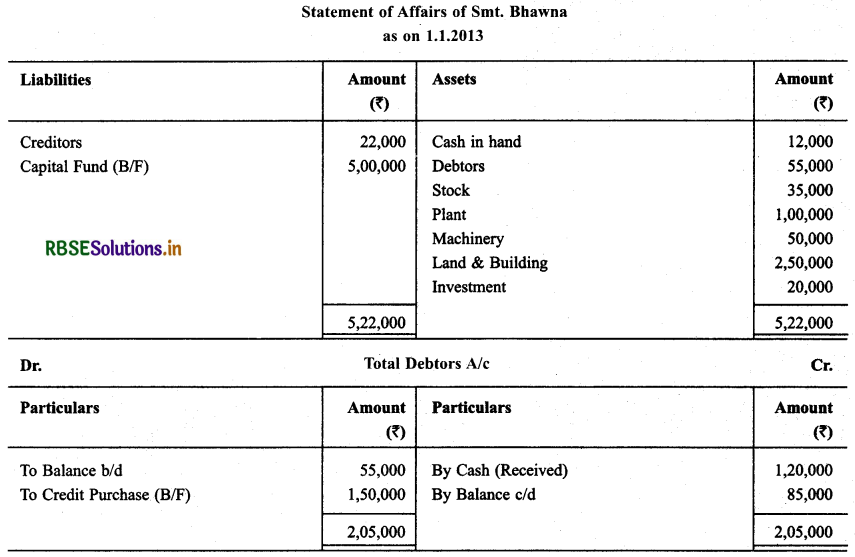
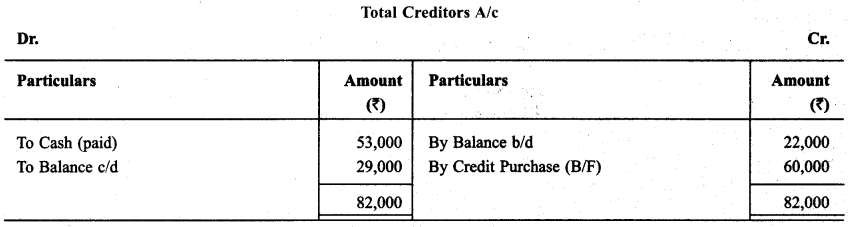
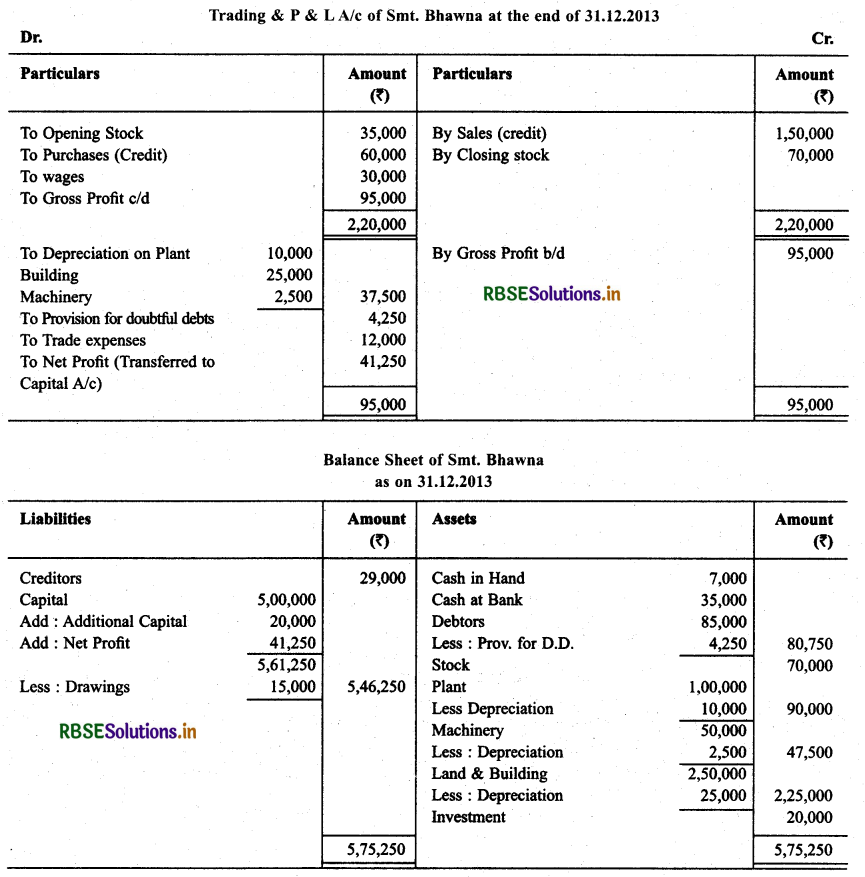
Smt. Bhawna keeps her books according to Single Entry System. Prepare Final Account for them for the year ending on December 31, 2013. Particulars regarding receipts and estimated payments for the session are as under:
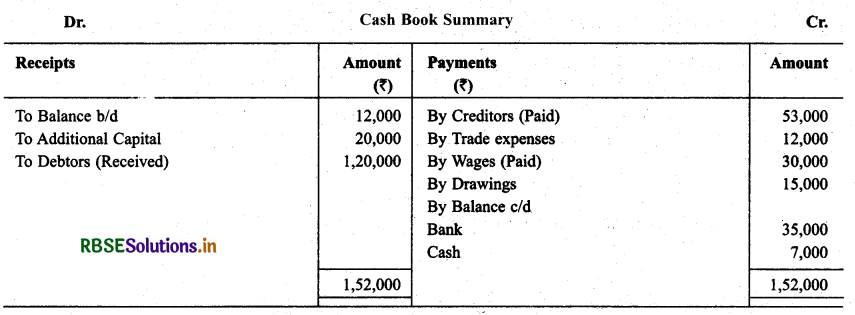

All Purchases and Sales are made on credit. Depreciate: Plant and Building @ 5% and Machinery by 5%, make a provision @ 5% on debtors for doubtful debts.
Solution:


- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 8 Bill of Exchange
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Psychology in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Psychology Chapter 1 मनोविज्ञान क्या है?
- RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions Chapter 1 मनोविज्ञान क्या है?
- RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions Chapter 9 अभिप्रेरणा एवं संवेग
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Psychology Chapter 6 अधिगम
- RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions Chapter 8 चिंतन
- RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions Chapter 7 मानव स्मृति
- RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions Chapter 6 अधिगम
- RBSE Class 11 Psychology Important Questions Chapter 5 संवेदी, अवधानिक एवं प्रात्यक्षिक प्रक्रियाएँ